Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Chapter 5
Chapter 5
Uploaded by
Nhóc Bướng BỉnhCopyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Chapter 5
Chapter 5
Uploaded by
Nhóc Bướng BỉnhCopyright:
Available Formats
Chapter 5
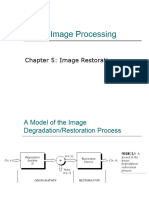
Image Restoration
Degradation/Restoration Process
) , ( y x f
) , ( y x g
) , ( y x q
Degradation
Function
H
Restoration
Filter(s)
+ ) , (
y x f
DEGRADATION
RESTORATION
Image Degradation
The degradation is modeled as a
degradation function that, together with
an additive noise term, operates on an
input image f(x,y) to produce a degraded
image g(x,y)
If H is a linear the the degraded image is
given in spatial domain by
) , ( ) , ( * ) , ( ) , ( y x y x f y x h y x g q + =
Where the symbol * indicates spatial convolution
Image Restoration
Given g(x,y), some knowledge about the
degradation function H, and some
information about the additive noise
The objective of the restoration is to
obtain an estimate of the original
image.
) , ( y x q
) , (
y x f
Noise Models
The principal source of noise in digital
images arise during image acquisition
(digitization) and/or transmission.
The performance of imaging sensors is
affected by a variety of factors.
Images are corrupted during
transmission due to interference in
channel
Spatial Properties of Noise
With the exception of spatially
periodic noise, noise is independent
of spatial coordinates, and it is
uncorrelated with respect to the
image itself.
We can describe that spatial noise is
concerned with the statistical
behavior of the gray-level values.
Some Importance Noise
These noises are common found.
Gaussian noise
Rayleigh noise
Erlang (Gamma) noise
Exponential noise
Uniform noise
Impulse (salt-and-pepper) noise
Gaussian noise
The PDF of a Gaussian noise is given by
2 2
2 / ) (
2
2
1
) (
o
to
=
z
e z p
p(z)
z
o o +
Rayleigh noise
The PDF of a Rayleigh noise is given by
<
>
=
a z f or
a z f or e a z
z p
b a z
b
0
) (
) (
/ ) (
2
2
p(z)
z a
4 / b a t + =
4
) 4 (
2
t
o
=
b
and
The mean and variance are given
2
b
a +
Erlang (Gamma) noise
The PDF of a Erlang noise is given by
<
>
0 0
0
)! 1 (
) (
1
z for
z for e
b
z a
z p
az
b b
p(z)
z
K
a
b
=
2
2
a
b
= o and
The mean and variance are given
a
b 1
) 1 (
1
)! 1 (
) 1 (
=
b
b
e
b
b a
K
Exponential noise
The PDF of a Exponential noise is given by
<
>
=
0 0
0
) (
z for
z for ae
z p
az
p(z)
z
a
a
1
=
2
2
1
a
= o and
The mean and variance are given
Note: It is a special case of Erlang PDF, with b=1.
Uniform noise
The PDF of a Uniform noise is given by
s s
=
otherwise
b z a if
a b
z p
0
1
) (
p(z)
z
a
2
b a +
=
12
) (
2
2
a b
= o
and
The mean and variance are given
b
a b
1
Impulse (salt-and-pepper) noise
The PDF of a (bipolar) impulse noise is given
by
=
=
=
otherwise
b z f or P
a z f or P
z p
b
a
0
) (
p(z)
z
a b
b
P
a
P
Restoration in the Presence of Noise
When the only degradation present in an
image is noise
The noise is unknown, so subtracting
them from g(x,y) is not a realistic option.
In fact, enhancement and restoration
become almost indistinguishable
disciplines in this particular case.
) , ( ) , ( ) , ( y x y x f y x g q + =
Mean Filters
This is the simply methods to reduce
noise in spatial domain.
Arithmetic mean filter
Geometric mean filter
Harmonic mean filter
Contraharmonic mean filter
Let S
xy
represent the set of coordinates in
a rectangular subimage window of size
mxn, centered at point (x,y).
Arithmetic mean filter
Compute the average value of the corrupted
image g(x,y) in the aread defined by S
x,y
.
The value of the restored image at any point
(x,y)
e
=
y x
S t s
t s g
mn
y x f
,
) , (
) , (
1
) , (
Note: Using a convolution mask in which all
coefficients have value 1/mn. Noise is reduced as a
result of blurring.
Geometric mean filter
Using a geometric mean filter is given by the
expression
mn
xy
S t s
t s g y x f
1
) , (
) , ( ) , (
(
(
=
[
e
Harmonic mean filter
The harmonic mean filter operation is given
by the expression
e
=
xy
S t s
t s g
mn
y x f
) , (
) , (
1
) , (
Contraharmonic mean filter
The contraharmonic mean filter operation is
given by the expression
e
e
+
=
xy
xy
S t s
Q
S t s
Q
t s g
t s g
y x f
) , (
) , (
1
) , (
) , (
) , (
Where Q is called the order of the filter. This filter is
well suited for reducing or virtually eliminating the
effects of salt-and-pepper noise.
Order-Statistics Filters
Order-Statictics filters are spatial filters
whose response is based on ordering
(ranking) the pixels contained in the
image area encompassed by the filter
Median filter
Max and Min filter
Midpoint filter
Alpha-trimmed mean filter
Median filter
Process is replaces the value of a pixel
by the median of the gray levels in region
S
xy
of that pixel:
{ } ) , ( ) , (
) , (
t s g median y x f
xy
S t s e
=
Max and Min filter
Using the 100
th
percentile results in the
so-called max filter, given by
The 0
th
percentile filter is min filter:
{ } ) , ( max ) , (
) , (
t s g y x f
xy
S t s e
=
{ } ) , ( min ) , (
) , (
t s g y x f
xy
S t s e
=
This filter is useful for finding the brightest points in an image.
Since pepper noise has very low values, it is reduced by this
filter as a result of the max selection processing the subimage
area S
xy
.
This filter is useful for finding the darkest points in an image.
Also, it reduces salt noise as a result of the min operation.
Midpoint filter
The midpoint filter simply computes the
midpoint between the maximum and
minimum values in the area encompassed by
the filter:
{ } { }
(
+ =
e e
) , ( min ) , ( max
2
1
) , (
) , ( ) , (
t s g t s g y x f
xy xy
S t s S t s
Note: This filter works best for randomly distributed
noise, like Gaussian or uniform noise.
Alpha-trimmed mean filter
Suppose that we delete the d/2 lowest and the
d/2 highest gray-level values of g(s,t) in the
area S
xy
.
Let g
r
(s,t) represent the remaining mn-d
pixels. And averaging these remain pixels is
denoted as:
=
xy
S t s
r
t s g
d mn
y x f
) , (
) , (
1
) , (
Where the value of d can range from 0 to mn-1. When d=0,
It is arithmetic mean filter and d=(mn-1)/2 is a median
filter. It is useful for the multiple types of noise such as the
combination of salt-and-pepper and Gaussian noise.
Adaptive Filters
Its behavior changes based on
statistical characteristics of the
image inside the filter region defined
by the mxn rectangular window S
xy
.
You might also like
- COMP 4421 - Image ProcessingDocument56 pagesCOMP 4421 - Image ProcessingLinh TaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 5 Image Restoration - 01Document37 pagesChapter 5 Image Restoration - 01Aman Ahmad SiddiqueeNo ratings yet
- Trisectores 2019-2020Document25 pagesTrisectores 2019-2020ericsson3gppNo ratings yet
- DIP7Document159 pagesDIP7Aravinth CpNo ratings yet
- Image Restoration (Sections 5.1, 5.5, 5.7, 5.9) : CS474/674 - Prof. BebisDocument67 pagesImage Restoration (Sections 5.1, 5.5, 5.7, 5.9) : CS474/674 - Prof. Bebissrc010850% (2)
- Image RestorationDocument41 pagesImage Restorationcsbits0% (1)
- RestorationDocument65 pagesRestorationNisa ZairaNo ratings yet
- EEE F435 (2020-21-I) : Digital Image ProcessingDocument30 pagesEEE F435 (2020-21-I) : Digital Image ProcessingVaib AgraNo ratings yet
- Image Restoration 1Document30 pagesImage Restoration 1A JNo ratings yet
- Image RestorationDocument28 pagesImage Restorationswatisingla786No ratings yet
- Part2 AttachementDocument8 pagesPart2 AttachementAMMU KAUSHIKNo ratings yet
- Image Restoration 影像復 原: Spring 2005, Jen-Chang LiuDocument58 pagesImage Restoration 影像復 原: Spring 2005, Jen-Chang Liupatelvaidehi07No ratings yet
- Digital Image Processing: Image Restoration: Noise RemovalDocument32 pagesDigital Image Processing: Image Restoration: Noise Removalsanjila parvinNo ratings yet
- Digital Image Processing: Image Restoration For Getting More Knowledge According To Miss Aneeba MasoodDocument38 pagesDigital Image Processing: Image Restoration For Getting More Knowledge According To Miss Aneeba MasoodSana KhanNo ratings yet
- NoiseDocument4 pagesNoisemcjack181No ratings yet
- Digital Image ProcessingDocument39 pagesDigital Image Processingstar xNo ratings yet
- 1.1 OverviewDocument51 pages1.1 Overviewjenish devNo ratings yet
- Lec-2 Image Enhancement in The Frequency DomainDocument74 pagesLec-2 Image Enhancement in The Frequency DomainravibabukancharlaNo ratings yet
- Image Restoration: Yinghua He School of Computer Science and Technology Tianjin UniversityDocument116 pagesImage Restoration: Yinghua He School of Computer Science and Technology Tianjin UniversityARUNA TNNo ratings yet
- Spatial Filtering ppt1Document66 pagesSpatial Filtering ppt1musicstand29No ratings yet
- Group 2 Members Hcse422 Image Processing and Machine Vision:Image RestorationDocument38 pagesGroup 2 Members Hcse422 Image Processing and Machine Vision:Image RestorationPrayerNo ratings yet
- EE 583 Lecture07Document34 pagesEE 583 Lecture07YazanAlomariNo ratings yet
- (MIP Lab) Noise Removal in Digital Image ProcessingDocument16 pages(MIP Lab) Noise Removal in Digital Image Processingmanashprotimdeori123No ratings yet
- Lect 10Document37 pagesLect 10raviNo ratings yet
- Image RestorationDocument62 pagesImage RestorationV.ThirunavukkarasuNo ratings yet
- Image FiltersDocument20 pagesImage FiltersV.ThirunavukkarasuNo ratings yet
- Dip S8ece Module4Document145 pagesDip S8ece Module4Neeraja JohnNo ratings yet
- Dip R20 Unit-3 NotesDocument18 pagesDip R20 Unit-3 Notesdeekshithavakalapudi31No ratings yet
- Image DenoisingDocument58 pagesImage DenoisingEmon KhanNo ratings yet
- SharpeningDocument60 pagesSharpeningADDY39No ratings yet
- Unit 3Document9 pagesUnit 3dixit.ramani7773No ratings yet
- Filtering in The Frequency DomainDocument34 pagesFiltering in The Frequency DomainK.R.Raguram100% (1)
- IPT Module 4Document19 pagesIPT Module 4b20cs36No ratings yet
- Image Restoration TechniquesDocument39 pagesImage Restoration TechniquesAbysz100% (1)
- DIP LectureDocument35 pagesDIP Lecturemajdiyjalalm2No ratings yet
- Chapter 19Document102 pagesChapter 19RichurajanNo ratings yet
- DIP Notes Unit-3Document57 pagesDIP Notes Unit-3gfgfdgfNo ratings yet
- Image Restoration_Updated (1)Document15 pagesImage Restoration_Updated (1)shivansh srivastavaNo ratings yet
- Chapter3 EnhancementDocument56 pagesChapter3 EnhancementasmaaNo ratings yet
- Lecture 4. Image RestorationDocument39 pagesLecture 4. Image Restorationenkhtsetseg enkhbat0% (1)
- Lecture 3Document37 pagesLecture 3bedline.salesNo ratings yet
- Image Processing: Gaurav GuptaDocument38 pagesImage Processing: Gaurav GuptaKoteswara Rao LNo ratings yet
- Lect3 6Document15 pagesLect3 6Chandan KumarNo ratings yet
- Lecture#27Document51 pagesLecture#27Afsheen ZaibNo ratings yet
- Lecture 3Document64 pagesLecture 3Reema AmgadNo ratings yet
- Unit 5 Degradation and Restoration Noise FilterDocument108 pagesUnit 5 Degradation and Restoration Noise Filterkashish singhNo ratings yet
- 5-SpatialFiltering 2Document74 pages5-SpatialFiltering 2pham tamNo ratings yet
- Image Processing: Gaurav GuptaDocument38 pagesImage Processing: Gaurav GuptaanithaNo ratings yet
- Frequency Domain Filtering (Chapter 4) : CS474/674 - Prof. BebisDocument59 pagesFrequency Domain Filtering (Chapter 4) : CS474/674 - Prof. BebisMohammed AL-MaaitahNo ratings yet
- 2-Image Formation, Filters and ConvolutionDocument46 pages2-Image Formation, Filters and ConvolutionBasudha PalNo ratings yet
- Ch5 RestorationDocument56 pagesCh5 Restorationabdoag1691998No ratings yet
- Ay Level Transformations and HistogramDocument50 pagesAy Level Transformations and HistogramRameshkumar JayaramanNo ratings yet
- Image Processing Chapter 5Document33 pagesImage Processing Chapter 5saeavana100% (3)
- Image Processing: Gaurav GuptaDocument38 pagesImage Processing: Gaurav GuptaSnehal ChotheNo ratings yet
- DIP Unit 2 (Enhancement, Binary, Colour)Document126 pagesDIP Unit 2 (Enhancement, Binary, Colour)Shubham DhundaleNo ratings yet
- Dip Unit2Document172 pagesDip Unit2Vaishnavi BavalekarNo ratings yet
- EC8093 Unit 3Document79 pagesEC8093 Unit 3Santhosh PaNo ratings yet
- Image Enhancement II-24-66Document43 pagesImage Enhancement II-24-66AshaNo ratings yet
- Image RestorationDocument108 pagesImage RestorationPurushotham Prasad KNo ratings yet
- Noise Reduction: Enhancing Clarity, Advanced Techniques for Noise Reduction in Computer VisionFrom EverandNoise Reduction: Enhancing Clarity, Advanced Techniques for Noise Reduction in Computer VisionNo ratings yet
- Disstres Signal BaruDocument14 pagesDisstres Signal BaruYunus Kautsart BahariNo ratings yet
- The Yagi Antenna or YagiDocument17 pagesThe Yagi Antenna or YagikattaswamyNo ratings yet
- Abc 5GDocument25 pagesAbc 5GMUHAMMED NASEEF MKNo ratings yet
- Practical-7 SeriesRLC REsonanceDocument5 pagesPractical-7 SeriesRLC REsonanceJay SathvaraNo ratings yet
- Lan Details0122Document1 pageLan Details0122t_syamprasadNo ratings yet
- Ic-7400 SM 3Document84 pagesIc-7400 SM 3Luciano HoraNo ratings yet
- DVB SadcDocument61 pagesDVB SadcMostafa BorhaniNo ratings yet
- QB 2Document4 pagesQB 2Veena Divya KrishnappaNo ratings yet
- UMTS Optimization Example Dr. Hatem MOKHTARIDocument35 pagesUMTS Optimization Example Dr. Hatem MOKHTARIHatem MOKHTARINo ratings yet
- Evolution-of-wireless-networks-technologies-history-and-emerging-technology-of-5GDocument5 pagesEvolution-of-wireless-networks-technologies-history-and-emerging-technology-of-5GultrahornytgtNo ratings yet
- Module 7Document17 pagesModule 7jimmyboyjr50% (2)
- The Basics of Bluetooth Low Energy BLE 2Document5 pagesThe Basics of Bluetooth Low Energy BLE 2fdsfsdfrgeNo ratings yet
- Session 2Document15 pagesSession 2Rumble kingNo ratings yet
- BSNL UPE (Mobile Prepaid at A Glance) (Updated Wef 27 May 2020)Document4 pagesBSNL UPE (Mobile Prepaid at A Glance) (Updated Wef 27 May 2020)VKNo ratings yet
- AQU4518R8Document2 pagesAQU4518R8pra4uk100% (3)
- Spec PMP450i AP 10022019Document3 pagesSpec PMP450i AP 10022019Edi SuryanaNo ratings yet
- Principle of MCDocument34 pagesPrinciple of MCeva sharmaNo ratings yet
- Experiment No 3. OcnDocument7 pagesExperiment No 3. Ocnshivani moreNo ratings yet
- Digital Radio Distribution in Europe: Recommendation Source: SP-DRPDocument3 pagesDigital Radio Distribution in Europe: Recommendation Source: SP-DRPLukáš PolákNo ratings yet
- Kraken AntennaDocument5 pagesKraken AntennaАлександр РадецкийNo ratings yet
- Amie Sec.a&bDocument25 pagesAmie Sec.a&bVasmate ShivarajNo ratings yet
- Kenwood Ts-990S: New Flagship HF & 50Mhz TransceiverDocument5 pagesKenwood Ts-990S: New Flagship HF & 50Mhz TransceiverNickEglezosNo ratings yet
- Multiplexing Techniques: Frequency Division Multiplexing (FDM)Document8 pagesMultiplexing Techniques: Frequency Division Multiplexing (FDM)freshpNo ratings yet
- Unbalanced UplinkDocument1 pageUnbalanced UplinkazkaNo ratings yet
- JBL Tune 115TWS HeadphoneDocument2 pagesJBL Tune 115TWS HeadphoneTimiNo ratings yet
- Lte Channel Estimation ThesisDocument4 pagesLte Channel Estimation Thesisgbxqaf9v100% (2)
- Tomasi Book PDFDocument191 pagesTomasi Book PDFJeremy JavierNo ratings yet
- 73 Magazine - Special Antenna Issue - May 1968Document116 pages73 Magazine - Special Antenna Issue - May 1968Benjamin Dover100% (1)
- Q1. (2 Marks) Compute The Output Volume and Total Parameters For The Given CNN Which Is A Slightly Modified Version of Lenet-5Document3 pagesQ1. (2 Marks) Compute The Output Volume and Total Parameters For The Given CNN Which Is A Slightly Modified Version of Lenet-5wellhellothere123No ratings yet