Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Dug Wells: Dug Well Construction Features
Dug Wells: Dug Well Construction Features
Uploaded by
dannytmroOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Dug Wells: Dug Well Construction Features
Dug Wells: Dug Well Construction Features
Uploaded by
dannytmroCopyright:
Available Formats
Dug Wells
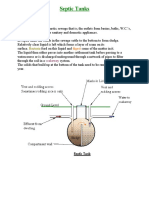
Dug wells are holes in the ground dug by shovel or backhoe. Historically, a dug well was excavated below the groundwater table until incoming water exceeded the diggers bailing rate. The well was then lined (cased) with stones, brick, tile, or other material to prevent collapse. It was covered with a cap of wood, stone, or concrete. Since it is so difficult to dig beneath the ground water table, dug wells are not very deep. Typically, they are only 10 to 30 feet deep. Being so shallow, dug wells have the highest risk of becoming contaminated. To minimize the likelihood of contamination, your dug well should have certain features. These features help to prevent contaminants from traveling along the outside of the casing or through the casing and into the well. Dug Well Construction Features The well should be cased with a watertight material (for example, tongue-and-groove precast concrete) and a cement grout or bentonite clay sealant poured along the outside of the casing to the top of the well. The well should be covered by a concrete curb and cap that stands about a foot above the ground. The land surface around the well should be mounded so that surface water runs away from the well and is not allowed to pond around the outside of the wellhead. Ideally, the pump for your well should be inside your home or in a separate pump house, rather than in a pit next to the well.
Land activities around a dug well can also contaminate it. (see our chart of activites that may contaminate a drinking water well) While dug wells have been used as a household water supply source for many years, most are relics of older homes, dug before drilling equipment was readily available or when drilling was considered too expensive. If you have a dug well on your property and are using it for drinking water, check to make sure it is properly covered and sealed. Another problem relating to the shallowness of a dug well is that it may go dry during a drought when the ground water table drops. Other types of wells: Driven Drilled
The information contained on this page, as well as the above graphic was provided by The Rhode Island Department of Environmental Management from their document: Health Drinking Water for Rhode Islanders: Private Drinking Water Wells (644KB PDF FILE, 4 pgs) (ALL ABOUT PDF FILES)
You might also like
- Fish Pond InfoDocument9 pagesFish Pond InfoDaniel Taiti KimathiNo ratings yet
- Intake WellDocument45 pagesIntake Wellsharmak_anilNo ratings yet
- Basic Information DrilledDocument1 pageBasic Information Drilledfatih_hideNo ratings yet
- Basicinformation DrilledDocument1 pageBasicinformation DrilledRob WillestoneNo ratings yet
- ISUX Well PluggingDocument4 pagesISUX Well Pluggingcacalot93No ratings yet
- Well Water BasicsDocument5 pagesWell Water Basicsbontu gadisaNo ratings yet
- Water Well ConstructionDocument5 pagesWater Well ConstructionrramadanNo ratings yet
- Getting Groundwater - Safe Wells and WaterholesDocument7 pagesGetting Groundwater - Safe Wells and WaterholesGreen Action Sustainable Technology Group100% (1)
- SPT SPTDocument7 pagesSPT SPTRadoNounNo ratings yet
- Hand Dug WellDocument29 pagesHand Dug WellMelikte100% (1)
- Well Completion Development and Maintenance of WellsDocument33 pagesWell Completion Development and Maintenance of WellsArun KumarNo ratings yet
- Underground Tanks2Document22 pagesUnderground Tanks2iuliandurdureanuNo ratings yet
- IChemE - Presentation - LPB Toolbox Talk - Bunding Should Be Simple & ReliableDocument12 pagesIChemE - Presentation - LPB Toolbox Talk - Bunding Should Be Simple & Reliablesl1828No ratings yet
- How Wells Are Drilled - by American Ground Water TrustDocument2 pagesHow Wells Are Drilled - by American Ground Water Trusthbpr9999No ratings yet
- Sub Surface Dams PDFDocument5 pagesSub Surface Dams PDFKwabena OtchereNo ratings yet
- Water WellsDocument20 pagesWater Wellsashraf habibNo ratings yet
- PM1561 PDFDocument4 pagesPM1561 PDFBooth TeleNo ratings yet
- How To Build A Natural Swimming PoolDocument3 pagesHow To Build A Natural Swimming PoolIgnacio Lopez DulceNo ratings yet
- Groundwater Is Used For Drinking Water by More Than 50 Percent of The People inDocument18 pagesGroundwater Is Used For Drinking Water by More Than 50 Percent of The People inMay de VeraNo ratings yet
- Ornamental Garden PoolsDocument16 pagesOrnamental Garden PoolsminiongskyNo ratings yet
- Development of Water SourcesDocument44 pagesDevelopment of Water SourcesJames Anthony TorresNo ratings yet
- Rainwater HarvestingDocument32 pagesRainwater HarvestingDomie KiharaNo ratings yet
- Soakage PitDocument3 pagesSoakage Pitjyotshna sahooNo ratings yet
- Unit-I: Sources and Treatment of WaterDocument24 pagesUnit-I: Sources and Treatment of WaterPavan G ReddyNo ratings yet
- WellsDocument25 pagesWellsTHEJSWINo ratings yet
- Pond InstallationDocument70 pagesPond Installationaraojose19No ratings yet
- Dug WellsDocument2 pagesDug WellsPrinceEnopiaNo ratings yet
- Pond - Build .Pack .04.07.2017Document11 pagesPond - Build .Pack .04.07.2017roaen.sabchevNo ratings yet
- Pond Construction:: Some Practical ConsiderationsDocument4 pagesPond Construction:: Some Practical ConsiderationsGeorge AtaherNo ratings yet
- Chapter 11 - Groundwater ProductionDocument24 pagesChapter 11 - Groundwater Productionنيرمين احمدNo ratings yet
- Water Pan For Runoff Water Harvesting PDFDocument4 pagesWater Pan For Runoff Water Harvesting PDFmulwa2009No ratings yet
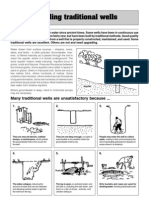
- Upgrading Traditional WellsDocument4 pagesUpgrading Traditional WellsGreen Action Sustainable Technology GroupNo ratings yet
- A Building Without Water Supply Is Unfit For Human HabitationDocument9 pagesA Building Without Water Supply Is Unfit For Human Habitationjurhym doteNo ratings yet
- Water WellsDocument8 pagesWater WellsJanine Arielle DanaoNo ratings yet
- Sinkholes - A Brief Lesson About Disaster ManagementDocument9 pagesSinkholes - A Brief Lesson About Disaster ManagementSANDRA MANANSALANo ratings yet
- Private Water SupplyDocument7 pagesPrivate Water SupplyNick Zeet RasonableNo ratings yet
- Biological PoolsDocument7 pagesBiological PoolsJUAN_LUIS_MENARES100% (2)
- Pond Construction and Management Fish Pond Design and ConstructionDocument9 pagesPond Construction and Management Fish Pond Design and Constructionpatelrt8No ratings yet
- Embankment DamDocument63 pagesEmbankment DamRanjan Dhungel100% (1)
- Nikhil HydrologyDocument16 pagesNikhil HydrologynavoNo ratings yet
- Pete 322 - Drilling Engineering - Ii Chapter 6 - Casing DesignDocument39 pagesPete 322 - Drilling Engineering - Ii Chapter 6 - Casing DesignTuran Amiraslanli100% (1)
- Creating A Water Garden Retreat (Brochure)Document32 pagesCreating A Water Garden Retreat (Brochure)manda_manuNo ratings yet
- Earthen DamDocument25 pagesEarthen DamDeeksha DeekshuNo ratings yet
- Dam & Reservoir: By: Aditya Katoch M.Tech 6 SemDocument31 pagesDam & Reservoir: By: Aditya Katoch M.Tech 6 SemATISH KUMAR SAHOONo ratings yet
- Well Completion2Document36 pagesWell Completion2kuda kwasheNo ratings yet
- Rubble Trench FoundationsDocument2 pagesRubble Trench FoundationsRaoul LfNo ratings yet
- Well - WikipediaDocument23 pagesWell - WikipediaDominic OkonNo ratings yet
- 3 - Private Water Supply SourceDocument20 pages3 - Private Water Supply SourceE&N CommissionNo ratings yet
- Handout Waste Catch BasinDocument2 pagesHandout Waste Catch BasinJonniel De GuzmanNo ratings yet
- Water Well Group 4Document29 pagesWater Well Group 4Alvin DeliroNo ratings yet
- Causes of Failure of Earth Dams Criteria For Safe Design of Earth Dams Slope Stability of Earth DamsDocument11 pagesCauses of Failure of Earth Dams Criteria For Safe Design of Earth Dams Slope Stability of Earth DamsAhmed AmediNo ratings yet
- 6 Major Types of Cofferdam - Construction Methods - UsesDocument8 pages6 Major Types of Cofferdam - Construction Methods - UsesNiluka EkanayakaNo ratings yet
- 5 Innovative Slurry Trench MethodsDocument9 pages5 Innovative Slurry Trench MethodsMalik BilalNo ratings yet
- Publications Water Sanitation Chapter12Document18 pagesPublications Water Sanitation Chapter12nelson_53No ratings yet
- Technical Seminar 2Document28 pagesTechnical Seminar 2Thulasilakshmi GNo ratings yet
- CTPM EarthworkDocument68 pagesCTPM Earthworkkalyan100% (1)
- Articles: by Douglas C. HooverDocument65 pagesArticles: by Douglas C. HooverJuan Carlos FernandezNo ratings yet
- Transactions of the American Society of Civil Engineers, vol. LXX, Dec. 1910 Reinforced Concrete Pier ConstructionFrom EverandTransactions of the American Society of Civil Engineers, vol. LXX, Dec. 1910 Reinforced Concrete Pier ConstructionNo ratings yet
- Popular Mechanics: How to Fix Anything: Essential Home Repairs Anyone Can DoFrom EverandPopular Mechanics: How to Fix Anything: Essential Home Repairs Anyone Can DoRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (2)
- WWW Youtube Com Watch V DzF9G NaO6YDocument4 pagesWWW Youtube Com Watch V DzF9G NaO6YdannytmroNo ratings yet
- WWW Youtube Com Watch V HcblKh2gfPQ Feature RelatedDocument4 pagesWWW Youtube Com Watch V HcblKh2gfPQ Feature RelateddannytmroNo ratings yet
- OTAC Executive Director AnnouncementDocument1 pageOTAC Executive Director AnnouncementdannytmroNo ratings yet
- SDS Ibt 00026 2011Document6 pagesSDS Ibt 00026 2011dannytmroNo ratings yet
- Manual Prodave MPI V6.0Document92 pagesManual Prodave MPI V6.0jg_jr2000No ratings yet
- Atlas Shopper 2011Document16 pagesAtlas Shopper 2011dannytmroNo ratings yet
- SwatyComet Resin ENGDocument56 pagesSwatyComet Resin ENGdannytmroNo ratings yet
- CroatianDocument48 pagesCroatiandannytmroNo ratings yet
- Glue ChartDocument1 pageGlue ChartdannytmroNo ratings yet