Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Back To Article 39: Sample Example of A 2-Branch System With A Single Centrifugal Pump First Pipe Branch
Back To Article 39: Sample Example of A 2-Branch System With A Single Centrifugal Pump First Pipe Branch
Uploaded by
Patricio TamayoOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Back To Article 39: Sample Example of A 2-Branch System With A Single Centrifugal Pump First Pipe Branch
Back To Article 39: Sample Example of A 2-Branch System With A Single Centrifugal Pump First Pipe Branch
Uploaded by
Patricio TamayoCopyright:
Available Formats
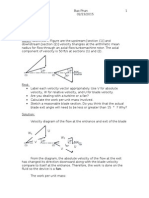
Sample example of a 2-branch system with a single centrifugal pump First pipe branch:
Equivallent pipe length L1, ft = Pipe Diamater D1, in = 200 3
Second pipe branch:
Equivallent pipe length L2, ft = Pipe diameter D2, in = 200 3
Pump Performance Curve:
Zero flow Q0, gpm = 50% flow Q50, gpm = BEP flow Q100, gpm = 0 200 500 Zero flow head H0, ft = Head at 50% flow H50, ft = BEP head H100, ft = 42 34 2
h1, feet - static head of water in tank 1 h2, feet - static head of water in tank 2 Q, gpm - guess until error_Q is small hpump, feet - calculated from H-Q curve Flow thru branch 1, Q1, gpm Flow thry branch 1, Q2, gpm Qresult, gpm (Q = Q1+Q2) error_Q
10 2 360 19.5 154.7 209.8 364.5 1.2%
Back to Article 39
gravitational constant g = sg = A1, in2 = f 1= 7.07 0.03
32.2 1.00
k1, friction in branch 1
A2, in2 = f 2=
0.000398405 7.07 0.03 0.000398405
k2, friction in branch 2
n= a= b=
1.756470797 -0.00072677 42
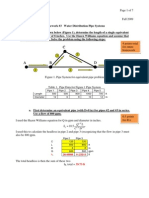
Sample example of a 2-branch system with a single positive displacement pump k1, friction in branch 1 0.002 enter as desired k2, friction in branch 2 0.003 enter as desired h1, feet - static head of water in tank 1 10 enter as given h1, feet - static head of water in tank 1 2 enter as given Q, gpm - given 120 enter as given hguess, feet - keep changing until error_Q is small 15.6 guess Q1, gpm 52.9 calculated Q2, gpm 67.3 calculated Qresult, gpm 120.2 calculated error_Q 0.2% calculated
Back to Article 39
You might also like
- HW2 - 2011 SolutionsDocument10 pagesHW2 - 2011 Solutionsrianto prayogo100% (2)
- Switching Power Supply Design: A Concise Practical HandbookFrom EverandSwitching Power Supply Design: A Concise Practical HandbookNo ratings yet
- Hidraulic Calculation For Hotel PDFDocument8 pagesHidraulic Calculation For Hotel PDFangel dario100% (1)
- 9 HYDRAULICALLY Plumbing System - ShopDocument5 pages9 HYDRAULICALLY Plumbing System - Shopjurhym doteNo ratings yet
- Pump Practice ProblemsDocument16 pagesPump Practice ProblemsKhaled SolimanNo ratings yet
- CTHS430-02 SPC R223.1394-01Document82 pagesCTHS430-02 SPC R223.1394-01Patricio Tamayo100% (1)
- CH430-02 WPC R223.1403-01Document22 pagesCH430-02 WPC R223.1403-01Patricio Tamayo100% (3)
- AerodynamicsDocument3 pagesAerodynamicsnanduslns07No ratings yet
- HW 5Document14 pagesHW 5Bao PhanNo ratings yet
- 345s02p2 PDFDocument10 pages345s02p2 PDFAdrian Antonio TorresNo ratings yet
- Addi Examples Pipe3Document10 pagesAddi Examples Pipe3Diego MorenoNo ratings yet
- CV1012 Tutorial 10 SolutionsDocument4 pagesCV1012 Tutorial 10 SolutionsleemariosanNo ratings yet
- 1 - Fluid Mechanics Takehome Project AssignmentDocument4 pages1 - Fluid Mechanics Takehome Project Assignmentazeem sheikhNo ratings yet
- TurbomachineDocument41 pagesTurbomachineshailendra_236No ratings yet
- 371 HW 03 SDocument7 pages371 HW 03 Sطريخم المشتاقNo ratings yet
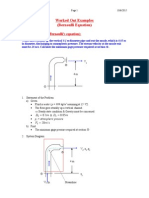
- Energy Conservation (Bernoulli'S Equation) : GDZ VDV DPDocument17 pagesEnergy Conservation (Bernoulli'S Equation) : GDZ VDV DPozgurturunc4No ratings yet
- Pump 07Document3 pagesPump 07AliNo ratings yet
- Core Ag Engineering Principles - Session 1Document101 pagesCore Ag Engineering Principles - Session 1peagricultureNo ratings yet
- Traditional Advanced Control Approaches - Feedforward, Cascade and Selected ControlDocument42 pagesTraditional Advanced Control Approaches - Feedforward, Cascade and Selected Controljricardo01976No ratings yet
- Applications of First LawDocument12 pagesApplications of First LawHarminder SinghNo ratings yet
- Fluids Machinery Power PointDocument257 pagesFluids Machinery Power PointNico67% (3)
- FMV Spreadsheets Master FMVIDocument13 pagesFMV Spreadsheets Master FMVIHect JulkNo ratings yet
- Problem 5.2: P V Z P V Z H L D V V K DDocument11 pagesProblem 5.2: P V Z P V Z H L D V V K Drameshaarya99No ratings yet
- Set of Answer of Fluid Mechanics II, UTHM. Based On Cengel 11th EditionDocument6 pagesSet of Answer of Fluid Mechanics II, UTHM. Based On Cengel 11th EditionIskandar BellNo ratings yet
- Piping SystemsDocument13 pagesPiping SystemsMmr MusaNo ratings yet
- .Pumps NotesDocument19 pages.Pumps NotesSean Esponge100% (1)
- Rig CalculationsDocument40 pagesRig Calculationsxiong hanNo ratings yet
- Pipe Flow Problems-III: Example 1Document10 pagesPipe Flow Problems-III: Example 1Chaithanya Kumar Dandu100% (1)
- Process Modelling, Simulation and Control For Chemical Engineers. Solved Problems. Chapter 7: Conventional Control Systems and Hardware: Part IIDocument16 pagesProcess Modelling, Simulation and Control For Chemical Engineers. Solved Problems. Chapter 7: Conventional Control Systems and Hardware: Part IIJohnNo ratings yet
- Sample Manual Hydraulic Calculation For BeginnersDocument38 pagesSample Manual Hydraulic Calculation For BeginnersJovani G. Ballon100% (4)
- FLUID MECHANICS D203 Otazky PDFDocument87 pagesFLUID MECHANICS D203 Otazky PDFKhoa NguyễnNo ratings yet
- PumpsDocument32 pagesPumpsAngela Paul PeterNo ratings yet
- Fluid Mechanics Benno 7Document25 pagesFluid Mechanics Benno 7Ella PurnamasariNo ratings yet
- Head Loss ExampDocument8 pagesHead Loss ExampMohd Amirul Mohd YusufNo ratings yet
- Chapter5 2Document32 pagesChapter5 2Shida ShidotNo ratings yet
- Seleccion de Bomba Con MathcadDocument13 pagesSeleccion de Bomba Con MathcadIsaias PerezNo ratings yet
- Sprinklers Coverage Area Calculation:: Areaof Coverage S LDocument9 pagesSprinklers Coverage Area Calculation:: Areaof Coverage S LMuhammad Raza Rafiq100% (1)
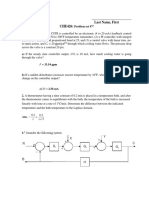
- Last Name, First CHE426:: F 33.54 GPMDocument5 pagesLast Name, First CHE426:: F 33.54 GPMGiancarlo HuertaNo ratings yet
- 02 Part6 Energy BalanceDocument28 pages02 Part6 Energy BalanceGunabalan SellanNo ratings yet
- Homework 08Document7 pagesHomework 08BasilLeeNo ratings yet
- Thermo HW SolutionsDocument35 pagesThermo HW SolutionsekantikdevoteeNo ratings yet
- Chapter 7Document6 pagesChapter 7Marco LuigiNo ratings yet
- Elevated TankDocument1 pageElevated Tankomer samaniNo ratings yet
- Fire Document CA 001Document5 pagesFire Document CA 001PRAKASH LAKSHMIPATHYNo ratings yet
- Homework of Bernoulli EqDocument8 pagesHomework of Bernoulli EqSinggih OktavianNo ratings yet
- Mathcad - 3B - Tut - 2 - PumpsDocument2 pagesMathcad - 3B - Tut - 2 - PumpsFabrizio NEBESSENo ratings yet
- WaterResDepthPECivilFall2009 - 10 8 09Document100 pagesWaterResDepthPECivilFall2009 - 10 8 09kohatian27796105No ratings yet
- 2 The 1st 2nd Laws of ThermodynamicsDocument135 pages2 The 1st 2nd Laws of ThermodynamicsPrince KevinNo ratings yet
- Fire Document Sa 001Document7 pagesFire Document Sa 001PRAKASH LAKSHMIPATHYNo ratings yet
- NAME 409 Pump MathsDocument10 pagesNAME 409 Pump Mathsisrat jahanNo ratings yet
- Pump MathsDocument10 pagesPump MathsSakib RafeeNo ratings yet
- CourseNotesProblemSets3 4Q SoltnsDocument30 pagesCourseNotesProblemSets3 4Q SoltnsBunNo ratings yet
- 11.31 A Centrifugal Pump With Backward-Curved Blades Has The Following MeasuredDocument1 page11.31 A Centrifugal Pump With Backward-Curved Blades Has The Following MeasuredMahmoud Abd El LateefNo ratings yet
- Ej Vol Control Pelu oDocument8 pagesEj Vol Control Pelu oPablo Martínez CavieresNo ratings yet
- Reference Guide To Useful Electronic Circuits And Circuit Design Techniques - Part 2From EverandReference Guide To Useful Electronic Circuits And Circuit Design Techniques - Part 2No ratings yet
- Reference Guide To Useful Electronic Circuits And Circuit Design Techniques - Part 1From EverandReference Guide To Useful Electronic Circuits And Circuit Design Techniques - Part 1Rating: 2.5 out of 5 stars2.5/5 (3)
- Control of DC Motor Using Different Control StrategiesFrom EverandControl of DC Motor Using Different Control StrategiesNo ratings yet
- Isometric Sketch SheetDocument1 pageIsometric Sketch SheetPatricio TamayoNo ratings yet
- Estimating Costs of Dust Control Systems: Neceissity For Cost EstimatesDocument10 pagesEstimating Costs of Dust Control Systems: Neceissity For Cost EstimatesPatricio TamayoNo ratings yet
- CTHS430-02 OMM S223.857.en-01Document118 pagesCTHS430-02 OMM S223.857.en-01Patricio Tamayo100% (5)
- CTHS430-02 IM S223.855.en-01Document80 pagesCTHS430-02 IM S223.855.en-01Patricio Tamayo100% (2)
- 0 CH430-02 Declaration of Conformity S058.203.en-01Document1 page0 CH430-02 Declaration of Conformity S058.203.en-01Patricio TamayoNo ratings yet
- RepairDocument0 pagesRepairPatricio TamayoNo ratings yet
- Technische Daten MRS 001 (GB)Document2 pagesTechnische Daten MRS 001 (GB)Patricio TamayoNo ratings yet
- Schieflaufschalter-Kiepe MRS001 - GBDocument16 pagesSchieflaufschalter-Kiepe MRS001 - GBPatricio TamayoNo ratings yet
- Seilzugschalter Kiepe PRS GBDocument30 pagesSeilzugschalter Kiepe PRS GBPatricio TamayoNo ratings yet