Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Electron Volt (Symbol Ev Also Written Electronvolt
Electron Volt (Symbol Ev Also Written Electronvolt
Uploaded by
senthilanviewCopyright:
Available Formats
You might also like
- Physics HandbookDocument10 pagesPhysics HandbookNational Physical Laboratory100% (1)
- Electron PhysicsDocument8 pagesElectron PhysicsMaryam KiyaniNo ratings yet
- Unit EnergiDocument3 pagesUnit EnergiDiniNo ratings yet
- Electrical BasicSDocument77 pagesElectrical BasicSsenthilanviewNo ratings yet
- Electronvolt - Wikipedia, The Free EncyclopediaDocument2 pagesElectronvolt - Wikipedia, The Free Encyclopediadonodoni0008No ratings yet
- Chapter11 Part1 PDFDocument40 pagesChapter11 Part1 PDFvampanezezNo ratings yet
- DVS PhysChem 6 2011Document35 pagesDVS PhysChem 6 2011Jake GaynonNo ratings yet
- Current ElectricityDocument23 pagesCurrent ElectricityGavin SamuelsNo ratings yet
- CHM 101 - 1Document6 pagesCHM 101 - 1alakaolamuhammadNo ratings yet
- Electronvolt - WikipediaDocument1 pageElectronvolt - WikipediaBraian De LeonNo ratings yet
- Electrical EnergyDocument3 pagesElectrical EnergyDražen KrajnikNo ratings yet
- Modern Physics: Larry D. Buban, Ph.D. (Scied - Physics)Document47 pagesModern Physics: Larry D. Buban, Ph.D. (Scied - Physics)Hannah Grace Romano ViceralNo ratings yet
- Bej10303 Electric Circuit I: Dr. Nur Anida Binti JumadiDocument61 pagesBej10303 Electric Circuit I: Dr. Nur Anida Binti JumadiDaneshSathaNo ratings yet
- ElectricityDocument28 pagesElectricityAbdel Rahman AymanNo ratings yet
- Question No 21: What Is Electrical Conduction Model? Derive Its Mathematical Relation by Explaining Each StepDocument21 pagesQuestion No 21: What Is Electrical Conduction Model? Derive Its Mathematical Relation by Explaining Each StepAbubakar ChaudhryNo ratings yet
- Lecture10 - Electric Field and Electric PotentialDocument5 pagesLecture10 - Electric Field and Electric PotentialYenelle Miranda AbuanNo ratings yet
- Electrical Energy and PowerDocument8 pagesElectrical Energy and Powerrudiskw456No ratings yet
- ELECTRICITY X NotesDocument14 pagesELECTRICITY X NotesAyushiNo ratings yet
- MIT6 013S09 Chap05Document25 pagesMIT6 013S09 Chap05Jasmien HassanienNo ratings yet
- Phy1161 05prelecture PotentialDocument10 pagesPhy1161 05prelecture PotentialBela RilloNo ratings yet
- An Electric Field Is Created by Electric Charges, and Can Be Represented by Electric Field LinesDocument12 pagesAn Electric Field Is Created by Electric Charges, and Can Be Represented by Electric Field LinesTom 'Bones' OckendenNo ratings yet
- CH-1 Basic Concept of CircuitsDocument26 pagesCH-1 Basic Concept of Circuitsyisakabera123No ratings yet
- Presentation On Chapter 9 Unit 2 (Class Ix Week29)Document10 pagesPresentation On Chapter 9 Unit 2 (Class Ix Week29)SpideyPro23No ratings yet
- IB CHAPTER 5 - Electricity and MagnetismDocument67 pagesIB CHAPTER 5 - Electricity and Magnetismkostas100% (1)
- Modern PhysicsDocument73 pagesModern PhysicsRodney Takundanashe MandizvidzaNo ratings yet
- 4 App Physics 22EL Q I VDocument17 pages4 App Physics 22EL Q I VRizwan MNo ratings yet
- ElectricityDocument87 pagesElectricityayushk68863No ratings yet
- Ec1semi2223 Chapter1 NurmizapdfDocument61 pagesEc1semi2223 Chapter1 NurmizapdfYathavan A/l KalaichlvanNo ratings yet
- Concept of Current:: Electrical EngineeringDocument7 pagesConcept of Current:: Electrical EngineeringRam VigneshNo ratings yet
- Ohm'S Law, Work and Power: What An Electric Circuit Is?Document4 pagesOhm'S Law, Work and Power: What An Electric Circuit Is?Esmeralda TapizNo ratings yet
- ElectricityDocument24 pagesElectricityPremela PremelaNo ratings yet
- Kvpy Electrostats PDFDocument29 pagesKvpy Electrostats PDFstudysteps.inNo ratings yet
- Basic Electrical Engineering: Fall 2015 Instructor: Dr. Hassan DawoodDocument34 pagesBasic Electrical Engineering: Fall 2015 Instructor: Dr. Hassan Dawoodbakhtawar saeedNo ratings yet
- Aberration of Electric Field and AccelerDocument7 pagesAberration of Electric Field and AccelerLuis PalaciosNo ratings yet
- Physics 11 September 2017: Re: Voltage: Potential Difference and Electromotive ForceDocument1 pagePhysics 11 September 2017: Re: Voltage: Potential Difference and Electromotive ForceNick CantoneNo ratings yet
- Electric Circuit Lec1Document12 pagesElectric Circuit Lec1Mohammed EmadNo ratings yet
- UntitledDocument4 pagesUntitledJoyce LonzagaNo ratings yet
- Electric Potential - Wikipedia PDFDocument23 pagesElectric Potential - Wikipedia PDFTamoor SultanNo ratings yet
- Electron Thepry of MetalsDocument32 pagesElectron Thepry of MetalsnavarajacseNo ratings yet
- Electricity and MagnetismDocument29 pagesElectricity and MagnetismNashrul HaqNo ratings yet
- 2nd Year Short Question Answers From Within ChaptersDocument40 pages2nd Year Short Question Answers From Within ChaptersZain ZuhabNo ratings yet
- Electrical Quantities (Teaching Notes)Document18 pagesElectrical Quantities (Teaching Notes)A.BensonNo ratings yet
- 1.0 Fundamentals of Electric CircuitsDocument12 pages1.0 Fundamentals of Electric CircuitsDiana ValenzuelaNo ratings yet
- Lect 2 - Units and Passive ComponentsDocument59 pagesLect 2 - Units and Passive ComponentsHusseni MolaNo ratings yet
- Volt Curr ResisDocument12 pagesVolt Curr ResisVíctor Manuel Villegas EscobarNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1Document15 pagesChapter 1سعيد بن إدريس100% (1)
- Teori Kimia Radiasi Pertemuan Ke 2 Rev PentDocument176 pagesTeori Kimia Radiasi Pertemuan Ke 2 Rev PentFakhriansyah WijayaNo ratings yet
- Electricity 1Document31 pagesElectricity 1macff217No ratings yet
- Electricity at HomeDocument10 pagesElectricity at HomeWilliam HaNo ratings yet
- Lecture 2 - Electric Potential and Electric Potential EnergyDocument17 pagesLecture 2 - Electric Potential and Electric Potential EnergyLight ChristopherNo ratings yet
- Electromagnetic Waves, Circuits and ApplicationsDocument46 pagesElectromagnetic Waves, Circuits and ApplicationsMayank AgarwalNo ratings yet
- 25 - Current, Resistance, and Electromotive Force - R K Parida - 2019Document13 pages25 - Current, Resistance, and Electromotive Force - R K Parida - 2019ayushkumarmaha patro100% (1)
- Electron PhysicsDocument8 pagesElectron PhysicsRezha PahleviNo ratings yet
- Lectures 1 and 2 Intro and PhotelecDocument9 pagesLectures 1 and 2 Intro and PhotelecNabil IshamNo ratings yet
- Physics MarathonDocument130 pagesPhysics MarathonSantosh TiwariNo ratings yet
- Electrostatics Is The Study of Stationary Electric Charges and All The Effects They ProduceDocument53 pagesElectrostatics Is The Study of Stationary Electric Charges and All The Effects They ProduceNo PainNo ratings yet
- 1) What Is An Electric Potential?: AB A BDocument24 pages1) What Is An Electric Potential?: AB A BReddyvari VenugopalNo ratings yet
- Electrical CircuitsDocument24 pagesElectrical CircuitsJoseph Kinley V. LumosadNo ratings yet
- Charge and Electrical VariableDocument44 pagesCharge and Electrical VariableNeverson RusipinNo ratings yet
- The Dashboard WarningDocument2 pagesThe Dashboard WarningsenthilanviewNo ratings yet
- Potential Transformer DefinitionDocument1 pagePotential Transformer DefinitionsenthilanviewNo ratings yet
- Working Principle of Oil Circuit BreakerDocument1 pageWorking Principle of Oil Circuit BreakersenthilanviewNo ratings yet
- Winding Temperature Simulation SystemDocument3 pagesWinding Temperature Simulation SystemsenthilanviewNo ratings yet
- VT Error Voltage Error or Ratio Error in Potential Transformer (PT) or Voltage Transformer (VT)Document1 pageVT Error Voltage Error or Ratio Error in Potential Transformer (PT) or Voltage Transformer (VT)senthilanviewNo ratings yet
- Just The Facts: Vehicle Warning LightsDocument1 pageJust The Facts: Vehicle Warning LightssenthilanviewNo ratings yet
- Two Winding Transformer 1Document1 pageTwo Winding Transformer 1senthilanviewNo ratings yet
- Your Dash Lights: Heavy-Duty EnginesDocument2 pagesYour Dash Lights: Heavy-Duty EnginessenthilanviewNo ratings yet
- Two Winding TransformerDocument3 pagesTwo Winding TransformersenthilanviewNo ratings yet
- Primary Duties and ResponsibilitiesDocument1 pagePrimary Duties and ResponsibilitiessenthilanviewNo ratings yet
- Figure 49: AC Method For Testing Transformer Polarities: POL H X 1 2 POL H X 1 2Document5 pagesFigure 49: AC Method For Testing Transformer Polarities: POL H X 1 2 POL H X 1 2senthilanviewNo ratings yet
- Experienced Driver Ongoing TrainingDocument3 pagesExperienced Driver Ongoing TrainingsenthilanviewNo ratings yet
- (Employee Signature) Post-Accident Drug Test Requests of - County ManagementDocument3 pages(Employee Signature) Post-Accident Drug Test Requests of - County ManagementsenthilanviewNo ratings yet
- Learn How To Study EffectivelyDocument1 pageLearn How To Study EffectivelysenthilanviewNo ratings yet
- What Happens When A Transformer Is Subjected To DC Voltage in The Primary? What Happens in The Saturation Mode?Document1 pageWhat Happens When A Transformer Is Subjected To DC Voltage in The Primary? What Happens in The Saturation Mode?senthilanviewNo ratings yet
- Polarity CheckDocument2 pagesPolarity ChecksenthilanviewNo ratings yet
- Module4 PKDocument21 pagesModule4 PKsenthilanviewNo ratings yet
- Current TransformersDocument2 pagesCurrent TransformerssenthilanviewNo ratings yet
- Identifying and Marking of Bushing CtsDocument2 pagesIdentifying and Marking of Bushing CtssenthilanviewNo ratings yet
- Effect of Transient DDocument1 pageEffect of Transient DsenthilanviewNo ratings yet
- Current Transformes:: Accuracy ClassDocument1 pageCurrent Transformes:: Accuracy ClasssenthilanviewNo ratings yet
- CT SaturationDocument2 pagesCT SaturationsenthilanviewNo ratings yet
Electron Volt (Symbol Ev Also Written Electronvolt
Electron Volt (Symbol Ev Also Written Electronvolt
Uploaded by
senthilanviewOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Electron Volt (Symbol Ev Also Written Electronvolt
Electron Volt (Symbol Ev Also Written Electronvolt
Uploaded by
senthilanviewCopyright:
Available Formats
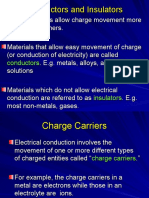
electron volt (symbol eV; also written electronvolt[1][2]) is a unit of energy equal to approximately 1.61019 joule (symbol J).
By definition, it is the amount of energy gained (or lost) by the charge of a single electron moved across an electric potential difference of one volt. Thus it is 1 volt (1 joule per coulomb, 1 J/C) multiplied by the negative of the electron charge (e, or1.602176565(35)1019 C). Therefore, one electron volt is equal to 1.602176565(35)1019 J.[3] Historically, the electron volt was devised as a standard unit of measure through its usefulness in electrostatic particle accelerator sciences because a particle with charge q has an energy E = qV after passing through the potential V; if q is quoted in integer units of theelementary charge and the terminal bias in volts, one gets an energy in eV. The electron volt is not an SI unit, and thus its value in SI units must be obtained experimentally.[4] Like the elementary charge on which it is based, it is not an independent quantity but is equal to 1 J/C(2ha/ 0c0). It is a common unit of energy within physics, widely used in solid state, atomic, nuclear, and particle physics. It is commonly used with the SI prefixes milli-, kilo-, mega-, giga-, tera-, peta- or exa- (meV, keV, MeV, GeV, TeV, PeV and EeV respectively). Thus meV stands for milli-electron volt.
In some older documents, and in the name Bevatron, the symbol BeV is used, which stands for billion electron volts; it is equivalent to the GeV.
The watt (/wt/ WOT; symbol: W)(1W=1kg.m^2/s^3) is a derived unit of power in the International System of Units (SI), named after the Scottish engineer James Watt (1736 1819). The unit, defined as one joule per second, measures the rate of energy conversion or transfer. One watt is the rate at which work is done when an object's velocity is held constant at one meter per second against constant opposing force of one newton.
In terms of electromagnetism, one watt is the rate at which work is done when one ampere (A) of current flows through an electrical potential difference of one volt (V).
Two additional unit conversions for watt can be found using the above equation and Ohm's Law.
Where ohm (
) is the SI derived unit of electrical resistance.
You might also like
- Physics HandbookDocument10 pagesPhysics HandbookNational Physical Laboratory100% (1)
- Electron PhysicsDocument8 pagesElectron PhysicsMaryam KiyaniNo ratings yet
- Unit EnergiDocument3 pagesUnit EnergiDiniNo ratings yet
- Electrical BasicSDocument77 pagesElectrical BasicSsenthilanviewNo ratings yet
- Electronvolt - Wikipedia, The Free EncyclopediaDocument2 pagesElectronvolt - Wikipedia, The Free Encyclopediadonodoni0008No ratings yet
- Chapter11 Part1 PDFDocument40 pagesChapter11 Part1 PDFvampanezezNo ratings yet
- DVS PhysChem 6 2011Document35 pagesDVS PhysChem 6 2011Jake GaynonNo ratings yet
- Current ElectricityDocument23 pagesCurrent ElectricityGavin SamuelsNo ratings yet
- CHM 101 - 1Document6 pagesCHM 101 - 1alakaolamuhammadNo ratings yet
- Electronvolt - WikipediaDocument1 pageElectronvolt - WikipediaBraian De LeonNo ratings yet
- Electrical EnergyDocument3 pagesElectrical EnergyDražen KrajnikNo ratings yet
- Modern Physics: Larry D. Buban, Ph.D. (Scied - Physics)Document47 pagesModern Physics: Larry D. Buban, Ph.D. (Scied - Physics)Hannah Grace Romano ViceralNo ratings yet
- Bej10303 Electric Circuit I: Dr. Nur Anida Binti JumadiDocument61 pagesBej10303 Electric Circuit I: Dr. Nur Anida Binti JumadiDaneshSathaNo ratings yet
- ElectricityDocument28 pagesElectricityAbdel Rahman AymanNo ratings yet
- Question No 21: What Is Electrical Conduction Model? Derive Its Mathematical Relation by Explaining Each StepDocument21 pagesQuestion No 21: What Is Electrical Conduction Model? Derive Its Mathematical Relation by Explaining Each StepAbubakar ChaudhryNo ratings yet
- Lecture10 - Electric Field and Electric PotentialDocument5 pagesLecture10 - Electric Field and Electric PotentialYenelle Miranda AbuanNo ratings yet
- Electrical Energy and PowerDocument8 pagesElectrical Energy and Powerrudiskw456No ratings yet
- ELECTRICITY X NotesDocument14 pagesELECTRICITY X NotesAyushiNo ratings yet
- MIT6 013S09 Chap05Document25 pagesMIT6 013S09 Chap05Jasmien HassanienNo ratings yet
- Phy1161 05prelecture PotentialDocument10 pagesPhy1161 05prelecture PotentialBela RilloNo ratings yet
- An Electric Field Is Created by Electric Charges, and Can Be Represented by Electric Field LinesDocument12 pagesAn Electric Field Is Created by Electric Charges, and Can Be Represented by Electric Field LinesTom 'Bones' OckendenNo ratings yet
- CH-1 Basic Concept of CircuitsDocument26 pagesCH-1 Basic Concept of Circuitsyisakabera123No ratings yet
- Presentation On Chapter 9 Unit 2 (Class Ix Week29)Document10 pagesPresentation On Chapter 9 Unit 2 (Class Ix Week29)SpideyPro23No ratings yet
- IB CHAPTER 5 - Electricity and MagnetismDocument67 pagesIB CHAPTER 5 - Electricity and Magnetismkostas100% (1)
- Modern PhysicsDocument73 pagesModern PhysicsRodney Takundanashe MandizvidzaNo ratings yet
- 4 App Physics 22EL Q I VDocument17 pages4 App Physics 22EL Q I VRizwan MNo ratings yet
- ElectricityDocument87 pagesElectricityayushk68863No ratings yet
- Ec1semi2223 Chapter1 NurmizapdfDocument61 pagesEc1semi2223 Chapter1 NurmizapdfYathavan A/l KalaichlvanNo ratings yet
- Concept of Current:: Electrical EngineeringDocument7 pagesConcept of Current:: Electrical EngineeringRam VigneshNo ratings yet
- Ohm'S Law, Work and Power: What An Electric Circuit Is?Document4 pagesOhm'S Law, Work and Power: What An Electric Circuit Is?Esmeralda TapizNo ratings yet
- ElectricityDocument24 pagesElectricityPremela PremelaNo ratings yet
- Kvpy Electrostats PDFDocument29 pagesKvpy Electrostats PDFstudysteps.inNo ratings yet
- Basic Electrical Engineering: Fall 2015 Instructor: Dr. Hassan DawoodDocument34 pagesBasic Electrical Engineering: Fall 2015 Instructor: Dr. Hassan Dawoodbakhtawar saeedNo ratings yet
- Aberration of Electric Field and AccelerDocument7 pagesAberration of Electric Field and AccelerLuis PalaciosNo ratings yet
- Physics 11 September 2017: Re: Voltage: Potential Difference and Electromotive ForceDocument1 pagePhysics 11 September 2017: Re: Voltage: Potential Difference and Electromotive ForceNick CantoneNo ratings yet
- Electric Circuit Lec1Document12 pagesElectric Circuit Lec1Mohammed EmadNo ratings yet
- UntitledDocument4 pagesUntitledJoyce LonzagaNo ratings yet
- Electric Potential - Wikipedia PDFDocument23 pagesElectric Potential - Wikipedia PDFTamoor SultanNo ratings yet
- Electron Thepry of MetalsDocument32 pagesElectron Thepry of MetalsnavarajacseNo ratings yet
- Electricity and MagnetismDocument29 pagesElectricity and MagnetismNashrul HaqNo ratings yet
- 2nd Year Short Question Answers From Within ChaptersDocument40 pages2nd Year Short Question Answers From Within ChaptersZain ZuhabNo ratings yet
- Electrical Quantities (Teaching Notes)Document18 pagesElectrical Quantities (Teaching Notes)A.BensonNo ratings yet
- 1.0 Fundamentals of Electric CircuitsDocument12 pages1.0 Fundamentals of Electric CircuitsDiana ValenzuelaNo ratings yet
- Lect 2 - Units and Passive ComponentsDocument59 pagesLect 2 - Units and Passive ComponentsHusseni MolaNo ratings yet
- Volt Curr ResisDocument12 pagesVolt Curr ResisVíctor Manuel Villegas EscobarNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1Document15 pagesChapter 1سعيد بن إدريس100% (1)
- Teori Kimia Radiasi Pertemuan Ke 2 Rev PentDocument176 pagesTeori Kimia Radiasi Pertemuan Ke 2 Rev PentFakhriansyah WijayaNo ratings yet
- Electricity 1Document31 pagesElectricity 1macff217No ratings yet
- Electricity at HomeDocument10 pagesElectricity at HomeWilliam HaNo ratings yet
- Lecture 2 - Electric Potential and Electric Potential EnergyDocument17 pagesLecture 2 - Electric Potential and Electric Potential EnergyLight ChristopherNo ratings yet
- Electromagnetic Waves, Circuits and ApplicationsDocument46 pagesElectromagnetic Waves, Circuits and ApplicationsMayank AgarwalNo ratings yet
- 25 - Current, Resistance, and Electromotive Force - R K Parida - 2019Document13 pages25 - Current, Resistance, and Electromotive Force - R K Parida - 2019ayushkumarmaha patro100% (1)
- Electron PhysicsDocument8 pagesElectron PhysicsRezha PahleviNo ratings yet
- Lectures 1 and 2 Intro and PhotelecDocument9 pagesLectures 1 and 2 Intro and PhotelecNabil IshamNo ratings yet
- Physics MarathonDocument130 pagesPhysics MarathonSantosh TiwariNo ratings yet
- Electrostatics Is The Study of Stationary Electric Charges and All The Effects They ProduceDocument53 pagesElectrostatics Is The Study of Stationary Electric Charges and All The Effects They ProduceNo PainNo ratings yet
- 1) What Is An Electric Potential?: AB A BDocument24 pages1) What Is An Electric Potential?: AB A BReddyvari VenugopalNo ratings yet
- Electrical CircuitsDocument24 pagesElectrical CircuitsJoseph Kinley V. LumosadNo ratings yet
- Charge and Electrical VariableDocument44 pagesCharge and Electrical VariableNeverson RusipinNo ratings yet
- The Dashboard WarningDocument2 pagesThe Dashboard WarningsenthilanviewNo ratings yet
- Potential Transformer DefinitionDocument1 pagePotential Transformer DefinitionsenthilanviewNo ratings yet
- Working Principle of Oil Circuit BreakerDocument1 pageWorking Principle of Oil Circuit BreakersenthilanviewNo ratings yet
- Winding Temperature Simulation SystemDocument3 pagesWinding Temperature Simulation SystemsenthilanviewNo ratings yet
- VT Error Voltage Error or Ratio Error in Potential Transformer (PT) or Voltage Transformer (VT)Document1 pageVT Error Voltage Error or Ratio Error in Potential Transformer (PT) or Voltage Transformer (VT)senthilanviewNo ratings yet
- Just The Facts: Vehicle Warning LightsDocument1 pageJust The Facts: Vehicle Warning LightssenthilanviewNo ratings yet
- Two Winding Transformer 1Document1 pageTwo Winding Transformer 1senthilanviewNo ratings yet
- Your Dash Lights: Heavy-Duty EnginesDocument2 pagesYour Dash Lights: Heavy-Duty EnginessenthilanviewNo ratings yet
- Two Winding TransformerDocument3 pagesTwo Winding TransformersenthilanviewNo ratings yet
- Primary Duties and ResponsibilitiesDocument1 pagePrimary Duties and ResponsibilitiessenthilanviewNo ratings yet
- Figure 49: AC Method For Testing Transformer Polarities: POL H X 1 2 POL H X 1 2Document5 pagesFigure 49: AC Method For Testing Transformer Polarities: POL H X 1 2 POL H X 1 2senthilanviewNo ratings yet
- Experienced Driver Ongoing TrainingDocument3 pagesExperienced Driver Ongoing TrainingsenthilanviewNo ratings yet
- (Employee Signature) Post-Accident Drug Test Requests of - County ManagementDocument3 pages(Employee Signature) Post-Accident Drug Test Requests of - County ManagementsenthilanviewNo ratings yet
- Learn How To Study EffectivelyDocument1 pageLearn How To Study EffectivelysenthilanviewNo ratings yet
- What Happens When A Transformer Is Subjected To DC Voltage in The Primary? What Happens in The Saturation Mode?Document1 pageWhat Happens When A Transformer Is Subjected To DC Voltage in The Primary? What Happens in The Saturation Mode?senthilanviewNo ratings yet
- Polarity CheckDocument2 pagesPolarity ChecksenthilanviewNo ratings yet
- Module4 PKDocument21 pagesModule4 PKsenthilanviewNo ratings yet
- Current TransformersDocument2 pagesCurrent TransformerssenthilanviewNo ratings yet
- Identifying and Marking of Bushing CtsDocument2 pagesIdentifying and Marking of Bushing CtssenthilanviewNo ratings yet
- Effect of Transient DDocument1 pageEffect of Transient DsenthilanviewNo ratings yet
- Current Transformes:: Accuracy ClassDocument1 pageCurrent Transformes:: Accuracy ClasssenthilanviewNo ratings yet
- CT SaturationDocument2 pagesCT SaturationsenthilanviewNo ratings yet