Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Condensate Line Sizing
Condensate Line Sizing
Uploaded by
Martin ZaballaCopyright:
Available Formats
You might also like
- Pipe Materials Blasting & Painting Areas CalculationDocument6 pagesPipe Materials Blasting & Painting Areas Calculationemmanuilmoulos633975% (4)
- Pipe Materials Blasting & Painting Areas CalculationDocument6 pagesPipe Materials Blasting & Painting Areas Calculationemmanuilmoulos633975% (4)
- API 620 DesignDocument27 pagesAPI 620 Designrsubramani100% (2)
- Regeneration of Waste Lubricant Oil by Extraction-Flocculation PDFDocument8 pagesRegeneration of Waste Lubricant Oil by Extraction-Flocculation PDFsasanNo ratings yet
- Control Valve SizingDocument21 pagesControl Valve Sizingtiwarishailendra2198No ratings yet
- 6DSUPP Desuperheater Supplement BrochureDocument4 pages6DSUPP Desuperheater Supplement BrochureПавел ЛукьяновNo ratings yet
- Desuperheater Equipment&SystemDocument12 pagesDesuperheater Equipment&Systemquoctrangbk02No ratings yet
- Pipe Sizing Steam Supply and Condensate Return Lines Sizing Charts Chart CG-25, page CG-51, is the basic chart for determining the flow rate and velocity of steam in Schedule 40 pipe for various values of pressure drop per 100 ft, based on 0 psig saturated steam. Using the multiplier chart (Chart CG-24), Chart CG-25 can be used at all saturation pressures between 0 and 200 psig (see Example). These Charts are based on the Moody Friction Factor, which considers the Reynolds number and the roughness of the internal pipe surfaces. Notes: Based on Moody Friction Factor where flow of condensate does not inhibit the flow of steam. See Chart CG-24 for obtaining flow rates and velocities of all saturation pressures between 0 to 200 psig: see Example. Pipe Sizing Two principal factors determine pipe sizing in a steam system: 1. The initial pressure at the boiler and the allowable pressure drop of the total system. The total pressure drop in the system should not exceed 20% ofDocument3 pagesPipe Sizing Steam Supply and Condensate Return Lines Sizing Charts Chart CG-25, page CG-51, is the basic chart for determining the flow rate and velocity of steam in Schedule 40 pipe for various values of pressure drop per 100 ft, based on 0 psig saturated steam. Using the multiplier chart (Chart CG-24), Chart CG-25 can be used at all saturation pressures between 0 and 200 psig (see Example). These Charts are based on the Moody Friction Factor, which considers the Reynolds number and the roughness of the internal pipe surfaces. Notes: Based on Moody Friction Factor where flow of condensate does not inhibit the flow of steam. See Chart CG-24 for obtaining flow rates and velocities of all saturation pressures between 0 to 200 psig: see Example. Pipe Sizing Two principal factors determine pipe sizing in a steam system: 1. The initial pressure at the boiler and the allowable pressure drop of the total system. The total pressure drop in the system should not exceed 20% of1970acoNo ratings yet
- STC (Buffer Tank 25KL) - Calc PDFDocument4 pagesSTC (Buffer Tank 25KL) - Calc PDFAvril Rindra T PNo ratings yet
- EmersonDocument21 pagesEmersoncrustytheclown99No ratings yet
- Steam Pipe Size Calculation PDFDocument16 pagesSteam Pipe Size Calculation PDFkhairul1989100% (5)
- CMTD Excel PDFDocument3 pagesCMTD Excel PDFJesús Alejandro González CañasNo ratings yet
- HORIZONTAL THREE-PHASE SEPARATOR DESIGN (No Boot or Weir) : Liquid / Liquid / Vapor ServiceDocument16 pagesHORIZONTAL THREE-PHASE SEPARATOR DESIGN (No Boot or Weir) : Liquid / Liquid / Vapor ServiceDhanny MiharjaNo ratings yet
- Steam Consumption and Line SizingDocument3 pagesSteam Consumption and Line SizingpavanNo ratings yet
- Nptel ReboilerDocument8 pagesNptel ReboilerGurubasavaraju T MNo ratings yet
- SP SP VP V PR) : Velocity Pressure Method Calculation SheetDocument6 pagesSP SP VP V PR) : Velocity Pressure Method Calculation SheetAnkit LonareNo ratings yet
- Pipe Flow Problems-III: Example 1Document10 pagesPipe Flow Problems-III: Example 1Chaithanya Kumar Dandu100% (1)
- PHE As CondensersDocument50 pagesPHE As CondensersHelga Ines BenzNo ratings yet
- Rosemount 1495 Orifice Plate, 1496 Flange Union, 1497 Meter SectionDocument24 pagesRosemount 1495 Orifice Plate, 1496 Flange Union, 1497 Meter SectionJames ThomasNo ratings yet
- Net Positive Suction Head or NPSHDocument4 pagesNet Positive Suction Head or NPSHSathish Lingam100% (1)
- Centrifugal Pump FundamentalsDocument140 pagesCentrifugal Pump FundamentalsLizbeth CamachoNo ratings yet
- Eductor SizingDocument2 pagesEductor SizingbudiprasNo ratings yet
- PSV-Tag No.: K K CFDocument3 pagesPSV-Tag No.: K K CFoas217No ratings yet
- NPSH Calculator For Process EngineerDocument14 pagesNPSH Calculator For Process Engineerluiasnadrade100% (1)
- For Exchanger Tube Rupture PDFDocument3 pagesFor Exchanger Tube Rupture PDFNikhil DivateNo ratings yet
- Relief Load CalculationDocument8 pagesRelief Load CalculationMuthuKumar ArunachalamNo ratings yet
- Section 7 - Separation EquipmentDocument9 pagesSection 7 - Separation Equipmentlulis171No ratings yet
- Expansion Vessel Calculation SheetDocument2 pagesExpansion Vessel Calculation SheetsmcsamindaNo ratings yet
- Liquid Orifice SizingDocument4 pagesLiquid Orifice SizingrmaganNo ratings yet
- Boiler CalculatorDocument4 pagesBoiler CalculatorMarc EdwardsNo ratings yet
- Cepde - Valve Sizing (U16ch036, U16ch037, U16ch083)Document15 pagesCepde - Valve Sizing (U16ch036, U16ch037, U16ch083)VRUSHABHNo ratings yet
- Vent Calc For Storage Tanks - CheresourcesDocument5 pagesVent Calc For Storage Tanks - CheresourcesSteve WanNo ratings yet
- Head Loss Calculation - Fire Hydrant Sys..Temporary ReiserDocument15 pagesHead Loss Calculation - Fire Hydrant Sys..Temporary ReiserEngFaisal AlraiNo ratings yet
- Ppgj-Pro-Cal-190 Hot Oil Return Pump (P-1004)Document10 pagesPpgj-Pro-Cal-190 Hot Oil Return Pump (P-1004)Tifano KhristiyantoNo ratings yet
- Pressure Drop in PipelineDocument13 pagesPressure Drop in PipelineNilambar BarihaNo ratings yet
- Chap 8. CondenserDocument9 pagesChap 8. CondenserAli Ahsan100% (1)
- Specifying Shell and Tube Heat ExchangersDocument10 pagesSpecifying Shell and Tube Heat ExchangersMicheal BrooksNo ratings yet
- Liquid Pressure Drop CalculationDocument9 pagesLiquid Pressure Drop CalculationMichaelMahonyNo ratings yet
- CBE 417 FlashDrumSizing WankatDocument7 pagesCBE 417 FlashDrumSizing WankatRahmansyah GaekNo ratings yet
- Air Cooled HX Data SheetDocument1 pageAir Cooled HX Data SheetHoney TiwariNo ratings yet
- Tube Rupture (Two Phase - API App-D Method)Document5 pagesTube Rupture (Two Phase - API App-D Method)Indra Kurniawan WijayaNo ratings yet
- Mixer SizingDocument0 pagesMixer SizingIlija RunjajicNo ratings yet
- MVAC Duct Pressure Drop (Reference Summary)Document19 pagesMVAC Duct Pressure Drop (Reference Summary)Cheng Chun TingNo ratings yet
- Sizing of Control Valves For Non-Turbulent Flow (Laminar and Transitional)Document14 pagesSizing of Control Valves For Non-Turbulent Flow (Laminar and Transitional)JOSE MARTIN MORA RIVEROSNo ratings yet
- 2 Way & 3 Way Modulating Valve Selection ProcedureDocument5 pages2 Way & 3 Way Modulating Valve Selection ProcedureJuan Altamirano RojasNo ratings yet
- Technical Data Pressure Drop Calculations: Case 1 Case 2Document1 pageTechnical Data Pressure Drop Calculations: Case 1 Case 2AJNo ratings yet
- Effect of Fouling FactorDocument5 pagesEffect of Fouling FactorMehta Mehul100% (1)
- Condensate Line SizingDocument2 pagesCondensate Line SizingAnonymous oVRvsdWzfBNo ratings yet
- 20 - Condensate Line SizingDocument2 pages20 - Condensate Line SizingJunaid MateenNo ratings yet
- Condensate Line SizingDocument2 pagesCondensate Line SizinglylyNo ratings yet
- Condensate Line SizingDocument3 pagesCondensate Line Sizingadrian sotoNo ratings yet
- Condensate Line SizingDocument4 pagesCondensate Line SizingMubin Ashraf SheikhNo ratings yet
- Condensate Line SizingDocument1 pageCondensate Line SizingShashi RaajNo ratings yet
- Condensate Line SizingDocument2 pagesCondensate Line SizingrohitkushNo ratings yet
- Final Ventury Working For Wet Alkaline ScrubberDocument11 pagesFinal Ventury Working For Wet Alkaline ScrubberNanasaheb JagtapNo ratings yet
- Calculation of Flow From PinholeDocument6 pagesCalculation of Flow From PinholeSubrata MukherjeeNo ratings yet
- Consequence AnalyserDocument23 pagesConsequence AnalyserGlacier RamkissoonNo ratings yet
- Steam Condensate in Return LinesDocument13 pagesSteam Condensate in Return LinesAayushi SinhaNo ratings yet
- Properties by Correlation For Process SimulationDocument4 pagesProperties by Correlation For Process SimulationSuryakant RanderiNo ratings yet
- Vessel NewDocument16 pagesVessel NewakshaybhuranNo ratings yet
- Scrubbing Tower DesignDocument10 pagesScrubbing Tower DesignPrathmesh GujaratiNo ratings yet
- DJM-MBA-PCS-CA-005 De-Etanizer Accumulator REV-1Document6 pagesDJM-MBA-PCS-CA-005 De-Etanizer Accumulator REV-1DIANTORONo ratings yet
- Two Phase Beggs BrillDocument4 pagesTwo Phase Beggs BrillOsmund MwangupiliNo ratings yet
- Pipe Size CalcDocument8 pagesPipe Size CalcNitin KumarNo ratings yet
- ASTM A53 Vs A500 EquivalenceDocument6 pagesASTM A53 Vs A500 Equivalenceemmanuilmoulos6339No ratings yet
- Heat Input Calculation From WeldingDocument9 pagesHeat Input Calculation From Weldingemmanuilmoulos6339No ratings yet
- Heat Input Calculation From WeldingDocument9 pagesHeat Input Calculation From Weldingemmanuilmoulos6339No ratings yet
- Saes A 004Document18 pagesSaes A 004emmanuilmoulos6339100% (1)
- Elbow Trimming Sample. Calculates Any Angle To Be Trimmed From 90o or 45o ElbowDocument6 pagesElbow Trimming Sample. Calculates Any Angle To Be Trimmed From 90o or 45o Elbowemmanuilmoulos6339No ratings yet
- Piping Design Reference InfoDocument254 pagesPiping Design Reference InfoDr. M. Praveen Sandeep100% (1)
- VacuumBook FundamentalsDocument200 pagesVacuumBook FundamentalsChirag DobariyaNo ratings yet
- 01 Exercise Solutions e PDFDocument9 pages01 Exercise Solutions e PDFouo So方No ratings yet
- 29.industrial Food-Freezing SystemsDocument17 pages29.industrial Food-Freezing Systemspratheesh100% (1)
- A Contemporary Guide To Mechnical Seal LeakageDocument10 pagesA Contemporary Guide To Mechnical Seal Leakageac2475No ratings yet
- Metals and Non-MetalsDocument11 pagesMetals and Non-MetalsdhandanikitaNo ratings yet
- Ordinary Level Heat NotesDocument44 pagesOrdinary Level Heat Notespatrick omonyNo ratings yet
- MTH 642 Mid Solve Paper: AnswerDocument3 pagesMTH 642 Mid Solve Paper: AnswerZain AhsanNo ratings yet
- Leadwell Instruction ManualDocument94 pagesLeadwell Instruction ManualDaniel Jimenez100% (3)
- Paper 1 May 2006 PhysicsDocument20 pagesPaper 1 May 2006 PhysicssolarixeNo ratings yet
- Science Clinic NotesDocument30 pagesScience Clinic Notescfar_0014918No ratings yet
- Introduction To Qualitative Chemistry (Review On Chemical Concepts)Document6 pagesIntroduction To Qualitative Chemistry (Review On Chemical Concepts)Rosalinda Frias GarciaNo ratings yet
- Karabelas - Liquid - Liquid Droplet Size Distribution PDFDocument11 pagesKarabelas - Liquid - Liquid Droplet Size Distribution PDFSwiftTGSolutionsNo ratings yet
- Matter in Our SurroundingsDocument47 pagesMatter in Our SurroundingsAnagha PradeepNo ratings yet
- of Surface TensionDocument24 pagesof Surface TensionSHIELA RUBIO100% (1)
- SOF Olympiad Air Water Rock Class 2Document3 pagesSOF Olympiad Air Water Rock Class 2Aayat Bazaz50% (2)
- MSA 130-01-076 - Instruction Manual and Parts List - Ed. 979Document102 pagesMSA 130-01-076 - Instruction Manual and Parts List - Ed. 979Centrifugal Separator100% (1)
- Equipment Description: Feed FurnacesDocument8 pagesEquipment Description: Feed FurnacesBalasubramanian CNo ratings yet
- 3238-Article Text-5879-1-10-20180104Document140 pages3238-Article Text-5879-1-10-20180104Maharajan McsNo ratings yet
- Dahlgren Division Naval Surface Warfare Center: NSWCDD/TR-12/68Document68 pagesDahlgren Division Naval Surface Warfare Center: NSWCDD/TR-12/68skr2010No ratings yet
- Example Fire ReportDocument9 pagesExample Fire Reporthenshin987No ratings yet
- Getu Plant Design Project FIXEDDocument23 pagesGetu Plant Design Project FIXEDDeavoNo ratings yet
- 624-1e Techn Data BE 1Document29 pages624-1e Techn Data BE 1maxilencinaNo ratings yet
- Preparing - Your - Lab - D-6660 July 2002Document11 pagesPreparing - Your - Lab - D-6660 July 2002Navi MoralesNo ratings yet
- 13.2 Identification of Ions and Gases CIE IGCSE Chemistry Practical QPDocument8 pages13.2 Identification of Ions and Gases CIE IGCSE Chemistry Practical QPdrcrafaelNo ratings yet
- Techniques To Measure Dynamic Surface Tension PDFDocument8 pagesTechniques To Measure Dynamic Surface Tension PDFjvchiqueNo ratings yet
- 06.improving Cycle Eff of Thermal Power Plants by Enhancing Vacuum Pump CapacityDocument8 pages06.improving Cycle Eff of Thermal Power Plants by Enhancing Vacuum Pump CapacityBalvir GangarNo ratings yet
- Types of Fluid FlowDocument7 pagesTypes of Fluid FlowVinoth PandiNo ratings yet
- Science 6 ModuleDocument6 pagesScience 6 ModulezaiiNo ratings yet
- Cai2009 PDFDocument5 pagesCai2009 PDFLeon Blažinović100% (1)
Condensate Line Sizing
Condensate Line Sizing
Uploaded by
Martin ZaballaCopyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Condensate Line Sizing
Condensate Line Sizing
Uploaded by
Martin ZaballaCopyright:
Available Formats
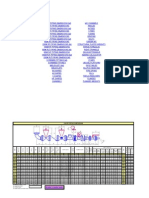
Pipe Diameter Mass Flow Rate of Condensate Condensate Pressure Before Flashing Flasher Condesate Header Pressure Constant
A Constant X Constant B
14 Inch 120000 Kg/hr
2 40 Kg/cm G 2 5 Kg/cm G
264552 lb/hr 583.143 psia 85.338 psia
0.198495 2.317087 0.009815
Weight Fraction of Condensate flashed to Vapour 0.199555 Flashed Steam Flow Rate Flashed Condensate Liquid Flow Temperature of Flashed Condensate Flashed Steam Density Flashed Condensate Liquid Density Density of Mixture (Flashed Condensate/Steam) For Turbulent Flow Friction Factor Pressure Drop of Flashed Condensate mixture Velocity of Flashed Condensate mixture 0.012571 23946.59 Kg/hr 96053.41 Kg/hr 253.2732 C
3 3.009158 kg/m 3 910.8139 kg/m
52792.65 lb/hr 211759.4 lb/hr 487.8917 F
3 0.187849 lb/ft 3 56.85835 lb/ft
3 14.88213 kg/m
3 0.92903 lb/ft
0.591644 psi/100ft
4437.05 ft/min
Line Size is adequate
Assumptions: 1. Most of the flow patterns for steam condensate headers fall within the annular or dispersed region on the baker map. Rarely flow pattern falls in slug flow region. 2. Flashed steam is less than 30% by weight. 3. Vapour-liquid mixture throughout the condensate line is represented by mixture conditions near the end of the line. Method: 1. Amount of condensate flashed is calculated. 2. Further to above the density of the mixture (condensate+flashed steam) is found out. 3. Using two pressure drop correlations, pressure per 100 ft. is calculated. 4. Also, the velocity of the mixture in the line of specified size is calculated. If the velocity is lower than 5000 Foot/Min., the specified line size is said to be adequate.
You might also like
- Pipe Materials Blasting & Painting Areas CalculationDocument6 pagesPipe Materials Blasting & Painting Areas Calculationemmanuilmoulos633975% (4)
- Pipe Materials Blasting & Painting Areas CalculationDocument6 pagesPipe Materials Blasting & Painting Areas Calculationemmanuilmoulos633975% (4)
- API 620 DesignDocument27 pagesAPI 620 Designrsubramani100% (2)
- Regeneration of Waste Lubricant Oil by Extraction-Flocculation PDFDocument8 pagesRegeneration of Waste Lubricant Oil by Extraction-Flocculation PDFsasanNo ratings yet
- Control Valve SizingDocument21 pagesControl Valve Sizingtiwarishailendra2198No ratings yet
- 6DSUPP Desuperheater Supplement BrochureDocument4 pages6DSUPP Desuperheater Supplement BrochureПавел ЛукьяновNo ratings yet
- Desuperheater Equipment&SystemDocument12 pagesDesuperheater Equipment&Systemquoctrangbk02No ratings yet
- Pipe Sizing Steam Supply and Condensate Return Lines Sizing Charts Chart CG-25, page CG-51, is the basic chart for determining the flow rate and velocity of steam in Schedule 40 pipe for various values of pressure drop per 100 ft, based on 0 psig saturated steam. Using the multiplier chart (Chart CG-24), Chart CG-25 can be used at all saturation pressures between 0 and 200 psig (see Example). These Charts are based on the Moody Friction Factor, which considers the Reynolds number and the roughness of the internal pipe surfaces. Notes: Based on Moody Friction Factor where flow of condensate does not inhibit the flow of steam. See Chart CG-24 for obtaining flow rates and velocities of all saturation pressures between 0 to 200 psig: see Example. Pipe Sizing Two principal factors determine pipe sizing in a steam system: 1. The initial pressure at the boiler and the allowable pressure drop of the total system. The total pressure drop in the system should not exceed 20% ofDocument3 pagesPipe Sizing Steam Supply and Condensate Return Lines Sizing Charts Chart CG-25, page CG-51, is the basic chart for determining the flow rate and velocity of steam in Schedule 40 pipe for various values of pressure drop per 100 ft, based on 0 psig saturated steam. Using the multiplier chart (Chart CG-24), Chart CG-25 can be used at all saturation pressures between 0 and 200 psig (see Example). These Charts are based on the Moody Friction Factor, which considers the Reynolds number and the roughness of the internal pipe surfaces. Notes: Based on Moody Friction Factor where flow of condensate does not inhibit the flow of steam. See Chart CG-24 for obtaining flow rates and velocities of all saturation pressures between 0 to 200 psig: see Example. Pipe Sizing Two principal factors determine pipe sizing in a steam system: 1. The initial pressure at the boiler and the allowable pressure drop of the total system. The total pressure drop in the system should not exceed 20% of1970acoNo ratings yet
- STC (Buffer Tank 25KL) - Calc PDFDocument4 pagesSTC (Buffer Tank 25KL) - Calc PDFAvril Rindra T PNo ratings yet
- EmersonDocument21 pagesEmersoncrustytheclown99No ratings yet
- Steam Pipe Size Calculation PDFDocument16 pagesSteam Pipe Size Calculation PDFkhairul1989100% (5)
- CMTD Excel PDFDocument3 pagesCMTD Excel PDFJesús Alejandro González CañasNo ratings yet
- HORIZONTAL THREE-PHASE SEPARATOR DESIGN (No Boot or Weir) : Liquid / Liquid / Vapor ServiceDocument16 pagesHORIZONTAL THREE-PHASE SEPARATOR DESIGN (No Boot or Weir) : Liquid / Liquid / Vapor ServiceDhanny MiharjaNo ratings yet
- Steam Consumption and Line SizingDocument3 pagesSteam Consumption and Line SizingpavanNo ratings yet
- Nptel ReboilerDocument8 pagesNptel ReboilerGurubasavaraju T MNo ratings yet
- SP SP VP V PR) : Velocity Pressure Method Calculation SheetDocument6 pagesSP SP VP V PR) : Velocity Pressure Method Calculation SheetAnkit LonareNo ratings yet
- Pipe Flow Problems-III: Example 1Document10 pagesPipe Flow Problems-III: Example 1Chaithanya Kumar Dandu100% (1)
- PHE As CondensersDocument50 pagesPHE As CondensersHelga Ines BenzNo ratings yet
- Rosemount 1495 Orifice Plate, 1496 Flange Union, 1497 Meter SectionDocument24 pagesRosemount 1495 Orifice Plate, 1496 Flange Union, 1497 Meter SectionJames ThomasNo ratings yet
- Net Positive Suction Head or NPSHDocument4 pagesNet Positive Suction Head or NPSHSathish Lingam100% (1)
- Centrifugal Pump FundamentalsDocument140 pagesCentrifugal Pump FundamentalsLizbeth CamachoNo ratings yet
- Eductor SizingDocument2 pagesEductor SizingbudiprasNo ratings yet
- PSV-Tag No.: K K CFDocument3 pagesPSV-Tag No.: K K CFoas217No ratings yet
- NPSH Calculator For Process EngineerDocument14 pagesNPSH Calculator For Process Engineerluiasnadrade100% (1)
- For Exchanger Tube Rupture PDFDocument3 pagesFor Exchanger Tube Rupture PDFNikhil DivateNo ratings yet
- Relief Load CalculationDocument8 pagesRelief Load CalculationMuthuKumar ArunachalamNo ratings yet
- Section 7 - Separation EquipmentDocument9 pagesSection 7 - Separation Equipmentlulis171No ratings yet
- Expansion Vessel Calculation SheetDocument2 pagesExpansion Vessel Calculation SheetsmcsamindaNo ratings yet
- Liquid Orifice SizingDocument4 pagesLiquid Orifice SizingrmaganNo ratings yet
- Boiler CalculatorDocument4 pagesBoiler CalculatorMarc EdwardsNo ratings yet
- Cepde - Valve Sizing (U16ch036, U16ch037, U16ch083)Document15 pagesCepde - Valve Sizing (U16ch036, U16ch037, U16ch083)VRUSHABHNo ratings yet
- Vent Calc For Storage Tanks - CheresourcesDocument5 pagesVent Calc For Storage Tanks - CheresourcesSteve WanNo ratings yet
- Head Loss Calculation - Fire Hydrant Sys..Temporary ReiserDocument15 pagesHead Loss Calculation - Fire Hydrant Sys..Temporary ReiserEngFaisal AlraiNo ratings yet
- Ppgj-Pro-Cal-190 Hot Oil Return Pump (P-1004)Document10 pagesPpgj-Pro-Cal-190 Hot Oil Return Pump (P-1004)Tifano KhristiyantoNo ratings yet
- Pressure Drop in PipelineDocument13 pagesPressure Drop in PipelineNilambar BarihaNo ratings yet
- Chap 8. CondenserDocument9 pagesChap 8. CondenserAli Ahsan100% (1)
- Specifying Shell and Tube Heat ExchangersDocument10 pagesSpecifying Shell and Tube Heat ExchangersMicheal BrooksNo ratings yet
- Liquid Pressure Drop CalculationDocument9 pagesLiquid Pressure Drop CalculationMichaelMahonyNo ratings yet
- CBE 417 FlashDrumSizing WankatDocument7 pagesCBE 417 FlashDrumSizing WankatRahmansyah GaekNo ratings yet
- Air Cooled HX Data SheetDocument1 pageAir Cooled HX Data SheetHoney TiwariNo ratings yet
- Tube Rupture (Two Phase - API App-D Method)Document5 pagesTube Rupture (Two Phase - API App-D Method)Indra Kurniawan WijayaNo ratings yet
- Mixer SizingDocument0 pagesMixer SizingIlija RunjajicNo ratings yet
- MVAC Duct Pressure Drop (Reference Summary)Document19 pagesMVAC Duct Pressure Drop (Reference Summary)Cheng Chun TingNo ratings yet
- Sizing of Control Valves For Non-Turbulent Flow (Laminar and Transitional)Document14 pagesSizing of Control Valves For Non-Turbulent Flow (Laminar and Transitional)JOSE MARTIN MORA RIVEROSNo ratings yet
- 2 Way & 3 Way Modulating Valve Selection ProcedureDocument5 pages2 Way & 3 Way Modulating Valve Selection ProcedureJuan Altamirano RojasNo ratings yet
- Technical Data Pressure Drop Calculations: Case 1 Case 2Document1 pageTechnical Data Pressure Drop Calculations: Case 1 Case 2AJNo ratings yet
- Effect of Fouling FactorDocument5 pagesEffect of Fouling FactorMehta Mehul100% (1)
- Condensate Line SizingDocument2 pagesCondensate Line SizingAnonymous oVRvsdWzfBNo ratings yet
- 20 - Condensate Line SizingDocument2 pages20 - Condensate Line SizingJunaid MateenNo ratings yet
- Condensate Line SizingDocument2 pagesCondensate Line SizinglylyNo ratings yet
- Condensate Line SizingDocument3 pagesCondensate Line Sizingadrian sotoNo ratings yet
- Condensate Line SizingDocument4 pagesCondensate Line SizingMubin Ashraf SheikhNo ratings yet
- Condensate Line SizingDocument1 pageCondensate Line SizingShashi RaajNo ratings yet
- Condensate Line SizingDocument2 pagesCondensate Line SizingrohitkushNo ratings yet
- Final Ventury Working For Wet Alkaline ScrubberDocument11 pagesFinal Ventury Working For Wet Alkaline ScrubberNanasaheb JagtapNo ratings yet
- Calculation of Flow From PinholeDocument6 pagesCalculation of Flow From PinholeSubrata MukherjeeNo ratings yet
- Consequence AnalyserDocument23 pagesConsequence AnalyserGlacier RamkissoonNo ratings yet
- Steam Condensate in Return LinesDocument13 pagesSteam Condensate in Return LinesAayushi SinhaNo ratings yet
- Properties by Correlation For Process SimulationDocument4 pagesProperties by Correlation For Process SimulationSuryakant RanderiNo ratings yet
- Vessel NewDocument16 pagesVessel NewakshaybhuranNo ratings yet
- Scrubbing Tower DesignDocument10 pagesScrubbing Tower DesignPrathmesh GujaratiNo ratings yet
- DJM-MBA-PCS-CA-005 De-Etanizer Accumulator REV-1Document6 pagesDJM-MBA-PCS-CA-005 De-Etanizer Accumulator REV-1DIANTORONo ratings yet
- Two Phase Beggs BrillDocument4 pagesTwo Phase Beggs BrillOsmund MwangupiliNo ratings yet
- Pipe Size CalcDocument8 pagesPipe Size CalcNitin KumarNo ratings yet
- ASTM A53 Vs A500 EquivalenceDocument6 pagesASTM A53 Vs A500 Equivalenceemmanuilmoulos6339No ratings yet
- Heat Input Calculation From WeldingDocument9 pagesHeat Input Calculation From Weldingemmanuilmoulos6339No ratings yet
- Heat Input Calculation From WeldingDocument9 pagesHeat Input Calculation From Weldingemmanuilmoulos6339No ratings yet
- Saes A 004Document18 pagesSaes A 004emmanuilmoulos6339100% (1)
- Elbow Trimming Sample. Calculates Any Angle To Be Trimmed From 90o or 45o ElbowDocument6 pagesElbow Trimming Sample. Calculates Any Angle To Be Trimmed From 90o or 45o Elbowemmanuilmoulos6339No ratings yet
- Piping Design Reference InfoDocument254 pagesPiping Design Reference InfoDr. M. Praveen Sandeep100% (1)
- VacuumBook FundamentalsDocument200 pagesVacuumBook FundamentalsChirag DobariyaNo ratings yet
- 01 Exercise Solutions e PDFDocument9 pages01 Exercise Solutions e PDFouo So方No ratings yet
- 29.industrial Food-Freezing SystemsDocument17 pages29.industrial Food-Freezing Systemspratheesh100% (1)
- A Contemporary Guide To Mechnical Seal LeakageDocument10 pagesA Contemporary Guide To Mechnical Seal Leakageac2475No ratings yet
- Metals and Non-MetalsDocument11 pagesMetals and Non-MetalsdhandanikitaNo ratings yet
- Ordinary Level Heat NotesDocument44 pagesOrdinary Level Heat Notespatrick omonyNo ratings yet
- MTH 642 Mid Solve Paper: AnswerDocument3 pagesMTH 642 Mid Solve Paper: AnswerZain AhsanNo ratings yet
- Leadwell Instruction ManualDocument94 pagesLeadwell Instruction ManualDaniel Jimenez100% (3)
- Paper 1 May 2006 PhysicsDocument20 pagesPaper 1 May 2006 PhysicssolarixeNo ratings yet
- Science Clinic NotesDocument30 pagesScience Clinic Notescfar_0014918No ratings yet
- Introduction To Qualitative Chemistry (Review On Chemical Concepts)Document6 pagesIntroduction To Qualitative Chemistry (Review On Chemical Concepts)Rosalinda Frias GarciaNo ratings yet
- Karabelas - Liquid - Liquid Droplet Size Distribution PDFDocument11 pagesKarabelas - Liquid - Liquid Droplet Size Distribution PDFSwiftTGSolutionsNo ratings yet
- Matter in Our SurroundingsDocument47 pagesMatter in Our SurroundingsAnagha PradeepNo ratings yet
- of Surface TensionDocument24 pagesof Surface TensionSHIELA RUBIO100% (1)
- SOF Olympiad Air Water Rock Class 2Document3 pagesSOF Olympiad Air Water Rock Class 2Aayat Bazaz50% (2)
- MSA 130-01-076 - Instruction Manual and Parts List - Ed. 979Document102 pagesMSA 130-01-076 - Instruction Manual and Parts List - Ed. 979Centrifugal Separator100% (1)
- Equipment Description: Feed FurnacesDocument8 pagesEquipment Description: Feed FurnacesBalasubramanian CNo ratings yet
- 3238-Article Text-5879-1-10-20180104Document140 pages3238-Article Text-5879-1-10-20180104Maharajan McsNo ratings yet
- Dahlgren Division Naval Surface Warfare Center: NSWCDD/TR-12/68Document68 pagesDahlgren Division Naval Surface Warfare Center: NSWCDD/TR-12/68skr2010No ratings yet
- Example Fire ReportDocument9 pagesExample Fire Reporthenshin987No ratings yet
- Getu Plant Design Project FIXEDDocument23 pagesGetu Plant Design Project FIXEDDeavoNo ratings yet
- 624-1e Techn Data BE 1Document29 pages624-1e Techn Data BE 1maxilencinaNo ratings yet
- Preparing - Your - Lab - D-6660 July 2002Document11 pagesPreparing - Your - Lab - D-6660 July 2002Navi MoralesNo ratings yet
- 13.2 Identification of Ions and Gases CIE IGCSE Chemistry Practical QPDocument8 pages13.2 Identification of Ions and Gases CIE IGCSE Chemistry Practical QPdrcrafaelNo ratings yet
- Techniques To Measure Dynamic Surface Tension PDFDocument8 pagesTechniques To Measure Dynamic Surface Tension PDFjvchiqueNo ratings yet
- 06.improving Cycle Eff of Thermal Power Plants by Enhancing Vacuum Pump CapacityDocument8 pages06.improving Cycle Eff of Thermal Power Plants by Enhancing Vacuum Pump CapacityBalvir GangarNo ratings yet
- Types of Fluid FlowDocument7 pagesTypes of Fluid FlowVinoth PandiNo ratings yet
- Science 6 ModuleDocument6 pagesScience 6 ModulezaiiNo ratings yet
- Cai2009 PDFDocument5 pagesCai2009 PDFLeon Blažinović100% (1)