Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Pa Tho Physiology of Ectopic Pregnancy
Pa Tho Physiology of Ectopic Pregnancy
Uploaded by
Roseben SomidoOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Pa Tho Physiology of Ectopic Pregnancy
Pa Tho Physiology of Ectopic Pregnancy
Uploaded by
Roseben SomidoCopyright:
Available Formats
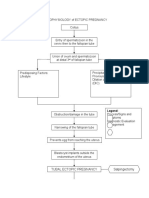
PATHOPHYSIOLOGY of ECTOPIC PREGNANCY
Coitus
Entry of spermatozoon in the cervix then to the fallopian tube Union of ovum and spermatozoon at distal 3rd of fallopian tube
Predisposing Factors: Beyond conceivable age Congenital anomalies in the fallopian tube
Precipitating Factors: Tubal damage caused by: o Chronic salphingitits o Pelvic Inflammatory Disease o Use of IUD more than 2 years o Previous pelvic/tubal surgery Previous ectopic pregnancy Maternal cigarette smoking
Legend: Signs and Symptoms Diagnostic evaluation Management Complications Manifested by the patient
Obstruction/damage in the tube
Narrowing of the fallopian tube
Prevents egg from reaching the uterus
Blastocyst implants outside the endometrium of the uterus (6-12 wks)
Abdomen
Fallopian tube: o Ampullary portion of the tube Isthmic segment of the tube Fimbrae Cornual and interstitial portion of the tube
Ovary and Cervix
Laparatomy o o o
Hysterectomy Oophorectomy
Salpingectomy Fimbraectomy Cornuectomy Co
Amenorrhea
Implantation within the fallopian tube
Limited decidual reaction
Much higher BP in tubal arteries than uterine arteries
Decreased muscle lining of the tube
Decreased resistance to the invading trophoblastic tissue
Serum pregnancy test shows HCG
Placental dislodgement
Growing zygote ruptures the slender tube/trophoblast cells break through with narrow base Cauldocentesis Ultrasound
Tearing and destruction of blood vessels
Progesterone secretion stops
Tube ruptures
Uterine decidua sloughs off
Bleeding/vaginal spotting Sharp stabbing pain at L/R lower abdomen
Tachycardia Tachypnea Hypotension Lightheadedness Narrowed pulse pressure
Pain radiating to shoulder Rigid abdomen Cullens sign
Blood accumulation in the peritoneum
Conception products expelled into pelvic cavity
Hct Hgb
Hemorrhage
Shock
Modified trendelenburg Fluid resuscitation O2 supplementation Blood transfusion as indicated
You might also like
- The Developing Human Clinically Oriented Embryology 9th Edition Test BankDocument15 pagesThe Developing Human Clinically Oriented Embryology 9th Edition Test BanktestbanklooNo ratings yet
- Ectopic Pregnancy PathophysiologyDocument1 pageEctopic Pregnancy PathophysiologyCyrus De Asis100% (2)
- Case Study Ectopic PregnancyDocument37 pagesCase Study Ectopic PregnancyJoule Peirre83% (6)
- Prostate Cancer PathophysiologyDocument1 pageProstate Cancer PathophysiologyDaniel Miller100% (6)
- Pa Tho Physiology of Incomplete AbortionDocument3 pagesPa Tho Physiology of Incomplete AbortionClaire Nimor Ventulan50% (4)
- ABORTION PathophysiologyDocument3 pagesABORTION PathophysiologyChiara FajardoNo ratings yet
- Pathophysiology of Ectopic PregnancyDocument1 pagePathophysiology of Ectopic PregnancyPaul Vincent Alfonso100% (2)
- TAHBSO PathophysiologyDocument5 pagesTAHBSO Pathophysiologybregette50% (2)
- Maternal & Child Care Nursing ReviewDocument37 pagesMaternal & Child Care Nursing Reviewɹǝʍdןnos98% (130)
- Hydatidiform MoleDocument23 pagesHydatidiform MoleKristel Rivamonte100% (1)
- Ectopic Pregnancy PathophysiologyDocument5 pagesEctopic Pregnancy Pathophysiologyjoyrena ochondraNo ratings yet
- Pa Tho Physiology of Ectopic PregnancyDocument2 pagesPa Tho Physiology of Ectopic Pregnancynelyang17100% (6)
- Pathophysiology of Ruptured Ectopic PregnancyDocument3 pagesPathophysiology of Ruptured Ectopic PregnancyDan Kenneth Liban Llanto89% (9)
- Pathophysiology of Ectopic PregnancyDocument3 pagesPathophysiology of Ectopic PregnancyJulienne Sanchez-Salazar100% (1)
- Placenta Previa PathophysiologyDocument1 pagePlacenta Previa Pathophysiologykathy85% (20)
- PATHOPHYSIOLOGY HmoleDocument4 pagesPATHOPHYSIOLOGY HmoleMonica Lyka Bancale100% (3)
- NCP: Premature Dilation of The CervixDocument6 pagesNCP: Premature Dilation of The CervixJavie80% (5)
- Pathophysiology of Hyperemesis Gravidarum DiagramDocument1 pagePathophysiology of Hyperemesis Gravidarum DiagramSonny Dizon Pareñas100% (11)
- Marjorie England - Life Before Birth PDFDocument244 pagesMarjorie England - Life Before Birth PDFiuliana100% (1)
- Luteal Phase Defect: Dr. Priyankur Roy Consultant Infertility Specialist & Laparoscopic SurgeonDocument45 pagesLuteal Phase Defect: Dr. Priyankur Roy Consultant Infertility Specialist & Laparoscopic SurgeonPriyankur RoyNo ratings yet
- How To Get Pregnant NaturallyDocument189 pagesHow To Get Pregnant NaturallyGede Adél-JúliaNo ratings yet
- PATHOPHYSIOLOGY of ECTOPIC PREGNANCYDocument2 pagesPATHOPHYSIOLOGY of ECTOPIC PREGNANCYrye100% (2)
- Physiology Ectopic PregnancyDocument1 pagePhysiology Ectopic Pregnancypinoynursetambay80% (5)
- Pathophysiology of Ectopic PregnancyDocument1 pagePathophysiology of Ectopic PregnancyLiza MinonaNo ratings yet
- Ectopic Pregnancy PathophysiologyDocument2 pagesEctopic Pregnancy PathophysiologySiergs Smith GervacioNo ratings yet
- PATHOPHYSIOLOGY ECTOPIC PREGNANCY SoftDocument11 pagesPATHOPHYSIOLOGY ECTOPIC PREGNANCY SoftJann ericka JaoNo ratings yet
- Ectopic Pregnancy Case StudyDocument81 pagesEctopic Pregnancy Case Studyjefroc90% (30)
- Patho PhysiologyDocument3 pagesPatho PhysiologyKeith MadarangNo ratings yet
- Ectopic PregnancyDocument78 pagesEctopic PregnancyCarie Manarondong80% (5)
- Pathophysiology of Ovarian Cyst (TCMC BSN III-B)Document1 pagePathophysiology of Ovarian Cyst (TCMC BSN III-B)jorden360100% (3)
- Diagram Myoma IDocument1 pageDiagram Myoma IJoann100% (12)
- Ectopic PregnancyDocument36 pagesEctopic PregnancyCham Ingalla Pascion100% (10)
- A Case Study of Ectopic PregnancyDocument24 pagesA Case Study of Ectopic PregnancymarkNo ratings yet
- EctopicDocument41 pagesEctopicVillanueva Ameera MaeNo ratings yet
- Ectopic PregnancyDocument9 pagesEctopic PregnancyCatherine ZamoraNo ratings yet
- Case Study Castillo H MoleDocument52 pagesCase Study Castillo H MoleGodfrey Bag-ao100% (1)
- Abruptio PlacentaDocument13 pagesAbruptio Placentamiss RN92% (12)
- Normal Spontaneous Vaginal DeliveryDocument35 pagesNormal Spontaneous Vaginal DeliveryJohn Edward EscoteNo ratings yet
- NCP For FT, SGADocument7 pagesNCP For FT, SGAJule Santoya80% (5)
- Incompetent CervixDocument4 pagesIncompetent CervixCharm Arroyo100% (1)
- Pathophysiology of Hyperemesis Gravidarum DiagramDocument1 pagePathophysiology of Hyperemesis Gravidarum DiagramQuintin Mangaoang100% (1)
- Ectopic Pregnancy Study GuideDocument5 pagesEctopic Pregnancy Study GuideCarl Elexer Cuyugan Ano100% (1)
- Ectopic and Abortion NCPDocument6 pagesEctopic and Abortion NCPElizabeth Quiñones100% (1)
- CASE ANALYSIS Ectopic Pregnancy Part 1Document10 pagesCASE ANALYSIS Ectopic Pregnancy Part 1Diane Celine SantianoNo ratings yet
- Pathophysiology of Benign Prostatic HyperplasiaDocument1 pagePathophysiology of Benign Prostatic HyperplasiaKevin Jade Herrera0% (2)
- Pa Tho Physiology of Uterine MyomaDocument2 pagesPa Tho Physiology of Uterine Myomaghettodawg187100% (7)
- CASE STUDY On Missed AbortionDocument5 pagesCASE STUDY On Missed AbortionOmotosho AlexNo ratings yet
- Pa Tho Physiology of Ectopic Pregnancy PDFDocument2 pagesPa Tho Physiology of Ectopic Pregnancy PDFbowki namoNo ratings yet
- Pa Tho Physiology of Ectopic PregnancyDocument2 pagesPa Tho Physiology of Ectopic PregnancySeth Elijah CaballeroNo ratings yet
- II. Schematic Pathophysiology Diagram: Risk FactorsDocument1 pageII. Schematic Pathophysiology Diagram: Risk FactorsEarl MarteNo ratings yet
- Ectopic Phatophysiology Tentative 2Document3 pagesEctopic Phatophysiology Tentative 2Alexe Nicole BiscanteNo ratings yet
- Placenta Previa PathoDocument2 pagesPlacenta Previa Pathoshakira0% (1)
- PATHOPHYSIOLOGYDocument1 pagePATHOPHYSIOLOGYcalarasheanNo ratings yet
- Radiology RecapDocument7 pagesRadiology RecapTony ZhongNo ratings yet
- 1.1 Pathophysiology of Ectopic Pregnancy BSN 2C FinalDocument3 pages1.1 Pathophysiology of Ectopic Pregnancy BSN 2C FinalArianne Rose Afable PagulayanNo ratings yet
- Ectopic Phatophysiology TentativeDocument3 pagesEctopic Phatophysiology TentativeAlexe Nicole BiscanteNo ratings yet
- Ectopic Pregnancy Mini CPDocument18 pagesEctopic Pregnancy Mini CPrasthy jay caligdongNo ratings yet
- ANATOMY Perineum Pelvis and RepDocument6 pagesANATOMY Perineum Pelvis and RepKaedehara KazuhaNo ratings yet
- ENT - Anatomy and Physiology of Aerodigestive Tract (2014)Document13 pagesENT - Anatomy and Physiology of Aerodigestive Tract (2014)pbmaristelaNo ratings yet
- Intestinal-Nematodes PDFDocument3 pagesIntestinal-Nematodes PDFKrisha Marie BadilloNo ratings yet
- Abdominal Inury 2Document8 pagesAbdominal Inury 2Chol Koryom CholNo ratings yet
- 08 - Types of DeliveryDocument2 pages08 - Types of DeliverylincimikaelartanNo ratings yet
- Pathophysiology of Ruptured Ectopic PregnancyDocument3 pagesPathophysiology of Ruptured Ectopic Pregnancybowki namoNo ratings yet
- Nemtodes BelizarioDocument7 pagesNemtodes BelizarioMarl EstradaNo ratings yet
- Observations on Abortion: Containing an account of the manner in which it is accomplished, the causes which produced it, and the method of preventing or treating itFrom EverandObservations on Abortion: Containing an account of the manner in which it is accomplished, the causes which produced it, and the method of preventing or treating itNo ratings yet
- (Text) Maternal and Child Health NursingDocument40 pages(Text) Maternal and Child Health NursingVia H.No ratings yet
- EmbryologyDocument26 pagesEmbryologyBryan Mae H. Degorio100% (3)
- Syllabus and Examination Pattern For Undergraduate Medical Course Part IDocument48 pagesSyllabus and Examination Pattern For Undergraduate Medical Course Part Isingh2manishNo ratings yet
- Fraction of The Peripheral Blood Concentration of CD56 /CD16 /CD3 Cells in Total Natural Killer Cells As An Indication of Fertility and InfertilityDocument7 pagesFraction of The Peripheral Blood Concentration of CD56 /CD16 /CD3 Cells in Total Natural Killer Cells As An Indication of Fertility and InfertilityqisthiaufaNo ratings yet
- Michael D. Johnson - Human Biology - Concepts and Current Issues, 6th Edition - Benjamin Cummings (2011) Bab 21Document24 pagesMichael D. Johnson - Human Biology - Concepts and Current Issues, 6th Edition - Benjamin Cummings (2011) Bab 21GABRYELLA DAMAYANTI BUTAR BUTAR S1 PENDIDIKAN KIMIANo ratings yet
- Basic of Human Embryology PDFDocument28 pagesBasic of Human Embryology PDFaureliatanasalNo ratings yet
- First Trimester TranslateDocument51 pagesFirst Trimester TranslateMuhammad Zakki Al FajriNo ratings yet
- MCN Reviewer: Basic ConceptsDocument22 pagesMCN Reviewer: Basic ConceptsPanJan BalNo ratings yet
- .Document544 pages.Bestiana SaraLiontina0% (1)
- Drug Therapy in Special Population GroupDocument120 pagesDrug Therapy in Special Population GroupNehimyaNo ratings yet
- Week 1 217 LecDocument15 pagesWeek 1 217 Leckristelaaa guevarraNo ratings yet
- A&P CH 28aDocument22 pagesA&P CH 28aSam KimNo ratings yet
- Female Reproductive HistologyDocument59 pagesFemale Reproductive HistologyIta Indriani100% (2)
- NCM 107 (OB) Module 1BDocument48 pagesNCM 107 (OB) Module 1BAmiel simon NgoNo ratings yet
- Scheme of Work BIOLOGY FORM 5, 2012Document46 pagesScheme of Work BIOLOGY FORM 5, 2012sitnorsyahidah100% (2)
- Physiology of Pregnancy 050918Document75 pagesPhysiology of Pregnancy 050918Anonymous 96LTCx100% (2)
- 1st Trimester ImagingDocument118 pages1st Trimester ImagingLajja Parikh Patel100% (2)
- SLGR 3 Biologi k2 JawapanDocument14 pagesSLGR 3 Biologi k2 JawapanFerguson TehNo ratings yet
- Acupuncture IVF by DR Lifang Liang PDFDocument226 pagesAcupuncture IVF by DR Lifang Liang PDFNick Max100% (1)
- Endometriosis PathophysiologyDocument4 pagesEndometriosis PathophysiologyGeLa GutierrezNo ratings yet
- DR Dini Sri Damayanti, MkesDocument48 pagesDR Dini Sri Damayanti, Mkes21701101016 - Juliana Ayu NugrahaNo ratings yet
- Senapati2018 Article SuperovulationAltersTheExpressDocument10 pagesSenapati2018 Article SuperovulationAltersTheExpressInneke NoerNo ratings yet
- Classification of Placenta PDFDocument5 pagesClassification of Placenta PDFAdarsh jainNo ratings yet
- Miscarriages and NutritionDocument70 pagesMiscarriages and NutritionErwin Ginting100% (2)
- Untitled28 PDFDocument14 pagesUntitled28 PDFElizabeth Leon100% (1)