Professional Documents
Culture Documents
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
14 viewsRevision Quiz Ch02
Revision Quiz Ch02
Uploaded by
Sweetygirl_16Biology For You Revision Quiz Ch02
Copyright:
Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You might also like
- Transpiration POGIL Answer KeyDocument8 pagesTranspiration POGIL Answer KeyJade Tapper50% (2)
- Inter 2nd Year Botany 1.transport - Plants Study Material PDFDocument8 pagesInter 2nd Year Botany 1.transport - Plants Study Material PDFsingoj.bhargava chary100% (10)
- 2nr Yr Botany Ch 1 to 14.DocxDocument57 pages2nr Yr Botany Ch 1 to 14.Docxlevi nnNo ratings yet
- Osmosis&diffusion 3NDocument8 pagesOsmosis&diffusion 3Nms_m_tan100% (7)
- Bio Absorbtion by Roots 988799Document3 pagesBio Absorbtion by Roots 988799Mridul BIHANI (11Q)No ratings yet
- Cellular Structure and FunctionDocument6 pagesCellular Structure and FunctiondonnaNo ratings yet
- Bio3 TransiDocument47 pagesBio3 TransichemasuetNo ratings yet
- PlasmolysisDocument5 pagesPlasmolysisMalin Hamdan0% (1)
- Mariam Toma Biology Micro Teaching - Osmosis and DiffusionDocument19 pagesMariam Toma Biology Micro Teaching - Osmosis and DiffusionMariam AmgadNo ratings yet
- Transport in Plants I PUC - Biology Chapter - 11 One MarkDocument7 pagesTransport in Plants I PUC - Biology Chapter - 11 One MarkPavan KumarNo ratings yet
- 2 2 OsmosisDocument25 pages2 2 OsmosisAyah FNo ratings yet
- Anatomy and Physiology of Animals-31-60Document30 pagesAnatomy and Physiology of Animals-31-60Pavan PatilNo ratings yet
- Biology Chapter 1Document7 pagesBiology Chapter 1Kuan LoongNo ratings yet
- Unit-I-IMTH-III (Osmosis, Types of Solution & Plasmolysis) PDFDocument47 pagesUnit-I-IMTH-III (Osmosis, Types of Solution & Plasmolysis) PDFanuksha aroraNo ratings yet
- CRP 2018 Final Semester Possible Q &ADocument32 pagesCRP 2018 Final Semester Possible Q &Adudeperfecta36No ratings yet
- AP Biology - Chapter 36 Discussion AnswersDocument4 pagesAP Biology - Chapter 36 Discussion Answersangel91me6371100% (6)
- Chapter 5Document8 pagesChapter 5Mia MistypuffNo ratings yet
- Cell - Transport Chapter SummaryDocument3 pagesCell - Transport Chapter SummaryAlfredo Mandia IIINo ratings yet
- Chapter-3 Absorption by RootsDocument24 pagesChapter-3 Absorption by RootsStudents ofclass10No ratings yet
- Grade IX Biology With CoverDocument19 pagesGrade IX Biology With CoverhamzaspeydNo ratings yet
- Movement - S-Cool, The Revision WebsiteDocument8 pagesMovement - S-Cool, The Revision WebsiteThilini BadugeNo ratings yet
- 2015 Cell Transport WorksheetDocument5 pages2015 Cell Transport Worksheetpaigemk1988No ratings yet
- Cell PhysiologyDocument12 pagesCell PhysiologyJaseme OtoyoNo ratings yet
- Effect of Osmosis Crossword Puzzle AnswerDocument2 pagesEffect of Osmosis Crossword Puzzle AnswerNovah GurulooNo ratings yet
- Absorption by RootsDocument7 pagesAbsorption by RootsSaswatNo ratings yet
- Cell Membranes 06Document5 pagesCell Membranes 06MohdZainiNawahwiNo ratings yet
- Topic-Osmosis, Reverse Osmosis and Its Applications: Chemistry Investigatory ProjectDocument21 pagesTopic-Osmosis, Reverse Osmosis and Its Applications: Chemistry Investigatory ProjectAmmar Adil100% (1)
- Movement in and Out of CellsDocument10 pagesMovement in and Out of CellsarhampracticeNo ratings yet
- Diffusion Lab Docx 1Document12 pagesDiffusion Lab Docx 1api-319962139No ratings yet
- Lab 3 Cell Permeability 2013Document14 pagesLab 3 Cell Permeability 2013Andrew MartiniNo ratings yet
- Osmosis: XCCC C CC CC CC CC CCCCDocument9 pagesOsmosis: XCCC C CC CC CC CC CCCCIwizpv DzimmieNo ratings yet
- 8th-Bio-Ch-1-Notes Class8Document18 pages8th-Bio-Ch-1-Notes Class8SaumyaNo ratings yet
- Topic 3: Diffusion AND Osmosis: ObjectivesDocument9 pagesTopic 3: Diffusion AND Osmosis: ObjectivesAidah JasniNo ratings yet
- Chapter-1 Transport in Plants: Very Short Answers QuestionsDocument8 pagesChapter-1 Transport in Plants: Very Short Answers QuestionsajayNo ratings yet
- Health Care SystemDocument2 pagesHealth Care SystempeytonNo ratings yet
- Movement of Molecules Notes (Year 10 Biology)Document16 pagesMovement of Molecules Notes (Year 10 Biology)Janki patelNo ratings yet
- Cell Transport: Match The Definition On The Left With The Term On The RightDocument5 pagesCell Transport: Match The Definition On The Left With The Term On The RightJay-ann Reyes CabarongNo ratings yet
- Movement in and Out of CellsDocument25 pagesMovement in and Out of Cellsmajanga johnNo ratings yet
- 02 Cells Biology Notes IGCSE 2014Document21 pages02 Cells Biology Notes IGCSE 2014Pablo CostaNo ratings yet
- AP Bio Essay 1983Document3 pagesAP Bio Essay 1983pezxo6No ratings yet
- Diffusion Diffusion in Living Organisms: Diffusion Across The Cell MembraneDocument11 pagesDiffusion Diffusion in Living Organisms: Diffusion Across The Cell MembraneRahil BhavanNo ratings yet
- Diffusion and OsmosisDocument4 pagesDiffusion and OsmosisdetNo ratings yet
- B1.3 - Transport in Cells Gap-Fill 2018 (Combined & Bio)Document4 pagesB1.3 - Transport in Cells Gap-Fill 2018 (Combined & Bio)roger busbyNo ratings yet
- Movement of Substances in CellsDocument18 pagesMovement of Substances in CellskeschikaaNo ratings yet
- MidtermDocument7 pagesMidtermJessica HaleemNo ratings yet
- AdditionalDocument7 pagesAdditionalzain ul AbideenNo ratings yet
- Biology TestDocument7 pagesBiology TestAgustina GibautNo ratings yet
- Cells and Its Environment Ss1 NoteDocument14 pagesCells and Its Environment Ss1 NoteEllaNo ratings yet
- PlasmodesmataDocument11 pagesPlasmodesmataGyandip DekaNo ratings yet
- General Biology - Cell Transport - MandiaDocument3 pagesGeneral Biology - Cell Transport - MandiaAlfredo Mandia IIINo ratings yet
- CH 1 Sec.1Document27 pagesCH 1 Sec.1Ayan HazharNo ratings yet
- Exercise1 DEMONSTRATION OF OSMOSISDocument5 pagesExercise1 DEMONSTRATION OF OSMOSISKristel Bliss RomanoNo ratings yet
- 3.1.3 Transport in PlantsDocument6 pages3.1.3 Transport in Plantsgeniusboo123No ratings yet
- Lab 1 - Osmosis & Diffusion - AU21Document10 pagesLab 1 - Osmosis & Diffusion - AU21Ava ChappellNo ratings yet
- 1 Osmosis DialysisDocument5 pages1 Osmosis DialysisRio SurNo ratings yet
- Bio Note 1Document11 pagesBio Note 1Aidah AmirNo ratings yet
- Notes - Separation TechniquesDocument10 pagesNotes - Separation TechniquesErlangga PanjiNo ratings yet
- Biology 110 Principles of Biology 17 3. Diffusion and OsmosisDocument10 pagesBiology 110 Principles of Biology 17 3. Diffusion and OsmosislauraningsihNo ratings yet
- O Level Biology Practice Questions And Answers Transport In PlantsFrom EverandO Level Biology Practice Questions And Answers Transport In PlantsNo ratings yet
- Camp's Botany by the Numbers: A comprehensive study guide in outline form for advanced biology courses, including AP, IB, DE, and college courses.From EverandCamp's Botany by the Numbers: A comprehensive study guide in outline form for advanced biology courses, including AP, IB, DE, and college courses.No ratings yet
- Art Terrorism Topic Key WordsDocument1 pageArt Terrorism Topic Key WordsSweetygirl_16No ratings yet
- New ECA Club OutlineDocument1 pageNew ECA Club OutlineSweetygirl_16No ratings yet
- SAT Vocab.Document6 pagesSAT Vocab.Sweetygirl_16No ratings yet
- Useful Phrases&Complex ConnectivesDocument3 pagesUseful Phrases&Complex ConnectivesSweetygirl_16No ratings yet
- Revision Quiz Ch19Document1 pageRevision Quiz Ch19Sweetygirl_16No ratings yet
- Revision Quiz Ch17Document1 pageRevision Quiz Ch17Sweetygirl_16No ratings yet
- 4400 Mark Schemes IGCSE November 2004Document33 pages4400 Mark Schemes IGCSE November 2004Sweetygirl_16No ratings yet
- Blood and Circulation: Use These Questions To Help You ReviseDocument1 pageBlood and Circulation: Use These Questions To Help You ReviseSweetygirl_16No ratings yet
- Revision Quiz Ch18Document1 pageRevision Quiz Ch18Sweetygirl_16No ratings yet
- Revision Quiz Ch13Document1 pageRevision Quiz Ch13Sweetygirl_16No ratings yet
- Revision Quiz Ch16Document1 pageRevision Quiz Ch16Sweetygirl_16No ratings yet
- Revision Quiz Ch15Document1 pageRevision Quiz Ch15Sweetygirl_16No ratings yet
- Support and Movement: Use These Questions To Help You ReviseDocument1 pageSupport and Movement: Use These Questions To Help You ReviseSweetygirl_16No ratings yet
- Revision Quiz Ch11Document1 pageRevision Quiz Ch11Sweetygirl_16No ratings yet
- Revision Quiz Ch10Document1 pageRevision Quiz Ch10Sweetygirl_16No ratings yet
- Revision Quiz Ch07Document1 pageRevision Quiz Ch07Sweetygirl_16No ratings yet
- Breathing and Respiration: Use These Questions To Help You ReviseDocument1 pageBreathing and Respiration: Use These Questions To Help You ReviseSweetygirl_16No ratings yet
- School Bus RouteDocument6 pagesSchool Bus RouteSweetygirl_16No ratings yet
- Edexcel IGCSE ChemistryDocument11 pagesEdexcel IGCSE ChemistrySweetygirl_1650% (2)
- Grammar SAT EnglishDocument32 pagesGrammar SAT EnglishSweetygirl_16100% (1)
- Edexcel IGCSE BiologyDocument11 pagesEdexcel IGCSE BiologySweetygirl_16100% (2)
Revision Quiz Ch02
Revision Quiz Ch02
Uploaded by
Sweetygirl_160 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
14 views1 pageBiology For You Revision Quiz Ch02
Copyright
© Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentBiology For You Revision Quiz Ch02
Copyright:
Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pdf or txt
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
14 views1 pageRevision Quiz Ch02
Revision Quiz Ch02
Uploaded by
Sweetygirl_16Biology For You Revision Quiz Ch02
Copyright:
Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pdf or txt
You are on page 1of 1
2
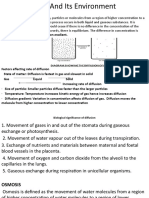
Diffusion
... solute and solvent.
Revision
QUIZ
Use these questions to help you revise
1 Name the 2 parts which make up a solution.
(page 16)
2 In this process, particles spread out from a
high concentration to a low concentration. (p. 16)
... diffusion.
3 When does diffusion stop? (p. 17) 4 The greater the difference in concentration,
the _ _ _ _ _ _ _ the rate of diffusion. (p. 17)
... when particles are spread out evenly. ... greater.
5 What effect would an increase in
temperature have on the rate of diffusion? (p. 17)
... increase it.
6 Two substances that diffuse out of our blood
into our cells. (p. 17)
... food and oxygen.
7 This type of membrane allows small
molecules (like water molecules) to pass through but not large ones. (p. 18)
... partially permeable.
8 What do we call the passage of water
molecules from a weaker solution into a stronger solution through a partially permeable membrane? (p. 18)
... osmosis.
9 This acts as a partially permeable
membrane in plant cells. (p. 19)
... cell membrane.
10 Water passes into plant cells by osmosis
making them _ _ _ _ _ _. (p. 20)
... turgid.
11 If plant cells are placed in a strong sugar
solution water will pass _ _ _ of these cells. (p. 21)
... out.
12 When cells are no longer firm and turgid, we
say that they are _ _ _ _ _ _ _. (p. 21)
... flaccid.
13 If red blood cells are placed into distilled
water they burst. This is called _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _. (p. 21)
... haemolysis.
14 Amoeba uses this to get rid of excess water.
(p. 22)
... contractile vacuole.
15 Salts can be taken up by cells against a
concentration gradient by _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _. (p. 23)
... active transport.
Gareth Williams, 2011
You might also like
- Transpiration POGIL Answer KeyDocument8 pagesTranspiration POGIL Answer KeyJade Tapper50% (2)
- Inter 2nd Year Botany 1.transport - Plants Study Material PDFDocument8 pagesInter 2nd Year Botany 1.transport - Plants Study Material PDFsingoj.bhargava chary100% (10)
- 2nr Yr Botany Ch 1 to 14.DocxDocument57 pages2nr Yr Botany Ch 1 to 14.Docxlevi nnNo ratings yet
- Osmosis&diffusion 3NDocument8 pagesOsmosis&diffusion 3Nms_m_tan100% (7)
- Bio Absorbtion by Roots 988799Document3 pagesBio Absorbtion by Roots 988799Mridul BIHANI (11Q)No ratings yet
- Cellular Structure and FunctionDocument6 pagesCellular Structure and FunctiondonnaNo ratings yet
- Bio3 TransiDocument47 pagesBio3 TransichemasuetNo ratings yet
- PlasmolysisDocument5 pagesPlasmolysisMalin Hamdan0% (1)
- Mariam Toma Biology Micro Teaching - Osmosis and DiffusionDocument19 pagesMariam Toma Biology Micro Teaching - Osmosis and DiffusionMariam AmgadNo ratings yet
- Transport in Plants I PUC - Biology Chapter - 11 One MarkDocument7 pagesTransport in Plants I PUC - Biology Chapter - 11 One MarkPavan KumarNo ratings yet
- 2 2 OsmosisDocument25 pages2 2 OsmosisAyah FNo ratings yet
- Anatomy and Physiology of Animals-31-60Document30 pagesAnatomy and Physiology of Animals-31-60Pavan PatilNo ratings yet
- Biology Chapter 1Document7 pagesBiology Chapter 1Kuan LoongNo ratings yet
- Unit-I-IMTH-III (Osmosis, Types of Solution & Plasmolysis) PDFDocument47 pagesUnit-I-IMTH-III (Osmosis, Types of Solution & Plasmolysis) PDFanuksha aroraNo ratings yet
- CRP 2018 Final Semester Possible Q &ADocument32 pagesCRP 2018 Final Semester Possible Q &Adudeperfecta36No ratings yet
- AP Biology - Chapter 36 Discussion AnswersDocument4 pagesAP Biology - Chapter 36 Discussion Answersangel91me6371100% (6)
- Chapter 5Document8 pagesChapter 5Mia MistypuffNo ratings yet
- Cell - Transport Chapter SummaryDocument3 pagesCell - Transport Chapter SummaryAlfredo Mandia IIINo ratings yet
- Chapter-3 Absorption by RootsDocument24 pagesChapter-3 Absorption by RootsStudents ofclass10No ratings yet
- Grade IX Biology With CoverDocument19 pagesGrade IX Biology With CoverhamzaspeydNo ratings yet
- Movement - S-Cool, The Revision WebsiteDocument8 pagesMovement - S-Cool, The Revision WebsiteThilini BadugeNo ratings yet
- 2015 Cell Transport WorksheetDocument5 pages2015 Cell Transport Worksheetpaigemk1988No ratings yet
- Cell PhysiologyDocument12 pagesCell PhysiologyJaseme OtoyoNo ratings yet
- Effect of Osmosis Crossword Puzzle AnswerDocument2 pagesEffect of Osmosis Crossword Puzzle AnswerNovah GurulooNo ratings yet
- Absorption by RootsDocument7 pagesAbsorption by RootsSaswatNo ratings yet
- Cell Membranes 06Document5 pagesCell Membranes 06MohdZainiNawahwiNo ratings yet
- Topic-Osmosis, Reverse Osmosis and Its Applications: Chemistry Investigatory ProjectDocument21 pagesTopic-Osmosis, Reverse Osmosis and Its Applications: Chemistry Investigatory ProjectAmmar Adil100% (1)
- Movement in and Out of CellsDocument10 pagesMovement in and Out of CellsarhampracticeNo ratings yet
- Diffusion Lab Docx 1Document12 pagesDiffusion Lab Docx 1api-319962139No ratings yet
- Lab 3 Cell Permeability 2013Document14 pagesLab 3 Cell Permeability 2013Andrew MartiniNo ratings yet
- Osmosis: XCCC C CC CC CC CC CCCCDocument9 pagesOsmosis: XCCC C CC CC CC CC CCCCIwizpv DzimmieNo ratings yet
- 8th-Bio-Ch-1-Notes Class8Document18 pages8th-Bio-Ch-1-Notes Class8SaumyaNo ratings yet
- Topic 3: Diffusion AND Osmosis: ObjectivesDocument9 pagesTopic 3: Diffusion AND Osmosis: ObjectivesAidah JasniNo ratings yet
- Chapter-1 Transport in Plants: Very Short Answers QuestionsDocument8 pagesChapter-1 Transport in Plants: Very Short Answers QuestionsajayNo ratings yet
- Health Care SystemDocument2 pagesHealth Care SystempeytonNo ratings yet
- Movement of Molecules Notes (Year 10 Biology)Document16 pagesMovement of Molecules Notes (Year 10 Biology)Janki patelNo ratings yet
- Cell Transport: Match The Definition On The Left With The Term On The RightDocument5 pagesCell Transport: Match The Definition On The Left With The Term On The RightJay-ann Reyes CabarongNo ratings yet
- Movement in and Out of CellsDocument25 pagesMovement in and Out of Cellsmajanga johnNo ratings yet
- 02 Cells Biology Notes IGCSE 2014Document21 pages02 Cells Biology Notes IGCSE 2014Pablo CostaNo ratings yet
- AP Bio Essay 1983Document3 pagesAP Bio Essay 1983pezxo6No ratings yet
- Diffusion Diffusion in Living Organisms: Diffusion Across The Cell MembraneDocument11 pagesDiffusion Diffusion in Living Organisms: Diffusion Across The Cell MembraneRahil BhavanNo ratings yet
- Diffusion and OsmosisDocument4 pagesDiffusion and OsmosisdetNo ratings yet
- B1.3 - Transport in Cells Gap-Fill 2018 (Combined & Bio)Document4 pagesB1.3 - Transport in Cells Gap-Fill 2018 (Combined & Bio)roger busbyNo ratings yet
- Movement of Substances in CellsDocument18 pagesMovement of Substances in CellskeschikaaNo ratings yet
- MidtermDocument7 pagesMidtermJessica HaleemNo ratings yet
- AdditionalDocument7 pagesAdditionalzain ul AbideenNo ratings yet
- Biology TestDocument7 pagesBiology TestAgustina GibautNo ratings yet
- Cells and Its Environment Ss1 NoteDocument14 pagesCells and Its Environment Ss1 NoteEllaNo ratings yet
- PlasmodesmataDocument11 pagesPlasmodesmataGyandip DekaNo ratings yet
- General Biology - Cell Transport - MandiaDocument3 pagesGeneral Biology - Cell Transport - MandiaAlfredo Mandia IIINo ratings yet
- CH 1 Sec.1Document27 pagesCH 1 Sec.1Ayan HazharNo ratings yet
- Exercise1 DEMONSTRATION OF OSMOSISDocument5 pagesExercise1 DEMONSTRATION OF OSMOSISKristel Bliss RomanoNo ratings yet
- 3.1.3 Transport in PlantsDocument6 pages3.1.3 Transport in Plantsgeniusboo123No ratings yet
- Lab 1 - Osmosis & Diffusion - AU21Document10 pagesLab 1 - Osmosis & Diffusion - AU21Ava ChappellNo ratings yet
- 1 Osmosis DialysisDocument5 pages1 Osmosis DialysisRio SurNo ratings yet
- Bio Note 1Document11 pagesBio Note 1Aidah AmirNo ratings yet
- Notes - Separation TechniquesDocument10 pagesNotes - Separation TechniquesErlangga PanjiNo ratings yet
- Biology 110 Principles of Biology 17 3. Diffusion and OsmosisDocument10 pagesBiology 110 Principles of Biology 17 3. Diffusion and OsmosislauraningsihNo ratings yet
- O Level Biology Practice Questions And Answers Transport In PlantsFrom EverandO Level Biology Practice Questions And Answers Transport In PlantsNo ratings yet
- Camp's Botany by the Numbers: A comprehensive study guide in outline form for advanced biology courses, including AP, IB, DE, and college courses.From EverandCamp's Botany by the Numbers: A comprehensive study guide in outline form for advanced biology courses, including AP, IB, DE, and college courses.No ratings yet
- Art Terrorism Topic Key WordsDocument1 pageArt Terrorism Topic Key WordsSweetygirl_16No ratings yet
- New ECA Club OutlineDocument1 pageNew ECA Club OutlineSweetygirl_16No ratings yet
- SAT Vocab.Document6 pagesSAT Vocab.Sweetygirl_16No ratings yet
- Useful Phrases&Complex ConnectivesDocument3 pagesUseful Phrases&Complex ConnectivesSweetygirl_16No ratings yet
- Revision Quiz Ch19Document1 pageRevision Quiz Ch19Sweetygirl_16No ratings yet
- Revision Quiz Ch17Document1 pageRevision Quiz Ch17Sweetygirl_16No ratings yet
- 4400 Mark Schemes IGCSE November 2004Document33 pages4400 Mark Schemes IGCSE November 2004Sweetygirl_16No ratings yet
- Blood and Circulation: Use These Questions To Help You ReviseDocument1 pageBlood and Circulation: Use These Questions To Help You ReviseSweetygirl_16No ratings yet
- Revision Quiz Ch18Document1 pageRevision Quiz Ch18Sweetygirl_16No ratings yet
- Revision Quiz Ch13Document1 pageRevision Quiz Ch13Sweetygirl_16No ratings yet
- Revision Quiz Ch16Document1 pageRevision Quiz Ch16Sweetygirl_16No ratings yet
- Revision Quiz Ch15Document1 pageRevision Quiz Ch15Sweetygirl_16No ratings yet
- Support and Movement: Use These Questions To Help You ReviseDocument1 pageSupport and Movement: Use These Questions To Help You ReviseSweetygirl_16No ratings yet
- Revision Quiz Ch11Document1 pageRevision Quiz Ch11Sweetygirl_16No ratings yet
- Revision Quiz Ch10Document1 pageRevision Quiz Ch10Sweetygirl_16No ratings yet
- Revision Quiz Ch07Document1 pageRevision Quiz Ch07Sweetygirl_16No ratings yet
- Breathing and Respiration: Use These Questions To Help You ReviseDocument1 pageBreathing and Respiration: Use These Questions To Help You ReviseSweetygirl_16No ratings yet
- School Bus RouteDocument6 pagesSchool Bus RouteSweetygirl_16No ratings yet
- Edexcel IGCSE ChemistryDocument11 pagesEdexcel IGCSE ChemistrySweetygirl_1650% (2)
- Grammar SAT EnglishDocument32 pagesGrammar SAT EnglishSweetygirl_16100% (1)
- Edexcel IGCSE BiologyDocument11 pagesEdexcel IGCSE BiologySweetygirl_16100% (2)