Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Problem 2.44: Solution
Problem 2.44: Solution
Uploaded by
Eric KialOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Problem 2.44: Solution
Problem 2.44: Solution
Uploaded by
Eric KialCopyright:
Available Formats
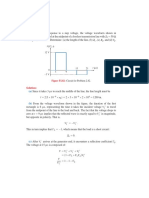
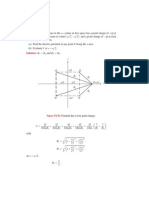
Problem 2.44 For the circuit shown in Fig. P2.
44, calculate the average incident power, the average reected power, and the average power transmitted into the innite 100- line. The /2 line is lossless and the innitely long line is slightly lossy. (Hint: The input impedance of an innitely long line is equal to its characteristic impedance so long as = 0.)
50
/2
+
2V Z0 = 50 Z1 = 100
i Pav r Pav t Pav
Figure P2.44: Circuit for Problem 2.44.
Solution: Considering the semi-innite transmission line as equivalent to a load (since all power sent down the line is lost to the rest of the circuit), ZL = Z1 = 100 . Since the feed line is /2 in length, Eq. (2.96) gives Zin = ZL = 100 and l = (2 / )( /2) = , so e j l = 1. Hence = ZL Z0 100 50 1 = = . ZL + Z0 100 + 50 3
Also, converting the generator to a phasor gives Vg = 2e j0 (V). Plugging all these results into Eq. (2.82), V0+ = Vg Zin Zg + Zin e j l 1 + e j l = 2 100 50 + 100
1 1 (1) (1) + 3
= 1e j180 = 1 (V). From Eqs. (2.104), (2.105), and (2.106),
i Pav =
V0+ |1e j180 |2 = = 10.0 mW, 2Z0 2 50
i r = Pav = ||2 Pav
1 2 10 mW = 1.1 mW, 3
t i r Pav = Pav = Pav + Pav = 10.0 mW 1.1 mW = 8.9 mW.
You might also like
- DrillsDocument93 pagesDrillsjulio100% (1)
- Problem 2.82: SolutionDocument2 pagesProblem 2.82: SolutionNickNo ratings yet
- Homework SolutionsDocument4 pagesHomework Solutionslookitsnichole0% (1)
- Problem 4.21: Y-Direction and Infinitely Long in The X-Direction. If The Strip Is in Air and Has ADocument2 pagesProblem 4.21: Y-Direction and Infinitely Long in The X-Direction. If The Strip Is in Air and Has AEric KialNo ratings yet
- METU EE 303 YR 200 9 Some Transmission Line Problems With SolutionsDocument7 pagesMETU EE 303 YR 200 9 Some Transmission Line Problems With SolutionsAliBaranIşıkNo ratings yet
- Tutorial PDFDocument54 pagesTutorial PDFReneboy Lambarte100% (4)
- Problem 2.46: SolutionDocument1 pageProblem 2.46: SolutionEric KialNo ratings yet
- Problem 4.17: SolutionDocument1 pageProblem 4.17: SolutionEric KialNo ratings yet
- Spring 2014 HW 4 SolnsDocument24 pagesSpring 2014 HW 4 SolnsZahraa TajAlssir AbouSwarNo ratings yet
- Alkendi 2Document4 pagesAlkendi 2Rizza L. MacarandanNo ratings yet
- HW3 SolutionDocument19 pagesHW3 SolutionNguyen Thanh HungNo ratings yet
- Solution - Assignment 3 - Diode CircuitsDocument12 pagesSolution - Assignment 3 - Diode Circuitsshirsodey21No ratings yet
- Tutorial 2 AnsDocument9 pagesTutorial 2 AnsKemproof100% (3)
- ESO 203A: Introduction To Electrical Engineering (2014-15 Second Semester) Assignment # 6 SolutionDocument7 pagesESO 203A: Introduction To Electrical Engineering (2014-15 Second Semester) Assignment # 6 SolutionTejasv RajputNo ratings yet
- Practice Midterm1Document30 pagesPractice Midterm1thisguypoorNo ratings yet
- Power Electronics Questions AnswersDocument59 pagesPower Electronics Questions AnswersPascal UZABAKIRIHONo ratings yet
- The School of Engineering and PhysicsDocument15 pagesThe School of Engineering and PhysicsNikheel sharmaNo ratings yet
- Homework # 2: Ch. 2 # 11 - 14, 17, 18 PozarDocument7 pagesHomework # 2: Ch. 2 # 11 - 14, 17, 18 PozarAbdulrahman behiryNo ratings yet
- Vol1 - (1.3) SolutionsDocument146 pagesVol1 - (1.3) SolutionsSksk SkskNo ratings yet
- 2 42Document2 pages2 42Eric KialNo ratings yet
- Electric Machinery 6ed Fitzgerald - Kingsley - Uman - C2Document15 pagesElectric Machinery 6ed Fitzgerald - Kingsley - Uman - C2பிரசன்னகுமார் ஆனந்தன்100% (1)
- Fall 2013 Set 1 SolutionsDocument4 pagesFall 2013 Set 1 SolutionsMuhammad RizwanNo ratings yet
- SolutionsDocument113 pagesSolutionsAlifNo ratings yet
- Problem 2.45: SolutionDocument1 pageProblem 2.45: SolutionEric KialNo ratings yet
- Fundamental of Power Electronics Week 8 Assignment SolutionsDocument4 pagesFundamental of Power Electronics Week 8 Assignment SolutionsDeep Gandhi100% (1)
- Chapter 11Document34 pagesChapter 11blooms93No ratings yet
- Power Systems With MATLABDocument156 pagesPower Systems With MATLABJuan Alex Arequipa ChecaNo ratings yet
- Applied Electromagnetics Test I Duration: 30 Minutes Total Marks: 85 Name: - Student No.Document4 pagesApplied Electromagnetics Test I Duration: 30 Minutes Total Marks: 85 Name: - Student No.Sam NgNo ratings yet
- Unit Value PDFDocument16 pagesUnit Value PDFEga FauziahNo ratings yet
- Homework SolutionsDocument46 pagesHomework SolutionsKashif AmjadNo ratings yet
- ECE 107, Quiz 1 (Jan 30, 2012) : NameDocument3 pagesECE 107, Quiz 1 (Jan 30, 2012) : Namecourse her o daNo ratings yet
- SMPS Simulation Sheet 2023Document7 pagesSMPS Simulation Sheet 2023yaaNo ratings yet
- Single and Three - 2Document28 pagesSingle and Three - 2Rafiq_HasanNo ratings yet
- Transformer (Basic)Document46 pagesTransformer (Basic)Jatin AggarwalNo ratings yet
- HW1 SolDocument4 pagesHW1 SolIsmael KhalilNo ratings yet
- The University of The West Indies: FEBRUARY, 2013Document10 pagesThe University of The West Indies: FEBRUARY, 2013Charlotte BNo ratings yet
- Exercise # (S) : Alternating CurrentDocument48 pagesExercise # (S) : Alternating CurrentASHWIN METALIYANo ratings yet
- E104 - Superposition Theorem and LinearityDocument19 pagesE104 - Superposition Theorem and LinearityRick AlvientoNo ratings yet
- ET4119 2007-12-07 Ten Met BundelDocument23 pagesET4119 2007-12-07 Ten Met BundelmeteNo ratings yet
- Homework8 Solution PDFDocument5 pagesHomework8 Solution PDFDean WinchesterNo ratings yet
- Circuit Theory - Solved Assignments - Semester Fall 2007Document30 pagesCircuit Theory - Solved Assignments - Semester Fall 2007Muhammad UmairNo ratings yet
- EE2006D Topic 11Document6 pagesEE2006D Topic 11Athul RameshNo ratings yet
- EE Prof Subject With SolutionDocument10 pagesEE Prof Subject With SolutionKim FetalverNo ratings yet
- Chapt 08Document17 pagesChapt 08md.daud.ul.islamNo ratings yet
- EIEN307 ch2Document54 pagesEIEN307 ch2Munkhsukh100% (1)
- Power System AnalysisDocument4 pagesPower System AnalysisnnkhanhvanNo ratings yet
- ELEC-E8427-transmission Lines Home Exercise With SolutionDocument4 pagesELEC-E8427-transmission Lines Home Exercise With SolutionOskari OllilaNo ratings yet
- Tutorial Sheet 1Document2 pagesTutorial Sheet 1Kanishka MahantyNo ratings yet
- Power Engineering Questions and SolutionDocument7 pagesPower Engineering Questions and SolutionMoz Asik0% (1)
- Taller 1 ElectrotecniaDocument17 pagesTaller 1 ElectrotecniaAlejoGonzalezNo ratings yet
- Be First Year Engineering Semester 1 2017 December Basic Electrical Engineering CbcgsDocument24 pagesBe First Year Engineering Semester 1 2017 December Basic Electrical Engineering CbcgsAzhagae ManiNo ratings yet
- Tutorial 1: EEN 206: Power Transmission and DistributionDocument28 pagesTutorial 1: EEN 206: Power Transmission and DistributionShreyas YewaleNo ratings yet
- DEE M1.2B Slides V4-WebinarDocument34 pagesDEE M1.2B Slides V4-Webinartcn ganmoNo ratings yet
- SpaceVector PWM InverterDocument35 pagesSpaceVector PWM Invertersolomong50% (2)
- EE2025 Tut1 SolutionsDocument6 pagesEE2025 Tut1 SolutionsGautam B ee22b162No ratings yet
- Experiment 5 (Modified)Document8 pagesExperiment 5 (Modified)Mark Sangalang100% (1)
- Feynman Lectures Simplified 2C: Electromagnetism: in Relativity & in Dense MatterFrom EverandFeynman Lectures Simplified 2C: Electromagnetism: in Relativity & in Dense MatterNo ratings yet
- Exercises in Electronics: Operational Amplifier CircuitsFrom EverandExercises in Electronics: Operational Amplifier CircuitsRating: 3 out of 5 stars3/5 (1)
- Analysis and Design of Multicell DC/DC Converters Using Vectorized ModelsFrom EverandAnalysis and Design of Multicell DC/DC Converters Using Vectorized ModelsNo ratings yet
- Fundamentals of Electronics 2: Continuous-time Signals and SystemsFrom EverandFundamentals of Electronics 2: Continuous-time Signals and SystemsNo ratings yet
- Problem 5.39: SolutionDocument1 pageProblem 5.39: SolutionEric KialNo ratings yet
- Problem 5.38: SolutionDocument2 pagesProblem 5.38: SolutionEric Kial0% (1)
- Problem 5.37: SolutionDocument2 pagesProblem 5.37: SolutionEric KialNo ratings yet
- Problem 5.41: SolutionDocument2 pagesProblem 5.41: SolutionEric KialNo ratings yet
- Problem 5.40: 20 A. Determine The Magnetic Flux Through TheDocument1 pageProblem 5.40: 20 A. Determine The Magnetic Flux Through TheEric KialNo ratings yet
- Problem 5.2: SolutionDocument1 pageProblem 5.2: SolutionEric KialNo ratings yet
- Problem 5.16: SolutionDocument2 pagesProblem 5.16: SolutionEric KialNo ratings yet
- Problem 5.17: SolutionDocument2 pagesProblem 5.17: SolutionEric KialNo ratings yet
- Problem 5.20: 5 A. If A Straight, Long Conductor Carrying A Current I 10 A IsDocument1 pageProblem 5.20: 5 A. If A Straight, Long Conductor Carrying A Current I 10 A IsEric KialNo ratings yet
- Problem 5.18: X-Direction Lies in The X-Y Plane and Carries A Current I in TheDocument2 pagesProblem 5.18: X-Direction Lies in The X-Y Plane and Carries A Current I in TheEric KialNo ratings yet
- Problem 5.12Document1 pageProblem 5.12Eric KialNo ratings yet
- Problem 5.4: SolutionDocument1 pageProblem 5.4: SolutionEric KialNo ratings yet
- Problem 5.8: 3 M and 7 M and Carries A Current I 15 A, Find H at P (2,, 0)Document1 pageProblem 5.8: 3 M and 7 M and Carries A Current I 15 A, Find H at P (2,, 0)Eric KialNo ratings yet
- Problem 5.15: SolutionDocument2 pagesProblem 5.15: SolutionEric KialNo ratings yet
- Problem 5.6: 30 CM and W 10 CM Is 10 A, Is in The Presence of A Magnetic 2 × 10 ( X + Y2) (T)Document3 pagesProblem 5.6: 30 CM and W 10 CM Is 10 A, Is in The Presence of A Magnetic 2 × 10 ( X + Y2) (T)Eric KialNo ratings yet
- Problem 5.13: SolutionDocument1 pageProblem 5.13: SolutionEric KialNo ratings yet
- Problem 5.14: 2 M. If The Two Loops Have 3 M, Determine The Magnetic Field At: 0 1 M 2 MDocument2 pagesProblem 5.14: 2 M. If The Two Loops Have 3 M, Determine The Magnetic Field At: 0 1 M 2 MEric KialNo ratings yet
- Problem 4.23: Repeat Problem 4.22 For D (C/M)Document1 pageProblem 4.23: Repeat Problem 4.22 For D (C/M)Eric KialNo ratings yet
- Problem 5.7: SolutionDocument1 pageProblem 5.7: SolutionEric KialNo ratings yet
- Problem 5.9: SolutionDocument1 pageProblem 5.9: SolutionEric KialNo ratings yet
- Problem 5.3: SolutionDocument1 pageProblem 5.3: SolutionEric KialNo ratings yet
- Problem 5.10: SolutionDocument2 pagesProblem 5.10: SolutionEric KialNo ratings yet
- Problem 5.5: 4 CM, /2, and 1 M Z 1 M. R 0.2 Cos 4 CM) ?Document2 pagesProblem 5.5: 4 CM, /2, and 1 M Z 1 M. R 0.2 Cos 4 CM) ?Eric KialNo ratings yet
- Problem 5.1: × 10 ( x4 z3) T. Given That e 1.6 × 10 9.1 × 10Document1 pageProblem 5.1: × 10 ( x4 z3) T. Given That e 1.6 × 10 9.1 × 10Eric KialNo ratings yet
- Problem 4.18: 9e, and The Other Located On The Positive X-Axis at 36e. Determine The LocationDocument2 pagesProblem 4.18: 9e, and The Other Located On The Positive X-Axis at 36e. Determine The LocationEric KialNo ratings yet
- Problem 4.19: SolutionDocument1 pageProblem 4.19: SolutionEric KialNo ratings yet
- Problem 4.28: If The Charge Density Increases Linearly With Distance From The Origin Such That Atr Variation of DDocument1 pageProblem 4.28: If The Charge Density Increases Linearly With Distance From The Origin Such That Atr Variation of DEric KialNo ratings yet
- Problem 4.30Document2 pagesProblem 4.30Eric KialNo ratings yet