Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Amit Kr. Masih
Amit Kr. Masih
Uploaded by
ashishtony06Original Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Amit Kr. Masih
Amit Kr. Masih
Uploaded by
ashishtony06Copyright:
Available Formats
Every square matrix can be associated to an expression or a number which is known as its determinant.
If is a square matrix of orders, then the determinant of A is denoted by or| |
A square arrangement of 4 numbers in horizontal rows and vertical columns enclosed between two vertical bars is called a determinant of 2nd order. Unlike a matrix it is not just a table of numerical data but (quite differently) a short hand way of writing an algebraic expression, whose value can be computed when the values of the terms or elements are known. The 4 numbers | arranged as
| is a determinant of 2nd order. are called the elements of the
The 4 numbers determinant
The value of the determinant is defined as | |
Any 9 numbers w arranged in a square form of three horizontal rows and three vertical columns enclosed between two vertical bars in the form
| Amit Kr. Masih|
are said to form a determinant of order. Take any row (or column); the value of the determinant is the sum of products of the elements of the row (or column) & The corresponding determinant obtained by omitting the row and the column of the element with a proper sign, given by the rule ( ) Where r and s are the number of row and the number of column respectively of the element of the row (or the column) chosen. Such a determinant is called the co-factor of the element and denoted by capital letters. Exercise: 1 in the determinant | Find the cofactors of the element Solution: Cofactor of Similarly cofactor of ( Find other yourself ) | | Occurs in the ( ) row & | column | |
| Amit Kr. Masih|
( Expansion of Determinant of order 3
In the expansion of determinant of order 3, each and every element of first row and first column is multiplied by that determinant of order two which remain left after abandoning the row and column passing through the elements. The sign in every step is respectively taken as positive and negative respectively as shown as below | | | | | |
Find the values of the following determinant | x Show that | z Operating x | y y y x y z z z x y | x y x z x y y z | |
Taking (x
z) common from first row, we get (x y z) | z x y|
We observe
are identical x y y | x x y x x x x x| x
Show that
| Amit Kr. Masih|
x | x x x x x|
x x x
x x| x |
y | y y
x x x
x x| x | are Identical hence
x x y|
In Second Determinant x | x | x [ x x x | | x or x | |] x |
Example: 2. If |
x x x x x x x x |y y | |y y y | y | |y y z z z z z z z z Operating in 1st Determinant and taking x,y,z from 2nd Determinant we get x x x x | y y| xyz | y y | z z z z Operating on first Determinant x x x x | y y | xyz | y y | z z z z
| Amit Kr. Masih|
xyz) | x y z y z
Applying x | y
x y | z x y
x x y y | z z
and y z |
z z Expanding in terms of , x y x y x| | y z y z |x y (x y)(x y)| y z (y z)(y z) Taking (x y) (y z) common from (x y) (x y)(x y) | | (x y) (x y)(x y)(y z x y) (x y)(x y)(z x) ( ) Using (1) and (2), the given equation becomes ( xyz)(x y)(x y)(z x) As x y z Therefore to fulfill the condition ( xyz)
Example: 3. Show that | Solution: Let Operating | |
)(
| Amit Kr. Masih|
| ( Operating ( ( ( ( )| )[ | )( )( )( ) ) )| | and
, we get | | ]
Example: 4. Show that | | Operating | ( Operating ( ( ( ( Show that )| )[ | ) ) | | ] )| and | | |
, we get
| Amit Kr. Masih|
| Let |
| |
( | ( ( ( Operating (
) ) ) )| and )|
| , we get |
Expanding along ( ( ( )[ | )( ) ) | ]
Evaluate the determinant | Solution: let | | |
| Amit Kr. Masih|
| Taking ( ( ( ( ( ( )( )( )( )( )( )
( ( ( )| )[ | )( )( )(
)| ) ) | | ) ) ) ]
Evaluate the determinant
Solution: Let Operating
| and |
| , we get |
( ( Operating ( )( )(
) )|
) | , we get
)|
| Amit Kr. Masih|
)(
)|
)(
)| ( )( ) ( | ( ( )( )( )( )( ) ) )( ) )
( (
)( )(
)| ) (
Example: 8. ( )( )( |( ( )( Solution: Let ( |( ( Operating |
Show that ) ( ) ) ( ) |=-2 ) ( ) be a given determinant )( ) ( ) )( ) ( ) | )( ) ( ) , we get |
| ( (
| ) ( ) ( ) )
| Amit Kr. Masih|
( Show that | Solution: ( Let | )
) ( ) ( ) | ( )
) ( ) ( ( )
( | ( | (
) ( ) ( ( ) (
( )
) |
)( )(
) ( ) ( ) ( ( ) ) ) ( (
)( )( ) | )
) | )
( ) | ( ( ) |
| |
| |
( ( )
) [
{(
)(
| Amit Kr. Masih|
10
) ( )
| Amit Kr. Masih|
11
Example: Show that | Solution: y ( | ( ( ( |( ( w | y w | y w | | ) ) ) w ) ) ) | w |
| Amit Kr. Masih|
12
Problems 1: Solve for x: | 2: If| | | | |
, find out the value of x. |
3: Find the value of |
4: without expanding prove that the following determinants vanish:(i) (ii) (iii) (iv) (v) S v | | | | | w y | y u : | | | |
(i) (ii) (iii) (iv) (v) (vi)
| Amit Kr. Masih|
13
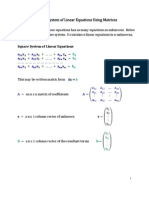
Using determinants, solve the following system of equations
The given equations are
Thus, the system has unique solution | |
Hence
is the solution of the system.
| Amit Kr. Masih|
14
1. (i) (ii) (iii) (iv) (v) (vi)
Find the values of , so that the following systems are consistent. Also find the solution for that value of x y z x y z x y x y x y x y x y x y x y ( )x ( )y )y x y x ( ( ) ( ) x ( ) y ( ) ( )x ( )y ( )x y x y x y x y
| Amit Kr. Masih|
15
You might also like
- Term 1 Chapter 3 - MatricesDocument4 pagesTerm 1 Chapter 3 - MatricesSou Voyage100% (2)
- Solving A System of Linear Equations Using Matrices: This May Be Written Matrix Form XDocument25 pagesSolving A System of Linear Equations Using Matrices: This May Be Written Matrix Form XStephanie O'GarroNo ratings yet
- Elementary Matrix Algebra - Jayalal WettasingheDocument13 pagesElementary Matrix Algebra - Jayalal WettasingheJayalal WettasingheNo ratings yet
- Unit3 NotesDocument34 pagesUnit3 NotesSruthi SundarNo ratings yet
- Class 12 Notes DeterminantsDocument8 pagesClass 12 Notes DeterminantsAasthaNo ratings yet
- Artificial Intelligence (Unit - 2) - Class - XIDocument60 pagesArtificial Intelligence (Unit - 2) - Class - XImoshikaa.pNo ratings yet
- Determinants: Element of ADocument7 pagesDeterminants: Element of ADARSHAN K MNo ratings yet
- An Overview of MATLABDocument28 pagesAn Overview of MATLABransantigerNo ratings yet
- 3 - DeterminantsDocument8 pages3 - DeterminantsDidula ThrimannaNo ratings yet
- AI in MathDocument32 pagesAI in MathSruthi Sundar100% (1)
- MatrixDocument44 pagesMatrixJomil John ReyesNo ratings yet
- ELDI2002 Ali Herssi Challenge 6Document11 pagesELDI2002 Ali Herssi Challenge 6ali herssiNo ratings yet
- MathDocument16 pagesMathArash Evan'sNo ratings yet
- 3 InequalitiesDocument30 pages3 InequalitiesKanokporn LeerungnavaratNo ratings yet
- Kedar ProjectDocument22 pagesKedar ProjectPratik EkaleNo ratings yet
- UNIT 4 MatricesDocument75 pagesUNIT 4 MatricesKamal MittalNo ratings yet
- Grade 10 Math ReviewDocument7 pagesGrade 10 Math Reviewnob100% (1)
- SFU MACM 409 Chapter 1 NotesDocument11 pagesSFU MACM 409 Chapter 1 NotesVincent NguyenNo ratings yet
- Rank of A MatrixDocument9 pagesRank of A MatrixJaya PrakashNo ratings yet
- Paper 23-A New Type Method For The Structured Variational Inequalities ProblemDocument4 pagesPaper 23-A New Type Method For The Structured Variational Inequalities ProblemEditor IJACSANo ratings yet
- Equation MatrixDocument24 pagesEquation MatrixShubham YadavNo ratings yet
- 2 (Ii) DeterminantsDocument9 pages2 (Ii) Determinantskps evilNo ratings yet
- Unit-3 MatricesDocument43 pagesUnit-3 Matricesstanygregor87No ratings yet
- Usme, Dtu Project On Matrices and Determinants Analysis BY Bharat Saini Tanmay ChhikaraDocument17 pagesUsme, Dtu Project On Matrices and Determinants Analysis BY Bharat Saini Tanmay ChhikaraTanmay ChhikaraNo ratings yet
- Class 2-6-2014Document13 pagesClass 2-6-2014Michael LeinerNo ratings yet
- DocumentDocument5 pagesDocumentShin NozenNo ratings yet
- Chapter 6Document20 pagesChapter 6Shimeque SmithNo ratings yet
- Matrices 1Document22 pagesMatrices 1Ekemini SundayNo ratings yet
- MargulisDocument7 pagesMargulisqbeecNo ratings yet
- DeterminantsDocument2 pagesDeterminantszeusNo ratings yet
- Image Compression Using Singular Value Decomposition (SVD)Document23 pagesImage Compression Using Singular Value Decomposition (SVD)M Chandan ShankarNo ratings yet
- Notes - NMADocument159 pagesNotes - NMAavishwasNo ratings yet
- Backup - Publis-Inggris-Paraprashing - JTAMDocument9 pagesBackup - Publis-Inggris-Paraprashing - JTAMsetiadyNo ratings yet
- XII 4 Determinants MCQDocument6 pagesXII 4 Determinants MCQamva754No ratings yet
- Experiment 2a2q2020Document25 pagesExperiment 2a2q2020Frenchesca Darlene CaliwliwNo ratings yet
- Matrices and System of Equations FinalDocument40 pagesMatrices and System of Equations FinalKalia “Aiko”No ratings yet
- Es202 4Document10 pagesEs202 4Abbas TufanNo ratings yet
- Engineering Maths 3 (Week1)Document44 pagesEngineering Maths 3 (Week1)Charles BongNo ratings yet
- Unit 1-MatricesDocument7 pagesUnit 1-MatricesMohammad SaleemNo ratings yet
- Chapter 4 DeterminantsDocument7 pagesChapter 4 DeterminantsXinhui PongNo ratings yet
- DeterminantsDocument19 pagesDeterminantsbithanyahaileNo ratings yet
- Rank of MatrixDocument11 pagesRank of MatrixNurfarina HusseinNo ratings yet
- Units and MeasurementsDocument12 pagesUnits and MeasurementsImranHashmiNo ratings yet
- Math C1 - Matrices and VectorsDocument7 pagesMath C1 - Matrices and VectorsIvetteNo ratings yet
- Cramer's RuleDocument22 pagesCramer's RuleMemyah AlNo ratings yet
- Rajendra Higher Secondary School, Balangir Academic Session 2020-21Document19 pagesRajendra Higher Secondary School, Balangir Academic Session 2020-21aaaa100% (1)
- Math C1 - Matrices and VectorsDocument14 pagesMath C1 - Matrices and VectorsIvetteNo ratings yet
- Numerical Treatment of Nonlinear Third Order Boundary Value ProblemDocument6 pagesNumerical Treatment of Nonlinear Third Order Boundary Value Problemdebbie131313No ratings yet
- MathDocument36 pagesMathRobert EspiñaNo ratings yet
- LN 3 Greedy TechniqueDocument73 pagesLN 3 Greedy TechniquepirtakozNo ratings yet
- Sheet 1-1Document3 pagesSheet 1-1Menna YousriNo ratings yet
- Kashif Khan Assignment of Linear Algebra.Document10 pagesKashif Khan Assignment of Linear Algebra.engineerkashif97No ratings yet
- Class Xii Chapter Wise Concept MapDocument18 pagesClass Xii Chapter Wise Concept MapAnu Radha40% (5)
- Maths 2 For Eng - Lesson 1Document9 pagesMaths 2 For Eng - Lesson 1Abdulkader TukaleNo ratings yet
- Nonlinear Programming UnconstrainedDocument182 pagesNonlinear Programming UnconstrainedkeerthanavijayaNo ratings yet
- Optimization Techniques: Dr. Muhammad Naeem Dr. Ashfaq AhmedDocument64 pagesOptimization Techniques: Dr. Muhammad Naeem Dr. Ashfaq AhmedMuhammad Ali Khan AwanNo ratings yet
- Grade 10 Math Exam ReviewDocument36 pagesGrade 10 Math Exam ReviewEddie LiangNo ratings yet
- Matrices with MATLAB (Taken from "MATLAB for Beginners: A Gentle Approach")From EverandMatrices with MATLAB (Taken from "MATLAB for Beginners: A Gentle Approach")Rating: 3 out of 5 stars3/5 (4)
- PricingDocument6 pagesPricingashishtony06No ratings yet
- Submitted To: Submitted By: Dr. Enid MDocument12 pagesSubmitted To: Submitted By: Dr. Enid Mashishtony06No ratings yet
- Champa SDocument12 pagesChampa Sashishtony06No ratings yet
- Champa SDocument12 pagesChampa Sashishtony06No ratings yet