Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Plant Diseases: Cell Wall
Plant Diseases: Cell Wall
Uploaded by
Anil KumarCopyright:
Available Formats
You might also like
- PEST AND DISEASES MANAGEMENT (Autosaved)Document44 pagesPEST AND DISEASES MANAGEMENT (Autosaved)Yeoj Secnarev100% (1)
- Plant - Pathogen Interaction & Disease Development - ppt-2003Document91 pagesPlant - Pathogen Interaction & Disease Development - ppt-2003lordniklaus100% (7)
- Fungal Dieases in PlantDocument9 pagesFungal Dieases in Plantsauravv7No ratings yet
- Fungal and Plants EnzymesDocument30 pagesFungal and Plants EnzymesMELISSANo ratings yet
- Diseases of Crops Notes CPP 311 2022 AnjorinDocument40 pagesDiseases of Crops Notes CPP 311 2022 AnjorinZinaNo ratings yet
- Terms and Concepts in Plant PathologyDocument48 pagesTerms and Concepts in Plant PathologytripsNo ratings yet
- FHH Forest PathologyDocument10 pagesFHH Forest PathologyMahiMehtabNo ratings yet
- 9-Introduction To Plant Pathogenic MicroorganismsDocument33 pages9-Introduction To Plant Pathogenic Microorganismsguestiam29No ratings yet
- Integrated Insect Pest ManagementDocument27 pagesIntegrated Insect Pest ManagementMuhammad MehranNo ratings yet
- PP-701 NotesDocument7 pagesPP-701 Noteskhanjatoi736No ratings yet
- Ingles Grupo FDocument12 pagesIngles Grupo FEva Marina Peralta FrancoNo ratings yet
- Plant Disease: Opics in ThisDocument16 pagesPlant Disease: Opics in Thispopa_marius_68100% (1)
- Fungal Pathogenesis Lecture NotesDocument4 pagesFungal Pathogenesis Lecture NotesElla BoyceNo ratings yet
- 01 Plant Path An Overview (JFB)Document18 pages01 Plant Path An Overview (JFB)Khatlya Rivana PutriNo ratings yet
- Plant ProtectionDocument9 pagesPlant ProtectionPooja BhusalNo ratings yet
- Plant Defences against Pathogens and Herbivores editedDocument7 pagesPlant Defences against Pathogens and Herbivores editedAwmtei OM INo ratings yet
- CPP 322 Lecture Notes NewDocument28 pagesCPP 322 Lecture Notes NewvesheNo ratings yet
- Chapter TwoDocument21 pagesChapter TwoAyoade opeyemiNo ratings yet
- AGR514 Chapter 1Document23 pagesAGR514 Chapter 1Muhamad Afif Abdul FatahNo ratings yet
- Definitions and Importance of Insect Pests 17.11.2014 PDFDocument24 pagesDefinitions and Importance of Insect Pests 17.11.2014 PDFmarcNo ratings yet
- 1470 3057 1 PBDocument17 pages1470 3057 1 PBagudaprecious4No ratings yet
- PEST MANAGEMENT ModuleDocument7 pagesPEST MANAGEMENT ModuleRenalyn OrioNo ratings yet
- PERM 324 - NOTES - For 2022-2023Document13 pagesPERM 324 - NOTES - For 2022-2023Sam RyanNo ratings yet
- Content ServerDocument15 pagesContent ServerJessica Sanchez GutierrezNo ratings yet
- Lecture Breeding For Biotic Resistance - Disease ResistanceDocument28 pagesLecture Breeding For Biotic Resistance - Disease Resistancehassignment0No ratings yet
- Disease in PlantsDocument6 pagesDisease in PlantsRyan Yusuf HardyNo ratings yet
- Def PathoDocument9 pagesDef PathoFrancis Ben BerjaNo ratings yet
- Minireviews: Molecular Genetics of Pathogenic OomycetesDocument9 pagesMinireviews: Molecular Genetics of Pathogenic OomycetesPaulo CésarNo ratings yet
- Care and Maintain CropsDocument36 pagesCare and Maintain CropsAllen Jade Pateña100% (1)
- Crop Protection ManagementDocument17 pagesCrop Protection ManagementArpita SonawaneNo ratings yet
- Concepts in Plant Disease SymtomologyDocument16 pagesConcepts in Plant Disease SymtomologyAzelyaNo ratings yet
- Crop Protection ManagementDocument17 pagesCrop Protection ManagementArpita SonawaneNo ratings yet
- Virus Plant InteractionDocument11 pagesVirus Plant InteractioncueraytvNo ratings yet
- Fungal Mycosis and Other InfectionsDocument34 pagesFungal Mycosis and Other InfectionsRajeev PotadarNo ratings yet
- Microbiology: Symbiotic Relationships Between Microbes and Their HostsDocument15 pagesMicrobiology: Symbiotic Relationships Between Microbes and Their HostsRAFAELLA SALVE MARIE GAETOSNo ratings yet
- Control BiologicoDocument13 pagesControl BiologicomurielNo ratings yet
- Plant Leaf Desis OrginalDocument33 pagesPlant Leaf Desis OrginalGuruprasadNo ratings yet
- 05c-Trout Update-Mold in Indoor EnvironmentsDocument51 pages05c-Trout Update-Mold in Indoor EnvironmentsIsworo RukmiNo ratings yet
- Unit 5 Pest Management in HorticultureDocument51 pagesUnit 5 Pest Management in HorticultureMonair MorganNo ratings yet
- Environmental Management of Horticultural Crops: Group 5 ReportDocument53 pagesEnvironmental Management of Horticultural Crops: Group 5 ReportamoressionetaNo ratings yet
- Parasitic Infections: Pathogenesis and Immunity: J. StewartDocument7 pagesParasitic Infections: Pathogenesis and Immunity: J. Stewartnour achkarNo ratings yet
- Production of Enzymes and Phytotoxins by The Plant PathogenDocument40 pagesProduction of Enzymes and Phytotoxins by The Plant PathogenMudit MisraNo ratings yet
- (I2M Week 6-7) Multicellular PathogensDocument40 pages(I2M Week 6-7) Multicellular PathogensellaNo ratings yet
- 05.causes of Plant DiseasesDocument28 pages05.causes of Plant DiseasesFrances Jay FerrerNo ratings yet
- Postharvest PathogensDocument70 pagesPostharvest PathogensMinh DuyNo ratings yet
- Types of Plant DiseasesDocument14 pagesTypes of Plant DiseasesMuqadas NoorNo ratings yet
- Overview of Plant DefencesDocument13 pagesOverview of Plant DefencesSomashekhara Achar KGNo ratings yet
- Bahan Tutorial 4Document5 pagesBahan Tutorial 4Alya RamadhiniNo ratings yet
- CHE581 ProjectDocument18 pagesCHE581 ProjectAbraham wisdomNo ratings yet
- An Introduction To Plant Pathology and Plant Disease Management PDFDocument29 pagesAn Introduction To Plant Pathology and Plant Disease Management PDFJasiz Philipe Ombugu75% (4)
- Plant Pathology: CMG Gardennotes #331Document15 pagesPlant Pathology: CMG Gardennotes #331andargashebirNo ratings yet
- 01 8.1 BPURO TrescDocument36 pages01 8.1 BPURO TrescSzymon KonkolNo ratings yet
- Plant Pests and Diseases Affect Food Crops, Causing Significant Losses ToDocument4 pagesPlant Pests and Diseases Affect Food Crops, Causing Significant Losses ToAvriLyn Palmero ELavigneNo ratings yet
- Plant Innate Immunity: Sub. - Biochem-506, IMMUNO CHEMISTRYDocument22 pagesPlant Innate Immunity: Sub. - Biochem-506, IMMUNO CHEMISTRYviralnanobio_4150420No ratings yet
- Lect. 1 Introduction-Pl Path 111 PDFDocument39 pagesLect. 1 Introduction-Pl Path 111 PDFneal198100% (1)
- Cp-Entomology Part 2Document165 pagesCp-Entomology Part 2RAFTITTI IncNo ratings yet
- BiopesticideDocument14 pagesBiopesticideSurendra KarkiNo ratings yet
- Plants AND Their Diseases - CompressedDocument29 pagesPlants AND Their Diseases - Compressed5933 Gokul B NairNo ratings yet
- Economic Importance of Fungi in AgricultDocument13 pagesEconomic Importance of Fungi in AgricultSai BharathNo ratings yet
- Bioactive Compounds in Phytomedicine BookDocument228 pagesBioactive Compounds in Phytomedicine BookAnil KumarNo ratings yet
- Epulopiscium Fishelsoni, Which Reaches Length of 0.7 Mm. This IsDocument1 pageEpulopiscium Fishelsoni, Which Reaches Length of 0.7 Mm. This IsAnil KumarNo ratings yet
- Pgem-T Easy Vector Systems ProtocolDocument28 pagesPgem-T Easy Vector Systems ProtocolAnil KumarNo ratings yet
- RBC TA Cloning KitDocument1 pageRBC TA Cloning KitAnil KumarNo ratings yet
- RBC TA Cloning KitDocument1 pageRBC TA Cloning KitAnil KumarNo ratings yet
- Colony PCR: CPSC265 Class 8Document11 pagesColony PCR: CPSC265 Class 8Anil KumarNo ratings yet
- pGEM VectorDocument10 pagespGEM VectorAnil KumarNo ratings yet
- Sem - IntroDocument1 pageSem - IntroAnil KumarNo ratings yet
Plant Diseases: Cell Wall
Plant Diseases: Cell Wall
Uploaded by
Anil KumarOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Plant Diseases: Cell Wall
Plant Diseases: Cell Wall
Uploaded by
Anil KumarCopyright:
Available Formats
PLANT DISEASES
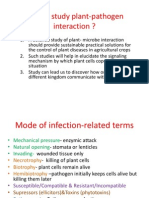
Common pathogenic infection methods
Cell wall-degrading enzymes: These are used to break down the plant cell wall in order to release the nutrients inside. Toxins: These can be non-host-specific, which damage all plants, or host-specific, which cause damage only on a host plant. Effector proteins: These can be secreted into the extracellular environment or directly into the host cell, often via the Type three secretion system. Some effectors are known to suppress host defense processes. This can include: reducing the plants internal signaling mechanisms or reduction of phytochemicals production. [1] Bacteria, fungus and oomycetes are known for this function.
Plant pathogens FungiBacteriaAscomycetes (Fusarium), Basidiomycetes (Rhizoctonia) and Oomycetes (Pythium spp., Phytophthora spp.). do no harm to the plant however, a small number, around 100 known species, are able to cause disease (Xanthomonas spp. Pseudomonas spp.)
VirusesNematodesParasitic plantsPhysiological plant disorders Natural Drought Frost damage, and breakage by snow and hail Flooding and poor drainage Nutrient deficiency Salt deposition and other soluble mineral excesses (e.g., gypsum) Wind (windburn, and breakage by hurricanes and tornadoes) Lightning and wildfire (also often man-made) Man-made (arguably not abiotic, but usually regarded as such) Soil compaction Pollution of air, soil, or both Salt from winter road salt application or irrigation Herbicide over-application Management Quarantine Cultural, Plant resistance, Chemical, Biological, Integrated
You might also like
- PEST AND DISEASES MANAGEMENT (Autosaved)Document44 pagesPEST AND DISEASES MANAGEMENT (Autosaved)Yeoj Secnarev100% (1)
- Plant - Pathogen Interaction & Disease Development - ppt-2003Document91 pagesPlant - Pathogen Interaction & Disease Development - ppt-2003lordniklaus100% (7)
- Fungal Dieases in PlantDocument9 pagesFungal Dieases in Plantsauravv7No ratings yet
- Fungal and Plants EnzymesDocument30 pagesFungal and Plants EnzymesMELISSANo ratings yet
- Diseases of Crops Notes CPP 311 2022 AnjorinDocument40 pagesDiseases of Crops Notes CPP 311 2022 AnjorinZinaNo ratings yet
- Terms and Concepts in Plant PathologyDocument48 pagesTerms and Concepts in Plant PathologytripsNo ratings yet
- FHH Forest PathologyDocument10 pagesFHH Forest PathologyMahiMehtabNo ratings yet
- 9-Introduction To Plant Pathogenic MicroorganismsDocument33 pages9-Introduction To Plant Pathogenic Microorganismsguestiam29No ratings yet
- Integrated Insect Pest ManagementDocument27 pagesIntegrated Insect Pest ManagementMuhammad MehranNo ratings yet
- PP-701 NotesDocument7 pagesPP-701 Noteskhanjatoi736No ratings yet
- Ingles Grupo FDocument12 pagesIngles Grupo FEva Marina Peralta FrancoNo ratings yet
- Plant Disease: Opics in ThisDocument16 pagesPlant Disease: Opics in Thispopa_marius_68100% (1)
- Fungal Pathogenesis Lecture NotesDocument4 pagesFungal Pathogenesis Lecture NotesElla BoyceNo ratings yet
- 01 Plant Path An Overview (JFB)Document18 pages01 Plant Path An Overview (JFB)Khatlya Rivana PutriNo ratings yet
- Plant ProtectionDocument9 pagesPlant ProtectionPooja BhusalNo ratings yet
- Plant Defences against Pathogens and Herbivores editedDocument7 pagesPlant Defences against Pathogens and Herbivores editedAwmtei OM INo ratings yet
- CPP 322 Lecture Notes NewDocument28 pagesCPP 322 Lecture Notes NewvesheNo ratings yet
- Chapter TwoDocument21 pagesChapter TwoAyoade opeyemiNo ratings yet
- AGR514 Chapter 1Document23 pagesAGR514 Chapter 1Muhamad Afif Abdul FatahNo ratings yet
- Definitions and Importance of Insect Pests 17.11.2014 PDFDocument24 pagesDefinitions and Importance of Insect Pests 17.11.2014 PDFmarcNo ratings yet
- 1470 3057 1 PBDocument17 pages1470 3057 1 PBagudaprecious4No ratings yet
- PEST MANAGEMENT ModuleDocument7 pagesPEST MANAGEMENT ModuleRenalyn OrioNo ratings yet
- PERM 324 - NOTES - For 2022-2023Document13 pagesPERM 324 - NOTES - For 2022-2023Sam RyanNo ratings yet
- Content ServerDocument15 pagesContent ServerJessica Sanchez GutierrezNo ratings yet
- Lecture Breeding For Biotic Resistance - Disease ResistanceDocument28 pagesLecture Breeding For Biotic Resistance - Disease Resistancehassignment0No ratings yet
- Disease in PlantsDocument6 pagesDisease in PlantsRyan Yusuf HardyNo ratings yet
- Def PathoDocument9 pagesDef PathoFrancis Ben BerjaNo ratings yet
- Minireviews: Molecular Genetics of Pathogenic OomycetesDocument9 pagesMinireviews: Molecular Genetics of Pathogenic OomycetesPaulo CésarNo ratings yet
- Care and Maintain CropsDocument36 pagesCare and Maintain CropsAllen Jade Pateña100% (1)
- Crop Protection ManagementDocument17 pagesCrop Protection ManagementArpita SonawaneNo ratings yet
- Concepts in Plant Disease SymtomologyDocument16 pagesConcepts in Plant Disease SymtomologyAzelyaNo ratings yet
- Crop Protection ManagementDocument17 pagesCrop Protection ManagementArpita SonawaneNo ratings yet
- Virus Plant InteractionDocument11 pagesVirus Plant InteractioncueraytvNo ratings yet
- Fungal Mycosis and Other InfectionsDocument34 pagesFungal Mycosis and Other InfectionsRajeev PotadarNo ratings yet
- Microbiology: Symbiotic Relationships Between Microbes and Their HostsDocument15 pagesMicrobiology: Symbiotic Relationships Between Microbes and Their HostsRAFAELLA SALVE MARIE GAETOSNo ratings yet
- Control BiologicoDocument13 pagesControl BiologicomurielNo ratings yet
- Plant Leaf Desis OrginalDocument33 pagesPlant Leaf Desis OrginalGuruprasadNo ratings yet
- 05c-Trout Update-Mold in Indoor EnvironmentsDocument51 pages05c-Trout Update-Mold in Indoor EnvironmentsIsworo RukmiNo ratings yet
- Unit 5 Pest Management in HorticultureDocument51 pagesUnit 5 Pest Management in HorticultureMonair MorganNo ratings yet
- Environmental Management of Horticultural Crops: Group 5 ReportDocument53 pagesEnvironmental Management of Horticultural Crops: Group 5 ReportamoressionetaNo ratings yet
- Parasitic Infections: Pathogenesis and Immunity: J. StewartDocument7 pagesParasitic Infections: Pathogenesis and Immunity: J. Stewartnour achkarNo ratings yet
- Production of Enzymes and Phytotoxins by The Plant PathogenDocument40 pagesProduction of Enzymes and Phytotoxins by The Plant PathogenMudit MisraNo ratings yet
- (I2M Week 6-7) Multicellular PathogensDocument40 pages(I2M Week 6-7) Multicellular PathogensellaNo ratings yet
- 05.causes of Plant DiseasesDocument28 pages05.causes of Plant DiseasesFrances Jay FerrerNo ratings yet
- Postharvest PathogensDocument70 pagesPostharvest PathogensMinh DuyNo ratings yet
- Types of Plant DiseasesDocument14 pagesTypes of Plant DiseasesMuqadas NoorNo ratings yet
- Overview of Plant DefencesDocument13 pagesOverview of Plant DefencesSomashekhara Achar KGNo ratings yet
- Bahan Tutorial 4Document5 pagesBahan Tutorial 4Alya RamadhiniNo ratings yet
- CHE581 ProjectDocument18 pagesCHE581 ProjectAbraham wisdomNo ratings yet
- An Introduction To Plant Pathology and Plant Disease Management PDFDocument29 pagesAn Introduction To Plant Pathology and Plant Disease Management PDFJasiz Philipe Ombugu75% (4)
- Plant Pathology: CMG Gardennotes #331Document15 pagesPlant Pathology: CMG Gardennotes #331andargashebirNo ratings yet
- 01 8.1 BPURO TrescDocument36 pages01 8.1 BPURO TrescSzymon KonkolNo ratings yet
- Plant Pests and Diseases Affect Food Crops, Causing Significant Losses ToDocument4 pagesPlant Pests and Diseases Affect Food Crops, Causing Significant Losses ToAvriLyn Palmero ELavigneNo ratings yet
- Plant Innate Immunity: Sub. - Biochem-506, IMMUNO CHEMISTRYDocument22 pagesPlant Innate Immunity: Sub. - Biochem-506, IMMUNO CHEMISTRYviralnanobio_4150420No ratings yet
- Lect. 1 Introduction-Pl Path 111 PDFDocument39 pagesLect. 1 Introduction-Pl Path 111 PDFneal198100% (1)
- Cp-Entomology Part 2Document165 pagesCp-Entomology Part 2RAFTITTI IncNo ratings yet
- BiopesticideDocument14 pagesBiopesticideSurendra KarkiNo ratings yet
- Plants AND Their Diseases - CompressedDocument29 pagesPlants AND Their Diseases - Compressed5933 Gokul B NairNo ratings yet
- Economic Importance of Fungi in AgricultDocument13 pagesEconomic Importance of Fungi in AgricultSai BharathNo ratings yet
- Bioactive Compounds in Phytomedicine BookDocument228 pagesBioactive Compounds in Phytomedicine BookAnil KumarNo ratings yet
- Epulopiscium Fishelsoni, Which Reaches Length of 0.7 Mm. This IsDocument1 pageEpulopiscium Fishelsoni, Which Reaches Length of 0.7 Mm. This IsAnil KumarNo ratings yet
- Pgem-T Easy Vector Systems ProtocolDocument28 pagesPgem-T Easy Vector Systems ProtocolAnil KumarNo ratings yet
- RBC TA Cloning KitDocument1 pageRBC TA Cloning KitAnil KumarNo ratings yet
- RBC TA Cloning KitDocument1 pageRBC TA Cloning KitAnil KumarNo ratings yet
- Colony PCR: CPSC265 Class 8Document11 pagesColony PCR: CPSC265 Class 8Anil KumarNo ratings yet
- pGEM VectorDocument10 pagespGEM VectorAnil KumarNo ratings yet
- Sem - IntroDocument1 pageSem - IntroAnil KumarNo ratings yet