Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Introduction To Vectors
Introduction To Vectors
Uploaded by
Ronald MulindeOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Introduction To Vectors
Introduction To Vectors
Uploaded by
Ronald MulindeCopyright:
Available Formats
STRUCTURAL ANALYSIS FOR ARCHITECTS ARCH 1203
Ronald Mulinde
PART II:STATICS
CHAPTER 1: INTRODUCTION
Mechanics - physical science which deals with the effects of forces on objects mechanics of rigid bodies, mechanics of deformable bodies, mechanics of fluids. Statics equilibrium of static bodies. Dynamics deals with motion of bodies
Basic concepts
Space - geometric region occupied by bodies whose positions are described by linear and angular measurements relative to a coordinate system. E.g 2D, 3D Time - measure of the succession of events. Mass -measure of the inertia of a body, (its resistance to a change of velocity). - quantity of matter in a body.
Basic concepts
Force - action of one body on another. Force tends to move a body in the direction of its action. (characterised by magnitude, direction, point of application). Particle - is a body of negligible dimensions Rigid body - change in distance between any two of its points is negligible for the purpose at hand.
Scalars and vectors
Scalars.- posses only magnitude (e.g time, volume, density, speed, energy) Vectors - possess direction as well as magnitude (e.g displacement, velocity, acceleration, force, moment, and momentum). - Free vector- action not constrained -Sliding vector-constrained to a line of action - Fixed vector-unique point of action.
Vectors: Notation
Vectors: The parallelogram rule
Vectors:2D
Vectors:3D
You might also like
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeFrom EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (5835)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreFrom EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1093)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItFrom EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (852)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceFrom EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (590)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceFrom EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (903)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeFrom EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (541)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersFrom EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (350)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureFrom EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (474)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesFrom EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (824)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)From EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (122)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerFrom EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (271)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingFrom EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (405)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyFrom EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2259)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)From EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Rating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (98)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaFrom EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (266)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryFrom EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (231)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnFrom EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (234)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealFrom EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (74)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaFrom EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (45)
- Lectures On Operational AmplifiersDocument22 pagesLectures On Operational AmplifiersRonald MulindeNo ratings yet
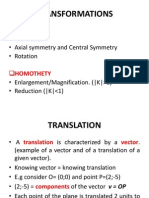
- TransformationsDocument2 pagesTransformationsRonald MulindeNo ratings yet
- Short DSP BooklistDocument3 pagesShort DSP BooklistRonald MulindeNo ratings yet
- Applied CalculusDocument12 pagesApplied CalculusRonald MulindeNo ratings yet
- MatlabDocument39 pagesMatlabRonald Mulinde100% (2)
- Short DSP BooklistDocument3 pagesShort DSP BooklistRonald MulindeNo ratings yet