Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Basic Formulae
Basic Formulae
Uploaded by
skrtamilCopyright:
Available Formats
You might also like
- Microsoft Word - Calculus 2 Formula Cheat SheetDocument2 pagesMicrosoft Word - Calculus 2 Formula Cheat SheetHunterKing199375% (4)
- HSC 3U Maths FormulaeDocument7 pagesHSC 3U Maths FormulaeHotz InatorNo ratings yet
- Calculus Cheat Sheet IntegralsDocument5 pagesCalculus Cheat Sheet Integralsapi-322359712No ratings yet
- Calculus Cheat Sheet Integrals ReducedDocument3 pagesCalculus Cheat Sheet Integrals ReducedShahnaz GazalNo ratings yet
- Eee.60-62Document3 pagesEee.60-62skrtamilNo ratings yet
- Basic Formula2342Document2 pagesBasic Formula2342asim_at_vital123No ratings yet
- Mathematics Revision of Formulae and Results: Surds Co-Ordinate GeometryDocument5 pagesMathematics Revision of Formulae and Results: Surds Co-Ordinate GeometryDarrenPurtillWrightNo ratings yet
- Essential Formulae: Number and AlgebraDocument7 pagesEssential Formulae: Number and AlgebraShinigami01001No ratings yet
- Derivadas: Reglas de Derivaci OnDocument11 pagesDerivadas: Reglas de Derivaci OnJosé Pablo ZubietaNo ratings yet
- Essential FormulaeDocument16 pagesEssential FormulaeMaruthappan Sundaram100% (1)
- LESSON 4 CAL 2 IntegralsDocument40 pagesLESSON 4 CAL 2 IntegralsZero DragneelNo ratings yet
- EMTH210: Formula Sheet 2015: Trigonometric (Circular) FunctionsDocument3 pagesEMTH210: Formula Sheet 2015: Trigonometric (Circular) FunctionsGlass-Half-EmptyNo ratings yet
- Formulario Calculo VectorialDocument20 pagesFormulario Calculo VectorialKevin Molina100% (1)
- Matek KepletekDocument2 pagesMatek KepletekblackjackkNo ratings yet
- Bab Xiii Integral: 13. 1 DefinisiDocument25 pagesBab Xiii Integral: 13. 1 DefinisiDeazzy AndriyaniNo ratings yet
- Reference PageDocument2 pagesReference PageYeung Amy HoNo ratings yet
- BasicsDocument2 pagesBasicsmadcow_scribdNo ratings yet
- Integration Formula: + C U Du VDX Udx DX V U Udx C CudxDocument5 pagesIntegration Formula: + C U Du VDX Udx DX V U Udx C CudxRon AtaNo ratings yet
- Mathematics Revision of Formulae and Results: Surds Co-Ordinate GeometryDocument5 pagesMathematics Revision of Formulae and Results: Surds Co-Ordinate GeometryabhiNo ratings yet
- Table of IntegralsDocument1 pageTable of IntegralsBrandonDurepoNo ratings yet
- Calc 2 Lecture Notes Section 5.1 1 of 6: y X YeDocument6 pagesCalc 2 Lecture Notes Section 5.1 1 of 6: y X Yemasyuki1979No ratings yet
- Math ReveiwDocument3 pagesMath ReveiwApache_mooNo ratings yet
- Integration FormulaeDocument7 pagesIntegration Formulaeommayekar19No ratings yet
- F (X) DX F (X) +C Symbol of IntegrationDocument13 pagesF (X) DX F (X) +C Symbol of IntegrationSyed Mohammad AskariNo ratings yet
- Coplex Number FormulasDocument7 pagesCoplex Number FormulasMohan KhedkarNo ratings yet
- Integration PDFDocument8 pagesIntegration PDFAre Peace El MananaNo ratings yet
- 151 S 05 FormulasDocument2 pages151 S 05 FormulasVineet PandeyNo ratings yet
- C CN I N (n+1) : Critical ValuesDocument10 pagesC CN I N (n+1) : Critical ValuesFolk NarongritNo ratings yet
- Basic Integration Formula SheetDocument1 pageBasic Integration Formula SheetbihanichandreshNo ratings yet
- Rules of Differentiation and IntegrationDocument10 pagesRules of Differentiation and IntegrationKitchanan KosalathipNo ratings yet
- FormulaeDocument2 pagesFormulaelaw1234836No ratings yet
- Formula Sheet - New Zealand Level 3 Calculus (2009)Document4 pagesFormula Sheet - New Zealand Level 3 Calculus (2009)naedkcinNo ratings yet
- 9 Integrals PDFDocument19 pages9 Integrals PDFthinkiitNo ratings yet
- Integrals: Definitions Definite Integral: Suppose Anti-Derivative: An Anti-Derivative ofDocument5 pagesIntegrals: Definitions Definite Integral: Suppose Anti-Derivative: An Anti-Derivative ofuditagarwal1997No ratings yet
- Calculus 2 SummaryDocument2 pagesCalculus 2 Summarydukefvr41No ratings yet
- AP BC ReviewDocument7 pagesAP BC ReviewchowmeinnoodleNo ratings yet
- Maths Class 12 FormulaDocument2 pagesMaths Class 12 Formulashubhamsingh1112006No ratings yet
- Math H Formula Booklet 2016 WebsiteDocument15 pagesMath H Formula Booklet 2016 WebsiteAmeena LundquistNo ratings yet
- FormulasDocument3 pagesFormulasGladwin BuquironNo ratings yet
- BC MC P1ansDocument17 pagesBC MC P1anssharon cha100% (1)
- P3notes Differential EquationsDocument16 pagesP3notes Differential EquationsCosithic8421No ratings yet
- Practice Exam3 21b SolDocument6 pagesPractice Exam3 21b SolUmer Iftikhar AhmedNo ratings yet
- MATH 259 - Review Sheet (Prerequisite Topics) : (This Is NOT A Comprehensive List!)Document4 pagesMATH 259 - Review Sheet (Prerequisite Topics) : (This Is NOT A Comprehensive List!)Celal KermangilNo ratings yet
- INTEGRAL CALCULUS HandoutsDocument7 pagesINTEGRAL CALCULUS Handoutsurfriend_jjn05No ratings yet
- Differential EquationsDocument28 pagesDifferential EquationsMichael DamianNo ratings yet
- IntegralesDocument2 pagesIntegralesAlex MirelNo ratings yet
- − z and let ψ = xDocument7 pages− z and let ψ = xalpha2122No ratings yet
- Integral CalculusDocument25 pagesIntegral CalculusCarl Kristopher PeloniaNo ratings yet
- Formulae,,key Points,, Algorithm (For Class 12 TH Maths)Document23 pagesFormulae,,key Points,, Algorithm (For Class 12 TH Maths)angusingh60No ratings yet
- Trigonometric Ratios to Transformations (Trigonometry) Mathematics E-Book For Public ExamsFrom EverandTrigonometric Ratios to Transformations (Trigonometry) Mathematics E-Book For Public ExamsRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- De Moiver's Theorem (Trigonometry) Mathematics Question BankFrom EverandDe Moiver's Theorem (Trigonometry) Mathematics Question BankNo ratings yet
- Analytic Geometry: Graphic Solutions Using Matlab LanguageFrom EverandAnalytic Geometry: Graphic Solutions Using Matlab LanguageNo ratings yet
- Transformation of Axes (Geometry) Mathematics Question BankFrom EverandTransformation of Axes (Geometry) Mathematics Question BankRating: 3 out of 5 stars3/5 (1)
- A-level Maths Revision: Cheeky Revision ShortcutsFrom EverandA-level Maths Revision: Cheeky Revision ShortcutsRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (8)
- Factoring and Algebra - A Selection of Classic Mathematical Articles Containing Examples and Exercises on the Subject of Algebra (Mathematics Series)From EverandFactoring and Algebra - A Selection of Classic Mathematical Articles Containing Examples and Exercises on the Subject of Algebra (Mathematics Series)No ratings yet
- SEEA1601Document104 pagesSEEA1601skrtamilNo ratings yet
- Design and Testing of Electrical MachinesDocument210 pagesDesign and Testing of Electrical MachinesskrtamilNo ratings yet
- Enhancing Photoelectric Conversion Efficiency of Solar Panel by WatercoolingDocument5 pagesEnhancing Photoelectric Conversion Efficiency of Solar Panel by WatercoolingskrtamilNo ratings yet
- Model1 EDDocument2 pagesModel1 EDskrtamilNo ratings yet
- Dhanalakshmi Srinivasan Institute of Technology: Samayapuram, Trichy - 621 112Document2 pagesDhanalakshmi Srinivasan Institute of Technology: Samayapuram, Trichy - 621 112skrtamilNo ratings yet
- Chapter Five: Inimization of OnductedDocument27 pagesChapter Five: Inimization of Onductedligrav007No ratings yet
- Lab Manual: Ee 2305 Electrical Machines Lab IiDocument38 pagesLab Manual: Ee 2305 Electrical Machines Lab IiskrtamilNo ratings yet
- Ram6n: Sliding Mode Controller For The Boost InverterDocument6 pagesRam6n: Sliding Mode Controller For The Boost InverterskrtamilNo ratings yet
Basic Formulae
Basic Formulae
Uploaded by
skrtamilOriginal Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Basic Formulae
Basic Formulae
Uploaded by
skrtamilCopyright:
Available Formats
Math 307- Summer 2004
Basic Formulas
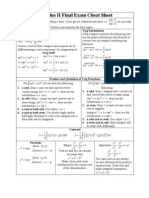
Algebra b b2 Completing the square: X 2 + bX + c = (X + )2 + c. 2 4 b b2 4ac Quadratic formula: roots of aX 2 + bX + c are . 2a ab bc b c bc 1/b b Exponents: ab ac = ab+c ; = a ; ( a ) = a ; a = a. ac Geometry 4 Circle: circumference = 2r; area = r2 . Sphere: vol = r3 ; surface area = 4r2 . 3 2 Cylinder: vol = r h; lateral area = 2rh; total surface area = 2rh + 2r2 . 1 Cone: vol = r2 h; lateral area = r r2 + h2 ; total surface area = r r2 + h2 + r2 . 3 Analytic geometry Point-slope formula for straight line: y = y0 + m(x x0 ). Circle centered at (h, k ): (x h)2 + (y k )2 = r2 . Ellipse with semimajor axis along x-axis and semiminor axis along y -axis: x2 y 2 + 2 = 1. a2 b
Trigonometry opposite adjacent opposite ; cos = ; tan = ; hypotenuse hypotenuse adjacent 1 1 1 sin cos sec = ; csc = ; cot = ; tan = ; cot = ; cos sin tan cos sin sin x = cos x ; cos x = sin x ; 2 2 sin(x + ) = sin x; cos(x + ) = cos x. a b c Law of sines: = = . Law of cosines: a2 = b2 + c2 2bc cos A. sin A sin B sin C Sum of angles: sin(x + y ) = sin x cos y + cos x sin y ; cos(x + y ) = cos x cos y sin x sin y ; tan x + tan y tan(x + y ) = 1 tan x tan y sin = sin2 and cos2 formulas: sin2 x + cos2 x = 1; tan2 x + 1 = sec2 x; 1 + cot2 x = csc2 x ; 1 cos(2x) 1 + cos(2x) ; cos2 x = . 2 2 x+y yx Product formula: cos x cos y = 2 sin sin . 2 2 sin2 x =
Calculus. Basic dierentiation formulae: du dv d dv du d (u + v ) = + , (uv ) = u +v . dx dx dx dx dx dx d u 1 du dv = 2 v u , for v = 0. dx v v dx dx
Chain rule:
dz dy dz = . dx dy dx Fundamental Theorem of Calculus:
b
if F (x) = f (x) then
a
f (x)dx = F (b) F (a) and d dx
g ( x)
f (x)dx = F (x) + C
Dierentiation of limits of integral: Derivatives of specic functions:
h(u) du = h (g (x)) g (x) h (f (x)) f (x)
f (x)
dxn dex dln|x| 1 = nxn1 ; = ex ; = ; dx dx dx x d sin x d cos x d tan x = cos x; = sin x; = sec2 x; dx dx dx dArcsin x 1 dArctan x 1 = ; = . 2 dx dx 1 + x2 1x (u + v ) dx = u dx + v dx; au dx = a u dx;
Basic integration formulae: Substitution:
f (u(x)) u (x) dx = F (u(x)) , where u dv = uv v du;
f (u)du = F (u);
Integration by parts: Standard integrals: xn dx =
xn+1 + C (n = 1); n+1
dx = ln |x| + C ; x
ex dx = ex + C ; tan x dx = ln | cos x| + C ;
sin x dx = cos x + C ;
cos x dx = sin x + C ;
dx xdx = Arcsin x + C ; = 1 x2 + C ; 1 x2 1 x2 x dx 1 dx = Arctan x + C ; = ln(1 + x2 ) + C 1 + x2 1 + x2 2 Rational with quadratic denominator: If the degree of the numerator is not smaller than the degree of the denominator, divide. If the denominator does not factor use above two integrals and substitution. If the denominator does factor, then write ax + b A B = + which is the same as: ax + b = A(x d) + B (x c) (x c)(x d) xc xd Set x=c then x=d to nd A and B, given a and b.
You might also like
- Microsoft Word - Calculus 2 Formula Cheat SheetDocument2 pagesMicrosoft Word - Calculus 2 Formula Cheat SheetHunterKing199375% (4)
- HSC 3U Maths FormulaeDocument7 pagesHSC 3U Maths FormulaeHotz InatorNo ratings yet
- Calculus Cheat Sheet IntegralsDocument5 pagesCalculus Cheat Sheet Integralsapi-322359712No ratings yet
- Calculus Cheat Sheet Integrals ReducedDocument3 pagesCalculus Cheat Sheet Integrals ReducedShahnaz GazalNo ratings yet
- Eee.60-62Document3 pagesEee.60-62skrtamilNo ratings yet
- Basic Formula2342Document2 pagesBasic Formula2342asim_at_vital123No ratings yet
- Mathematics Revision of Formulae and Results: Surds Co-Ordinate GeometryDocument5 pagesMathematics Revision of Formulae and Results: Surds Co-Ordinate GeometryDarrenPurtillWrightNo ratings yet
- Essential Formulae: Number and AlgebraDocument7 pagesEssential Formulae: Number and AlgebraShinigami01001No ratings yet
- Derivadas: Reglas de Derivaci OnDocument11 pagesDerivadas: Reglas de Derivaci OnJosé Pablo ZubietaNo ratings yet
- Essential FormulaeDocument16 pagesEssential FormulaeMaruthappan Sundaram100% (1)
- LESSON 4 CAL 2 IntegralsDocument40 pagesLESSON 4 CAL 2 IntegralsZero DragneelNo ratings yet
- EMTH210: Formula Sheet 2015: Trigonometric (Circular) FunctionsDocument3 pagesEMTH210: Formula Sheet 2015: Trigonometric (Circular) FunctionsGlass-Half-EmptyNo ratings yet
- Formulario Calculo VectorialDocument20 pagesFormulario Calculo VectorialKevin Molina100% (1)
- Matek KepletekDocument2 pagesMatek KepletekblackjackkNo ratings yet
- Bab Xiii Integral: 13. 1 DefinisiDocument25 pagesBab Xiii Integral: 13. 1 DefinisiDeazzy AndriyaniNo ratings yet
- Reference PageDocument2 pagesReference PageYeung Amy HoNo ratings yet
- BasicsDocument2 pagesBasicsmadcow_scribdNo ratings yet
- Integration Formula: + C U Du VDX Udx DX V U Udx C CudxDocument5 pagesIntegration Formula: + C U Du VDX Udx DX V U Udx C CudxRon AtaNo ratings yet
- Mathematics Revision of Formulae and Results: Surds Co-Ordinate GeometryDocument5 pagesMathematics Revision of Formulae and Results: Surds Co-Ordinate GeometryabhiNo ratings yet
- Table of IntegralsDocument1 pageTable of IntegralsBrandonDurepoNo ratings yet
- Calc 2 Lecture Notes Section 5.1 1 of 6: y X YeDocument6 pagesCalc 2 Lecture Notes Section 5.1 1 of 6: y X Yemasyuki1979No ratings yet
- Math ReveiwDocument3 pagesMath ReveiwApache_mooNo ratings yet
- Integration FormulaeDocument7 pagesIntegration Formulaeommayekar19No ratings yet
- F (X) DX F (X) +C Symbol of IntegrationDocument13 pagesF (X) DX F (X) +C Symbol of IntegrationSyed Mohammad AskariNo ratings yet
- Coplex Number FormulasDocument7 pagesCoplex Number FormulasMohan KhedkarNo ratings yet
- Integration PDFDocument8 pagesIntegration PDFAre Peace El MananaNo ratings yet
- 151 S 05 FormulasDocument2 pages151 S 05 FormulasVineet PandeyNo ratings yet
- C CN I N (n+1) : Critical ValuesDocument10 pagesC CN I N (n+1) : Critical ValuesFolk NarongritNo ratings yet
- Basic Integration Formula SheetDocument1 pageBasic Integration Formula SheetbihanichandreshNo ratings yet
- Rules of Differentiation and IntegrationDocument10 pagesRules of Differentiation and IntegrationKitchanan KosalathipNo ratings yet
- FormulaeDocument2 pagesFormulaelaw1234836No ratings yet
- Formula Sheet - New Zealand Level 3 Calculus (2009)Document4 pagesFormula Sheet - New Zealand Level 3 Calculus (2009)naedkcinNo ratings yet
- 9 Integrals PDFDocument19 pages9 Integrals PDFthinkiitNo ratings yet
- Integrals: Definitions Definite Integral: Suppose Anti-Derivative: An Anti-Derivative ofDocument5 pagesIntegrals: Definitions Definite Integral: Suppose Anti-Derivative: An Anti-Derivative ofuditagarwal1997No ratings yet
- Calculus 2 SummaryDocument2 pagesCalculus 2 Summarydukefvr41No ratings yet
- AP BC ReviewDocument7 pagesAP BC ReviewchowmeinnoodleNo ratings yet
- Maths Class 12 FormulaDocument2 pagesMaths Class 12 Formulashubhamsingh1112006No ratings yet
- Math H Formula Booklet 2016 WebsiteDocument15 pagesMath H Formula Booklet 2016 WebsiteAmeena LundquistNo ratings yet
- FormulasDocument3 pagesFormulasGladwin BuquironNo ratings yet
- BC MC P1ansDocument17 pagesBC MC P1anssharon cha100% (1)
- P3notes Differential EquationsDocument16 pagesP3notes Differential EquationsCosithic8421No ratings yet
- Practice Exam3 21b SolDocument6 pagesPractice Exam3 21b SolUmer Iftikhar AhmedNo ratings yet
- MATH 259 - Review Sheet (Prerequisite Topics) : (This Is NOT A Comprehensive List!)Document4 pagesMATH 259 - Review Sheet (Prerequisite Topics) : (This Is NOT A Comprehensive List!)Celal KermangilNo ratings yet
- INTEGRAL CALCULUS HandoutsDocument7 pagesINTEGRAL CALCULUS Handoutsurfriend_jjn05No ratings yet
- Differential EquationsDocument28 pagesDifferential EquationsMichael DamianNo ratings yet
- IntegralesDocument2 pagesIntegralesAlex MirelNo ratings yet
- − z and let ψ = xDocument7 pages− z and let ψ = xalpha2122No ratings yet
- Integral CalculusDocument25 pagesIntegral CalculusCarl Kristopher PeloniaNo ratings yet
- Formulae,,key Points,, Algorithm (For Class 12 TH Maths)Document23 pagesFormulae,,key Points,, Algorithm (For Class 12 TH Maths)angusingh60No ratings yet
- Trigonometric Ratios to Transformations (Trigonometry) Mathematics E-Book For Public ExamsFrom EverandTrigonometric Ratios to Transformations (Trigonometry) Mathematics E-Book For Public ExamsRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- De Moiver's Theorem (Trigonometry) Mathematics Question BankFrom EverandDe Moiver's Theorem (Trigonometry) Mathematics Question BankNo ratings yet
- Analytic Geometry: Graphic Solutions Using Matlab LanguageFrom EverandAnalytic Geometry: Graphic Solutions Using Matlab LanguageNo ratings yet
- Transformation of Axes (Geometry) Mathematics Question BankFrom EverandTransformation of Axes (Geometry) Mathematics Question BankRating: 3 out of 5 stars3/5 (1)
- A-level Maths Revision: Cheeky Revision ShortcutsFrom EverandA-level Maths Revision: Cheeky Revision ShortcutsRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (8)
- Factoring and Algebra - A Selection of Classic Mathematical Articles Containing Examples and Exercises on the Subject of Algebra (Mathematics Series)From EverandFactoring and Algebra - A Selection of Classic Mathematical Articles Containing Examples and Exercises on the Subject of Algebra (Mathematics Series)No ratings yet
- SEEA1601Document104 pagesSEEA1601skrtamilNo ratings yet
- Design and Testing of Electrical MachinesDocument210 pagesDesign and Testing of Electrical MachinesskrtamilNo ratings yet
- Enhancing Photoelectric Conversion Efficiency of Solar Panel by WatercoolingDocument5 pagesEnhancing Photoelectric Conversion Efficiency of Solar Panel by WatercoolingskrtamilNo ratings yet
- Model1 EDDocument2 pagesModel1 EDskrtamilNo ratings yet
- Dhanalakshmi Srinivasan Institute of Technology: Samayapuram, Trichy - 621 112Document2 pagesDhanalakshmi Srinivasan Institute of Technology: Samayapuram, Trichy - 621 112skrtamilNo ratings yet
- Chapter Five: Inimization of OnductedDocument27 pagesChapter Five: Inimization of Onductedligrav007No ratings yet
- Lab Manual: Ee 2305 Electrical Machines Lab IiDocument38 pagesLab Manual: Ee 2305 Electrical Machines Lab IiskrtamilNo ratings yet
- Ram6n: Sliding Mode Controller For The Boost InverterDocument6 pagesRam6n: Sliding Mode Controller For The Boost InverterskrtamilNo ratings yet