Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Bacterium Bacillus B. Anthracis
Bacterium Bacillus B. Anthracis
Uploaded by
spinedr07Original Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Bacterium Bacillus B. Anthracis
Bacterium Bacillus B. Anthracis
Uploaded by
spinedr07Copyright:
Available Formats
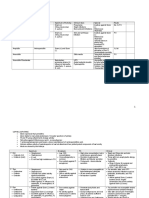
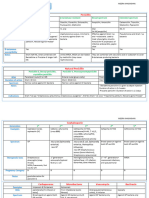
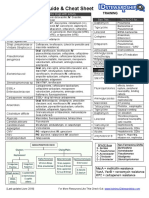
Bacterium Diseases Virulence Factors Diagnostic Tests Treatment Gm Motile?
Metabolism Special
Notes
Bacillus + Most Aerobic or Spore
rod are facultative formers
motile anaerobic
B. anthracis Cutaneous anthrax *plasmid encoded *cultures: long Penicillin no Facultative -the only
-95% of cases -polyglutamic serpentine chain anaerobic strict
-may disseminate to acid capsule *clinical specimen: -for PCN pathogen
septicemia -anthrax exotoxin single/paired bacilli; allergic:
Inhalation anthrax 1) edema factor NO spores! erythromycin,
-flu-like symp., high fever, 2) lethal factor *absence of hemolysis tetracycline,
dyspnea, hypotension 3) protective Ag & motility chloramphenicol
-hemorrhagic necrosis, -Gm stain or
bacteremia fluorescence Ag stain
-dead <24 hr. -biochem tests
Gastrointestinal anthrax
-fever, nausea, vomiting,
diarrhea
-shock & death
B. cereus -food poisoning ENTEROTOXINS -supportive Yes aerobic
-gastroenteritis -heat-labile measures for
-ingestion of spores diarrhea food poisoning
-heat labile enterotoxin -heat-stable
-long incubation emesis -for ocular
-intoxication infections:
-ingestion of heat- -Cereolysin vancomycin,
stable enterotoxin (hemosylin) gentamycin,
-short incubation -phospholipase C ciprofloxacin
-ocular infections (lecithinase)
-intravenous catheter- *resistant to
related sepsis *no capsule PCN &
cephalosporins
You might also like
- Antibiotic Study Cheat Sheet August 2019Document1 pageAntibiotic Study Cheat Sheet August 2019Ryan TurnerNo ratings yet
- SketchyMicro ChartDocument14 pagesSketchyMicro ChartSonia100% (8)
- Systemic BacteriologyDocument495 pagesSystemic BacteriologyAkash KaranwalNo ratings yet
- Infectious Diseases IDocument7 pagesInfectious Diseases ITiff VoNo ratings yet
- Ampicillin - Drug StudyDocument2 pagesAmpicillin - Drug StudyLegendX100% (5)
- Adult Infectious Diseases Over 200 Case Studies: Intended For: Medical Students, Ambulists, Hospitalists, Nurse Practitioners, Physician AssistantsFrom EverandAdult Infectious Diseases Over 200 Case Studies: Intended For: Medical Students, Ambulists, Hospitalists, Nurse Practitioners, Physician AssistantsRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (7)
- An Infectious Disease of Skin MCQsDocument111 pagesAn Infectious Disease of Skin MCQsDr.Tawheed67% (6)
- S. Aureus: Bacteriology G Virulence Factors Clinical Diseases Treatment Staphylococcus +Document4 pagesS. Aureus: Bacteriology G Virulence Factors Clinical Diseases Treatment Staphylococcus +MARIA FREDIJEAN CARIÑONo ratings yet
- InfectionDocument96 pagesInfectionBassem Georguos LabibNo ratings yet
- S. Aureus, Cons: S.Epidermidis, Cons: S.SaprophyticusDocument14 pagesS. Aureus, Cons: S.Epidermidis, Cons: S.SaprophyticusMugiNo ratings yet
- Dr. Constatntino: PneumomiaDocument4 pagesDr. Constatntino: PneumomiaAnn Ross VidalNo ratings yet
- Penicillins: Strep Pneumoniae S. AureusDocument10 pagesPenicillins: Strep Pneumoniae S. AureusMaxine Alba100% (1)
- Group A StrepDocument2 pagesGroup A Strepspinedr07No ratings yet
- Kingdom Monera ZoologyDocument2 pagesKingdom Monera ZoologyBASI, HEINDRICH LLOYD M.No ratings yet
- 4 IGP Basics of Antimicrobial TherapyDocument11 pages4 IGP Basics of Antimicrobial TherapyTin NatividadNo ratings yet
- Every Drug EverDocument72 pagesEvery Drug EverMalNo ratings yet
- Fluxgrama MeningitesDocument1 pageFluxgrama Meningiteswns2njbs9tNo ratings yet
- Agata Infectious DiseasesDocument34 pagesAgata Infectious DiseasesMartaNo ratings yet
- Tables of Spore Forming BacilliDocument3 pagesTables of Spore Forming BacilliLobna ElkilanyNo ratings yet
- 7fa8e6ac-47db-4f0f-90f3-bb6e1ece863cDocument18 pages7fa8e6ac-47db-4f0f-90f3-bb6e1ece863cSatendra SrivastavaNo ratings yet
- Bordetella: Drying - Highly Susceptible To Toxic Substance andDocument38 pagesBordetella: Drying - Highly Susceptible To Toxic Substance andkrstnkyslNo ratings yet
- Elanco Parvovirus DXTX GDocument2 pagesElanco Parvovirus DXTX Gazamkhan60No ratings yet
- Other Bacteria: Gram-NegativeDocument18 pagesOther Bacteria: Gram-NegativeZeth MoturiNo ratings yet
- Antibiotics 1Document34 pagesAntibiotics 1Tommy ZeusNo ratings yet
- Bacteria Summary TableDocument10 pagesBacteria Summary TableNur Alia YasminNo ratings yet
- 7.2 BacteriologyDocument12 pages7.2 BacteriologyClinical PharmersNo ratings yet
- Microbiology PinkDocument3 pagesMicrobiology PinkBenjamin GaliaNo ratings yet
- AntibioticsDocument9 pagesAntibiotics7aith22No ratings yet
- Antibiotics TableDocument4 pagesAntibiotics Tablewhiteoakers clonskeaghNo ratings yet
- Bacteria List Exam 1 PDFDocument16 pagesBacteria List Exam 1 PDFJamesHowsonNo ratings yet
- Topic - Neutropenic Fever OutlineDocument5 pagesTopic - Neutropenic Fever Outlineapi-549451092No ratings yet
- Legion EllaDocument2 pagesLegion EllaJacklyn M. oNo ratings yet
- Bacteria ChartsDocument11 pagesBacteria ChartsFlowerNo ratings yet
- Quizlet Bacte 3Document4 pagesQuizlet Bacte 3Michelle San Miguel FeguroNo ratings yet
- Student Notes: Micro 1: Davao Doctors College Medical Laboratory Science DepartmentDocument5 pagesStudent Notes: Micro 1: Davao Doctors College Medical Laboratory Science DepartmentMelody Jane PardilloNo ratings yet
- Bacteriology 1: - Non MotileDocument27 pagesBacteriology 1: - Non MotileYeshaa MiraniNo ratings yet
- Ppra Ab Terapi PDFDocument83 pagesPpra Ab Terapi PDFDIONYSIUS BENINo ratings yet
- Antibiotics in Periodontal DiseaseDocument57 pagesAntibiotics in Periodontal DiseaseReshmaaRajendranNo ratings yet
- Micro by DR - Hesham (GIT)Document65 pagesMicro by DR - Hesham (GIT)abcde990075No ratings yet
- Module 6.5 MycologyDocument4 pagesModule 6.5 MycologyPNo ratings yet
- Para 2Document4 pagesPara 265O6O78 ฐิติพันธ์ เพชรกระจายแสงNo ratings yet
- ReviewerDocument1 pageReviewerElla Mae SadiuaNo ratings yet
- Microbiology Mnemonics: Study Online atDocument3 pagesMicrobiology Mnemonics: Study Online atKriselda May Torio100% (3)
- Summary of MicroDocument25 pagesSummary of MicroAyeshaNo ratings yet
- Streptococci ReviewDocument5 pagesStreptococci ReviewEl-rohyKalongoNo ratings yet
- Im Dude HandoutDocument1 pageIm Dude Handoutapi-535001113No ratings yet
- Bacteria-Borne Diseases Handout 2022Document3 pagesBacteria-Borne Diseases Handout 2022Anna CrisNo ratings yet
- Drug Name Indications Actions Contraindications and Cautions Adverse Effects Side Effects Nursing Responsibilities BeforeDocument3 pagesDrug Name Indications Actions Contraindications and Cautions Adverse Effects Side Effects Nursing Responsibilities BeforeArdel LabadaNo ratings yet
- Pseudo, Burk, Histo, Glae, Avi, Actino, Fuso, Bacte, Dichelo DiseasesDocument14 pagesPseudo, Burk, Histo, Glae, Avi, Actino, Fuso, Bacte, Dichelo DiseasesTricia Mae JuanitasNo ratings yet
- Antibiotic Policy 2011Document27 pagesAntibiotic Policy 2011Mahendran R MahiNo ratings yet
- تَـلـخـيـص شَـابـتـر ٢٣?Document10 pagesتَـلـخـيـص شَـابـتـر ٢٣?سلطان محمد فوزي سلمانNo ratings yet
- Streptococcus: PneumoniaeDocument12 pagesStreptococcus: PneumoniaeZeth MoturiNo ratings yet
- Organism Description Drug of ChoiceDocument14 pagesOrganism Description Drug of ChoiceMary YongcoNo ratings yet
- Activity 2Document2 pagesActivity 2Cyril LumibaoNo ratings yet
- ملخص بكتريا PDFDocument27 pagesملخص بكتريا PDFDjdjjd SiisusNo ratings yet
- MBL 1 Bacterial PneumoniaDocument5 pagesMBL 1 Bacterial PneumoniaFadhlina OmarNo ratings yet
- BenadrylDocument2 pagesBenadrylsamfandood10No ratings yet
- Virus - SystemsDocument9 pagesVirus - SystemsHanunNo ratings yet
- Bacteria Chart FINAL 3 2Document32 pagesBacteria Chart FINAL 3 2Йеша Маниш МираниNo ratings yet
- BASIC CONCEPTS IN MEDICINAL CHEMISTRY, 3RD EDITION. (MARC W.. ZAVOD HARROLD (ROBIN M.) ) (Z-Library)Document1 pageBASIC CONCEPTS IN MEDICINAL CHEMISTRY, 3RD EDITION. (MARC W.. ZAVOD HARROLD (ROBIN M.) ) (Z-Library)duy luuNo ratings yet
- Prinsip Penggunaan Antibiotik Untuk Terapi: Khie ChenDocument66 pagesPrinsip Penggunaan Antibiotik Untuk Terapi: Khie ChenAnindia LarasatiNo ratings yet
- AnthraxDocument47 pagesAnthraxabel semuNo ratings yet
- World Health Organization: WHO/EMC/ZDI/98.6Document106 pagesWorld Health Organization: WHO/EMC/ZDI/98.6ye yeNo ratings yet
- UGE 1 Practice Set - Fact or OpinionDocument15 pagesUGE 1 Practice Set - Fact or OpinionzyrianNo ratings yet
- Animal Diseases CollectionDocument94 pagesAnimal Diseases CollectionNabin Kumar YadavNo ratings yet
- Botany AssignmentDocument21 pagesBotany Assignmentabdul hadiNo ratings yet
- Handout 13 Biotechnology in Promoting Law and Order PDFDocument36 pagesHandout 13 Biotechnology in Promoting Law and Order PDFMiccah Angela Parreño FraynaNo ratings yet
- The Agweek Bull Sale Guide - January 2024Document36 pagesThe Agweek Bull Sale Guide - January 2024inforumdocsNo ratings yet
- Clostridia and Bacillus Lecture SlideDocument37 pagesClostridia and Bacillus Lecture SlidePrincewill SeiyefaNo ratings yet
- Bacteriology Lec - Aerobic Gram Positive BacilliDocument30 pagesBacteriology Lec - Aerobic Gram Positive BacilliMeg Dianne V. CañedaNo ratings yet
- 20 - Anthrax and BrucellosisDocument4 pages20 - Anthrax and BrucellosisAhmer IsrarNo ratings yet
- .Class BacillusDocument38 pages.Class BacillusManoj KumarNo ratings yet
- Infectious Diseases MidtermDocument50 pagesInfectious Diseases MidtermKathleen Joy Costales MagtanongNo ratings yet
- Microbiology and Parasitology Summary and ChartsDocument54 pagesMicrobiology and Parasitology Summary and Chartssciencetopic4No ratings yet
- NCM 417 - Final Exam 2014Document12 pagesNCM 417 - Final Exam 2014Mae DacerNo ratings yet
- Branches & Clasification of MicrobiologyDocument66 pagesBranches & Clasification of MicrobiologyJareena BegumNo ratings yet
- OIE - Terrestrial Animal Health Code - Version 8 - 2014 - Volume IIDocument312 pagesOIE - Terrestrial Animal Health Code - Version 8 - 2014 - Volume IIWormInchNo ratings yet
- 1 - Systemic BacteriologyDocument316 pages1 - Systemic BacteriologyAlsirNo ratings yet
- Community Health Nursing NotesDocument4 pagesCommunity Health Nursing NoteswhitNo ratings yet
- Cardiovascular and Lymphatic Systems: Modulename: Content Title: Microbes Affecting The CardiovascularDocument73 pagesCardiovascular and Lymphatic Systems: Modulename: Content Title: Microbes Affecting The CardiovascularAmanuel MaruNo ratings yet
- Tabani Deo SDocument664 pagesTabani Deo SSimone BM MinduimNo ratings yet
- Emerging and Re-Emerging Bacterial Diseases in IndiaDocument7 pagesEmerging and Re-Emerging Bacterial Diseases in IndiaPoorna ChandarNo ratings yet
- Microbiology Flowchart Dr. NikitaDocument2 pagesMicrobiology Flowchart Dr. NikitaKshitij Singh RajputNo ratings yet
- Bioterrorism - A Public Health Perspective-DikonversiDocument9 pagesBioterrorism - A Public Health Perspective-DikonversiFira LasenaNo ratings yet
- Bayer Ag - Anthrax and CiproDocument4 pagesBayer Ag - Anthrax and CiproPreyanshu SainiNo ratings yet
- BioterrorismDocument20 pagesBioterrorismChhaviNo ratings yet
- Daedly DeasesrabiesDocument144 pagesDaedly Deasesrabieslepoete40No ratings yet
- Chapter 1 Part 1-Microbial World and YouDocument77 pagesChapter 1 Part 1-Microbial World and YouLudyNo ratings yet
- Chemotherapy Leukemia: B. Administer Varicella-Zoster Immune Globulin To The ClientDocument12 pagesChemotherapy Leukemia: B. Administer Varicella-Zoster Immune Globulin To The ClientAsterlyn ConiendoNo ratings yet