Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Most Common Malignancy of GT!! Definition
Most Common Malignancy of GT!! Definition
Uploaded by
vizinho2000Original Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Most Common Malignancy of GT!! Definition
Most Common Malignancy of GT!! Definition
Uploaded by
vizinho2000Copyright:
Available Formats
Cervical Cancer
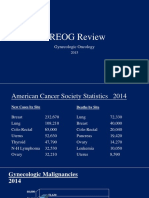
Most common malignancy of GT!! Definition: Epithelial Malignancy originated from the cervix CIN: Cervical Intraepithelial Neoplasia Epidemiology: Incidence: 3.89/100,000 Elderly women, mean age 52.2y Social: sex behavior, vaginal delivery, smoking, contraceptive method, nutrition, economic status, race, geographical environment Biology: HPV, HSV, HIV Clinical Progressing: Multiple Stages CIN I CIN II CIN III Cancer Histological Classification: Squamoscell cancer Adenocarcinoma Metastasis: Invasion Lymphatic Blood Manifestation: Symptoms: constipation, dysuria, urinary retentron, pelvic pain Signs and subtype: Contact bleeding , Bloody dischaging Tumor markers The STAGING of Cervical Cancer: FIGO 2009 I: limited to uterus Ia: Only viewed under microscope, any naked eyes viewed disease is Ib Ia1: depth <3mm, width7mm Ia2: depth 3-5mm, width7mm Ib: any naked eyes viewed disease or >Ia2 Ib1: D4cm, Ib2: D>4cm II: extended out of uterus IIa: without parametrium invasion IIa1: D4cm, vagina<1/3 IIa2: D>4cm, vagina<1/3 III: pelvis wall invasion IIIa: vagina>1/3, no pelvis invasion IIIb: pelvis side wall involved IVa: bladder, rectum invasion IVb: distant metastasis
Diagnosis: Pap Smear, HPV Lugols test Acetate White test Cervicalgraphy Coloscopy Intrinsic fluorescence check Bioposy Cold Knife CONIZATION Differential Diagnosis: Inflammation Tuberculosis Endometriosis Treatment: Surgery Radiation Chemotherapy Surgical treatment CIN: CIN I: follow or medical treatment CIN II: physical treatment/LEEP CIN III: conization Surgical treatment: Out facial Hys.class I Modify Weitherm Hys.class II Weitherm Hys.class III Wilded Hysclass IV Pelvic externationclass V Pelvic /aortic lymphodenectomy Radiation therapy: Prognosis: I 90% II 80% III 60% IV 40%
You might also like
- CA Cervix NewDocument54 pagesCA Cervix NewBi PinNo ratings yet
- Cervical CancerDocument28 pagesCervical CancerAngetile KasangaNo ratings yet
- Cancer Cervix: Predisposing FactorsDocument5 pagesCancer Cervix: Predisposing Factorsmed.progressNo ratings yet
- Cancer of The CervixDocument68 pagesCancer of The CervixSandra mugunzvaNo ratings yet
- Ob-Gyn Review Part 3Document101 pagesOb-Gyn Review Part 3filchibuffNo ratings yet
- Cervical CancerDocument53 pagesCervical Cancera_m_elsheemy1931100% (5)
- Carcinoma of The Cervix: DR Baidaa AbdallahDocument30 pagesCarcinoma of The Cervix: DR Baidaa AbdallahNashat SaadiNo ratings yet
- Cervical CancerDocument3 pagesCervical CancerWayne GretzkyNo ratings yet
- Management and Prevention of Cervical CancerDocument43 pagesManagement and Prevention of Cervical CancerMax ZealNo ratings yet
- Endometrial CancerDocument21 pagesEndometrial CancerRachel Lalaine Marie SialanaNo ratings yet
- Abnormal Cervical SmearDocument63 pagesAbnormal Cervical SmearAkhmal SidekNo ratings yet
- Stages of Cervical CancerDocument2 pagesStages of Cervical CancerMalakeNo ratings yet
- Pathologic Types: o o o oDocument2 pagesPathologic Types: o o o orexzordNo ratings yet
- Cervical Intraepithilial NeoplasiaDocument41 pagesCervical Intraepithilial Neoplasiadrtasmiaakter100% (1)
- Staging in Cancer: DR - Atul VermaDocument25 pagesStaging in Cancer: DR - Atul VermaDr VermaNo ratings yet
- ENDOMETRIAL CANCERS and Vin and VULVAR CANCERDocument53 pagesENDOMETRIAL CANCERS and Vin and VULVAR CANCERManuel MercyNo ratings yet
- Case Series of Rare Breast Diseases and Their Unusual PresentationDocument36 pagesCase Series of Rare Breast Diseases and Their Unusual Presentationdodo1No ratings yet
- Cervical CancerDocument32 pagesCervical Cancermvs16973100% (2)
- Malignant Lesions of CervixDocument40 pagesMalignant Lesions of Cervixeno100% (1)
- GynecologyDocument247 pagesGynecologyDitaNo ratings yet
- Final Handouts (Cervica Cancer)Document3 pagesFinal Handouts (Cervica Cancer)lisette_sakuraNo ratings yet
- Cervical Cancer: Santos, Maxime Ella L. Gecera, Alondra KateDocument22 pagesCervical Cancer: Santos, Maxime Ella L. Gecera, Alondra KateLyssaMarieKathryneEgeNo ratings yet
- Cervical CancerDocument36 pagesCervical CancerPro fatherNo ratings yet
- Cervical Pathology 4Document104 pagesCervical Pathology 4Arie PratamaNo ratings yet
- Staging of Gyn .OncDocument29 pagesStaging of Gyn .OncMohamed Atef MohamedNo ratings yet
- Carcinoma Endometrium 1Document42 pagesCarcinoma Endometrium 1Sapna SNo ratings yet
- Ca Colon: Pembimbing Dr. Yanti, SP.B KBDDocument47 pagesCa Colon: Pembimbing Dr. Yanti, SP.B KBDRichard HadinataNo ratings yet
- Endometrial Cancer LDocument26 pagesEndometrial Cancer Lapi-19916399No ratings yet
- Cervical Cancer Protocol: ScreeningDocument5 pagesCervical Cancer Protocol: ScreeningEugène NkusiNo ratings yet
- Common Gastrointesti NAL Malignancies: Kristine Flor D. Renomeron Group 2 Schwartz ClubDocument56 pagesCommon Gastrointesti NAL Malignancies: Kristine Flor D. Renomeron Group 2 Schwartz ClubEC BaldzNo ratings yet
- Cervical Cancer: Dr. Vijay PrakashDocument23 pagesCervical Cancer: Dr. Vijay PrakashVijay PrakashNo ratings yet
- CA Cervix - StagingDocument13 pagesCA Cervix - StagingStella DaimariNo ratings yet
- CA ColonDocument47 pagesCA ColonrahayuNo ratings yet
- Endometrial Carcinoma: Amina Adel Al-QaysiDocument42 pagesEndometrial Carcinoma: Amina Adel Al-Qaysitaufik perdanaNo ratings yet
- Case Presentation: Presented By-Deeksha Sharma B.SC (Hons) Nursing 3 YearDocument35 pagesCase Presentation: Presented By-Deeksha Sharma B.SC (Hons) Nursing 3 YearMinakshi MawariNo ratings yet
- Different Pathologies of The UterusDocument74 pagesDifferent Pathologies of The UterusAmal100% (1)
- Benign Tumor Malignant Tumor: Ms. Sneha Sehrawat AIIMS RishikeshDocument37 pagesBenign Tumor Malignant Tumor: Ms. Sneha Sehrawat AIIMS RishikeshRajaNo ratings yet
- 9.cancer of The Female Genital Tract.Document58 pages9.cancer of The Female Genital Tract.vichramNo ratings yet
- Pathology - 24 Breast PathologyDocument9 pagesPathology - 24 Breast PathologyNicole William100% (1)
- 2015 Oncology CREOG Review PDFDocument76 pages2015 Oncology CREOG Review PDFRima HajjarNo ratings yet
- 000 Cervical CancerDocument8 pages000 Cervical CancerIgwe SolomonNo ratings yet
- Kabwe Central Hospital KCH: Breast Cancer"Document34 pagesKabwe Central Hospital KCH: Breast Cancer"Emmanuel MukukaNo ratings yet
- Premalignant & Malignant Disease of Cervix Not CompletedDocument10 pagesPremalignant & Malignant Disease of Cervix Not CompletedMelissa Aina Mohd YusofNo ratings yet
- PID PresentationDocument23 pagesPID Presentationakankiza.lucky83No ratings yet
- Endometrial CancerDocument16 pagesEndometrial CancerSusan Powell-ProctorNo ratings yet
- Figo Općenito:: (Common In,, And)Document4 pagesFigo Općenito:: (Common In,, And)perolegendaNo ratings yet
- Ovarian Carsinoma: Divisi Onkologi Ginekologi Bagian Obstetri & Ginekologi FK - UsuDocument25 pagesOvarian Carsinoma: Divisi Onkologi Ginekologi Bagian Obstetri & Ginekologi FK - UsuThe Ray MedicsterNo ratings yet
- Cervical Cancer: Presented by Shashi TripathiDocument39 pagesCervical Cancer: Presented by Shashi TripathiShashi TripathiNo ratings yet
- Breast Cancer: Presented By: Meity Masitha A.K Class BDocument14 pagesBreast Cancer: Presented By: Meity Masitha A.K Class BMeity MasithaNo ratings yet
- Cervical CancerDocument6 pagesCervical CancerCnette S. LumboNo ratings yet
- Breast CancerDocument4 pagesBreast CancerNyrhtak17No ratings yet
- Endometrial Cancer: BY: Muhammad Munawwar Mohamed Aidil Syahir Wan Salahuddin Ahmad JairullahDocument16 pagesEndometrial Cancer: BY: Muhammad Munawwar Mohamed Aidil Syahir Wan Salahuddin Ahmad JairullahMunawwar AwaNo ratings yet
- Ictc 2Document31 pagesIctc 2Gamer StarNo ratings yet
- Malignant Tumors of Uterus: DR Tahira RizwanDocument52 pagesMalignant Tumors of Uterus: DR Tahira RizwanSadia YousafNo ratings yet
- Session 3 - Cervical Carcinoma 2Document25 pagesSession 3 - Cervical Carcinoma 2ht7qh5k27fNo ratings yet
- Endometrial CancerDocument34 pagesEndometrial CancertyasdwiarumNo ratings yet
- The New FIGO Staging For Carcinoma of The Vulva, Cervix, Endometrium, and SarcomasDocument9 pagesThe New FIGO Staging For Carcinoma of The Vulva, Cervix, Endometrium, and SarcomasAji PatriajatiNo ratings yet
- 2 PidDocument31 pages2 PidNatif BoteNo ratings yet
- Guidelines For Management of Endometrial CarcinomaDocument41 pagesGuidelines For Management of Endometrial CarcinomaVeenaNo ratings yet
- Clinical Examination Specifications PDFDocument34 pagesClinical Examination Specifications PDFvizinho20000% (1)
- Chapter 6: Gastroduodenal DiseaseDocument12 pagesChapter 6: Gastroduodenal Diseasevizinho2000No ratings yet
- Chapter 4: Abdominal Injury Blunt Abdominal InjuryDocument12 pagesChapter 4: Abdominal Injury Blunt Abdominal Injuryvizinho2000No ratings yet
- Chapter 6: Gastroduodenal DiseaseDocument12 pagesChapter 6: Gastroduodenal Diseasevizinho2000No ratings yet