Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Chapter 7-Respiration (Form 4) : Inspiration / Inhalation: Expiration / Exhalation
Chapter 7-Respiration (Form 4) : Inspiration / Inhalation: Expiration / Exhalation
Uploaded by
mentos999Original Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Chapter 7-Respiration (Form 4) : Inspiration / Inhalation: Expiration / Exhalation
Chapter 7-Respiration (Form 4) : Inspiration / Inhalation: Expiration / Exhalation
Uploaded by
mentos999Copyright:
Available Formats
CHAPTER 7-RESPIRATION (FORM 4)
Surface Protozoa
RESPIRATI
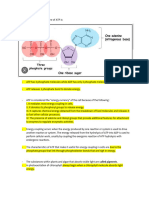
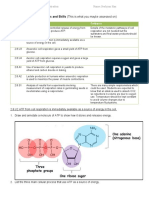
Main substrate needed Divided 2. Internal: -also called cellular respiration. -a biochemical process. -energy released from Divided Inspiration / Inhalation: -O2 taken in through mouth / (b) yeast / plants: -glucose is converted into ethanol + energy + CO2. process is also called fermentation. -ethanol is converted back to CO2 and energy when O2 is present.
gluco se 1.External: -a mechanical process -also known as breathing -maintains a
Gills Fishes Lungs Tracheal system Lungs, skin, Amphibians
Respirat ory Structure s Of
2. Aerobic respiration: -requires O2. -breakdown of glucose is complete. -large amount of energy . -energy is used toform ATP. -occur in mitochondria. -CO2 released as waste 1.Anaerobic respiration: - require O2. -breakdown of glucose is not complete. -less amount of energy. -occur in cytoplasm. -by products are: i)lactic acid in animals. ii)ethanol in yeast&plants.
Divided Expiration / Exhalation: -CO2 released through mouth / (a) Human muscle: -happens during vigorous exercise. -lactic acid builds up in muscle causes muscle fatigue. -after exercise, deep and fast breathing occurs to break down lactic acid.(in muscle and liver) -amount of O2 needed for the breakdown is called Oxygen debt. -lactic acid is broken down to form CO2 and energy.
Occur in
You might also like
- Class 10 RespirationDocument3 pagesClass 10 RespirationHimanshu singh100% (1)
- Chapter 7-Respiration (Form 4) : Inspiration / Inhalation: Expiration / ExhalationDocument1 pageChapter 7-Respiration (Form 4) : Inspiration / Inhalation: Expiration / ExhalationXuan Deng FamNo ratings yet
- RESPIRATION Notes 2ADocument9 pagesRESPIRATION Notes 2AGeorginah NjambiNo ratings yet
- 2.8 Cell Respiration SL: Chapter 2 Molecular Biology p.98-103Document46 pages2.8 Cell Respiration SL: Chapter 2 Molecular Biology p.98-103PaolaNo ratings yet
- Aerobic Cellular Respiration: Pea Plants Zophobus Morio LarvaeDocument29 pagesAerobic Cellular Respiration: Pea Plants Zophobus Morio LarvaezulaikhaabdrahmanNo ratings yet
- RespirationDocument7 pagesRespirationmandonaldboikanyoNo ratings yet
- Bio 5 - Cellular Respiration 2022-2023Document17 pagesBio 5 - Cellular Respiration 2022-2023Gillion lordNo ratings yet
- Q2 Module 5Document15 pagesQ2 Module 5margudo.tchiNo ratings yet
- Class 11 3 ChapDocument22 pagesClass 11 3 ChapMani TsheringNo ratings yet
- Form 4 Biology Chapter 7 - RespirationDocument22 pagesForm 4 Biology Chapter 7 - RespirationChew Han Hoong0% (2)
- Respiration Chapter 7 Biology Form 4Document90 pagesRespiration Chapter 7 Biology Form 4edain84No ratings yet
- Respiration Chapter 7 Biology Form 4Document90 pagesRespiration Chapter 7 Biology Form 4Faida Hamid87% (23)
- 7.1 The Respiratory Process: Atp Adp + P + EnergyDocument3 pages7.1 The Respiratory Process: Atp Adp + P + EnergyireneNo ratings yet
- Lesson 2 Group 1Document7 pagesLesson 2 Group 1Zyreine MenoriasNo ratings yet
- CH 9 Cellular Respiration and Fermentation NotesDocument11 pagesCH 9 Cellular Respiration and Fermentation NotesEvannaCoronaNo ratings yet
- 7.1 Respiratory Process in Energy ProductionDocument13 pages7.1 Respiratory Process in Energy ProductionNor Rafidah Che YusofNo ratings yet
- Today's Objective: SOL 3.dDocument11 pagesToday's Objective: SOL 3.dzameershahNo ratings yet
- ?respiratory SystemDocument13 pages?respiratory Systemmatthewverse5No ratings yet
- 6-Life ProcessesDocument39 pages6-Life ProcessesKaushal Solanke0% (1)
- Online Lecture No.4 Class:9 (A, B&C) Subject:Biology Chapter:-Plant CellDocument14 pagesOnline Lecture No.4 Class:9 (A, B&C) Subject:Biology Chapter:-Plant CellwatashiwayakinikuNo ratings yet
- Photosynthesis & RespirationDocument32 pagesPhotosynthesis & RespirationCarson Schultz100% (1)
- Presentation 5Document15 pagesPresentation 5Rahanie Gadungan PajijiNo ratings yet
- Reviewer-In-Gen Bio 1 - Q2Document5 pagesReviewer-In-Gen Bio 1 - Q2alamagelyzaNo ratings yet
- Respiration BiologyDocument20 pagesRespiration BiologySaidatul Atyah Mohd ApendaiNo ratings yet
- Inbound 9168743087088869744Document9 pagesInbound 9168743087088869744MarkNo ratings yet
- Cell Systems Fact Sheet - GLDocument8 pagesCell Systems Fact Sheet - GLdavidtamuedjoun2No ratings yet
- Chapter 7-Respiration (Form 4) : Expiration / Exhalation:: Inspiration / InhalationDocument1 pageChapter 7-Respiration (Form 4) : Expiration / Exhalation:: Inspiration / InhalationSharmini RajagopalNo ratings yet
- RESPIRATION2Document3 pagesRESPIRATION2zainabsagheerNo ratings yet
- 16 Quarter 1 Module 16-Introduction-To-Cellular-RespirationDocument21 pages16 Quarter 1 Module 16-Introduction-To-Cellular-RespirationBRYAN ZAFENo ratings yet
- Biology FolioDocument2 pagesBiology Folio黃將賓No ratings yet
- Respiration: Raja Fayaz AliDocument12 pagesRespiration: Raja Fayaz AliSuchitra SharmaNo ratings yet
- Living Organisms Require Energy: The Respiratory Process in Energy ProductionDocument38 pagesLiving Organisms Require Energy: The Respiratory Process in Energy ProductionWen Shan ChuaNo ratings yet
- G10 Biology - 8Document9 pagesG10 Biology - 8hasithsemalNo ratings yet
- Chapter 7Document138 pagesChapter 7Bëar MëNo ratings yet
- Anaerobic Respiration NotesDocument6 pagesAnaerobic Respiration NotesFaysall BorhanNo ratings yet
- Chapter 7-Respiration (Form 4) : Inspiration / Inhalation: Expiration / ExhalationDocument1 pageChapter 7-Respiration (Form 4) : Inspiration / Inhalation: Expiration / ExhalationJoanna JoriseNo ratings yet
- Biology 2.1: Electrical Energy (Electrons Become Excited (Energised) )Document3 pagesBiology 2.1: Electrical Energy (Electrons Become Excited (Energised) )Sel 7No ratings yet
- GR 11 LS Cellular Respiration NotesDocument5 pagesGR 11 LS Cellular Respiration Notestshidinaomi5No ratings yet
- Respiration: Respiratory SubstrateDocument8 pagesRespiration: Respiratory SubstrateEdwins MaranduNo ratings yet
- 6-LIFE PROCESSES(1)Document43 pages6-LIFE PROCESSES(1)43madhavmahajanNo ratings yet
- 2.25 Respiration H 2.28, 2.2.10Document22 pages2.25 Respiration H 2.28, 2.2.10George Oswald Junior CarringtonNo ratings yet
- # Form 4 Chapter 7 Cellular Respiration (Student Copy)Document7 pages# Form 4 Chapter 7 Cellular Respiration (Student Copy)VELLAMMAH A/P NARAYANASAMY MoeNo ratings yet
- Aerobic Cellular Respiration Digital Lab PosterDocument1 pageAerobic Cellular Respiration Digital Lab Posterapi-309712203No ratings yet
- Lec 9 Energy of LifeDocument29 pagesLec 9 Energy of LifeFahim AbidNo ratings yet
- 7.1 Respiration: by Ana Nurnasuha & Irina KesumaDocument15 pages7.1 Respiration: by Ana Nurnasuha & Irina KesumaLyana AhmadNo ratings yet
- Respiration and Gas ExchangeDocument24 pagesRespiration and Gas ExchangeEizelle100% (2)
- 2.8-Cell Respiration:: Cell Respiration Is The Controlled Release of Energy From Organic Compounds To Produce ATPDocument4 pages2.8-Cell Respiration:: Cell Respiration Is The Controlled Release of Energy From Organic Compounds To Produce ATPTanvir KauraNo ratings yet
- CROP SCI 2 PPT - Sept 25 292023 2Document11 pagesCROP SCI 2 PPT - Sept 25 292023 2Arjie TVNo ratings yet
- Chapter 12 RespirationDocument5 pagesChapter 12 RespirationKai TongNo ratings yet
- Respiration in PlantsDocument3 pagesRespiration in PlantsaarushpancholiNo ratings yet
- Life Processes: RespirationDocument17 pagesLife Processes: RespirationYashaswini.V.No ratings yet
- General Biology-Q3W4Document3 pagesGeneral Biology-Q3W4Geronimo, Jonamae S.No ratings yet
- Respiration 1Document30 pagesRespiration 1tshireletso.kodisangNo ratings yet
- General Biology q2 Week 4Document11 pagesGeneral Biology q2 Week 4cherrylmoanamarieaemfatNo ratings yet
- Solution 1382559Document2 pagesSolution 1382559tanishgoel83No ratings yet
- Respiration WorksheetDocument7 pagesRespiration Worksheet한서현No ratings yet
- ECOSYSTEMDocument39 pagesECOSYSTEMJessica Manawes NavorNo ratings yet
- A-level Biology Revision: Cheeky Revision ShortcutsFrom EverandA-level Biology Revision: Cheeky Revision ShortcutsRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (5)
- GCSE Biology Revision: Cheeky Revision ShortcutsFrom EverandGCSE Biology Revision: Cheeky Revision ShortcutsRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (2)