Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Renal Diseases
Renal Diseases
Uploaded by
marisa978Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Renal Diseases
Renal Diseases
Uploaded by
marisa978Copyright:
Available Formats
RENAL DISEASES Terms: 1. aldosterone hormone synthesized and released cortex; causes the kidneys to absorb Na 2.
. antidiuretic hormone(AD ! hormone secreted by the "osterior "ituitary #land; causes the kidneys to reabsorb more $ater %. anuria total urine out"ut less than &'m( in 2)hrs. ). bacteriuria * bacteria in the urine; bacterial count hi#her than 1''+''' colonies,m( &. clearance -ol. o. "lasma that the kidneys can clear o. s"eci.ic solute(e#+ creatinine!; ex"ressed in milliliters "er minute /. dysuria "ain.ul or di..icult urination 0. .re1uency -oidin# more .re1uently than e-ery %hrs. 2. 3lomerular .iltration rate(345! -ol. o. "lasma .iltered at the #lomerulus into the kidney tubles each minute; normal rate is a""roximately 12'm(,min 6. hematuria red blood cells in the urine 1'. nocturia a$akenin# at ni#ht to urinate 11. oli#uria * total urine out"ut less than )''m( in 2)hrs. 12. "roteinuria "rotein in the urine 1%. "yuria "us in the urine 1). 7alsal-a (eak 8oint 9aneu-er (7(88! amount o. abdominal "ressure a#ainst the urethra to o"en and leak urine 1&. -esicoureteral re.lux back .lo$ o. urine .rom the bladder into the ureters Anatomy of the Upper and Lower Urinary Tracts :idneys *retro"eritoneal or#ans *12' 10'# *12cm lon#+ /cm $ide and 2.&cm thick *$ith 2 12 "yramids *$ith ) *1% minor calyces *$ith 2 % ma;or calyces *$ith "rotecti-e structures: a. 8ararenal .at b. 3erota<s .ascia c. 8erirenal .at d. 5enal ca"sule Ne"hron *basic structural and .unctional unit o. the kidney =reter+ >ladder+ and =rethra =reter* narro$+ muscular tubes+ each 2) to %' cm lon# that ori#inates at the lo$er "roton o. the renal "el-is * connects each kidney to the bladder >ladder* tem"orary stora#e o. urine =rethra* $here the urine comes out
% 8rocesses o. =rine 4ormation
1. 3lomerular 4iltration* this $here 2?+electrolytes other substance are .iltered 2. Tubular 5eabsor"tion* some o. these substances are reabsorb %. Tubular @ecretion* some o. these substances are secreted in .orm o. urine Test o. =rine @"eci.ic 3ra-ity: 1. ?smolality* no. o. "articles(electrolytes and other molecules! dissol-ed "er kilo#ram o. the urine 2. @"eci.ic #ra-ity* 1.'1' to 1.'2& 5enal .unction be#ins to decrease at a rate o. 1A each year at %'. URINARY DISORDERS A. Acute ye!onephritis *bacterial in.ection o. the renal "el-is+ tubules and interstitial tissue *an ascendin# in.ection *"redis"osin# .actors: a. -esico*ureteral re.lux b. urinary tract obstruction *enlar#ed kidney *$ith abscess on the renal ca"sule and at the cortico*medullary ;unction *s,sx: .e-er and chills costo*-ertebral an#le leucocytosis tenderness bacteriuria and "yuria dysuria .lank "ain inc urinary .re1uency *dx: =TB Nuclear scan CT scan =rine Culture and @ensiti-ity Test D78 *medical mana#ement: a. Acute uncom"licated 8yelone"hritis *no dehydration+ no nausea and -omitin#+ no se"sis E2 $eeks o. oral antibiotics Trimetho"rim*@ul.amethoxazole Ci"ro.loxacin 3entamicin $ith or $ithout Am"icillin Third 3eneration Ce"halos"orins E/ $eeks o. oral antibiotics i. $ith rela"se Furine culture 2 $eeks a.ter antibiotic thera"y b. com"licated *"re#nant "atients Ehos"italization (antibiotics .rom D7 to oral!
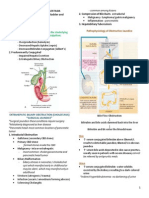
". #hronic ye!onephritis *re"eated acute "yelone"hritis E chronic "yelone"hritis *no s,sx unless there<s an acute exacerbation *kidneys scarred+ contracted and non .unctional *commomn cause o. end sta#e renal disease (G@5D! *s,sx: .ati#ue "olyuria headache excessi-e thirst anorexia $ei#ht loss *dia#nosis: creatinine and >=N clearance creatinine le-els intra-enous "yelo#ra"hy *com"lications: a. G@5D b. hy"ertension c. .ormation o. renal stones *may be due to the "resence o. urea s"littin# microor#anisms *medical mana#ement: urine culture and sensiti-ity #uided antibiotic thera"y i. the urine cannot be made bacteria .ree *Nitro.urantoin to su""ress *T98*@9B bacterial #ro$th *nursin# mana#ement: a. monitorin# *DH? b. oral .luids (%*)(,day!* to dilute urine+ dec+. burnin# on urination+ and "re-ent dehydration *unless contraindicated c. monitor tem".e-ery )hrs *anti"yretics d. education *ad-ise bed rest *"re-ention o. =TD #. Acute $!omeru!onephritis *Dn.lammation o. the #lomerular ca"illaries *"rimarily a disease o. children older than 2 years old *may a..ect any a#e *causes: Eautoimmune @(G Estre"tococcal Acute 8ost @tre"tococcal 3lomerulone"hritis *most common
D. Acute ost Streptococca! $!omeru!onephritis *2 to % $eeks a.ter Eim"eti#o Esore throat *s,sx: hematuria hy"ertension tea colored urine headache+ malaise+ .lank "ain "roteinuria (I! kidney "unch inc serum >=N and creatinine con#estion anemia con.usion+ somnolence and seizures edema 3rou" A >eta* emolytic @tre"tococcal Dn.ection Anti#en*Antibody 5eaction De"osition in the 3lomerulus Dncreased 8roduction o. G"ithelial Cells in the 3lomerulus J>C Dn.iltration Thickenin# @carrin# Decreased 345 *dia#nosis: a. kidney bio"sy b. electron microsco"y c. immuno.lourescence analysis d. Anti*@tre"tolysin ? Titer Anti*DNAse > Titer e. @erum Com"lement Determination *decreased *$ill normalize in 2 2 $eeks E. #hronic $!omeru!onephritis *re"eated acute #lomerulone"hritis *com"onents: re"eated acute #lomerulone"hritis hy"ertensi-e ne"hrosclerosis hy"erli"idemia chronic tubulo*interstitial in;ury hemodynamically mediated #lomerular sclerosis *contraction o. the kidneys to 1,& o. its ori#inal size
*de.ormed kidneys *may result to G@5D *s,sx: may be asym"tomatic hy"ertension or inc >=N and Creatinine edema 5outine eye exam. (o"hthalmosco"y!: retinal hemorrha#es "a"illedema 3en. sym"tom: $ei#ht loss $eakness and irritability nocturia 3DT disturbances anemia heart .ailure "eri"heral neuro"athy+ decreased DT5 "ulsus "aradosus *dia#nosis: 1. =rinalysis* .ixed s". 3ra-ity at 1.'1' "roteinuria; urinary casts("rotein "lu#s secreted by dama#ed kidney tubules! 345 .alls belo$ &'m(,min 2. electrolyte imbalances *hy"erkalemia due to dec. "otassium excretion,excessi-e intake *hy"oalbuminemia $ith edema secondary to "rotein loss(dama#ed #lomerlar membrane! *hy"er"hos"hatemia due to dec.renal excretion o. "hos"orus *hy"ocalcemia (cal. >inds to"hos"orus tocom"ensate .or ele-ated serum "hos"orus le-el! *hy"erma#nesemia dec exceretion inad-ertent in#estion o. antacids containin# ma#nesium %. C>C *anemia ). Chest K*5ay *cardiome#aly *"ulmonary edema &. GC3 *le.t -entricular hy"ertro"hy *mana#ement: 1. treatment o. hy"ertension 2. $ei#ht monitorin# %. #i-e "roteins o. hi#h biolo#ic -alue ). ade1uate calories &. dialysis
*nursin# mana#ement: 1. monitorin# %. Acute Rena! %ai!ure *sudden and almost com"lete loss o. renal .unction *Dec. in 345 *s,sx: *oli#uria *normal urine -ol.(not as common! *anuria *risin# serum creatinine and >=N #ate&ories of AR% 1. 8rerenal *ocuur as a result o. im"aired blood .lo$ *shock 2. Dntrarenal *the result o. actual "arenchymal dama#e to the kidney tubules *use o. ne"hrotoxic dru#s (N@ADDs and ACG inh! %. 8ostrenal *obstruction some$here in distal kidney %our #!inica! hases of AR% 1. Dnitiation *be#ins $ith the initial insult and ends $hen oli#uria de-elo"s 2. ?li#uria *rise in the serum o. $aste "roducts o. metabolism *rise in serum "otassium and ma#nesium %. Diuresis *$ith #radually increasin# urine out"ut *renal .unction may still be markedly abnormal ). 5eco-ery 8eriod *im"ro-ement o. renal .unction *may take %*12 months *$ith normal laboratory -alues *$ith "ermanent 1*%A reduction in 345 *assessment and dia#nostic .indin# *chan#es in urine (scanty to normal! *chan#es in contour(=tz! *Azotemia * y"erkalemia *metabolic acidosis *hy"er"ho"hatemia and hy"ocalcemia *anemia
*"re-ention: *"re-ention o. ex"osure to ne"hrotoxic dru#s *amino#lycosides+ cyclos"orine+ am"hotericin > *serum >=N and creatinine monitorin# *mana#ement: a. restore chemical balance and "re-ent com"lications b. Any "ossible casue is identi.ied c. maintain .luid balance *>8+ C78+ serum and urine electrolyte. 4luid loses d. monitorin# .or o-er hydration *dys"nea+ crackles+ distended neck -eins *4urosemide+ Gthacrynic Acid e. dialysis *to "re-ent serious com"lications Fhy"erkalemia Fse-ere metabolic acidosis F"ericarditis F"ulmonary edema .. "harmacolo#ic *cation exchan#e resin (sodium "olystyrene sul.onate*kayexalate! *retention enema *diuretic thera"y *lo$ do"amine dose (1*%#,k#! *"hos"hate bindin# a#ents (Al? ! #. nutritional thera"y *#i-e additional "roteins (1#,k#,day durin# the oli#uric "hase! *hi#h "otassium and "hos"hate .oods are restricted (banana+ citrus and co..ee! *"otassium restricted to 2'*)'mG1,day *sodium restricted to 2#,day *may re1uire "arenteral nutrition *nursin# mana#ement: a. monitorin# .luid and electrolyte balance b. reducin# metabolic rate *bed rest+ "re-ention o. .e-er and in.ection c. "romotin# "ulmonary .unction *assistance in chan#in# "ositions *ad-ise to cou#h and dee" breath d. "re-entin# in.ection *ase"sis *a-oid insertin# an ind$ellin# urinary catheter
e. "ro-idin# skin care .. "ro-idin# su""ort $. #hronic Rena! %ai!ure 'END(STA$E RENAL DISEASE) *is a "ro#ressi-e irre-ersible deterioration in renal .unction *maintain metabolic and .luid and electrolyte balance .ails resultin# in uremia or azotemia (retention o. urea and other nitro#enous $astes in the blood! *"ro#nosis $ill be determined by the "resence or absence o. hy"ertension and "roteinuria *causes: diabetes mellitus* most common hy"ertension chronic #lomerulone"hritis obstruction o. the urinary tract "olycystic kidney disease in.ections ne"hrotoxic medications * sta#es: @ta#e 1 *5educed 5enal 5eser-e *)'A*0&A loss o. ne"hron .unction *usually asym"tomatic @ta#e 2 *5enal Dnsu..iciency *0&A*6'A loss o. ne"hron .unction *increase in serum >=N and creatinine *inability to concentrate urine *anemia may de-elo" *$ith "olyuria and nocturia @ta#e % *Gnd @ta#e 5enal Disease *L1'A o. ne"hron .unction remainin# *re#ulatory+ excretory and hormonal .unctions are lost *re1uires dialysis *s,sx: cardio-ascular hy"ertension "ulmonary edema heart .ailure "ericarditis dermatolo#ic F"ruritus Furemic .rost (de"osit o. urea crystals!
3D and Neurolo#ic sHsx *assessment and dia#nosis a. #lomerular .iltration rate creatinine clearance b. Na retention and $ater c. Acidosis d. Anemia *com"lications a. y"erkalemia b. 8ericarditis+ 8leural G..usion and Cardiac Tam"onade c. y"ertension d. Anemia e. >one Disease *medical mana#ement: a. maintain kidney .unction and homeostasis b. treat the underlyin# cause and contributory .actors *medications Edialysis *diet thera"y 8harmacolo#ic Thera"y a. antihy"ertensi-es *includes intra-ascular -olume control F.luid restriction Fsodium restriction b. sodium bicarbonate c. erythro"oietin *thera"y G"o#en(recombinant erythro"oietin! D7 or subcutaneous+ may take 2*/ $eeks to increase ct. d. iron su""lementation e. antiseizure a#ents EDiaze"am E8henytoin .. antacids .or hy"er"hos"hatemia and hy"ocalcemia *aluminum based antacids Toxicity my result to: *neurolo#ic sym"toms *osteomalacia *calcium carbonate Nutritional Thera"y *re#ulation o. "rotein intake *re#ulation o. .luid intake (&''*/''ml more than the "re-ious day<s 2) hour =?! *re#ulation o. sodium intake *re#ulation o. "otassium *ade1uate calories and -itamins
%. Dialysis *to "re-ent hy"erkalemia *nursin# mana#ement: a. a-oid the com"lications o. reduced renal .unction b. assess .luid status c. identi.y "otential sources o. the imbalance d. im"lement a dietary "ro#ram e. encoura#e sel. care and inde"endence
You might also like
- Coding Cheat Sheet For Residents in Outpatient MedicineDocument3 pagesCoding Cheat Sheet For Residents in Outpatient MedicineRayCTsai86% (21)
- 102 TOP Pediatrics Multiple Choice Questions and Answers All Medical Questions and Answers PDFDocument4 pages102 TOP Pediatrics Multiple Choice Questions and Answers All Medical Questions and Answers PDFrevathidadam5555575% (4)
- Paeds Crack Notes-1Document111 pagesPaeds Crack Notes-1Ashutosh Krishna JadhavNo ratings yet
- Renal FailureDocument56 pagesRenal FailureKoRnflakes100% (2)
- t2 Kidney DiseaseDocument52 pagest2 Kidney Diseasewany.fyza54No ratings yet
- OUM Tutorial 1 SBNS3504 RenalDocument51 pagesOUM Tutorial 1 SBNS3504 RenalMashanimy HoneyNo ratings yet
- Renal FailureDocument35 pagesRenal FailureaditNo ratings yet
- AKI in OBSTETRICSDocument41 pagesAKI in OBSTETRICSDebajyoti DasNo ratings yet
- Kidney Function and DiseasesDocument70 pagesKidney Function and DiseasesGovind SharmaNo ratings yet
- Dr. H Tadjoedin SP - PD: Renal FailureDocument18 pagesDr. H Tadjoedin SP - PD: Renal FailureLuvita RonteltapNo ratings yet
- Management of Patient With Urinary Disorder1Document14 pagesManagement of Patient With Urinary Disorder1eighkheideeNo ratings yet
- Final CC EdemaDocument31 pagesFinal CC EdematabatchNo ratings yet
- Triệu Chứng - Hội Chứng Bệnh Thận Y3Document58 pagesTriệu Chứng - Hội Chứng Bệnh Thận Y3trungNo ratings yet
- Genitourinary System Acute Poststreptoccal GlomerulonephritisDocument26 pagesGenitourinary System Acute Poststreptoccal GlomerulonephritisLemuel GuevarraNo ratings yet
- RenalDocument11 pagesRenalHero StoreNo ratings yet
- Acute Kidney Injury (AKI) : by Prof Grace Irimu Consultant Pediatrician and NephrologistDocument43 pagesAcute Kidney Injury (AKI) : by Prof Grace Irimu Consultant Pediatrician and Nephrologistokwadha simionNo ratings yet
- CKD - For Concept MappingDocument7 pagesCKD - For Concept MappingKennette Lim0% (1)
- 313 - Disorders of Renal and Urinary SystemsDocument8 pages313 - Disorders of Renal and Urinary SystemsChrissy Mendoza100% (2)
- NEPHROPATHOLOGYDocument54 pagesNEPHROPATHOLOGYAbu Habib100% (2)
- F Kuliah-Nephritic Syndrome-FK UiSUDocument40 pagesF Kuliah-Nephritic Syndrome-FK UiSUandreNo ratings yet
- Acute Kidney Injury: Dana BabaDocument31 pagesAcute Kidney Injury: Dana Babanaheel98shNo ratings yet
- GU Blackboard OutlineDocument15 pagesGU Blackboard Outlinedlneisha61No ratings yet
- Urology NotesDocument8 pagesUrology NotesCzarinah Bacuado67% (3)
- Acute Renal FailureDocument6 pagesAcute Renal FailureFrancine Kyle SusanoNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care of Clients With Urinary Tract DisordersDocument70 pagesNursing Care of Clients With Urinary Tract DisordersYuu Ayu'k LifestarNo ratings yet
- Nephrology: I. ProteinuriaDocument7 pagesNephrology: I. ProteinuriaBenjamin NgNo ratings yet
- Modul 7 Kegawatan Ginjal AnakDocument24 pagesModul 7 Kegawatan Ginjal AnakSanti IskandarNo ratings yet
- NephrologyDocument54 pagesNephrologyAndarge ImperialNo ratings yet
- Renal Function TestsDocument38 pagesRenal Function TestsSupriya NayakNo ratings yet
- Genitourinary System: Billy Ray A. Marcelo, RNDocument35 pagesGenitourinary System: Billy Ray A. Marcelo, RNDarell M. BookNo ratings yet
- AKI in ChildrenDocument43 pagesAKI in ChildrenYonas AwgichewNo ratings yet
- Management of Patients With Renal DisordersDocument14 pagesManagement of Patients With Renal DisordersJhosita Flora LarocoNo ratings yet
- Pedoman Tatalaksana Sindrom Koroner Akut 2015Document29 pagesPedoman Tatalaksana Sindrom Koroner Akut 2015Vittorio bagscenterNo ratings yet
- AKI and CKDDocument73 pagesAKI and CKDzaw wai aungNo ratings yet
- Kidney Disorders: Dr. Venkatesh M. ShashidharDocument30 pagesKidney Disorders: Dr. Venkatesh M. ShashidharDrHassan AbdirahmanNo ratings yet
- Sistem UrinariaDocument42 pagesSistem UrinariaHanny da GamaNo ratings yet
- Diseases o F Urinary System 5 LevelDocument6 pagesDiseases o F Urinary System 5 LevelABDULLAH AMROONNo ratings yet
- Renal Exam Class TestDocument8 pagesRenal Exam Class Test1fleetingNo ratings yet
- Extrahepatic CholestasisDocument9 pagesExtrahepatic CholestasisMatet MonjeNo ratings yet
- 2014 Curs Nefrologie-De Prezentat 4-Ian 2014Document291 pages2014 Curs Nefrologie-De Prezentat 4-Ian 2014Violeta Malina Bîrsan Hodivoianu100% (1)
- Nephritic, Nephrotic Syndrome and Acute Kidney Injury in ChildrenDocument79 pagesNephritic, Nephrotic Syndrome and Acute Kidney Injury in ChildrenB AuNo ratings yet
- Acute and Chronic Kidney DiseaseDocument20 pagesAcute and Chronic Kidney DiseaseCabdi WaliNo ratings yet
- Vanguardia's Online Review Program: Genito-Urinary TractDocument8 pagesVanguardia's Online Review Program: Genito-Urinary TractBobet ReñaNo ratings yet
- Arf NotesDocument28 pagesArf NotesEllen Hennings100% (1)
- Pathoma Notes Part 2 - TPDocument48 pagesPathoma Notes Part 2 - TPJey DeeNo ratings yet
- Renal Tutorial 1Document38 pagesRenal Tutorial 1luckyswiss7776848No ratings yet
- Sistemul RENALDocument108 pagesSistemul RENALAndrada OargăNo ratings yet
- Renal FailureDocument11 pagesRenal FailureLindsey MeimbanNo ratings yet
- Hepatobiliary System: BY Pranjal Kulkarni Neha ManeDocument85 pagesHepatobiliary System: BY Pranjal Kulkarni Neha ManeGurneetNo ratings yet
- View A Negative Experience in Your Life Like You'd Look at A Photo Negative. A Single Negative Can Create An Unlimited Number of Positive Prints.Document90 pagesView A Negative Experience in Your Life Like You'd Look at A Photo Negative. A Single Negative Can Create An Unlimited Number of Positive Prints.madhuNo ratings yet
- Approach To Patient With Diseases of The Kidney and Urinary Tract FINALDocument9 pagesApproach To Patient With Diseases of The Kidney and Urinary Tract FINALgelskNo ratings yet
- Chronic Kidney Disease: 1. Reduction in FunctionDocument6 pagesChronic Kidney Disease: 1. Reduction in FunctionKelebogile NkomoNo ratings yet
- Ms Reviewer Renal UrinaryDocument5 pagesMs Reviewer Renal UrinaryAlyssa Nicole CajayonNo ratings yet
- Acute Kidney Injury and Chronic Kidney DiseaseDocument59 pagesAcute Kidney Injury and Chronic Kidney Diseasesho bartNo ratings yet
- Week 8 Activity Renal DiseasesDocument3 pagesWeek 8 Activity Renal DiseasesHANNA CASANDRA GARCIANo ratings yet
- Cirrhosis AndrewDocument33 pagesCirrhosis Andrewlionel andreaNo ratings yet
- AkiDocument42 pagesAkimarauder_popNo ratings yet
- Chronic Kidney Disease: Uremia SyndromeDocument8 pagesChronic Kidney Disease: Uremia SyndromeMartien Silviandy SetiawanNo ratings yet
- Liver Cirrhosis, A Simple Guide To The Condition, Treatment And Related DiseasesFrom EverandLiver Cirrhosis, A Simple Guide To The Condition, Treatment And Related DiseasesNo ratings yet
- Urinary Tract Infection in Children - Classification, Diagnosis and TreatmentFrom EverandUrinary Tract Infection in Children - Classification, Diagnosis and TreatmentNo ratings yet
- Jurnal Tentang Nipah VirusDocument6 pagesJurnal Tentang Nipah VirusSosial EkonomiNo ratings yet
- Parasitic ArthropodsDocument3 pagesParasitic ArthropodsVicky V. Herpworld100% (1)
- 82 - Identification of An Effective Fraction From Ampelopsis Radix With Anti-Dengue Virus Activities in Vitro and in Vivo - ScienceDirectDocument6 pages82 - Identification of An Effective Fraction From Ampelopsis Radix With Anti-Dengue Virus Activities in Vitro and in Vivo - ScienceDirectsuhasmhaskeNo ratings yet
- Perioperative Management of The Patients With Liver DiseaseDocument94 pagesPerioperative Management of The Patients With Liver DiseaseUmar Farooq GondalNo ratings yet
- Mononeuropathy MultiplexDocument2 pagesMononeuropathy MultiplexElena EllaNo ratings yet
- Micro OBSDocument10 pagesMicro OBSMelchor Felipe SalvosaNo ratings yet
- AmVetPub August2016Document20 pagesAmVetPub August2016NoSpamNo ratings yet
- Group 8 - Microbiology 1 - BacteriologyDocument14 pagesGroup 8 - Microbiology 1 - Bacteriologyjulo_05No ratings yet
- Bovine Tuberculosis: The Role of BadgersDocument5 pagesBovine Tuberculosis: The Role of BadgerspranalinshahNo ratings yet
- Awareness Session: Current Novel Corona Virus (Covid 19)Document8 pagesAwareness Session: Current Novel Corona Virus (Covid 19)danishali03No ratings yet
- Otology: Dave Pothier ST Mary's 2003Document36 pagesOtology: Dave Pothier ST Mary's 2003Mamadovic MubarekNo ratings yet
- Foot and Mouth Disease in Bovine: DR - Jibachha Sah VHRTC (P) LTD Lankupul, NrayangarhDocument63 pagesFoot and Mouth Disease in Bovine: DR - Jibachha Sah VHRTC (P) LTD Lankupul, NrayangarhJibachha Shah100% (1)
- Provides Protective Immunity To Rainbow Trout. A Conserved Aeromonas Salmonicida PorinDocument7 pagesProvides Protective Immunity To Rainbow Trout. A Conserved Aeromonas Salmonicida PorinKasagalaNo ratings yet
- M2 FinalDocument61 pagesM2 FinalJeranz ColansiNo ratings yet
- Revised Syllabus NCM 104Document7 pagesRevised Syllabus NCM 104aby50% (4)
- Rancangan Pengajaran Harian Fizik MicroteachingDocument3 pagesRancangan Pengajaran Harian Fizik MicroteachingwakajoaNo ratings yet
- 2010 - Octenidine Dihydrochloride, A Modern Antiseptic For Skin, Mucous Membranes and WoundsDocument15 pages2010 - Octenidine Dihydrochloride, A Modern Antiseptic For Skin, Mucous Membranes and Woundsnovia100% (2)
- Vaccination Recommendations For The Adult ImmunosuppressedDocument28 pagesVaccination Recommendations For The Adult ImmunosuppressedMirzania Mahya FathiaNo ratings yet
- African Trypanosomiasis African Trypanosomiasis: Sleeping SicknessDocument65 pagesAfrican Trypanosomiasis African Trypanosomiasis: Sleeping SicknessdrgunavetNo ratings yet
- Immunization New ContentDocument11 pagesImmunization New ContentkrishnasreeNo ratings yet
- Me7 o Lab Quiz QuestionsDocument25 pagesMe7 o Lab Quiz QuestionsJen CANo ratings yet
- Food Code HaccpDocument37 pagesFood Code HaccpjucabrerasoNo ratings yet
- Biology Terms Grade 9 ReviewerDocument3 pagesBiology Terms Grade 9 ReviewerGreta Uy Sevilla100% (1)
- What Is A Blood TransfusionDocument6 pagesWhat Is A Blood TransfusionCarlo TolentinoNo ratings yet
- CD Hiv-Aids PDF ReviewerDocument33 pagesCD Hiv-Aids PDF ReviewerMeryville JacildoNo ratings yet
- 8 InfectiousDocument113 pages8 InfectiousLeng IlyNo ratings yet
- Summary Table of AmoebaDocument5 pagesSummary Table of AmoebaFatty BalotoNo ratings yet
- Summer Diseases and Its PreventionDocument6 pagesSummer Diseases and Its PreventionJithin M Krishna EzhuthachanNo ratings yet