Professional Documents
Culture Documents
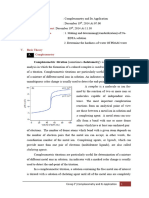
Experiment: Determination of The Total Hardness (Permanent and Temporary)
Experiment: Determination of The Total Hardness (Permanent and Temporary)
Uploaded by
Subhash DhungelOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Experiment: Determination of The Total Hardness (Permanent and Temporary)
Experiment: Determination of The Total Hardness (Permanent and Temporary)
Uploaded by
Subhash DhungelCopyright:
Available Formats
EXPERIMENT: DETERMINATION OF THE TOTAL HARDNESS (PERMANENT AND TEMPORARY) OF WATER.
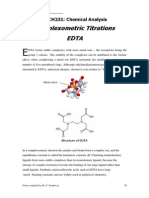
THEORY: The hardness of water is generally due to dissolved calcium and magnesium salts and may be determined by complexometric titration. EDTA is a good complex forming agent. When EDTA reacts with metal there is the formation of complex.
Indicator standard EDTA
Metal ions
metal ions indicator complex
metal ion EDTA complex + indicator.
This process is known as complexometric titration. Buffer solution is used to maintain the pH value about 10. The efficiency of complex formation with EDTA varies with change in pH of the solution. Basic medium is most favorable for complex formation.
HOOC-CH2 N-CH2-CH2-N
CH2-COOH + M2+ M-EDTA
HOOC-CH2
CH2-COOH
The EDTA solution may be standardized by using standard Zn ion solution, using metal ion indicator, Erichrome black -T. It forms the complex with the Zn ion which is red in color. When it is titrated with EDTA, it removes the metal ion indicator forming metal EDTA complex which gives blue solution.
M-In (wine red) + EDTA
M-EDTA + In (blue)
The total hardness of water can be determined by titrating the buffer solution with EDTA whose strength is known. The end point corresponds to cation Ca2+ and Mg2+ forming EDTA complex at pH 10.0. The total hardness is expressed in parts of CaCO3 per million of water. If the solution does not contain Mg2+ ion, little known amount of Mg2+ should be added which forms the wine red colored complex,Ca2+ cannot form a stable complex with the indicator. Mg2+ indicator later on adding EDTA gives more stable Mg2+ EDTA complex leaving free indicator which is blue in color. To remove the interfere due to traces of other metals Co, Ni, Cu, Zn, Hg, Mn little hydroxyl ammonium chloride (which refers some of metals to their lower oxidation state so cannot from complex).
You might also like
- Transformation of SentencesDocument11 pagesTransformation of SentencesSubhash Dhungel100% (8)
- EdtaDocument13 pagesEdtaChongZY100% (1)
- Advanced Pharmaceutical analysisFrom EverandAdvanced Pharmaceutical analysisRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (2)
- Practicum 8 Complexometric Titration Experiment Summary: ObjectivesDocument4 pagesPracticum 8 Complexometric Titration Experiment Summary: ObjectivesMia RismaliaNo ratings yet
- TitrationDocument14 pagesTitrationManP13No ratings yet
- Complexometric TitrationDocument25 pagesComplexometric Titrationpumeananda100% (1)
- Complexometric Lab Report Experiment 02Document10 pagesComplexometric Lab Report Experiment 02PDPPPMAT0621 Ruhilin Binti NasserNo ratings yet
- Complexometric Titration With EDTADocument8 pagesComplexometric Titration With EDTAManP13100% (1)
- EdtaDocument7 pagesEdtaRega Wahyu AnggrainiNo ratings yet
- Analytical 1.2.2Document5 pagesAnalytical 1.2.2Seyram DavidNo ratings yet
- 05229ce14c4135 Practical Eng Chemistry CH 1Document5 pages05229ce14c4135 Practical Eng Chemistry CH 1Mohit RajaiNo ratings yet
- Chemistry Lab Manual: Session: Jan-May Subject Code: BTCH102-18 Semester: 2 SEM B.TechDocument36 pagesChemistry Lab Manual: Session: Jan-May Subject Code: BTCH102-18 Semester: 2 SEM B.TechrajaaNo ratings yet
- Chem 301-Experiment 2: Edta Determination of Total Water Hardness and CalciumDocument4 pagesChem 301-Experiment 2: Edta Determination of Total Water Hardness and CalciumThapelo TjezNo ratings yet
- Engineering Chemistry (CHY1701) : Schedule (A2+TA2)Document24 pagesEngineering Chemistry (CHY1701) : Schedule (A2+TA2)Sooraj DevNo ratings yet
- Complexometric TitrationDocument4 pagesComplexometric TitrationWendell Kim LlanetaNo ratings yet
- Course Name: Volumetric and Gravimetric Analytical Chemistry Course Code: 4022133-3Document26 pagesCourse Name: Volumetric and Gravimetric Analytical Chemistry Course Code: 4022133-3faycalfaidiNo ratings yet
- Tittrations Based On Complex FormationDocument5 pagesTittrations Based On Complex FormationNisaNo ratings yet
- 2023 Chemistry ManualDocument43 pages2023 Chemistry Manualsenthilsrinesh6799No ratings yet
- Complexometric TitrationDocument8 pagesComplexometric TitrationYUNITA DWINo ratings yet
- Experiment 01Document6 pagesExperiment 01avirupg31No ratings yet
- Chem 26.1 Formal Report 2Document7 pagesChem 26.1 Formal Report 2Jo Fernandez100% (1)
- Expt. 6 Determination of The Hardness of A Given Water Sample by Complexometric TitrationDocument8 pagesExpt. 6 Determination of The Hardness of A Given Water Sample by Complexometric TitrationManoj KhanalNo ratings yet
- Question Answer of ComplexometryDocument19 pagesQuestion Answer of ComplexometryNahzim RahmatNo ratings yet
- Complexometry Determination Hardness ofDocument30 pagesComplexometry Determination Hardness ofMichael CarloNo ratings yet
- Experiment 2: Complexometric Titration 1.0 ObjectivesDocument4 pagesExperiment 2: Complexometric Titration 1.0 ObjectivesSangetha ChelladoraiNo ratings yet
- Lab Exp - Locality Water SampleDocument5 pagesLab Exp - Locality Water Samplerikiw17874No ratings yet
- Complejos InorgánicosDocument2 pagesComplejos InorgánicosKthryn93No ratings yet
- Quantitative Determination of Total Hardness in Drinking Water by Complexometric EDTA TitrationDocument14 pagesQuantitative Determination of Total Hardness in Drinking Water by Complexometric EDTA TitrationJoza Juan100% (2)
- Complexometric TitrationDocument12 pagesComplexometric TitrationBwhzad HameedNo ratings yet
- ATQ7Document3 pagesATQ7Joeco Abay-abayNo ratings yet
- Coordination Assignment 2Document6 pagesCoordination Assignment 2sara noorNo ratings yet
- Quantitative Determination of Total Hardness in Drinking Water by Complexometric Edta TitrationDocument12 pagesQuantitative Determination of Total Hardness in Drinking Water by Complexometric Edta TitrationmariemfranciscoNo ratings yet
- Water Hardness by EDTA TitrationDocument3 pagesWater Hardness by EDTA TitrationKimNo ratings yet
- Complexometric Titration 1Document14 pagesComplexometric Titration 1Girma Selale0% (1)
- ComplexiometryDocument19 pagesComplexiometryNur HalimahNo ratings yet
- Apch231 EdtaDocument13 pagesApch231 EdtaTan Ze KaiNo ratings yet
- Project ChemDocument24 pagesProject Chemsiddharth jugaleNo ratings yet
- Complexometric TitrationDocument30 pagesComplexometric TitrationSarthakAggarwalNo ratings yet
- Chapter-9 ComplexmetricDocument21 pagesChapter-9 Complexmetricmohamedzyad7717No ratings yet
- Complexometry: Pharmaceutical Analysis For Liquid and Semisolid PreparationDocument32 pagesComplexometry: Pharmaceutical Analysis For Liquid and Semisolid PreparationaulianiNo ratings yet
- EDTA TitrationDocument8 pagesEDTA TitrationJelaNo ratings yet
- Chem 26.1 Quantitative Determination of Total Hardness in Drinking Water by Complexometric EDTA TitrationDocument4 pagesChem 26.1 Quantitative Determination of Total Hardness in Drinking Water by Complexometric EDTA TitrationBuiHopeNo ratings yet
- 9 - PHAN111 ComplexationDocument34 pages9 - PHAN111 ComplexationAyille Dorado ArcigalNo ratings yet
- Water Technology & Green ChemistryDocument36 pagesWater Technology & Green ChemistryĀrav ShuklaNo ratings yet
- Complexometric TitrationDocument29 pagesComplexometric TitrationLive Happy100% (1)
- Classical Method of Quantitative AnalysisDocument35 pagesClassical Method of Quantitative AnalysisWillmann Jimenez MoralesNo ratings yet
- Water Hardness ReportDocument8 pagesWater Hardness ReportScott MuthuriNo ratings yet
- Ac Lab Report 2 - Abs and IntroDocument3 pagesAc Lab Report 2 - Abs and IntroThrishnaa BalasupurManiamNo ratings yet
- CompleximetryDocument29 pagesCompleximetrychamp delacruzNo ratings yet
- EdtaDocument6 pagesEdtasam310justNo ratings yet
- Quantitative Determination of Total Hardness in Drinking Water by Complexometric Edta TitrationDocument5 pagesQuantitative Determination of Total Hardness in Drinking Water by Complexometric Edta TitrationJoNo ratings yet
- Chemistry 232 Water Hardness: EDTA Titrimetric Method: PurposeDocument4 pagesChemistry 232 Water Hardness: EDTA Titrimetric Method: PurposekuochsochinNo ratings yet
- CHY1701 Exp1Document5 pagesCHY1701 Exp1HI-TECH MANNo ratings yet
- Experiment 4 Determination of Total Hardness As PPM Calcium CarbonateDocument26 pagesExperiment 4 Determination of Total Hardness As PPM Calcium CarbonateJordanNo ratings yet
- Reading: Chapter 11, Quantitative Chemical Analysis, 8 Edition, Daniel C. Harris (7 Edition: Chapter 12)Document7 pagesReading: Chapter 11, Quantitative Chemical Analysis, 8 Edition, Daniel C. Harris (7 Edition: Chapter 12)TYSON PETRO JONATHANNo ratings yet
- Water and Its Treatment: Unit 1Document72 pagesWater and Its Treatment: Unit 1Amal RasheedNo ratings yet
- SOL 6 Water HardnessDocument3 pagesSOL 6 Water HardnessRahimi ShahimiNo ratings yet
- Experiment - Detection of Hardness of WaterDocument8 pagesExperiment - Detection of Hardness of WaterRudra ChouhanNo ratings yet
- Practice Makes Perfect in Chemistry: Acids, Bases, and Salts with AnswersFrom EverandPractice Makes Perfect in Chemistry: Acids, Bases, and Salts with AnswersNo ratings yet
- Biological AssaysDocument19 pagesBiological AssaysSubhash DhungelNo ratings yet
- LiquidDocument7 pagesLiquidSubhash DhungelNo ratings yet
- AnalysisDocument4 pagesAnalysisSubhash DhungelNo ratings yet
- Experiments On Gramimetry and Precipitation TitrationDocument4 pagesExperiments On Gramimetry and Precipitation TitrationSubhash DhungelNo ratings yet
- Assay of Acetyl Salicylic Acid and Limit of Salicylic Acid.: Title:Quality Assurance of Aspirin Tablets On The Basis ofDocument4 pagesAssay of Acetyl Salicylic Acid and Limit of Salicylic Acid.: Title:Quality Assurance of Aspirin Tablets On The Basis ofSubhash DhungelNo ratings yet
- Absorption Methods: I) Transmittance (T)Document2 pagesAbsorption Methods: I) Transmittance (T)Subhash DhungelNo ratings yet
- How To Do A Patient Follow-UpDocument3 pagesHow To Do A Patient Follow-UpSubhash DhungelNo ratings yet
- Mathematical Description of A WaveDocument3 pagesMathematical Description of A WaveSubhash DhungelNo ratings yet
- Quantum Mechanical ConceptDocument4 pagesQuantum Mechanical ConceptSubhash DhungelNo ratings yet
- Superposition of WavesDocument3 pagesSuperposition of WavesSubhash DhungelNo ratings yet
- ErrorsDocument6 pagesErrorsSubhash DhungelNo ratings yet
- Quantum Mechanical ConceptDocument4 pagesQuantum Mechanical ConceptSubhash DhungelNo ratings yet
- Laser Sources:: ComponentsDocument5 pagesLaser Sources:: ComponentsSubhash DhungelNo ratings yet
- Diffraction of RadiationDocument3 pagesDiffraction of RadiationSubhash DhungelNo ratings yet
- Energy States of Chemical Species: Two Important Postulates of Quantum TheoryDocument2 pagesEnergy States of Chemical Species: Two Important Postulates of Quantum TheorySubhash DhungelNo ratings yet
- Sources of Coherent RadiationDocument7 pagesSources of Coherent RadiationSubhash DhungelNo ratings yet
- Analytical MethodsDocument16 pagesAnalytical MethodsSubhash Dhungel100% (1)