Professional Documents
Culture Documents
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
10 viewsPathophys - Neuro - CVD
Pathophys - Neuro - CVD
Uploaded by
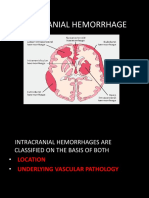
Mario TedjoIntracerebral hemorrhage can be classified based on location, with deep hemorrhages usually caused by hypertension and lobar hemorrhages often due to vascular malformations or coagulopathies. Subarachnoid hemorrhage typically arises from aneurysms and can be rapidly lethal or cause chronic hydrocephalus. Parenchymal brain injuries range from mild concussions to severe lacerations, with clinical features depending on the location and extent of injury. Traumatic vascular injuries also vary based on the source of bleeding such as dural or parenchymal vessels and severity of trauma.
Copyright:
Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Available Formats
Download as DOC, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You might also like
- Neurology Multiple Choice Questions With Explanations: Volume IIFrom EverandNeurology Multiple Choice Questions With Explanations: Volume IIRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (2)
- How Not to Drop Dead!: A Guide for Prevention of 201 Causes of Sudden or Rapid DeathFrom EverandHow Not to Drop Dead!: A Guide for Prevention of 201 Causes of Sudden or Rapid DeathNo ratings yet
- Intracranial HemorrhageDocument75 pagesIntracranial HemorrhageDea DNo ratings yet
- StrokeDocument44 pagesStrokeres.shreyathapaNo ratings yet
- CT BrainDocument230 pagesCT BrainpraveenbhavniNo ratings yet
- Nervous System AlterationsDocument45 pagesNervous System AlterationsMajesty ParkerNo ratings yet
- Neurosurgery: UnprotectedDocument39 pagesNeurosurgery: UnprotectedMaulana Taufik100% (2)
- Head Injury 5Document68 pagesHead Injury 5drvishal bhattNo ratings yet
- Subarachnoid Haemorrhage:Pathology, Clinical Features and ManagementDocument48 pagesSubarachnoid Haemorrhage:Pathology, Clinical Features and Managementesene1100% (1)
- SOL PresentationDocument11 pagesSOL Presentationvony wirawatiNo ratings yet
- Neurology Clerkship UWORLDDocument50 pagesNeurology Clerkship UWORLDHaadi AliNo ratings yet
- Pediatric StrokeDocument90 pagesPediatric StrokeJanaki SethuramanNo ratings yet
- Stroke: Nivedita MPT (Neuro)Document27 pagesStroke: Nivedita MPT (Neuro)MenakaNo ratings yet
- Raised ICP, SOL, HerniationDocument5 pagesRaised ICP, SOL, HerniationGrilled CroweNo ratings yet
- Stroke Hemoragik: Yuneldi Anwar Sps Departemen Neurologi FK UsuDocument28 pagesStroke Hemoragik: Yuneldi Anwar Sps Departemen Neurologi FK UsuJuliana Sari HarahapNo ratings yet
- Kegawatdaruratan Sistem Persarafan: Ners. Feandi Putera, M.KepDocument40 pagesKegawatdaruratan Sistem Persarafan: Ners. Feandi Putera, M.KepDiLahNo ratings yet
- DR NavjeetDocument76 pagesDR NavjeetShubha DiwakarNo ratings yet
- Cerebrovascular DiseaseDocument9 pagesCerebrovascular DiseaseDenzel ColeNo ratings yet
- Stroke Hemoragik: Yuneldi Anwar Sps Departemen Neurologi FK UsuDocument20 pagesStroke Hemoragik: Yuneldi Anwar Sps Departemen Neurologi FK UsuBrolie BarsebaNo ratings yet
- Hypertensive ICHDocument49 pagesHypertensive ICHmingchuan chuNo ratings yet
- 1 Head InjuryDocument17 pages1 Head InjuryAhmeed SafaaNo ratings yet
- Stroke Hemoragik: Yuneldi Anwar Sps Departemen Neurologi FK UsuDocument22 pagesStroke Hemoragik: Yuneldi Anwar Sps Departemen Neurologi FK UsuWinson ChitraNo ratings yet
- Anatomy and PhysiologyDocument38 pagesAnatomy and PhysiologyEka HayatiNo ratings yet
- Cedera KepalaDocument102 pagesCedera KepalaNesaNo ratings yet
- Head Injury 8Document48 pagesHead Injury 8drvishal bhattNo ratings yet
- Neuro NotesDocument54 pagesNeuro Notesmed s100% (1)
- Cerebrospinal Fluid Hypotension As A Cause of Cortical Vein ThrombosisDocument2 pagesCerebrospinal Fluid Hypotension As A Cause of Cortical Vein ThrombosisFernandoNo ratings yet
- KUL 8 Stroke Nursing ManagementDocument45 pagesKUL 8 Stroke Nursing ManagementErina NopiyantiNo ratings yet
- Kuliah 3 - Tumor OtakDocument150 pagesKuliah 3 - Tumor Otaktutorial. aNo ratings yet
- Intracranial PressureDocument27 pagesIntracranial PressureAnggaSunaryaNo ratings yet
- Stroke Hemoragik: Dr. Puji Pinta O. Sinurat, Sps Bagian Neurologi Fk-Umi 2019Document28 pagesStroke Hemoragik: Dr. Puji Pinta O. Sinurat, Sps Bagian Neurologi Fk-Umi 2019Desima Tamara sinuratNo ratings yet
- Stroke: Physiotherapy Treatment ApproachesDocument92 pagesStroke: Physiotherapy Treatment ApproachesHimani Kaushik100% (1)
- Stroke Syndromes and Localization 2007Document56 pagesStroke Syndromes and Localization 2007SaintPaul Univ100% (1)
- Complication of Csom1Document61 pagesComplication of Csom1drtpkNo ratings yet
- Arachnoid CystDocument18 pagesArachnoid CystMirunalakshmi M100% (2)
- Brain HerniationsDocument1 pageBrain Herniationsdragtoss2No ratings yet
- Stroke Hemoragik: Yuneldi Anwar Sps Departemen Neurologi FK UsuDocument28 pagesStroke Hemoragik: Yuneldi Anwar Sps Departemen Neurologi FK UsuDwi Meutia IndriatiNo ratings yet
- Disorders of The Brainstem and Cranial Nerves SY 2022-2023Document141 pagesDisorders of The Brainstem and Cranial Nerves SY 2022-2023Geraldine Teopy100% (1)
- WEBINAR Trauma Kepala PREMIER IDKI Mei 2020 FinalDocument130 pagesWEBINAR Trauma Kepala PREMIER IDKI Mei 2020 FinalAndiNo ratings yet
- Bms166 Slide Stroke HemoragikDocument20 pagesBms166 Slide Stroke HemoragikTriana AmaliaNo ratings yet
- Nurkholis, DR., SpbsDocument72 pagesNurkholis, DR., SpbsRifa Nur MahmudahNo ratings yet
- Increased Intracranial Pressure: DR - Muhammad Yusuf, Sps FinsDocument61 pagesIncreased Intracranial Pressure: DR - Muhammad Yusuf, Sps FinsFidhiyahR100% (1)
- Arteri Cerebellar: Presenter: Dr. Andre Lona Moderator: Dr. Iskandar Nasution, SP.S, FINSDocument40 pagesArteri Cerebellar: Presenter: Dr. Andre Lona Moderator: Dr. Iskandar Nasution, SP.S, FINSAlon RiderNo ratings yet
- Neurology Clerkship UWORLD: Brain TumoursDocument13 pagesNeurology Clerkship UWORLD: Brain TumoursHaadi AliNo ratings yet
- Stroke Hemoragik: Dr. Rusli Dhanu, SP.S (K)Document20 pagesStroke Hemoragik: Dr. Rusli Dhanu, SP.S (K)Lestari Amelia Adm100% (1)
- Stroke Hemoragik: Dr. Rusli Dhanu, SP.S (K)Document20 pagesStroke Hemoragik: Dr. Rusli Dhanu, SP.S (K)BonitavanyNo ratings yet
- Head Trauma: Victor LibertoDocument40 pagesHead Trauma: Victor LibertoMuhamad Fernando MahardikaNo ratings yet
- Lecture 3Document54 pagesLecture 3HazaNo ratings yet
- Cerebrovascular V 2018 MedicinaDocument71 pagesCerebrovascular V 2018 MedicinaAlberto MayorgaNo ratings yet
- Head Trauma: Yoon Seung-Hwan, M.DDocument53 pagesHead Trauma: Yoon Seung-Hwan, M.Dilham darnoNo ratings yet
- Cns Pathology: Cerebral InfarctionDocument24 pagesCns Pathology: Cerebral InfarctionElvisNo ratings yet
- Neurorehabilitation 1Document439 pagesNeurorehabilitation 1Duncan D'AmicoNo ratings yet
- Neurosurgery: Signs of Neurosurgical Disease Raised Intracranial Pressure Meningeal Irritation Brain Tumours Head InjuryDocument10 pagesNeurosurgery: Signs of Neurosurgical Disease Raised Intracranial Pressure Meningeal Irritation Brain Tumours Head InjuryAlman Pratama ManaluNo ratings yet
- Transient Paraparesis As A Manifestation of Left Carotid StenosisDocument4 pagesTransient Paraparesis As A Manifestation of Left Carotid StenosisRommel PorrasNo ratings yet
- Multiple Cranial NeuropathyDocument13 pagesMultiple Cranial NeuropathyChaerani SalamNo ratings yet
- Neuro 10 Cerebrovascular Supply StudentDocument36 pagesNeuro 10 Cerebrovascular Supply StudentLeoNo ratings yet
- 1 Headinjury 5Document39 pages1 Headinjury 5drvishal bhattNo ratings yet
- External Carotid Artery: Imaging Anatomy Atlas for Endovascular TreatmentFrom EverandExternal Carotid Artery: Imaging Anatomy Atlas for Endovascular TreatmentHiro KiyosueNo ratings yet
- Text Atlas of Practical Electrocardiography: A Basic Guide to ECG InterpretationFrom EverandText Atlas of Practical Electrocardiography: A Basic Guide to ECG InterpretationNo ratings yet
Pathophys - Neuro - CVD
Pathophys - Neuro - CVD
Uploaded by
Mario Tedjo0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
10 views1 pageIntracerebral hemorrhage can be classified based on location, with deep hemorrhages usually caused by hypertension and lobar hemorrhages often due to vascular malformations or coagulopathies. Subarachnoid hemorrhage typically arises from aneurysms and can be rapidly lethal or cause chronic hydrocephalus. Parenchymal brain injuries range from mild concussions to severe lacerations, with clinical features depending on the location and extent of injury. Traumatic vascular injuries also vary based on the source of bleeding such as dural or parenchymal vessels and severity of trauma.
Original Description:
Patofisiologi, CVD dan hubunganya dengan saraf
Copyright
© Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Available Formats
DOC, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentIntracerebral hemorrhage can be classified based on location, with deep hemorrhages usually caused by hypertension and lobar hemorrhages often due to vascular malformations or coagulopathies. Subarachnoid hemorrhage typically arises from aneurysms and can be rapidly lethal or cause chronic hydrocephalus. Parenchymal brain injuries range from mild concussions to severe lacerations, with clinical features depending on the location and extent of injury. Traumatic vascular injuries also vary based on the source of bleeding such as dural or parenchymal vessels and severity of trauma.
Copyright:
Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Available Formats
Download as DOC, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as doc, pdf, or txt
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
10 views1 pagePathophys - Neuro - CVD
Pathophys - Neuro - CVD
Uploaded by
Mario TedjoIntracerebral hemorrhage can be classified based on location, with deep hemorrhages usually caused by hypertension and lobar hemorrhages often due to vascular malformations or coagulopathies. Subarachnoid hemorrhage typically arises from aneurysms and can be rapidly lethal or cause chronic hydrocephalus. Parenchymal brain injuries range from mild concussions to severe lacerations, with clinical features depending on the location and extent of injury. Traumatic vascular injuries also vary based on the source of bleeding such as dural or parenchymal vessels and severity of trauma.
Copyright:
Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Available Formats
Download as DOC, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as doc, pdf, or txt
You are on page 1of 1
Classification of Intracerebral Hemorrhage
Features: Sudden onset of headache, focal deficits, and signs of increasing ICP IPH: ganglionic IPH: lobar SITE Basal ganglia, thalamus, pons, deep Cerebral lobes cerebellum USUAL CAUSE Hypertensive vascular disease arious !malformation, coagulopathy, etc" OUTCOME %ften lethal variable Subarachnoid Base of brain, convexities Berry aneurysm, # $ %ften lethal, acute vasospasm, chronic hydrocephalis
Parenchymal Brain In&ury presentations:
TYPE Concussion Con usion Lac!ra ion "i##us! A$onal "a%ag! CLINICAL FEATURES 'ransient loc( +%C ,-. deficits +%C , deficits Prolonged +%C CHARACTERISTICS $ild )#)* Intact Pia.#rachnoid, frontal-temporal poles, lateral temporal 'orn Pia.#rachnoid 'earing of axons in CC, long tracts
'raumatic ascular In&ury
&IN" E'idural h!%a o%a Subdural h!%a o%a Subarachnoid( in ra'ar!nch)%al h!%a o%a "i##us! *ascular in+ur) SOURCE )ural arteries Bridging veins Parenchymal laceration Shearing of axons and vessels CLINICAL FEATURES +%C, then silent interval #cute, subacute, chronic ariable Similar to )#) CAUSES S/ull fracture 'rauma can be mild0 brain atrophy, coagulopathy ariable, usually severe trauma Similar to )#)
You might also like
- Neurology Multiple Choice Questions With Explanations: Volume IIFrom EverandNeurology Multiple Choice Questions With Explanations: Volume IIRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (2)
- How Not to Drop Dead!: A Guide for Prevention of 201 Causes of Sudden or Rapid DeathFrom EverandHow Not to Drop Dead!: A Guide for Prevention of 201 Causes of Sudden or Rapid DeathNo ratings yet
- Intracranial HemorrhageDocument75 pagesIntracranial HemorrhageDea DNo ratings yet
- StrokeDocument44 pagesStrokeres.shreyathapaNo ratings yet
- CT BrainDocument230 pagesCT BrainpraveenbhavniNo ratings yet
- Nervous System AlterationsDocument45 pagesNervous System AlterationsMajesty ParkerNo ratings yet
- Neurosurgery: UnprotectedDocument39 pagesNeurosurgery: UnprotectedMaulana Taufik100% (2)
- Head Injury 5Document68 pagesHead Injury 5drvishal bhattNo ratings yet
- Subarachnoid Haemorrhage:Pathology, Clinical Features and ManagementDocument48 pagesSubarachnoid Haemorrhage:Pathology, Clinical Features and Managementesene1100% (1)
- SOL PresentationDocument11 pagesSOL Presentationvony wirawatiNo ratings yet
- Neurology Clerkship UWORLDDocument50 pagesNeurology Clerkship UWORLDHaadi AliNo ratings yet
- Pediatric StrokeDocument90 pagesPediatric StrokeJanaki SethuramanNo ratings yet
- Stroke: Nivedita MPT (Neuro)Document27 pagesStroke: Nivedita MPT (Neuro)MenakaNo ratings yet
- Raised ICP, SOL, HerniationDocument5 pagesRaised ICP, SOL, HerniationGrilled CroweNo ratings yet
- Stroke Hemoragik: Yuneldi Anwar Sps Departemen Neurologi FK UsuDocument28 pagesStroke Hemoragik: Yuneldi Anwar Sps Departemen Neurologi FK UsuJuliana Sari HarahapNo ratings yet
- Kegawatdaruratan Sistem Persarafan: Ners. Feandi Putera, M.KepDocument40 pagesKegawatdaruratan Sistem Persarafan: Ners. Feandi Putera, M.KepDiLahNo ratings yet
- DR NavjeetDocument76 pagesDR NavjeetShubha DiwakarNo ratings yet
- Cerebrovascular DiseaseDocument9 pagesCerebrovascular DiseaseDenzel ColeNo ratings yet
- Stroke Hemoragik: Yuneldi Anwar Sps Departemen Neurologi FK UsuDocument20 pagesStroke Hemoragik: Yuneldi Anwar Sps Departemen Neurologi FK UsuBrolie BarsebaNo ratings yet
- Hypertensive ICHDocument49 pagesHypertensive ICHmingchuan chuNo ratings yet
- 1 Head InjuryDocument17 pages1 Head InjuryAhmeed SafaaNo ratings yet
- Stroke Hemoragik: Yuneldi Anwar Sps Departemen Neurologi FK UsuDocument22 pagesStroke Hemoragik: Yuneldi Anwar Sps Departemen Neurologi FK UsuWinson ChitraNo ratings yet
- Anatomy and PhysiologyDocument38 pagesAnatomy and PhysiologyEka HayatiNo ratings yet
- Cedera KepalaDocument102 pagesCedera KepalaNesaNo ratings yet
- Head Injury 8Document48 pagesHead Injury 8drvishal bhattNo ratings yet
- Neuro NotesDocument54 pagesNeuro Notesmed s100% (1)
- Cerebrospinal Fluid Hypotension As A Cause of Cortical Vein ThrombosisDocument2 pagesCerebrospinal Fluid Hypotension As A Cause of Cortical Vein ThrombosisFernandoNo ratings yet
- KUL 8 Stroke Nursing ManagementDocument45 pagesKUL 8 Stroke Nursing ManagementErina NopiyantiNo ratings yet
- Kuliah 3 - Tumor OtakDocument150 pagesKuliah 3 - Tumor Otaktutorial. aNo ratings yet
- Intracranial PressureDocument27 pagesIntracranial PressureAnggaSunaryaNo ratings yet
- Stroke Hemoragik: Dr. Puji Pinta O. Sinurat, Sps Bagian Neurologi Fk-Umi 2019Document28 pagesStroke Hemoragik: Dr. Puji Pinta O. Sinurat, Sps Bagian Neurologi Fk-Umi 2019Desima Tamara sinuratNo ratings yet
- Stroke: Physiotherapy Treatment ApproachesDocument92 pagesStroke: Physiotherapy Treatment ApproachesHimani Kaushik100% (1)
- Stroke Syndromes and Localization 2007Document56 pagesStroke Syndromes and Localization 2007SaintPaul Univ100% (1)
- Complication of Csom1Document61 pagesComplication of Csom1drtpkNo ratings yet
- Arachnoid CystDocument18 pagesArachnoid CystMirunalakshmi M100% (2)
- Brain HerniationsDocument1 pageBrain Herniationsdragtoss2No ratings yet
- Stroke Hemoragik: Yuneldi Anwar Sps Departemen Neurologi FK UsuDocument28 pagesStroke Hemoragik: Yuneldi Anwar Sps Departemen Neurologi FK UsuDwi Meutia IndriatiNo ratings yet
- Disorders of The Brainstem and Cranial Nerves SY 2022-2023Document141 pagesDisorders of The Brainstem and Cranial Nerves SY 2022-2023Geraldine Teopy100% (1)
- WEBINAR Trauma Kepala PREMIER IDKI Mei 2020 FinalDocument130 pagesWEBINAR Trauma Kepala PREMIER IDKI Mei 2020 FinalAndiNo ratings yet
- Bms166 Slide Stroke HemoragikDocument20 pagesBms166 Slide Stroke HemoragikTriana AmaliaNo ratings yet
- Nurkholis, DR., SpbsDocument72 pagesNurkholis, DR., SpbsRifa Nur MahmudahNo ratings yet
- Increased Intracranial Pressure: DR - Muhammad Yusuf, Sps FinsDocument61 pagesIncreased Intracranial Pressure: DR - Muhammad Yusuf, Sps FinsFidhiyahR100% (1)
- Arteri Cerebellar: Presenter: Dr. Andre Lona Moderator: Dr. Iskandar Nasution, SP.S, FINSDocument40 pagesArteri Cerebellar: Presenter: Dr. Andre Lona Moderator: Dr. Iskandar Nasution, SP.S, FINSAlon RiderNo ratings yet
- Neurology Clerkship UWORLD: Brain TumoursDocument13 pagesNeurology Clerkship UWORLD: Brain TumoursHaadi AliNo ratings yet
- Stroke Hemoragik: Dr. Rusli Dhanu, SP.S (K)Document20 pagesStroke Hemoragik: Dr. Rusli Dhanu, SP.S (K)Lestari Amelia Adm100% (1)
- Stroke Hemoragik: Dr. Rusli Dhanu, SP.S (K)Document20 pagesStroke Hemoragik: Dr. Rusli Dhanu, SP.S (K)BonitavanyNo ratings yet
- Head Trauma: Victor LibertoDocument40 pagesHead Trauma: Victor LibertoMuhamad Fernando MahardikaNo ratings yet
- Lecture 3Document54 pagesLecture 3HazaNo ratings yet
- Cerebrovascular V 2018 MedicinaDocument71 pagesCerebrovascular V 2018 MedicinaAlberto MayorgaNo ratings yet
- Head Trauma: Yoon Seung-Hwan, M.DDocument53 pagesHead Trauma: Yoon Seung-Hwan, M.Dilham darnoNo ratings yet
- Cns Pathology: Cerebral InfarctionDocument24 pagesCns Pathology: Cerebral InfarctionElvisNo ratings yet
- Neurorehabilitation 1Document439 pagesNeurorehabilitation 1Duncan D'AmicoNo ratings yet
- Neurosurgery: Signs of Neurosurgical Disease Raised Intracranial Pressure Meningeal Irritation Brain Tumours Head InjuryDocument10 pagesNeurosurgery: Signs of Neurosurgical Disease Raised Intracranial Pressure Meningeal Irritation Brain Tumours Head InjuryAlman Pratama ManaluNo ratings yet
- Transient Paraparesis As A Manifestation of Left Carotid StenosisDocument4 pagesTransient Paraparesis As A Manifestation of Left Carotid StenosisRommel PorrasNo ratings yet
- Multiple Cranial NeuropathyDocument13 pagesMultiple Cranial NeuropathyChaerani SalamNo ratings yet
- Neuro 10 Cerebrovascular Supply StudentDocument36 pagesNeuro 10 Cerebrovascular Supply StudentLeoNo ratings yet
- 1 Headinjury 5Document39 pages1 Headinjury 5drvishal bhattNo ratings yet
- External Carotid Artery: Imaging Anatomy Atlas for Endovascular TreatmentFrom EverandExternal Carotid Artery: Imaging Anatomy Atlas for Endovascular TreatmentHiro KiyosueNo ratings yet
- Text Atlas of Practical Electrocardiography: A Basic Guide to ECG InterpretationFrom EverandText Atlas of Practical Electrocardiography: A Basic Guide to ECG InterpretationNo ratings yet