Professional Documents
Culture Documents
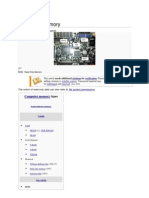
Glossary: CPU (Central Processing Unit)
Glossary: CPU (Central Processing Unit)
Uploaded by
Sturm TigerCopyright:
Available Formats
You might also like
- Heriot-Watt University Dubai Campus: ReceiptDocument2 pagesHeriot-Watt University Dubai Campus: ReceiptMuhammadnasidiNo ratings yet
- INCOME TAX Ready Reckoner - by CA HARSHIL SHETHDocument38 pagesINCOME TAX Ready Reckoner - by CA HARSHIL SHETHCA Harshil ShethNo ratings yet
- Communications, Navigation and Identification (CNI) Avionics For The F-35 Lightning IIDocument2 pagesCommunications, Navigation and Identification (CNI) Avionics For The F-35 Lightning IIjhawkes100% (1)
- Memory and Its TypesDocument4 pagesMemory and Its TypesNikku100% (2)
- Performing Mensuration Q3Document10 pagesPerforming Mensuration Q3Janice Agbuya TamondongNo ratings yet
- The Notion of ReadDocument5 pagesThe Notion of ReadDharan ChowdharyNo ratings yet
- Memory and Its TypesDocument29 pagesMemory and Its Typesneelneel89No ratings yet
- History: Storage ComputersDocument4 pagesHistory: Storage ComputersDana TimushNo ratings yet
- THE Rom and Ram: Technical Vocational & Livelihood Computer Systems Servicing 12 First QuarterDocument4 pagesTHE Rom and Ram: Technical Vocational & Livelihood Computer Systems Servicing 12 First QuarterbogusbaikawNo ratings yet
- Memory: Mohana S.H, Usmrfg College, Kuvempu UniversityDocument6 pagesMemory: Mohana S.H, Usmrfg College, Kuvempu UniversityMohana KurubaNo ratings yet
- Defination of ROMDocument4 pagesDefination of ROMshubham shakyaNo ratings yet
- Basic of ComputerDocument30 pagesBasic of Computermansi sahaiNo ratings yet
- Unit III RAM-ROM-CACHE-HDD-FLOPPY-CDDocument12 pagesUnit III RAM-ROM-CACHE-HDD-FLOPPY-CDxagal74444No ratings yet
- Ram, RomDocument12 pagesRam, Romheanyvoskowskyl.ar.sy.9.48.6No ratings yet
- Fundamentals of Information Technology222222Document49 pagesFundamentals of Information Technology222222mounikagupta021No ratings yet
- Ram and RomDocument3 pagesRam and RomMEENA J RCBSNo ratings yet
- Memory Unit 1Document4 pagesMemory Unit 1Naina KumariNo ratings yet
- BCE Unit 1 Part 3Document42 pagesBCE Unit 1 Part 3AbhiraNo ratings yet
- Read-Only MemoryDocument13 pagesRead-Only MemoryAmbuj RaiNo ratings yet
- Rom 1Document14 pagesRom 1manoj kumar rout100% (2)
- Chapter 3 Computer Memory and ProcessorsDocument45 pagesChapter 3 Computer Memory and ProcessorsshobaNo ratings yet
- Group 1 Comp SystemDocument5 pagesGroup 1 Comp SystemfadzimushayiNo ratings yet
- Module 2 - Reading7 - ReadOnlyMemoryDocument8 pagesModule 2 - Reading7 - ReadOnlyMemoryChristopher AdvinculaNo ratings yet
- Memory Unit - 5 Coa PDFDocument18 pagesMemory Unit - 5 Coa PDFArun KrishNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3 Computer Memory and ProcessorsDocument45 pagesChapter 3 Computer Memory and ProcessorsPraphulla GummaNo ratings yet
- Ram & Rom 2Document13 pagesRam & Rom 2Rashi GurnaniNo ratings yet
- Hand Out-Computer ComponentsDocument16 pagesHand Out-Computer ComponentsFidelis AijouNo ratings yet
- CFOS Unit II by - ErrorDocument22 pagesCFOS Unit II by - ErrorminatiummalikNo ratings yet
- Computer MemoryDocument8 pagesComputer MemoryTakudzwa TapaNo ratings yet
- Textbook U6 U7Document29 pagesTextbook U6 U7Thanh Bình ĐàoNo ratings yet
- Computer MemoryDocument4 pagesComputer MemoryRVRM1995No ratings yet
- Digital Ram & RomDocument4 pagesDigital Ram & Romanilgahlawat1987No ratings yet
- Computer Memories ExplainedDocument6 pagesComputer Memories ExplainedMuhammad UmairNo ratings yet
- ROM ReportDocument8 pagesROM Reportkarwan.il.ahmad1No ratings yet
- Computer Project: Topic: Storage DevicesDocument12 pagesComputer Project: Topic: Storage DevicesPalash ShahNo ratings yet
- Computer MemoryDocument5 pagesComputer Memorynasironlineshoping001No ratings yet
- Memory and Its TypesDocument36 pagesMemory and Its TypesAaruni100% (1)
- Unit 3 Memory OrganisationDocument23 pagesUnit 3 Memory Organisation586ayushNo ratings yet
- BBA SEM II Memory System by Dr. Rakesh RanjanDocument7 pagesBBA SEM II Memory System by Dr. Rakesh RanjanVaibhav TripathiNo ratings yet
- Chapter 09 Memory - Coa KUDocument30 pagesChapter 09 Memory - Coa KUSujan TimalsinaNo ratings yet
- Computer PresentationDocument14 pagesComputer PresentationAayush Niroula OfficialNo ratings yet
- ITM MbaDocument93 pagesITM MbaPrince kumarNo ratings yet
- 6 RamDocument1 page6 RamshakilhmNo ratings yet
- UNIT 2 Microprocessor Architecture and Operations.pptxDocument18 pagesUNIT 2 Microprocessor Architecture and Operations.pptxkinjalbenanilbhaisolankiNo ratings yet
- Unit-1 1 (PPS)Document11 pagesUnit-1 1 (PPS)ayushidwivediviibNo ratings yet
- Computer Memories and StorageDocument6 pagesComputer Memories and StorageShah ZaibNo ratings yet
- New Microsoft Word DocumentDocument7 pagesNew Microsoft Word DocumentKOdy IOryNo ratings yet
- Storage DevicesDocument11 pagesStorage DevicesHuma aliNo ratings yet
- Computer MemoryDocument12 pagesComputer MemoryErmin Sehic100% (1)
- Data Center College of The Philippines, Incorporated Corner Sumulong, Upper Bonifacio ST., Baguio CityDocument13 pagesData Center College of The Philippines, Incorporated Corner Sumulong, Upper Bonifacio ST., Baguio CityMIS syNo ratings yet
- CSC113 AssignmentDocument3 pagesCSC113 AssignmentAlphus DavidNo ratings yet
- Syallabus of Mid Term ExamDocument10 pagesSyallabus of Mid Term Exammuhammadahmadonstrike8No ratings yet
- RAM and ROM AND CPUDocument15 pagesRAM and ROM AND CPUJed SorollaNo ratings yet
- Names: Rafal Hassan Ali, Supervised By: Sadiq H. Abdulhussain Goulshin Adnan Fadhil, Edia Nail Saeed, Zainab Haidar HafedDocument9 pagesNames: Rafal Hassan Ali, Supervised By: Sadiq H. Abdulhussain Goulshin Adnan Fadhil, Edia Nail Saeed, Zainab Haidar Hafedرفل حسن عليNo ratings yet
- Conventional Storage Platforms (Handouts - Group 3)Document35 pagesConventional Storage Platforms (Handouts - Group 3)Maricris Galman SalamatNo ratings yet
- Storage DevicesDocument31 pagesStorage DevicesfaithNo ratings yet
- Computer Data StorageDocument12 pagesComputer Data StorageChristina MagnetaNo ratings yet
- Textbook U6 U7Document29 pagesTextbook U6 U7Mai Thị Thảo ChiNo ratings yet
- Chap 1Document17 pagesChap 1Jannatul FerdousNo ratings yet
- Computer Science: Learn about Algorithms, Cybersecurity, Databases, Operating Systems, and Web DesignFrom EverandComputer Science: Learn about Algorithms, Cybersecurity, Databases, Operating Systems, and Web DesignNo ratings yet
- Fundamentals of Modern Computer Architecture: From Logic Gates to Parallel ProcessingFrom EverandFundamentals of Modern Computer Architecture: From Logic Gates to Parallel ProcessingNo ratings yet
- E 20240407 Charge Calc MethodsDocument3 pagesE 20240407 Charge Calc Methodsamarsoni03697No ratings yet
- Sf4 ConceptDocument10 pagesSf4 ConceptAndrás FarkasNo ratings yet
- Peopleware Chapter 20Document14 pagesPeopleware Chapter 20Umar AshrafNo ratings yet
- Mixing Metaphor PDFDocument286 pagesMixing Metaphor PDFdphvuNo ratings yet
- .. Thesis Title .Document31 pages.. Thesis Title .Tanut VongsoontornNo ratings yet
- GL Period CloseDocument12 pagesGL Period CloseMd MuzaffarNo ratings yet
- Siva VaidhyanathanDocument1 pageSiva VaidhyanathantreborschNo ratings yet
- CMS Farming SystemDocument3 pagesCMS Farming SystemCarylSaycoNo ratings yet
- Word Music, LLC Et Al v. Priddis Music, Inc. Et Al - Document No. 66Document4 pagesWord Music, LLC Et Al v. Priddis Music, Inc. Et Al - Document No. 66Justia.comNo ratings yet
- File System - Node - Js v12.10.0 DocumentationDocument82 pagesFile System - Node - Js v12.10.0 DocumentationMarcos GarciaNo ratings yet
- Axial Flow Valves AMDocument28 pagesAxial Flow Valves AMDavid SaldarriagaNo ratings yet
- FG Riskadjustmentmethodology Module1Document12 pagesFG Riskadjustmentmethodology Module1J CHANGNo ratings yet
- GST RegistrationDocument3 pagesGST RegistrationJabagodu SP & CoNo ratings yet
- 100 so sánh trắc nghiệm-đã chuyển đổiDocument13 pages100 so sánh trắc nghiệm-đã chuyển đổiNguyễn Minh ĐứcNo ratings yet
- User Manual: Promia 50 Application - Material HandlingDocument110 pagesUser Manual: Promia 50 Application - Material Handlingred_shobo_85100% (2)
- Protocol Germ CellDocument82 pagesProtocol Germ CellTanh NguyenNo ratings yet
- Double Flower CelticDocument2 pagesDouble Flower CelticRubi Perla OrozcoNo ratings yet
- Service Experience (OCSE) Using The Emerging Consensus Technique (ECT)Document41 pagesService Experience (OCSE) Using The Emerging Consensus Technique (ECT)Naveen KNo ratings yet
- Ireland Climate Action Plan 2024Document7 pagesIreland Climate Action Plan 2024Fursey WhyteNo ratings yet
- WA-LD-45 PPP For New Direction PAC (March 2017)Document2 pagesWA-LD-45 PPP For New Direction PAC (March 2017)Daily Kos ElectionsNo ratings yet
- Darkeden Legend - The Rare Skills ListDocument6 pagesDarkeden Legend - The Rare Skills ListGM Badr100% (4)
- Recall AcknowledgementDocument3 pagesRecall AcknowledgementNational Content Desk100% (1)
- Kalkulus Multivariat-4Document25 pagesKalkulus Multivariat-4Akbar RizkyNo ratings yet
- Ringwood Pha 1Document167 pagesRingwood Pha 1api-608967166No ratings yet
- Pada Wanita MenstruasiDocument7 pagesPada Wanita MenstruasiLab RS MMCNo ratings yet
- CH-06-Web, Nonstore-Based, and Other Firms of Nontraditional RetailingDocument39 pagesCH-06-Web, Nonstore-Based, and Other Firms of Nontraditional RetailingRama NaveedNo ratings yet
- Action ResearchDocument27 pagesAction Researchreymarie hermosillaNo ratings yet
Glossary: CPU (Central Processing Unit)
Glossary: CPU (Central Processing Unit)
Uploaded by
Sturm TigerOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Glossary: CPU (Central Processing Unit)
Glossary: CPU (Central Processing Unit)
Uploaded by
Sturm TigerCopyright:
Available Formats
Joe Student
Glossary
CPU (Central processing unit)
A central processing unit (CPU), also referred to as a central processor unit,[1] is the hardware within a computer that carries out the instructions of a computer program by performing the basic arithmetical, logical, and input/output operations of the system. The term has been in use in the computer industry at least since the early 1960s.[2] The form, design, and implementation of CPUs have changed over the course of their history, but their fundamental operation remains much the same.
RAM (Random-access memory)
Random-access memory (RAM /rm/) is a form of computer data storage. A random-access device allows stored data to be accessed directly in any random order. In contrast, other data storage media such as hard disks, CDs, DVDs and magnetic tape, as well as early primary memory types such as drum memory, read and write data only in a predetermined order, consecutively, because of mechanical design limitations. Therefore, the time to access a given data location varies significantly depending on its physical location.
ROM (Read-only memory) Read-only memory (ROM) is a class of storage medium used in computers and other electronic devices. Data stored in ROM cannot be modified, or can be modified only slowly or with difficulty, so it is mainly used to distribute firmware (software that is very closely tied to specific hardware, and unlikely to need frequent updates).
In its strictest sense, ROM refers only to mask ROM (the oldest type of solid state ROM), which is fabricated with the desired data permanently stored in it, and thus can never be modified. Despite the simplicity, speed and economies of scale of mask ROM, field-programmability often make reprogrammable memories more flexible and inexpensive. As of 2007, actual ROM circuitry is therefore mainly used for applications such as microcode, and similar structures, on various kinds of processors.
Australian Institute of Commerce and Technology
1/1
You might also like
- Heriot-Watt University Dubai Campus: ReceiptDocument2 pagesHeriot-Watt University Dubai Campus: ReceiptMuhammadnasidiNo ratings yet
- INCOME TAX Ready Reckoner - by CA HARSHIL SHETHDocument38 pagesINCOME TAX Ready Reckoner - by CA HARSHIL SHETHCA Harshil ShethNo ratings yet
- Communications, Navigation and Identification (CNI) Avionics For The F-35 Lightning IIDocument2 pagesCommunications, Navigation and Identification (CNI) Avionics For The F-35 Lightning IIjhawkes100% (1)
- Memory and Its TypesDocument4 pagesMemory and Its TypesNikku100% (2)
- Performing Mensuration Q3Document10 pagesPerforming Mensuration Q3Janice Agbuya TamondongNo ratings yet
- The Notion of ReadDocument5 pagesThe Notion of ReadDharan ChowdharyNo ratings yet
- Memory and Its TypesDocument29 pagesMemory and Its Typesneelneel89No ratings yet
- History: Storage ComputersDocument4 pagesHistory: Storage ComputersDana TimushNo ratings yet
- THE Rom and Ram: Technical Vocational & Livelihood Computer Systems Servicing 12 First QuarterDocument4 pagesTHE Rom and Ram: Technical Vocational & Livelihood Computer Systems Servicing 12 First QuarterbogusbaikawNo ratings yet
- Memory: Mohana S.H, Usmrfg College, Kuvempu UniversityDocument6 pagesMemory: Mohana S.H, Usmrfg College, Kuvempu UniversityMohana KurubaNo ratings yet
- Defination of ROMDocument4 pagesDefination of ROMshubham shakyaNo ratings yet
- Basic of ComputerDocument30 pagesBasic of Computermansi sahaiNo ratings yet
- Unit III RAM-ROM-CACHE-HDD-FLOPPY-CDDocument12 pagesUnit III RAM-ROM-CACHE-HDD-FLOPPY-CDxagal74444No ratings yet
- Ram, RomDocument12 pagesRam, Romheanyvoskowskyl.ar.sy.9.48.6No ratings yet
- Fundamentals of Information Technology222222Document49 pagesFundamentals of Information Technology222222mounikagupta021No ratings yet
- Ram and RomDocument3 pagesRam and RomMEENA J RCBSNo ratings yet
- Memory Unit 1Document4 pagesMemory Unit 1Naina KumariNo ratings yet
- BCE Unit 1 Part 3Document42 pagesBCE Unit 1 Part 3AbhiraNo ratings yet
- Read-Only MemoryDocument13 pagesRead-Only MemoryAmbuj RaiNo ratings yet
- Rom 1Document14 pagesRom 1manoj kumar rout100% (2)
- Chapter 3 Computer Memory and ProcessorsDocument45 pagesChapter 3 Computer Memory and ProcessorsshobaNo ratings yet
- Group 1 Comp SystemDocument5 pagesGroup 1 Comp SystemfadzimushayiNo ratings yet
- Module 2 - Reading7 - ReadOnlyMemoryDocument8 pagesModule 2 - Reading7 - ReadOnlyMemoryChristopher AdvinculaNo ratings yet
- Memory Unit - 5 Coa PDFDocument18 pagesMemory Unit - 5 Coa PDFArun KrishNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3 Computer Memory and ProcessorsDocument45 pagesChapter 3 Computer Memory and ProcessorsPraphulla GummaNo ratings yet
- Ram & Rom 2Document13 pagesRam & Rom 2Rashi GurnaniNo ratings yet
- Hand Out-Computer ComponentsDocument16 pagesHand Out-Computer ComponentsFidelis AijouNo ratings yet
- CFOS Unit II by - ErrorDocument22 pagesCFOS Unit II by - ErrorminatiummalikNo ratings yet
- Computer MemoryDocument8 pagesComputer MemoryTakudzwa TapaNo ratings yet
- Textbook U6 U7Document29 pagesTextbook U6 U7Thanh Bình ĐàoNo ratings yet
- Computer MemoryDocument4 pagesComputer MemoryRVRM1995No ratings yet
- Digital Ram & RomDocument4 pagesDigital Ram & Romanilgahlawat1987No ratings yet
- Computer Memories ExplainedDocument6 pagesComputer Memories ExplainedMuhammad UmairNo ratings yet
- ROM ReportDocument8 pagesROM Reportkarwan.il.ahmad1No ratings yet
- Computer Project: Topic: Storage DevicesDocument12 pagesComputer Project: Topic: Storage DevicesPalash ShahNo ratings yet
- Computer MemoryDocument5 pagesComputer Memorynasironlineshoping001No ratings yet
- Memory and Its TypesDocument36 pagesMemory and Its TypesAaruni100% (1)
- Unit 3 Memory OrganisationDocument23 pagesUnit 3 Memory Organisation586ayushNo ratings yet
- BBA SEM II Memory System by Dr. Rakesh RanjanDocument7 pagesBBA SEM II Memory System by Dr. Rakesh RanjanVaibhav TripathiNo ratings yet
- Chapter 09 Memory - Coa KUDocument30 pagesChapter 09 Memory - Coa KUSujan TimalsinaNo ratings yet
- Computer PresentationDocument14 pagesComputer PresentationAayush Niroula OfficialNo ratings yet
- ITM MbaDocument93 pagesITM MbaPrince kumarNo ratings yet
- 6 RamDocument1 page6 RamshakilhmNo ratings yet
- UNIT 2 Microprocessor Architecture and Operations.pptxDocument18 pagesUNIT 2 Microprocessor Architecture and Operations.pptxkinjalbenanilbhaisolankiNo ratings yet
- Unit-1 1 (PPS)Document11 pagesUnit-1 1 (PPS)ayushidwivediviibNo ratings yet
- Computer Memories and StorageDocument6 pagesComputer Memories and StorageShah ZaibNo ratings yet
- New Microsoft Word DocumentDocument7 pagesNew Microsoft Word DocumentKOdy IOryNo ratings yet
- Storage DevicesDocument11 pagesStorage DevicesHuma aliNo ratings yet
- Computer MemoryDocument12 pagesComputer MemoryErmin Sehic100% (1)
- Data Center College of The Philippines, Incorporated Corner Sumulong, Upper Bonifacio ST., Baguio CityDocument13 pagesData Center College of The Philippines, Incorporated Corner Sumulong, Upper Bonifacio ST., Baguio CityMIS syNo ratings yet
- CSC113 AssignmentDocument3 pagesCSC113 AssignmentAlphus DavidNo ratings yet
- Syallabus of Mid Term ExamDocument10 pagesSyallabus of Mid Term Exammuhammadahmadonstrike8No ratings yet
- RAM and ROM AND CPUDocument15 pagesRAM and ROM AND CPUJed SorollaNo ratings yet
- Names: Rafal Hassan Ali, Supervised By: Sadiq H. Abdulhussain Goulshin Adnan Fadhil, Edia Nail Saeed, Zainab Haidar HafedDocument9 pagesNames: Rafal Hassan Ali, Supervised By: Sadiq H. Abdulhussain Goulshin Adnan Fadhil, Edia Nail Saeed, Zainab Haidar Hafedرفل حسن عليNo ratings yet
- Conventional Storage Platforms (Handouts - Group 3)Document35 pagesConventional Storage Platforms (Handouts - Group 3)Maricris Galman SalamatNo ratings yet
- Storage DevicesDocument31 pagesStorage DevicesfaithNo ratings yet
- Computer Data StorageDocument12 pagesComputer Data StorageChristina MagnetaNo ratings yet
- Textbook U6 U7Document29 pagesTextbook U6 U7Mai Thị Thảo ChiNo ratings yet
- Chap 1Document17 pagesChap 1Jannatul FerdousNo ratings yet
- Computer Science: Learn about Algorithms, Cybersecurity, Databases, Operating Systems, and Web DesignFrom EverandComputer Science: Learn about Algorithms, Cybersecurity, Databases, Operating Systems, and Web DesignNo ratings yet
- Fundamentals of Modern Computer Architecture: From Logic Gates to Parallel ProcessingFrom EverandFundamentals of Modern Computer Architecture: From Logic Gates to Parallel ProcessingNo ratings yet
- E 20240407 Charge Calc MethodsDocument3 pagesE 20240407 Charge Calc Methodsamarsoni03697No ratings yet
- Sf4 ConceptDocument10 pagesSf4 ConceptAndrás FarkasNo ratings yet
- Peopleware Chapter 20Document14 pagesPeopleware Chapter 20Umar AshrafNo ratings yet
- Mixing Metaphor PDFDocument286 pagesMixing Metaphor PDFdphvuNo ratings yet
- .. Thesis Title .Document31 pages.. Thesis Title .Tanut VongsoontornNo ratings yet
- GL Period CloseDocument12 pagesGL Period CloseMd MuzaffarNo ratings yet
- Siva VaidhyanathanDocument1 pageSiva VaidhyanathantreborschNo ratings yet
- CMS Farming SystemDocument3 pagesCMS Farming SystemCarylSaycoNo ratings yet
- Word Music, LLC Et Al v. Priddis Music, Inc. Et Al - Document No. 66Document4 pagesWord Music, LLC Et Al v. Priddis Music, Inc. Et Al - Document No. 66Justia.comNo ratings yet
- File System - Node - Js v12.10.0 DocumentationDocument82 pagesFile System - Node - Js v12.10.0 DocumentationMarcos GarciaNo ratings yet
- Axial Flow Valves AMDocument28 pagesAxial Flow Valves AMDavid SaldarriagaNo ratings yet
- FG Riskadjustmentmethodology Module1Document12 pagesFG Riskadjustmentmethodology Module1J CHANGNo ratings yet
- GST RegistrationDocument3 pagesGST RegistrationJabagodu SP & CoNo ratings yet
- 100 so sánh trắc nghiệm-đã chuyển đổiDocument13 pages100 so sánh trắc nghiệm-đã chuyển đổiNguyễn Minh ĐứcNo ratings yet
- User Manual: Promia 50 Application - Material HandlingDocument110 pagesUser Manual: Promia 50 Application - Material Handlingred_shobo_85100% (2)
- Protocol Germ CellDocument82 pagesProtocol Germ CellTanh NguyenNo ratings yet
- Double Flower CelticDocument2 pagesDouble Flower CelticRubi Perla OrozcoNo ratings yet
- Service Experience (OCSE) Using The Emerging Consensus Technique (ECT)Document41 pagesService Experience (OCSE) Using The Emerging Consensus Technique (ECT)Naveen KNo ratings yet
- Ireland Climate Action Plan 2024Document7 pagesIreland Climate Action Plan 2024Fursey WhyteNo ratings yet
- WA-LD-45 PPP For New Direction PAC (March 2017)Document2 pagesWA-LD-45 PPP For New Direction PAC (March 2017)Daily Kos ElectionsNo ratings yet
- Darkeden Legend - The Rare Skills ListDocument6 pagesDarkeden Legend - The Rare Skills ListGM Badr100% (4)
- Recall AcknowledgementDocument3 pagesRecall AcknowledgementNational Content Desk100% (1)
- Kalkulus Multivariat-4Document25 pagesKalkulus Multivariat-4Akbar RizkyNo ratings yet
- Ringwood Pha 1Document167 pagesRingwood Pha 1api-608967166No ratings yet
- Pada Wanita MenstruasiDocument7 pagesPada Wanita MenstruasiLab RS MMCNo ratings yet
- CH-06-Web, Nonstore-Based, and Other Firms of Nontraditional RetailingDocument39 pagesCH-06-Web, Nonstore-Based, and Other Firms of Nontraditional RetailingRama NaveedNo ratings yet
- Action ResearchDocument27 pagesAction Researchreymarie hermosillaNo ratings yet