Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Kaasu Lapp A
Kaasu Lapp A
Uploaded by
mnbvqwertOriginal Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Kaasu Lapp A
Kaasu Lapp A
Uploaded by
mnbvqwertCopyright:
Available Formats
Throttle Valve Module (Electronic Accelerator Pedal) A new throttle valve module is featured.
A fully electronic throttle valve servo motor and two throttle valve potentiometers are integrated into it. The crosssection of the throttle body is 50 mm. The idle speed is controlled by the position of the throttle valve in the main flow. It is actuated by the throttle valve adjuster. The throttle potentiometer, throttle body and throttle valve adjuster are combined in one modular unit and can only be replaced as one unit.
S ervice After replacement of the throttle valve module and/or engine control unit, it is essential that the adaptation values for the throttle valve in the EEPROM of the engine control unit are deleted and reentered using TECH 2 - see corresponding Checking Procedures. 4.79.2 Throttle Valve Module (Electronic Accelerator Pedal) (Continued)
The structure and function of the integrated throttle valve potentiometer are as follows: Two throttle valve potentiometers are fastened to the throttle body and are seated on one shaft together with the throttle valve. Voltage is supplied to both potentiometers via one common plus and minus connection. The potentiometers register the angular position of the throttle valve and transmit the voltage ratio to the engine control unit. The engine control unit then calculates the required fuel quantity. The 1st potentiometer has a control range of 0.0 V to 5.0 V (positive curve). The 2nd potentiometer has a negative curve for checking the 1st potentiometer. Its control range is from 5.0 V to 0.0 V. As a result, both potentiometers can only supply the same output voltage at one operating point (approx. halfway of throttle valve opening) during faultfree operation.
1 2 3
Transmission Throttle valve Directcurrent motor
4.79.2
Throttle Valve Module (Electronic Accelerator Pedal) (Continued)
The throttle valve is driven by a directcurrent motor via a twostage transmission. The directcurrent motor receives a signal from the control unit that is converted into a rotational movement of the throttle valve.
You might also like
- Alfa Romeo SelespeedDocument63 pagesAlfa Romeo SelespeedDavid Felipe Lazo Libano86% (21)
- Drive ActiveHybrid - V.4 GA8P70HZDocument15 pagesDrive ActiveHybrid - V.4 GA8P70HZTimur GorgievNo ratings yet
- 14cux Fuel InjectionDocument80 pages14cux Fuel InjectionJuanjo Chamizo Naranjo100% (2)
- Hyundai Sonata Workshop Manual (V6-3.3L (2006) ) - OptimizedDocument16,706 pagesHyundai Sonata Workshop Manual (V6-3.3L (2006) ) - Optimizedmnbvqwert80% (5)
- Panasonic Lx7 Service ManualDocument101 pagesPanasonic Lx7 Service Manualmofared100% (1)
- Engine Control System DiagramDocument8 pagesEngine Control System DiagramGowher QadriNo ratings yet
- Governing System of Turbines (200 MW)Document18 pagesGoverning System of Turbines (200 MW)Debasish Dewan100% (3)
- Case Study PneumaticDocument16 pagesCase Study PneumaticHazwan Jamhuri100% (7)
- High Pressure Turbine Governing System PDFDocument28 pagesHigh Pressure Turbine Governing System PDFAnonymous ZnuMEWN1100% (6)
- 1477640352901-GE Governor ALCODocument19 pages1477640352901-GE Governor ALCOManikanta ReddyNo ratings yet
- MB W114Document162 pagesMB W114mnbvqwert100% (1)
- MB W100Document43 pagesMB W100mnbvqwert0% (1)
- Unit Iv - 1Document10 pagesUnit Iv - 1akhilkrrish143No ratings yet
- Chapter10 (Governors)Document10 pagesChapter10 (Governors)Zohaib Anser100% (1)
- Control Etc MotorizadoDocument19 pagesControl Etc Motorizadofreddys merchanNo ratings yet
- AutoretardersystemforBH50M-MODIFIED 20110307124628.788 X.pdfmhrsDocument10 pagesAutoretardersystemforBH50M-MODIFIED 20110307124628.788 X.pdfmhrsbmlNo ratings yet
- Engine GovernorDocument23 pagesEngine GovernorRamprabu Chandrasekar100% (1)
- A330 Rolls-Royce RB211-Trent 700 Virtual Reality 360Document20 pagesA330 Rolls-Royce RB211-Trent 700 Virtual Reality 360Edison Vianney Cardona Montoya100% (2)
- phần 4Document9 pagesphần 4Phạm HùngNo ratings yet
- Implement Electronic Control System 966Document4 pagesImplement Electronic Control System 966Ahmed RezkNo ratings yet
- 2128 TCT Dual Clutch Transmission External ControlsDocument19 pages2128 TCT Dual Clutch Transmission External Controlsgkx5pp2sghNo ratings yet
- Operation: Mechanical Operation Operating ConditionsDocument7 pagesOperation: Mechanical Operation Operating Conditionshybrid_motorsports_llcNo ratings yet
- ElectronicsDocument4 pagesElectronicsMarcusNo ratings yet
- New EHC For KWU GoverningDocument13 pagesNew EHC For KWU GoverningMohammad Ibnul Hossain100% (1)
- Prpc27 Mechatronics and Industrial AUTOMATION (Theory & Lab)Document5 pagesPrpc27 Mechatronics and Industrial AUTOMATION (Theory & Lab)Ajith KumarNo ratings yet
- Overspeeding of Turbine During First Tolling Due To EHG FailureDocument6 pagesOverspeeding of Turbine During First Tolling Due To EHG FailureCharu Chhabra100% (4)
- Learning Objectives: Servo ValvesDocument21 pagesLearning Objectives: Servo ValvesAkshay AggrawalNo ratings yet
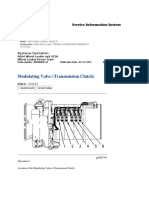
- Modulating Valve (Transmission Clutch) 966Document3 pagesModulating Valve (Transmission Clutch) 966Ahmed Rezk100% (1)
- Modulating Valve (Transmission Clutch) 966Document3 pagesModulating Valve (Transmission Clutch) 966Ahmed Rezk100% (3)
- Faculty of Engineering Department of Aerospace Engineering: Lab InstructorDocument24 pagesFaculty of Engineering Department of Aerospace Engineering: Lab InstructorhishamwahidinNo ratings yet
- The Overall Motronic SystemDocument12 pagesThe Overall Motronic SystemKanagasundram JathursajanNo ratings yet
- MIET/Department of Mechanical Engg: Case Studies of Mechatronics SystemsDocument9 pagesMIET/Department of Mechanical Engg: Case Studies of Mechatronics SystemsRaunak GuptaNo ratings yet
- Soochna 2012 FinalDocument140 pagesSoochna 2012 FinalHanuma Reddy100% (1)
- Prepared By: Amanuel Gebisa May 2015Document69 pagesPrepared By: Amanuel Gebisa May 2015Yalew MekonnenNo ratings yet
- Chapter 20 BennetDocument66 pagesChapter 20 BennetpapipapiiNo ratings yet
- System: Section 2Document72 pagesSystem: Section 2Tú Xuân Lương100% (1)
- Multi Point Fuel InjectionDocument15 pagesMulti Point Fuel Injectionಶಿವರಾಜ್ ಎನ್No ratings yet
- KGW Double Deck Crane Eh 2x25t - 22m - Lo-Ro CarrierDocument167 pagesKGW Double Deck Crane Eh 2x25t - 22m - Lo-Ro CarrierArun Tiwari100% (1)
- Electro Hydraulics: Control Technology ConceptsDocument98 pagesElectro Hydraulics: Control Technology Concepts@nshu_theachiever89% (9)
- SSP 020 Common - RailDocument30 pagesSSP 020 Common - Railvenkateshyadav2116No ratings yet
- Electronic Diesel Fuel System (Common Rail)Document30 pagesElectronic Diesel Fuel System (Common Rail)Katu2010100% (1)
- Common RailDocument30 pagesCommon RailAnonymous 9QkTHFNo ratings yet
- Turbine Governing System Commissioning & Troubleshooting MhepDocument6 pagesTurbine Governing System Commissioning & Troubleshooting MhepAshish Subramanian100% (1)
- 3 934584 28 4Document3 pages3 934584 28 4Joan LuijkxNo ratings yet
- 4.1 Engine Management System-R1-1 MINYI EFFADocument24 pages4.1 Engine Management System-R1-1 MINYI EFFARusonegroNo ratings yet
- 418000E4422 R0 Write Up On Electro Hydraulic ControllerDocument10 pages418000E4422 R0 Write Up On Electro Hydraulic ControllerkoinsuriNo ratings yet
- Systems Operation Sistema Electrico 2301Document26 pagesSystems Operation Sistema Electrico 2301Victor Timana SilvaNo ratings yet
- Stages in Designing Mechatronic SystemsDocument12 pagesStages in Designing Mechatronic SystemsVibin JacobNo ratings yet
- Governor: BY Er. Tanuj Sharma Student of PGDC Hydro POWER PLANT (2010-11), NPTI NangalDocument24 pagesGovernor: BY Er. Tanuj Sharma Student of PGDC Hydro POWER PLANT (2010-11), NPTI NangalTanuj SharmaNo ratings yet
- Turbine IndicationDocument45 pagesTurbine IndicationSThaneasMurNo ratings yet
- Wabco Brakes 3Document60 pagesWabco Brakes 3Shyam Srinivasan100% (5)
- Chapter 2 Generator Excitation System: Speaker:Huang HaijunDocument24 pagesChapter 2 Generator Excitation System: Speaker:Huang HaijunMinh Tien DangNo ratings yet
- Diesel Engine ManagementDocument56 pagesDiesel Engine Managementbravo6dNo ratings yet
- ZX200 - 270W (2) HitachiDocument7 pagesZX200 - 270W (2) Hitachigalvis1020No ratings yet
- Denso CR - Hp2 NissanDocument31 pagesDenso CR - Hp2 NissanMarcelo Diesel86% (7)
- Introduction To Hydraulics, Servo Drive and PLCDocument5 pagesIntroduction To Hydraulics, Servo Drive and PLCHeather Reyes100% (1)
- Hydraulic 1Document37 pagesHydraulic 1Ahmed ElkhateebNo ratings yet
- Maroti Kalganche 1904061Document5 pagesMaroti Kalganche 1904061069-Arjun KharatNo ratings yet
- 3350904-Microprocessor and Controller Applications Date: - / - / - Experiment No-02Document3 pages3350904-Microprocessor and Controller Applications Date: - / - / - Experiment No-02Ashfaq QureshiNo ratings yet
- CRDIDocument31 pagesCRDIJawahar Raj100% (3)
- Simulation of Some Power Electronics Case Studies in Matlab Simpowersystem BlocksetFrom EverandSimulation of Some Power Electronics Case Studies in Matlab Simpowersystem BlocksetNo ratings yet
- Simulation of Some Power Electronics Case Studies in Matlab Simpowersystem BlocksetFrom EverandSimulation of Some Power Electronics Case Studies in Matlab Simpowersystem BlocksetRating: 2 out of 5 stars2/5 (1)
- Some Power Electronics Case Studies Using Matlab Simpowersystem BlocksetFrom EverandSome Power Electronics Case Studies Using Matlab Simpowersystem BlocksetNo ratings yet
- Simulation of Some Power System, Control System and Power Electronics Case Studies Using Matlab and PowerWorld SimulatorFrom EverandSimulation of Some Power System, Control System and Power Electronics Case Studies Using Matlab and PowerWorld SimulatorNo ratings yet
- 2007 CR V BrochureDocument17 pages2007 CR V BrochuremnbvqwertNo ratings yet
- Brake Fluid Level Switch: CONN..Document1 pageBrake Fluid Level Switch: CONN..mnbvqwertNo ratings yet
- Yamarin Motorboats Technical Information Old ModelsDocument19 pagesYamarin Motorboats Technical Information Old Modelsmnbvqwert100% (1)
- Abs VsapdfDocument6 pagesAbs VsapdfmnbvqwertNo ratings yet
- Saab 900 Engineering FeaturesDocument55 pagesSaab 900 Engineering FeaturesmnbvqwertNo ratings yet
- BMW E39 Brochure 2003 EuroDocument10 pagesBMW E39 Brochure 2003 EuromnbvqwertNo ratings yet
- Tpms Tpms TPMS: System Description 2011 CR-V - System Description Control Unit Inputs and Outputs For 20P ConnectorDocument4 pagesTpms Tpms TPMS: System Description 2011 CR-V - System Description Control Unit Inputs and Outputs For 20P ConnectormnbvqwertNo ratings yet
- AUR - 62 - MAST - WEB - tcm-11-1217032Document62 pagesAUR - 62 - MAST - WEB - tcm-11-1217032mnbvqwertNo ratings yet
- TheTimesSundayTimes TheTimesSundayTimes 20190912 534125Document64 pagesTheTimesSundayTimes TheTimesSundayTimes 20190912 534125mnbvqwertNo ratings yet
- Newsweek 20190802 Newsweek INTLDocument52 pagesNewsweek 20190802 Newsweek INTLmnbvqwertNo ratings yet
- Tpms VSA 1 2011Document9 pagesTpms VSA 1 2011mnbvqwertNo ratings yet
- TheStraitsTimes TheStraitsTimes 20190913 534406Document54 pagesTheStraitsTimes TheStraitsTimes 20190913 534406mnbvqwertNo ratings yet
- Saab 9000 - 1994Document38 pagesSaab 9000 - 1994mnbvqwertNo ratings yet
- MB W111Document36 pagesMB W111mnbvqwertNo ratings yet
- MB R107Document74 pagesMB R107mnbvqwertNo ratings yet
- Volvo 1800eDocument6 pagesVolvo 1800emnbvqwertNo ratings yet
- Volvo 140Document10 pagesVolvo 140mnbvqwertNo ratings yet
- Saab 900 5 SpeedDocument63 pagesSaab 900 5 Speedmnbvqwert100% (2)
- VW Type 1 BeetleDocument16 pagesVW Type 1 Beetlemnbvqwert100% (3)
- Toyota CressidaDocument52 pagesToyota Cressidamnbvqwert50% (2)
- Peugeot 505Document106 pagesPeugeot 505mnbvqwert100% (4)
- MB W113Document32 pagesMB W113mnbvqwertNo ratings yet
- MB C126Document35 pagesMB C126mnbvqwert100% (1)
- MB 190eDocument39 pagesMB 190emnbvqwertNo ratings yet
- MB C107Document106 pagesMB C107mnbvqwertNo ratings yet