Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Worksheet2 Rightface2013
Worksheet2 Rightface2013
Uploaded by
api-239713754Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Worksheet2 Rightface2013
Worksheet2 Rightface2013
Uploaded by
api-239713754Copyright:
Available Formats
Worksheet: Right Face
Introduction to Mobile Robotics > Right Face
Follow the steps in the online directions, and answer the questions at the appropriate times.
Construct
Observations:
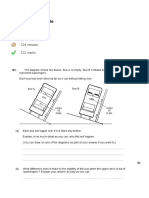
1. What happened when you ran the program? The robot turned to the right just as we programmed it to. 2. Which motor(s) spun? Motor C turned the right wheel that made the robot go anti clockwise. 3. What direction did each motor spin? Motor B didnt move at all and motor C turned forwards. 4. Did the robots body turn to its left or its right? The robot turned its body left. 5. About how much did the robots body turn, relative to a full turn? The robot did a 180 degree spin. 6. This behaviour is called a swing turn. Around what point does the robot swing? It swung at the It swung at the right side or the point where the left wheel was placed. Contemplate
7. Write a brief one or two sentence description of what each icon in the program Swing Turn does.
Block 1 made the right motor run to turn the right wheel forward. Block 2 made the left wheel stay still. Block 3 made the wheel turn 720 degrees
forward. Block 4 stopped motor C at 720 degrees. Block 5 stopped motor B from turning the wheel.
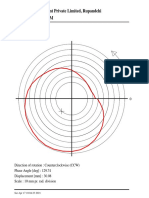
8. The robot started at position A on the diagram shown here. It then turned in place until it reached position B.
i.
Suppose the robot turned to its left to reach position B. What fraction of a full turn did it make to get from A to B? It would turn a 270 degree rotation.
ii.
Suppose the robot turned to its right to reach position B. What fraction of a full turn did it make to get from A to B? It would turn a 90 degree rotation.
9. Consider the effects of some additional factors. i. How do you think different wheels will affect the robots ability to turn? Does it matter? The robot will still go forward but will veer to one side. ii. Does the surface on which the robot is turning matter? Yes it matters, it needs to be smooth surface otherwise it would be hard for the wheels to turn.
10. The robot in the given program turned right by moving its left wheel forward while holding its right wheel stationary. i. Could you also turn right by holding the left wheel stationary and running the right wheel in reverse? Yes because you are still making the robot face the right. ii. Write the program to make the robot do the backward right turn proposed in part (i).
Continue: Left Turn
Answer the following:
11. What program blocks are different between the left turn and original right turn behaviours? The first two blocks because you can change which direction the wheel spins. 12. Could a left turn also be done with the backward-moving wheel idea from question 10? Program your robot to make the backward-left turn.
Continue Point Turn
Answer the following:
13. Describe the difference between the motion of a swing turn and a point turn. The differences are that a point turn keeps the robots body in the same place while the wheels are moving around it and it also turns the robot around. The swing turn makes it turn left or right. 14. Describe a situation where: i. A swing turn is more useful than a point turn. When wanting to put the robot to face the other way. ii. A point turn is more useful than a swing turn. When wanting to turn the robot left or right.
You might also like
- Rotation and Revolution WorksheetDocument2 pagesRotation and Revolution WorksheetEngga Swari100% (6)
- The Colonization of Tiamat V (Phoenix III, Daniel) PDFDocument44 pagesThe Colonization of Tiamat V (Phoenix III, Daniel) PDFKonstantina GlezakouNo ratings yet
- Seaperch Engineering Design Report 2021Document6 pagesSeaperch Engineering Design Report 2021Thomas Wu100% (1)
- Concrete Design Using PROKONDocument114 pagesConcrete Design Using PROKONHesham Mohamed100% (2)
- Bowin Service Manual (Ceiling Led)Document28 pagesBowin Service Manual (Ceiling Led)Marcelo TaboadaNo ratings yet
- Worksheet2 Rightface2013Document3 pagesWorksheet2 Rightface2013api-233732442No ratings yet
- Worksheet 2 Right FaceDocument3 pagesWorksheet 2 Right Faceapi-239713895No ratings yet
- Right FaceDocument3 pagesRight Faceapi-239713542No ratings yet
- Worksheet2 Rightface2013Document3 pagesWorksheet2 Rightface2013api-239713626No ratings yet
- Worksheet2 Rightface2013Document3 pagesWorksheet2 Rightface2013api-239712567No ratings yet
- Robotics Worksheet Right FaceDocument3 pagesRobotics Worksheet Right Faceapi-239713189No ratings yet
- Marked Work-Sheet Full Speed AheadDocument4 pagesMarked Work-Sheet Full Speed Aheadapi-233276394No ratings yet
- Full Speed AheadDocument3 pagesFull Speed Aheadapi-239713542No ratings yet
- Worksheet RoboticsDocument4 pagesWorksheet Roboticsapi-239713189No ratings yet
- Chapter 4 Challenges: The QuestionsDocument2 pagesChapter 4 Challenges: The Questionsapi-358351105No ratings yet
- Worksheet - Rull Speed AheadDocument4 pagesWorksheet - Rull Speed Aheadapi-233727526No ratings yet
- Chapter 4 ChallengesDocument3 pagesChapter 4 Challengesapi-358099446No ratings yet
- 004 Zeeshan AiprDocument26 pages004 Zeeshan Aipr26- Amal SathyanNo ratings yet
- Bipedal Robot PresentationDocument16 pagesBipedal Robot PresentationJagannath Prasad SahooNo ratings yet
- Chapter 4 Challenges By: Rubi Contreras CET-6: QuestionsDocument2 pagesChapter 4 Challenges By: Rubi Contreras CET-6: Questionsapi-358353351No ratings yet
- Assessment QDocument1 pageAssessment QJeremy AshworthNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3Document24 pagesChapter 3HAAVINESHNo ratings yet
- Worksheet 1Document4 pagesWorksheet 1api-239713268No ratings yet
- Lesson 2 5 Minute BotDocument9 pagesLesson 2 5 Minute Botapi-273620669No ratings yet
- Esp32 Wi-Fi Self Balancing RobotDocument8 pagesEsp32 Wi-Fi Self Balancing Robotmayanksharmag123No ratings yet
- 10 - A Spherical Hopping Robot For Exploration in Complex EnvironmentsDocument6 pages10 - A Spherical Hopping Robot For Exploration in Complex EnvironmentsjowdiverNo ratings yet
- Lesson 1 Make The Car MoveDocument9 pagesLesson 1 Make The Car MoveAdrian ChelenNo ratings yet
- A Beginners Guide To RoboticsDocument9 pagesA Beginners Guide To RoboticsUdit PeAce SangwanNo ratings yet
- AVR ATmega8 Based LFR - Differential DriveDocument8 pagesAVR ATmega8 Based LFR - Differential DriveAbril de VeraNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Servo MotorsDocument21 pagesIntroduction To Servo MotorsGeetha VenugopalNo ratings yet
- Modul PRDDocument3 pagesModul PRDSiti AisyahNo ratings yet
- Modul 1 Basic - Make It Move - Make It SmartDocument3 pagesModul 1 Basic - Make It Move - Make It SmartSuci Ayu ChairunaNo ratings yet
- Beginner Programming Lesson: Basic TurningDocument11 pagesBeginner Programming Lesson: Basic TurningZyber Dcode SirRodNo ratings yet
- Chapter 4Document2 pagesChapter 4api-357697027No ratings yet
- Movement ChallengeDocument6 pagesMovement ChallengeBarbara Denisse IrulaNo ratings yet
- Elecbits - Self Balancing RobotDocument4 pagesElecbits - Self Balancing RobotKeshav SharmaNo ratings yet
- How To Build A Self Balancing Gyroscopic VehicleDocument48 pagesHow To Build A Self Balancing Gyroscopic VehicleJames Demello0% (1)
- How To Build A Robot at HomeDocument37 pagesHow To Build A Robot at Homesureshya22No ratings yet
- Holo No Mic Omni Wheel DriveDocument13 pagesHolo No Mic Omni Wheel Drivemoosa seikhNo ratings yet
- Construcción Base de RobotsDocument3 pagesConstrucción Base de RobotsEmmanuel CuadrosNo ratings yet
- ECE - 3641 Project ProposalDocument11 pagesECE - 3641 Project Proposalananya RupaNo ratings yet
- SubtitleDocument1 pageSubtitleshiva100cNo ratings yet
- Falcon ConstruccionDocument33 pagesFalcon ConstruccionSANDY VELANo ratings yet
- Gyro TurningDocument13 pagesGyro Turningsuthirth pNo ratings yet
- Hands On 1 BasicDocument2 pagesHands On 1 BasicdianahulfahNo ratings yet
- TechnologyDocument1 pageTechnologyLeonid LebedevNo ratings yet
- Tutorial 1Document8 pagesTutorial 1Sudheshnan T SudheshNo ratings yet
- A Simple DIY Walking RobotDocument6 pagesA Simple DIY Walking RobotRAVI Ranjan0% (1)
- Types of RobotsDocument15 pagesTypes of RobotsItsmesammy yahhhNo ratings yet
- Technical Report - Steering (Fall 2007)Document26 pagesTechnical Report - Steering (Fall 2007)Mahmoud El-MahdyNo ratings yet
- Generation of Whole Body Motion PatternsDocument24 pagesGeneration of Whole Body Motion PatternsCuriosoCuriosoCuriosoNo ratings yet
- Aerial Robotics Lecture 1B - 5 Agility and ManoeuvrabilityDocument4 pagesAerial Robotics Lecture 1B - 5 Agility and ManoeuvrabilityIain McCulloch100% (1)
- Preguntas RoboDocument9 pagesPreguntas Roboadriyeb75No ratings yet
- Wheel Control TheoryDocument7 pagesWheel Control TheoryNgurah BimantaraNo ratings yet
- Chapter 4 Challenges: QuestionsDocument4 pagesChapter 4 Challenges: Questionsapi-358351971No ratings yet
- Clase 3 Scratch TurningDocument12 pagesClase 3 Scratch TurningSandra Patricia Motoa SabalaNo ratings yet
- GYRO SENSO EnglishDocument7 pagesGYRO SENSO Englisharsanymagdy904No ratings yet
- Unit 2 - Automobile Engineering - WWW - Rgpvnotes.in PDFDocument13 pagesUnit 2 - Automobile Engineering - WWW - Rgpvnotes.in PDFPushpkant RayNo ratings yet
- Flowcharts PDFDocument9 pagesFlowcharts PDFceciceciceci100% (1)
- Unit 10Document5 pagesUnit 10phamhathy12a2No ratings yet
- Addey - A2. Robotics - Driving Base - Set Movement and Turning LabDocument2 pagesAddey - A2. Robotics - Driving Base - Set Movement and Turning LabMohannad AlyNo ratings yet
- Manual Robotics Tutorial 1Document8 pagesManual Robotics Tutorial 1MSierra Diaz del AlamoNo ratings yet
- School and Metro Bus Driving Skills: Essential Step By Step Guide for Maneuvering Large VehiclesFrom EverandSchool and Metro Bus Driving Skills: Essential Step By Step Guide for Maneuvering Large VehiclesNo ratings yet
- Physical Pendulum - Angular SHM - Solved ProblemsDocument7 pagesPhysical Pendulum - Angular SHM - Solved ProblemsHomayoon GeramifarNo ratings yet
- 06 - 01+ (7) - Analysis of The 155 MM Erfbbb Projectile TrajectoryDocument24 pages06 - 01+ (7) - Analysis of The 155 MM Erfbbb Projectile Trajectoryeldubi1970No ratings yet
- Sine-And-Cosine-Rules 3Document10 pagesSine-And-Cosine-Rules 3Farzad FarhadNo ratings yet
- Ex.108 - Sliding Mesh For A Single Screw ExtruderDocument9 pagesEx.108 - Sliding Mesh For A Single Screw ExtruderjacksayshiNo ratings yet
- Practical Applications For Mobile Robots Based On Mecanum Wheels - A Systematic SurveyDocument13 pagesPractical Applications For Mobile Robots Based On Mecanum Wheels - A Systematic SurveyFlorentina AdascaliteiNo ratings yet
- Custom Components Guide 211 EnuDocument112 pagesCustom Components Guide 211 Enurazvan bossNo ratings yet
- Line 1 Polar Enclosure.Document36 pagesLine 1 Polar Enclosure.Sunil T V SuniNo ratings yet
- The Physics of Stone SkippingDocument7 pagesThe Physics of Stone Skippingapi-26504090100% (1)
- Rigid Bodies: 2.1 Many-Body SystemsDocument17 pagesRigid Bodies: 2.1 Many-Body SystemsRyan TraversNo ratings yet
- Geometry Tutor - Worksheet 3 - Complimentary and Supplementary AnglesDocument17 pagesGeometry Tutor - Worksheet 3 - Complimentary and Supplementary AnglesCydrick P DescalzoNo ratings yet
- Question Bank - Brain Books An E Learning PlatformDocument3 pagesQuestion Bank - Brain Books An E Learning PlatformBabri masjid Ghistosof Babrii masjadNo ratings yet
- Monolithic Parallel Linear Compliant Mechanism For Two Axes Ultraprecision Linear MotionDocument8 pagesMonolithic Parallel Linear Compliant Mechanism For Two Axes Ultraprecision Linear Motionmaulikshah_23No ratings yet
- CH 3. Circulation Motion (Phy - 1)Document48 pagesCH 3. Circulation Motion (Phy - 1)kingstar122004No ratings yet
- TCD CS 2006 46Document10 pagesTCD CS 2006 46masterhacksNo ratings yet
- Rotational MotionDocument3 pagesRotational MotionbluejackbroNo ratings yet
- Physics Numericals: STD XII SciDocument7 pagesPhysics Numericals: STD XII SciSagarNo ratings yet
- Calculating Missing AnglesDocument18 pagesCalculating Missing AnglesDairo AbiodunNo ratings yet
- CIRCULAR MOTION 25 Imp McqsDocument4 pagesCIRCULAR MOTION 25 Imp Mcqskshitijchavan1018No ratings yet
- Yield Line Analysis - 1Document19 pagesYield Line Analysis - 1Ahmed NabilNo ratings yet
- Sto. Nino, Binan, Laguna: University of Perpetual Help System LagunaDocument5 pagesSto. Nino, Binan, Laguna: University of Perpetual Help System LagunaWinchelle Dawn Ramos LoyolaNo ratings yet
- IPSF Pole Sports Code of Points 2021 - 24 - VFFF 30.01.2022Document166 pagesIPSF Pole Sports Code of Points 2021 - 24 - VFFF 30.01.2022Angel SanabriaNo ratings yet
- Assign Torque 28 10 2019Document15 pagesAssign Torque 28 10 2019Harsh KumarNo ratings yet
- P3 07 MomentsDocument76 pagesP3 07 MomentsOmar AbdallaNo ratings yet
- Lip Seal ParkerDocument170 pagesLip Seal Parkersport2008100% (1)
- Chapter 16 PDFDocument65 pagesChapter 16 PDFAmirulHanif AlyahyaNo ratings yet
- 1Document3 pages1yamini seshakalaNo ratings yet