Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Iep Parent Handbook
Iep Parent Handbook
Uploaded by
api-236207623Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Iep Parent Handbook
Iep Parent Handbook
Uploaded by
api-236207623Copyright:
Available Formats
KEY POINTS
KEY POINTS
Eligible students at all public schools including charter schools have the right to FAPE (free appropriate public
education). 300.320
o
o
IDEA 2004 requires that the school keep copies of school records if not having copies would prevent the parent
from inspecting and reviewing those records. 300.613
KEY POINTS
The initial evaluation must be completed within 45 school days of receiving parental consent for the evaluation.
There are additional rules regarding reevaluation in specific situations. These rules can be found in the Utah
Special Education Rules available at www.schools.utah.gov
o
o
o
o
This is a sample. If you need to request an independent evaluation, this sample may help you get started.
It should only be used as a guide and is not the only way to request the evaluation.
KEY POINTS
If the student requires only accommodations, and not special education (specifically designed instruction), that
student is not a student with a disability under IDEA. Such a student may be eligible for an accommodation plan
under Section 504 of the Vocational Rehabilitation Act. Contact your school or the Utah Parent Center for more
information. Additional information is also available on the website of the Utah State Office of Education at
www.schools.utah.gov/equity/section504/default.html
School districts may choose to use the Developmentally Delayed category (which is used in Early Intervention age 0-
3) for children ages 3-7 instead of another category if the child meets the eligibility criteria.
Significant changes were made in IDEA 2004 regarding the identification of students with specific learning disabilities.
An LEA may use one of two methods or a combination of both for determining a students eligibility.
1. A process based on the student response to scientific, research-based intervention. OR
2. Identification of a severe discrepancy between intellectual ability and achievement. OR
3. A combination of these.
Parents who have questions about how this process works should not hesitate to bring their questions to the school.
More detailed information can be found on the Utah State Office of Education website at www.utah.schools.gov.
Decisions about eligibility are made by a team that includes the parents. Parental input is considered. If the child is
determined not eligible, parents have the right to disagree and use any of the dispute resolution remedies.
For more information on the rules regarding cochlear implants, please refer to the Utah Special Education Rules.
While special education is free to the student, the student is still required to pay for school fees and expenses that
typical students pay for.
KEY POINTS
Teachers and other school personnel are not held accountable if a child with a disability does not achieve the goals
and objectives set forth in the IEP, but they are held accountable for providing the services outlined in the IEP.
Refer to sample profiles and instructions in the appendix to record your thoughts and observations about your child.
Completing a profile can help you to develop your list of concerns and priorities and can be a written form for sharing
information about your child.
See Utah State Office of Educations parent booklet on writing health care plans for a sample health care plan. A
copy may be requested from the Utah Parent Center. This information is also available at the Medical Home
website, www.utahmedhomeportal.org
The Utah Parent Center provides a workshop and written information on communication and conferencing skills.
Call the UPC at 801.272.1051 or visit www.utahparentcenter.org for more information.
The parent must receive a notice of meeting which indicates the purpose(s), time, and location of the meeting and
who will be in attendance. It must also inform the parents of their right to bring other individuals who have
knowledge or special expertise.
The determination of who has knowledge or special expertise is up to the person who is doing the inviting, so
parents may invite whomever they think will be helpful. It is important to inform the team ahead of time about
additional people that you are inviting.
The Utah Parent Center has a specialty workshop on transition planning to help families plan for students adult
lives. A copy of From NO Whereto Know Where, A Parent Handbook for the Transition to Adult Services may
be obtained by contacting the Center at 801.272.1051 or www.utahparentcenter.org
Staffs in some school districts have been trained in interest based negotiation. Interest based negotiation is a WIN-
WIN process that helps groups to work together to address the interests or needs of all parties who are involved.
The Utah Parent Center teaches a workshop called Negotiation and Advocacy Skills which gives instruction and
practice in using interest based negotiation. Contact the Center for more information about upcoming workshops on
this topic at 801.272.1051 or at www.utahparentcenter.org
The Core Curriculum represents those standards of learning that are essential for all students. They are ideas,
concepts, and skills that provide a foundation on which subsequent learning may be built. The Utah State Office of
Education sets the standards which must be completed by all students K-12 as a requisite to graduate from Utahs
secondary schools.
More information about transition is available in this handbook on page 55. The Utah Parent Centers From NO
Where to KNOW Where Transition to Adult Services A Parent Handbook also has additional information on
guardianship and other related topics.
Some of the considerations in the IEP may be embedded in a section of the IEP as a checkbox. Checking off the
special considerations is a team decision. If you have a question about one of these considerations, be sure to
bring it up at the IEP meeting.
If parents disagree with any of the decisions made by the IEP team, all of the parental rights to dispute resolution
remedies apply. These rights are explained in the Procedural Safeguards Notice. Additional information on problem
solving can be found section 14 of this booklet.
o
o
o
o
ESY is not necessarily held in the same location as your child receives services during the regular school year, and
is usually a shorter amount of time per day and per week. The purpose of ESY is to maintain skills so that the gains
made during the regular school period will not be lost. The extent of the ESY program should be individualized
according to the needs of your child.
KEY POINTS
School personnel should know how to write appropriate measurable annual goals. It is not necessarily the
responsibility of the parents. However, having a good understanding of how the process works and what makes a
good goal can help parents to be more knowledgeable participants in the process and to monitor the students
progress. Parents have every right to expect that the childs goals will match the childs needs and be calculated to
help the child be successful.
o
o
o
o
o
o
o
Parents should carefully examine school policies to determine whether modifications need to be made to
accommodate the unique needs of their child.
More information on accommodations in state and district assessments can be found in the Utah Performance
Assessment System for Students Assessment Participation and Accommodations Policy. This information is
available from the Utah State Office of Education and on their website, www.utah.schools.gov
More examples of accommodations and modifications are available from the Utah State Office of Education website,
www.schools.utah.gov or by contacting the Utah Parent Center at 801.272.1051 or www.utahparentcenter.org
o
o
o
o
o
o
o
o
KEY POINTS
o
o
o
o
o
o
Positive Interventions: Parents Need to Know. (May 1999) Reprinted with permission from PACER Center
KEY POINTS
Please see the Utah Special Education Rules from the Utah State Office of Education for definitions of the
above terms.
It is important to have the general education teacher participate when developing the Behavioral Intervention
Plan. One of the functions of the general educator on the IEP team is to help determine appropriate positive
behavioral interventions, supports and other strategies for the student.
Parents should consider a Functional Behavior Assessment and Behavioral Intervention Plan for the IEP of
any special education student who has behavior challenges. Using a BIP to include positive behavioral
supports greatly lessens the likelihood of serious discipline problems and also provides better documentation
of the childs needs in the event that an infraction does occur.
KEY POINTS
One way for parents to help facilitate and encourage the attendance of agency representatives at the IEP meeting
is for the student or the parent to give the invitation. This may reduce the red tape the school faces in getting
consent and may also persuade the representative that he or she is needed and welcome at the meeting.
Transition goals may be included at an earlier age. This may be particularly important for students who are at
risk for dropping out of school or for those individuals with the most significant disabilities.
The Utah Parent Center also offers a workshop and companion parent handbook called From NO Where to KNOW
Where Transition to Adult Services A Parent Handbook. The presentation and handbook provide detailed
information on many topics related to transition planning. Please contact the Utah Parent Center at 801.272.1051 or
www.utahparentcenter.org to obtain a copy of this handbook or to attend an upcoming workshop.
The issuance of a regular high school diploma terminates a students eligibility for public education services.
Some agencies will not serve eligible adults with significant disabilities in day programs until the turn 22, even
if they have graduated. A parent may not require the school district to withhold the issuance of a diploma until
age 22 if the student with disabilities has met the graduation requirements. It is necessary to make an
informed decision in selecting a graduation option and to make certain it is recorded on the IEP. This should
reduce misunderstandings and clarify the time frame available to attain transition goals, including whether to
graduate with peers or continue with additional schooling.
KEY POINTS
It is best to start working on amendments to graduation requirements before the student enters the 9
th
grade
(when credits start to count for graduation).
If graduation requirements as amended in the IEP are not completed due to factors that are not a direct
manifestation of the students disability, the student is not eligible to participate in graduation ceremonies or
receive a diploma until the amended requirements are met. The local principal is authorized to make this
decision.
KEY POINTS
For additional information about students with disabilities in other settings including private schools and home
schools, please see the Utah State Office of Educations Special Education Rules, available at
www.schools.utah.gov
KEY POINTS
KEY POINTS
At this point, it is critical to remember good communication skills. The old saying, You can catch more flies
with honey, rings true in these situations. Be prepared to negotiate! Also, it is good to have support. Some
people you might consider asking for support are: a friend or relative, an advocate, or a representative from a
disability organization or support group, and /or legal representation.
KEY POINTS
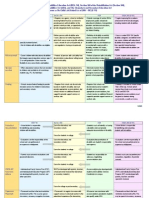
Angela reads
slowly and
confuses words
when reading
Teachers notes
and report cars
mention the
problem
Angela wears
glasses and may
not be able to see
the words well
Vision assessment
Extra time for
reading, Reading
remediation
Teacher agreed
3/16 to provide
Angela with extra
help in reading
while she is
waiting to be
assessed.
Mispronounces
words when
reading aloud
Tape recording
Phonics
assessment
Extra phonics
assistance
Angela has
problems getting
organized to do
her homework
Forgets
assignments, cant
find paper and
pencil, cant seem
to focus
Overall, she
seems very
disorganized
Assessment of
executive
functions
Homework planner
and a system to
help her remember
her assignments;
extra set of books
at home, desk
organizer at home.
I agreed 3/16
with teacher to
help her get
started on
assignments
Has problems
with spelling,
doesnt
recognize root
words
Poor grads,
teachers notes,
spelling tests
May stem from
reading problems
Tutoring with
spelling?
Teacher agreed
3/16 to give
additional spelling
instruction
You might also like
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeFrom EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (5825)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreFrom EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1093)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItFrom EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (852)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceFrom EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (590)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceFrom EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (903)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeFrom EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (541)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersFrom EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (349)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureFrom EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (474)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesFrom EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (823)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)From EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (122)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerFrom EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (271)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingFrom EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (403)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyFrom EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2259)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)From EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Rating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (98)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaFrom EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (266)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryFrom EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (231)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnFrom EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (234)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealFrom EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (74)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaFrom EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (45)
- 5e Investment Lesson PlanDocument4 pages5e Investment Lesson Planapi-268608991No ratings yet
- 5th Grade Colonial Village Unit PlanDocument25 pages5th Grade Colonial Village Unit Planapi-350023470100% (1)
- Developmental DelayDocument2 pagesDevelopmental Delayapi-236207623No ratings yet
- Or Ws Tea Elem 02 DiffinstDocument9 pagesOr Ws Tea Elem 02 Diffinstapi-230724261No ratings yet
- Critical Evaluation of Content-Based AppDocument1 pageCritical Evaluation of Content-Based Appapi-236207623No ratings yet
- Sped Ieps and AssessmentDocument32 pagesSped Ieps and Assessmentapi-236207623No ratings yet
- Paraeducators and Peer TutorsDocument11 pagesParaeducators and Peer Tutorsapi-236207623No ratings yet
- Other Health Impairment (OHI) : Teacher Tips/Learning StrategiesDocument1 pageOther Health Impairment (OHI) : Teacher Tips/Learning Strategiesapi-236207623No ratings yet
- Other Health Impairment (OHI) HandoutDocument1 pageOther Health Impairment (OHI) Handoutapi-236207623No ratings yet
- Orthopedic ImpairmentDocument2 pagesOrthopedic Impairmentapi-236207623No ratings yet
- AutismDocument1 pageAutismapi-236207623No ratings yet
- Sped Acronyms W DefinitionsDocument16 pagesSped Acronyms W Definitionsapi-236207623No ratings yet
- Idea 504 Ada Beduc491comparisonDocument2 pagesIdea 504 Ada Beduc491comparisonapi-234489875No ratings yet
- Sped Laws and Principals Including IepsDocument30 pagesSped Laws and Principals Including Iepsapi-236207623No ratings yet
- KG2-Registration FormDocument3 pagesKG2-Registration FormJohn Patrick IquinNo ratings yet
- Newell Zoe Scholarly Article Draft1Document13 pagesNewell Zoe Scholarly Article Draft1api-549332678No ratings yet
- Salemlaurie Case 38 Analysis 09252022Document5 pagesSalemlaurie Case 38 Analysis 09252022api-628625061No ratings yet
- Chapter 4 Components of Special and Inclusive EducationDocument23 pagesChapter 4 Components of Special and Inclusive EducationDe Vera Thristan Blue100% (1)
- Education For Sustainable Development in BangladeshDocument8 pagesEducation For Sustainable Development in BangladeshASA UpomaNo ratings yet
- Mayra Cruz-Williams ResumeDocument4 pagesMayra Cruz-Williams Resumeapi-393130053No ratings yet
- Resume 1Document1 pageResume 1api-480999867No ratings yet
- Guidance and Career EducationDocument140 pagesGuidance and Career EducationMoses ReconallaNo ratings yet
- 2nd Quarter FbsDocument28 pages2nd Quarter FbsmichelleNo ratings yet
- Pre-Test: Session 3: The K-12 Inclusive Education Lazabelle BagallonDocument10 pagesPre-Test: Session 3: The K-12 Inclusive Education Lazabelle BagallonLAZABELLE BAGALLONNo ratings yet
- John Paz ResumeDocument2 pagesJohn Paz Resumeapi-467933578No ratings yet
- Practises and Classroom Management in Inclusive EducationDocument8 pagesPractises and Classroom Management in Inclusive EducationShreya Manjari (B.A. LLB 14)No ratings yet
- Key Charter Application 2013Document994 pagesKey Charter Application 2013Emily PrevitiNo ratings yet
- Parameter DDocument6 pagesParameter DLet it beNo ratings yet
- Ishaan Awashti Was An 8 Year Old Who Tended To Be Alone While Creating His Own World by The Aid of His Own Imaginative ConceptDocument5 pagesIshaan Awashti Was An 8 Year Old Who Tended To Be Alone While Creating His Own World by The Aid of His Own Imaginative ConceptRaymond ChinNo ratings yet
- Special Education Law ReviewDocument24 pagesSpecial Education Law Reviewjmitchominion2No ratings yet
- Sousa ReadingsDocument8 pagesSousa Readingsapi-639899853No ratings yet
- KHDA - Jumeira Baccalaureate School 2015 2016Document25 pagesKHDA - Jumeira Baccalaureate School 2015 2016Edarabia.comNo ratings yet
- PVAAS 014 FAQ Roster VerificationDocument30 pagesPVAAS 014 FAQ Roster VerificationInnovative Educational Services, CCIUNo ratings yet
- g9 To 12 JournalismDocument27 pagesg9 To 12 JournalismLove LeeNo ratings yet
- A Survey of Barriers To Employment For Individuals Who Are DeafDocument21 pagesA Survey of Barriers To Employment For Individuals Who Are DeafSin Jian ChanNo ratings yet
- Chapter 8 Reporting Group 2Document19 pagesChapter 8 Reporting Group 2Jilyn Mae Lastimoso TopiaNo ratings yet
- Stephanie Kondogonis Resume 2016Document4 pagesStephanie Kondogonis Resume 2016api-335914615No ratings yet
- Position Description Form Revised 2017 New VersionDocument263 pagesPosition Description Form Revised 2017 New VersionJennette BelliotNo ratings yet
- Educational PsychologyDocument364 pagesEducational PsychologyАнна Желобовская100% (7)
- MALDEF ComplaintDocument55 pagesMALDEF Complaintcorey_c_mitchellNo ratings yet
- Lesson Plan 5: Prezi PresentationDocument2 pagesLesson Plan 5: Prezi PresentationamygotmoxyNo ratings yet
- Community Music Therapy and Intellectual DisabilityDocument111 pagesCommunity Music Therapy and Intellectual DisabilityTitokNo ratings yet