Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Code: DE06 Subject: Basic Electronics: N P N P N N
Code: DE06 Subject: Basic Electronics: N P N P N N
Uploaded by
sanshinde10Original Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Code: DE06 Subject: Basic Electronics: N P N P N N
Code: DE06 Subject: Basic Electronics: N P N P N N
Uploaded by
sanshinde10Copyright:
Available Formats
Code: DE06
Subject: BASIC ELECTRONICS
Q.66 Ans:
What are the applications of SCR ?
Marks (3)
Applications of SCR: (i) It is used as Half-Wave and Full-Wave Controlled Rectifier (ii) It is used as a Static Contactor (iii) Use of SCR for Speed Control of DC Shunt Motors (iv) SCRs are used in Static AC Circuit Breaker and Static DC circuit Breaker as a switch (v)SCRs are used in zero voltage switching (vi)Used in Over-Voltage Protection (vii)Used in Pulse Circuits (viii)Used in Battery Charging Regulator. Marks (5)
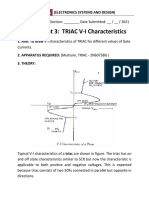
Q.67 Describe the basic structure of TRIAC. Draw and discuss its volt-ampere characteristics. Ans
Basic Structure of TRIAC: A triac shown in fig.67. basically consists of two SCRs connected in inverse parallel with gate common. In external appearance, the triac is similar to an SCR, but triac is bi-directional device. The internal layers and doping are arranged so that current can flow in either direction. The gate terminal G makes ohmic contacts with both the N and P materials. This permits trigger pulse of either polarity to start conduction. Since the triac is a bilateral device, the term anode and cathode has no meaning, and therefore, terminals are designated as Main Terminal 1 (MT1) and main terminal 2 (MT2) and gate G.
MAIN TERMINAL 2
MT2
MAIN TERMINAL 2
MT
N4 P
1
MT
N1
SCR 1
P N3
(P N
1
P N)
2 2 GATE
SCR 2
G
1 4
(P N P N )
(G)
2 1
N2
GATE
(G)
MAIN TERMINAL 1
MT
MAIN TERMINAL 1
MT 1
MT 1
(a) Basic Structure
(b) Electrical Equivalent Circuit Fig.67 TRIAC
(c) Schematic Symbol
V-I Characteristics of TRIAC: Typical V-I characteristics of a triac are shown in fig.67.4. The triac has on and off characteristics similar to SCR but the characteristic is applicable to both positive and negative voltages. Because triac consists of two SCRs connected in parallel but opposite in directions. Forward Characteristics: Terminal MT2 and gate are positive with respect to terminal MT1: When terminal st MT2 is positive with respect to terminal MT1. The two junctions P1-N1(1 diode) and P2rd nd N2(3 diode) are forward, whereas junction N1-P2(2 diode) is reverse biased. So there is a blockage of current flow across the triac. This state is called Blocking State. When a small positive gate voltage (G1) is applied to the P2 -terminal of second diode, the gate
78
You might also like
- EEE 4228Document53 pagesEEE 4228nimojem963No ratings yet
- Presented By:-: Suresh MohtaDocument14 pagesPresented By:-: Suresh MohtaAmanuel GereziherNo ratings yet
- Special Semiconductor Devices: Mr. Jay Mehta Asst. Professor St. Francis Institute of TechnologyDocument35 pagesSpecial Semiconductor Devices: Mr. Jay Mehta Asst. Professor St. Francis Institute of Technologyjay mehtaNo ratings yet
- AC Voltage Controller (Using DIAC and TRIAC)Document9 pagesAC Voltage Controller (Using DIAC and TRIAC)Khan Elme100% (2)
- TRIACDocument3 pagesTRIACkirushruNo ratings yet
- ECE 523 Expt No. 1Document5 pagesECE 523 Expt No. 1Jerichson LautaNo ratings yet
- Experiment 3: TRIAC V-I Characteristics: (Electronics Systems and Design)Document6 pagesExperiment 3: TRIAC V-I Characteristics: (Electronics Systems and Design)Kì Hyö Jüng50% (2)
- Exp1 - SCR IGBT and MOSFET CharacteristicsDocument24 pagesExp1 - SCR IGBT and MOSFET CharacteristicsAaaa DdddNo ratings yet
- TRIAC LectureDocument2 pagesTRIAC Lecturetinonoy KulitlitNo ratings yet
- TRAICDocument14 pagesTRAICManav JainNo ratings yet
- PE Course File 09Document64 pagesPE Course File 09NageshKudupudi67% (3)
- Exp No 2Document12 pagesExp No 2arooj aslamNo ratings yet
- Power ElectronicsDocument9 pagesPower ElectronicsViviana VergelNo ratings yet
- TriacDocument13 pagesTriacNaveedNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Triac-Its Construction and Operation: SCR ControlsDocument6 pagesIntroduction To Triac-Its Construction and Operation: SCR ControlsSurendra ChouhanNo ratings yet
- Power Electronics Lab ManualDocument51 pagesPower Electronics Lab ManualArun DasNo ratings yet
- Assignment of BPE - Question BankDocument3 pagesAssignment of BPE - Question BankJiya ShindeNo ratings yet
- ThyristorDocument40 pagesThyristorDibyansheeNo ratings yet
- Lab SheetDocument29 pagesLab SheetKennedy KoluteNo ratings yet
- PE Lab ManualDocument47 pagesPE Lab ManualRutwik PadalkarNo ratings yet
- Power Electronics LabDocument62 pagesPower Electronics LabtumpudiNo ratings yet
- TriacDocument3 pagesTriacMuhd Zulhusni Ag JaludinNo ratings yet
- QB NewDocument13 pagesQB NewNarasimman DonNo ratings yet
- EEE 482 - Power - Electronics - LabDocument23 pagesEEE 482 - Power - Electronics - Labjery tomNo ratings yet
- Experiment in ElectronicsDocument8 pagesExperiment in ElectronicsPercival Cylas CabralesNo ratings yet
- Genetic Algorithm Based 7-Level Step-Up Inverter With Reduced Harmonics and Switching DevicesDocument17 pagesGenetic Algorithm Based 7-Level Step-Up Inverter With Reduced Harmonics and Switching DevicesMasudur RahmanNo ratings yet
- Industrial Electronics CbcgsDocument28 pagesIndustrial Electronics Cbcgshadesg895No ratings yet
- Pe May 18Document2 pagesPe May 18SAURABH BHISENo ratings yet
- Single Phase AC Motor Speed Controller: Abstract:qrtuqwhedasjgruewrhfDocument1 pageSingle Phase AC Motor Speed Controller: Abstract:qrtuqwhedasjgruewrhfnareshhhhhNo ratings yet
- (Experiment 4) BJT - Common Collector AmplifierDocument13 pages(Experiment 4) BJT - Common Collector AmplifierArik JuniarNo ratings yet
- Diac - TriacDocument18 pagesDiac - TriacBabe O.No ratings yet
- Pe Lab Manual E&c Dept DsceDocument45 pagesPe Lab Manual E&c Dept DsceJeevan PreethuNo ratings yet
- Triac Symbol and Construction: MT MT G MTDocument2 pagesTriac Symbol and Construction: MT MT G MTRonsonel TajanNo ratings yet
- Power Semiconductor Devices: EE 3036 D: Presented byDocument10 pagesPower Semiconductor Devices: EE 3036 D: Presented byShubham ranjanNo ratings yet
- Background: 1.1 Theory About The Power ElectronicsDocument51 pagesBackground: 1.1 Theory About The Power ElectronicsEngr Syed Bilal AliNo ratings yet
- CT Polarity On SIPROTEC Quick StartDocument12 pagesCT Polarity On SIPROTEC Quick StartarifirmansyahtingtingNo ratings yet
- Special Semiconductor Devices: DR - Debashis de Associate Professor West Bengal University of TechnologyDocument24 pagesSpecial Semiconductor Devices: DR - Debashis de Associate Professor West Bengal University of TechnologySrinivasan SubramanianNo ratings yet
- Nota Unit 6Document19 pagesNota Unit 6F1036No ratings yet
- EEE 482 Power Electronics PDFDocument23 pagesEEE 482 Power Electronics PDFrontojoyNo ratings yet
- TRIAC Operation: Equivalent Circuit of A TRIACDocument1 pageTRIAC Operation: Equivalent Circuit of A TRIACMild SteelNo ratings yet
- (Power Electronics) Semester: IIDocument52 pages(Power Electronics) Semester: IIp19209425No ratings yet
- 1.characteristics of SCRDocument6 pages1.characteristics of SCRVenkat Sai ChowdaryNo ratings yet
- Characteristics of SCR and TriacDocument4 pagesCharacteristics of SCR and TriacKhadar Basha ShaikNo ratings yet
- 3-2power Electronics Lab ManualDocument50 pages3-2power Electronics Lab ManualSivareddy MudiyalaNo ratings yet
- ECE 306 Manual 1 MergedDocument13 pagesECE 306 Manual 1 MergedErwin PiaNo ratings yet
- Diac & Triac: Er. Faruk Bin Poyen Asst. Professor Dept. of Aeie, Uit, BuDocument27 pagesDiac & Triac: Er. Faruk Bin Poyen Asst. Professor Dept. of Aeie, Uit, BuRohit BariNo ratings yet
- Optoelectronics: Application Note Solid State Relay and Application CircuitsDocument13 pagesOptoelectronics: Application Note Solid State Relay and Application Circuitsght113No ratings yet
- Design and Control of A Three-Phase T-Type Inverter Using Reverse-Blocking IgbtsDocument6 pagesDesign and Control of A Three-Phase T-Type Inverter Using Reverse-Blocking IgbtsMaulik ShahNo ratings yet
- P.E Ug Lab ManualDocument52 pagesP.E Ug Lab ManualSonali SinghNo ratings yet
- Case Study (1) Pe Ca1Document10 pagesCase Study (1) Pe Ca1vikas mokasheNo ratings yet
- Triac PDFDocument4 pagesTriac PDFgopu705204No ratings yet
- Vubibknnnnnnnnnnnnnniouvbiubbincykjogydjinodjbdfuksin Gle Phase Ac Motor Speed ControllerDocument2 pagesVubibknnnnnnnnnnnnnniouvbiubbincykjogydjinodjbdfuksin Gle Phase Ac Motor Speed ControllernareshhhhhNo ratings yet
- MCGG OcrDocument14 pagesMCGG OcrAgus BuchariNo ratings yet
- Fundamentals of Electronics 1: Electronic Components and Elementary FunctionsFrom EverandFundamentals of Electronics 1: Electronic Components and Elementary FunctionsNo ratings yet
- Heterojunction Bipolar Transistors for Circuit Design: Microwave Modeling and Parameter ExtractionFrom EverandHeterojunction Bipolar Transistors for Circuit Design: Microwave Modeling and Parameter ExtractionNo ratings yet
- Analog Dialogue, Volume 48, Number 1: Analog Dialogue, #13From EverandAnalog Dialogue, Volume 48, Number 1: Analog Dialogue, #13Rating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1)
- Reference Guide To Useful Electronic Circuits And Circuit Design Techniques - Part 2From EverandReference Guide To Useful Electronic Circuits And Circuit Design Techniques - Part 2No ratings yet
- Advanced Electric Drives: Analysis, Control, and Modeling Using MATLAB / SimulinkFrom EverandAdvanced Electric Drives: Analysis, Control, and Modeling Using MATLAB / SimulinkNo ratings yet
- Physics and Technology of Crystalline Oxide Semiconductor CAAC-IGZO: Application to LSIFrom EverandPhysics and Technology of Crystalline Oxide Semiconductor CAAC-IGZO: Application to LSINo ratings yet
- Fengshui Santosh Page1Document1 pageFengshui Santosh Page1sanshinde10No ratings yet
- Basic Electronics 9Document1 pageBasic Electronics 9sanshinde10No ratings yet
- Hi My Name Is Santosh I Will Be Training You One Fengshui BasicDocument1 pageHi My Name Is Santosh I Will Be Training You One Fengshui Basicsanshinde10No ratings yet
- Hi My Name Is Santosh I Will Be Training You One Fengshui BasicDocument1 pageHi My Name Is Santosh I Will Be Training You One Fengshui Basicsanshinde10No ratings yet
- Chapter 1. What's The Story?Document5 pagesChapter 1. What's The Story?sanshinde10No ratings yet
- Basic Electronics 45Document1 pageBasic Electronics 45sanshinde10No ratings yet
- Cbt13 Schooldays.1Document1 pageCbt13 Schooldays.1sanshinde10No ratings yet
- Basic Electronics 10Document1 pageBasic Electronics 10sanshinde10No ratings yet
- Basic Electronics 6Document1 pageBasic Electronics 6sanshinde10No ratings yet
- PLD (Programmable Logic Device) : - All Layers Already ExistDocument1 pagePLD (Programmable Logic Device) : - All Layers Already Existsanshinde10No ratings yet
- Enno 3Document1 pageEnno 3sanshinde10No ratings yet
- Full-custom/VLSI: - All Layers Are Optimized For An Embedded System's Particular Digital ImplementationDocument1 pageFull-custom/VLSI: - All Layers Are Optimized For An Embedded System's Particular Digital Implementationsanshinde10No ratings yet
- Semi-Custom: - Lower Layers Are Fully or Partially BuiltDocument1 pageSemi-Custom: - Lower Layers Are Fully or Partially Builtsanshinde10No ratings yet
- IC Technology: - Three Types of IC TechnologiesDocument1 pageIC Technology: - Three Types of IC Technologiessanshinde10No ratings yet
- General-Purpose Processors: - Programmable Device Used in A Variety of Applications - FeaturesDocument1 pageGeneral-Purpose Processors: - Programmable Device Used in A Variety of Applications - Featuressanshinde10No ratings yet