Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Greece: Key Indicators
Greece: Key Indicators
Uploaded by
api-26143576Copyright:
Available Formats
You might also like
- Trade Finance Database - Feb'19Document12 pagesTrade Finance Database - Feb'19sheelNo ratings yet
- Group 2 Mahindra - GenZe - Marketing - Plan PDFDocument24 pagesGroup 2 Mahindra - GenZe - Marketing - Plan PDFAnanditaKarNo ratings yet
- Payroll US Best PracticesDocument7 pagesPayroll US Best PracticesJuba99350No ratings yet
- Consumer Behaviour Report On OlpersDocument25 pagesConsumer Behaviour Report On OlpersAnam TariqNo ratings yet
- Colombia: Key Indicators, 2010Document2 pagesColombia: Key Indicators, 2010Jack TorresNo ratings yet
- MexicocompetividadDocument2 pagesMexicocompetividadgregaladoNo ratings yet
- ParaguayDocument2 pagesParaguaymalonso1234No ratings yet
- United States: Key IndicatorsDocument2 pagesUnited States: Key IndicatorsgregaladoNo ratings yet
- Philippines: Key Indicators, 2014Document2 pagesPhilippines: Key Indicators, 2014alelie_germanNo ratings yet
- India: Key Indicators, 2014Document2 pagesIndia: Key Indicators, 2014Gokul BaskerNo ratings yet
- Key Indicators, 2014: 2: Country/Economy ProfilesDocument2 pagesKey Indicators, 2014: 2: Country/Economy ProfilesluisrengNo ratings yet
- Switzerland: Key Indicators, 2014Document2 pagesSwitzerland: Key Indicators, 2014Dinu Maria-AndreeaNo ratings yet
- Honduras: Key Indicators, 2013Document2 pagesHonduras: Key Indicators, 2013Bladimir BastidaNo ratings yet
- Malaysia: Key Indicators, 2013Document2 pagesMalaysia: Key Indicators, 2013Rudy QuismorioNo ratings yet
- Egypt: Key Indicators, 2013Document2 pagesEgypt: Key Indicators, 2013Alhassan GamalNo ratings yet
- Chile: Networked Readiness Index........................ 38 ..4.6Document1 pageChile: Networked Readiness Index........................ 38 ..4.6Víctor Alfonso Castillo VillchezNo ratings yet
- Networked Readiness Index........................ 77 ..4.0: Rank Value (Out of 139) (1-7)Document1 pageNetworked Readiness Index........................ 77 ..4.0: Rank Value (Out of 139) (1-7)Veda MariaNo ratings yet
- En WBNR Other SRGCM4042 EBookSustainabilityGoodforBusinessDocument196 pagesEn WBNR Other SRGCM4042 EBookSustainabilityGoodforBusinessPedro OliveiraNo ratings yet
- En CNTNT Other ExecutivePlaybookDocument197 pagesEn CNTNT Other ExecutivePlaybookNhat Ngoc TrinhNo ratings yet
- Indonesia: Global Innovation Index (Out of 127) ................... 30.1 87 I: Co Untr Y/e Con Om y Pro File SDocument2 pagesIndonesia: Global Innovation Index (Out of 127) ................... 30.1 87 I: Co Untr Y/e Con Om y Pro File SStefie Laimeheriwa KybernNo ratings yet
- Work X Whitepaper V5Document47 pagesWork X Whitepaper V5ibrahimmohammed6702No ratings yet
- Real Estate Development and ValuationDocument157 pagesReal Estate Development and Valuationmarx dessie100% (1)
- The Global Economy. NYE Stern. Macro 2Document289 pagesThe Global Economy. NYE Stern. Macro 2CRISTIAN MAURICIO GONZALES MURILLONo ratings yet
- Technology and Industry Scoreboard 2009Document146 pagesTechnology and Industry Scoreboard 2009MARYPAZ SILVANo ratings yet
- 8th Pillar: Tourism InfrastructureDocument2 pages8th Pillar: Tourism Infrastructureapi-25966334No ratings yet
- Sustainable Performance Analysis of Selected Smes For DigitalizationDocument24 pagesSustainable Performance Analysis of Selected Smes For DigitalizationKRISHNA PRASAD SAMUDRALANo ratings yet
- Cookbook Inside Final 7.15Document92 pagesCookbook Inside Final 7.15Fe Guerra QuanicoNo ratings yet
- PhilippinesDocument1 pagePhilippinesegghead2point0No ratings yet
- QMS RequirementsDocument60 pagesQMS Requirementsvishwas salunkheNo ratings yet
- Communication Strategy For InstitutionDocument124 pagesCommunication Strategy For InstitutionHPNo ratings yet
- EIC Work Programme 2022Document156 pagesEIC Work Programme 2022irinaNo ratings yet
- Vision 2030 - MTP 2008-2012 - First Annual Progress ReportDocument198 pagesVision 2030 - MTP 2008-2012 - First Annual Progress ReportRyan RoweNo ratings yet
- APA Guideline FinalDocument198 pagesAPA Guideline FinalsolomonNo ratings yet
- 0 DESI 2021 Thematic Chapters Full European Analysis DhhO6dGif25zTsq4LXZQCIrI 80563Document108 pages0 DESI 2021 Thematic Chapters Full European Analysis DhhO6dGif25zTsq4LXZQCIrI 80563Corina CosteaNo ratings yet
- EITM Call For Proposals Guidelines 23-25 - Final Version - Amended 01juneDocument51 pagesEITM Call For Proposals Guidelines 23-25 - Final Version - Amended 01juneIvo HaladinNo ratings yet
- 01 Beyond Strategic Kaizen - Performing Synchronous Profitable Operations - Alin Posteucă - Routledge - Productivity Press (2023)Document324 pages01 Beyond Strategic Kaizen - Performing Synchronous Profitable Operations - Alin Posteucă - Routledge - Productivity Press (2023)phuoc.daoduy1704No ratings yet
- Global Information Technology ReportDocument1 pageGlobal Information Technology Reportcocoy.dayao831100% (2)
- Perfilde Peru 2014Document2 pagesPerfilde Peru 2014Jorge RodríguezNo ratings yet
- Uribe PDFDocument225 pagesUribe PDFSzabó TamásNo ratings yet
- Cotton GinningDocument48 pagesCotton GinningTariq ShafiNo ratings yet
- IbmDocument59 pagesIbmDarren_Fung_8729No ratings yet
- Innovation and Industrial Policies Deschamps Full Chapter PDFDocument61 pagesInnovation and Industrial Policies Deschamps Full Chapter PDFripperblowes100% (6)
- UNIDO IndustrialStatistics Yearbook 2023Document162 pagesUNIDO IndustrialStatistics Yearbook 2023Uzair Khaleeq uz ZamanNo ratings yet
- Microsoft Yahoo! Merger: Novel Innovative Businessmodel of ADocument38 pagesMicrosoft Yahoo! Merger: Novel Innovative Businessmodel of APirmin HeinzerNo ratings yet
- TM-Entrepreneurship and Employabilityskill - TwoDocument228 pagesTM-Entrepreneurship and Employabilityskill - TwoKiya Abdi100% (2)
- Lecture - Notes in Open Economy MacroDocument183 pagesLecture - Notes in Open Economy MacroMadMinarchNo ratings yet
- UNIDO IndustrialStatistics Yearbook 2022Document138 pagesUNIDO IndustrialStatistics Yearbook 2022Miền ĐinhNo ratings yet
- Study Eu Cosmetics Industry PDFDocument165 pagesStudy Eu Cosmetics Industry PDFJa JUOINo ratings yet
- Barend Rogier Final ThesisDocument167 pagesBarend Rogier Final ThesisIrakli SheroziaNo ratings yet
- 88 - Evaluation of Phase 2 of The Commonwealth Private Investment Initia...Document81 pages88 - Evaluation of Phase 2 of The Commonwealth Private Investment Initia...B VNo ratings yet
- Project Report ON Pakistan Telecommunication Company Limited (PTCL)Document20 pagesProject Report ON Pakistan Telecommunication Company Limited (PTCL)Sumera Arif MalikNo ratings yet
- Tsirimpas 2015Document212 pagesTsirimpas 2015fantasy azerbaijanNo ratings yet
- TN Vision 2023 PDFDocument68 pagesTN Vision 2023 PDFRajanbabu100% (1)
- Level III - Cadastral Surveying and Mapping ServiceDocument267 pagesLevel III - Cadastral Surveying and Mapping Servicekenna abdetenNo ratings yet
- Next Generation Manufacturing Technology Initiative PDFDocument253 pagesNext Generation Manufacturing Technology Initiative PDFAndriya Narasimhulu100% (1)
- Convergence: User Expectations, Communications Enablers and Business OpportunitiesFrom EverandConvergence: User Expectations, Communications Enablers and Business OpportunitiesNo ratings yet
- Evaluation of the International Finance Corporation's Global Trade Finance Program, 2006-12From EverandEvaluation of the International Finance Corporation's Global Trade Finance Program, 2006-12No ratings yet
- The Strategy Gap: Leveraging Technology to Execute Winning StrategiesFrom EverandThe Strategy Gap: Leveraging Technology to Execute Winning StrategiesNo ratings yet
- Business Administration PapersDocument36 pagesBusiness Administration Papersinfiniti786No ratings yet
- SSCDocument67 pagesSSCSukanya Ray100% (1)
- Qatar Visa ProcedureDocument4 pagesQatar Visa ProcedureSeven Seas BPONo ratings yet
- Webinar - CPR SAVES TRADES - A MULTI-TIMEFRAME APPROACH - ELMDocument5 pagesWebinar - CPR SAVES TRADES - A MULTI-TIMEFRAME APPROACH - ELMParminder Singh MatharuNo ratings yet
- Micros CoffeeDocument7 pagesMicros CoffeeBlessy LapinaNo ratings yet
- Είδη Μεταφοράς ή Συσκευασίας Από Πλαστικές Ύλες.2016714104726Document959 pagesΕίδη Μεταφοράς ή Συσκευασίας Από Πλαστικές Ύλες.2016714104726traceNo ratings yet
- FirmsDocument5 pagesFirmsl.mufaddalNo ratings yet
- Shy Chapter 7Document18 pagesShy Chapter 7Prinny ThomasNo ratings yet
- Lección 1 / Actividad 1Document2 pagesLección 1 / Actividad 1Marina D'AnconiaNo ratings yet
- James Cantorne Corporation Liquidation and ReorganizationDocument8 pagesJames Cantorne Corporation Liquidation and ReorganizationJames CantorneNo ratings yet
- About CIPETDocument37 pagesAbout CIPETTool Room CIPET VijayawadaNo ratings yet
- Netvault Backup Compatibility Guide For Hardware and Software TechnicalDocument71 pagesNetvault Backup Compatibility Guide For Hardware and Software TechnicalArunmurNo ratings yet
- IFRS 5, Non-Current Assets Held For Sale and Discontinued Operations: Practical Guide To Application and Expected ChangesDocument42 pagesIFRS 5, Non-Current Assets Held For Sale and Discontinued Operations: Practical Guide To Application and Expected ChangesJahidul ShahNo ratings yet
- E Book On ADC ProductsDocument29 pagesE Book On ADC ProductsSudharani YellapragadaNo ratings yet
- Health IQ A - Q-246847 - v1Document3 pagesHealth IQ A - Q-246847 - v1racrabeNo ratings yet
- The Link Between SD and MMDocument3 pagesThe Link Between SD and MMSuneetha MathukumalliNo ratings yet
- Chik-Shampoo Sachet: DR Amit RangnekarDocument46 pagesChik-Shampoo Sachet: DR Amit RangnekarDr Amit Rangnekar67% (3)
- Anmol Setia Project On New Scheme Launch by Present Govement Like Jhan Dhan and Bima Yojana - Undertaken in Oriental Bank of Commerce .Document87 pagesAnmol Setia Project On New Scheme Launch by Present Govement Like Jhan Dhan and Bima Yojana - Undertaken in Oriental Bank of Commerce .ANMOLNo ratings yet
- Securing AnexgateDocument2 pagesSecuring Anexgatebsatish_70No ratings yet
- Class Exercise 1Document2 pagesClass Exercise 1KenWuNo ratings yet
- Doc. 153-1 - Affidavit of R. Lance FloresDocument13 pagesDoc. 153-1 - Affidavit of R. Lance FloresR. Lance FloresNo ratings yet
- Client Feedback FormDocument3 pagesClient Feedback FormnissreenbarakatNo ratings yet
- Sub Topic 2: Approaches To The Study of Agricultural MarketingDocument23 pagesSub Topic 2: Approaches To The Study of Agricultural MarketingRoberto GarciaNo ratings yet
- Dela Rama Et Al Vs Mao - Ao Sugar - CentralDocument2 pagesDela Rama Et Al Vs Mao - Ao Sugar - CentralJude MaiquezNo ratings yet
- Dosti Codename Dosti Group Thane Archstones ASPS Bhavik BhattDocument11 pagesDosti Codename Dosti Group Thane Archstones ASPS Bhavik BhattArchstones Property SolutionsNo ratings yet
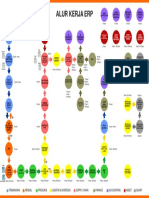
- Alur Kerja Erp: Pemasaran Rendal Produksi Logistik & Ekspedisi Supply Chain Finance Accounting Asset QuaryDocument1 pageAlur Kerja Erp: Pemasaran Rendal Produksi Logistik & Ekspedisi Supply Chain Finance Accounting Asset QuaryMuhammad FairusNo ratings yet
- 02 WholeDocument230 pages02 WholeAgnes LiewNo ratings yet
Greece: Key Indicators
Greece: Key Indicators
Uploaded by
api-26143576Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Greece: Key Indicators
Greece: Key Indicators
Uploaded by
api-26143576Copyright:
Available Formats
Part 2A.
r2 8/31/09 10:31 AM Page 156
Greece
2.1: Country/Economy Profiles
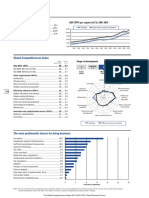
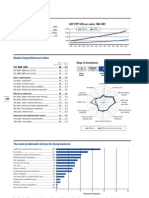
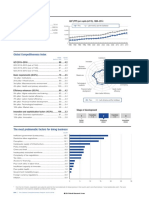
Key indicators
GDP (PPP int'l $) per capita, 1980–2008
Population (millions), 2008.......................................11.2
40,000 Greece OECD
GDP (US$ billions), 2008.........................................357.5
GDP per capita (US$), 2008 ..............................32,004.6 30,000
GDP (PPP) as share (%) of world total, 2008 .......0.49 20,000
10,000
0
1980 1982 1984 1986 1988 1990 1992 1994 1996 1998 2000 2002 2004 2006 2008
Global Competitiveness Index
Rank Score Stage of development
(out of 133) (1–7)
GCI 2009–2010.........................................................71 ......4.0 Transition Transition
1 1–2 2 2–3 3
GCI 2008–2009 (out of 134)..................................................67 ........4.1
GCI 2007–2008 (out of 131)..................................................65 ........4.1 Factor Efficiency Innovation
driven driven driven
Basic requirements.............................................................56 ........4.5
1st pillar: Institutions ...........................................................70 ........3.8
2nd pillar: Infrastructure.....................................................47 ........4.3 Institutions
7
3rd pillar: Macroeconomic stability................................103 ........4.0 Innovation Infrastructure
6
4th pillar: Health and primary education .........................41 ........5.8
5
Business Macroeconomic
Efficiency enhancers..........................................................57 ........4.1 4
stability
sophistication
5th pillar: Higher education and training .........................43 ........4.4 3
156 6th pillar: Goods market efficiency...................................75 ........4.1 2
Health and
7th pillar: Labor market efficiency ..................................116 ........3.8 Market size 1 primary
education
8th pillar: Financial market sophistication.......................83 ........4.0
9th pillar: Technological readiness...................................53 ........3.9
Technological Higher education
10th pillar: Market size........................................................34 ........4.6 readiness and training
Innovation and sophistication factors ............................66 ........3.6 Financial market Goods market
11th pillar: Business sophistication..................................66 ........4.0 sophistication efficiency
12th pillar: Innovation..........................................................65 ........3.1 Labor market efficiency
Greece Innovation-driven economies
The most problematic factors for doing business
Inefficient government bureaucracy.........................25.3
Restrictive labor regulations .......................................14.2
Corruption.......................................................................14.0
Tax regulations ..............................................................12.0
Policy instability...............................................................8.7
Access to financing ........................................................6.5
Tax rates ...........................................................................5.0
Inadequate supply of infrastructure ............................4.8
Inadequately educated workforce...............................2.3
Poor work ethic in national labor force ......................2.3
Government instability/coups .......................................2.2
Poor public health ...........................................................0.9
Crime and theft ................................................................0.8
Inflation .............................................................................0.8
Foreign currency regulations........................................0.2
0 5 10 15 20 25 30
Percent of responses
Note: From a list of 15 factors, respondents were asked to select the five most problematic for doing business in their country/economy and to rank them
between 1 (most problematic) and 5. The bars in the figure show the responses weighted according to their rankings.
The Global Competitiveness Report 2009-2010 © 2009 World Economic Forum
You might also like
- Trade Finance Database - Feb'19Document12 pagesTrade Finance Database - Feb'19sheelNo ratings yet
- Group 2 Mahindra - GenZe - Marketing - Plan PDFDocument24 pagesGroup 2 Mahindra - GenZe - Marketing - Plan PDFAnanditaKarNo ratings yet
- Payroll US Best PracticesDocument7 pagesPayroll US Best PracticesJuba99350No ratings yet
- Consumer Behaviour Report On OlpersDocument25 pagesConsumer Behaviour Report On OlpersAnam TariqNo ratings yet
- Colombia: Key Indicators, 2010Document2 pagesColombia: Key Indicators, 2010Jack TorresNo ratings yet
- MexicocompetividadDocument2 pagesMexicocompetividadgregaladoNo ratings yet
- ParaguayDocument2 pagesParaguaymalonso1234No ratings yet
- United States: Key IndicatorsDocument2 pagesUnited States: Key IndicatorsgregaladoNo ratings yet
- Philippines: Key Indicators, 2014Document2 pagesPhilippines: Key Indicators, 2014alelie_germanNo ratings yet
- India: Key Indicators, 2014Document2 pagesIndia: Key Indicators, 2014Gokul BaskerNo ratings yet
- Key Indicators, 2014: 2: Country/Economy ProfilesDocument2 pagesKey Indicators, 2014: 2: Country/Economy ProfilesluisrengNo ratings yet
- Switzerland: Key Indicators, 2014Document2 pagesSwitzerland: Key Indicators, 2014Dinu Maria-AndreeaNo ratings yet
- Honduras: Key Indicators, 2013Document2 pagesHonduras: Key Indicators, 2013Bladimir BastidaNo ratings yet
- Malaysia: Key Indicators, 2013Document2 pagesMalaysia: Key Indicators, 2013Rudy QuismorioNo ratings yet
- Egypt: Key Indicators, 2013Document2 pagesEgypt: Key Indicators, 2013Alhassan GamalNo ratings yet
- Chile: Networked Readiness Index........................ 38 ..4.6Document1 pageChile: Networked Readiness Index........................ 38 ..4.6Víctor Alfonso Castillo VillchezNo ratings yet
- Networked Readiness Index........................ 77 ..4.0: Rank Value (Out of 139) (1-7)Document1 pageNetworked Readiness Index........................ 77 ..4.0: Rank Value (Out of 139) (1-7)Veda MariaNo ratings yet
- En WBNR Other SRGCM4042 EBookSustainabilityGoodforBusinessDocument196 pagesEn WBNR Other SRGCM4042 EBookSustainabilityGoodforBusinessPedro OliveiraNo ratings yet
- En CNTNT Other ExecutivePlaybookDocument197 pagesEn CNTNT Other ExecutivePlaybookNhat Ngoc TrinhNo ratings yet
- Indonesia: Global Innovation Index (Out of 127) ................... 30.1 87 I: Co Untr Y/e Con Om y Pro File SDocument2 pagesIndonesia: Global Innovation Index (Out of 127) ................... 30.1 87 I: Co Untr Y/e Con Om y Pro File SStefie Laimeheriwa KybernNo ratings yet
- Work X Whitepaper V5Document47 pagesWork X Whitepaper V5ibrahimmohammed6702No ratings yet
- Real Estate Development and ValuationDocument157 pagesReal Estate Development and Valuationmarx dessie100% (1)
- The Global Economy. NYE Stern. Macro 2Document289 pagesThe Global Economy. NYE Stern. Macro 2CRISTIAN MAURICIO GONZALES MURILLONo ratings yet
- Technology and Industry Scoreboard 2009Document146 pagesTechnology and Industry Scoreboard 2009MARYPAZ SILVANo ratings yet
- 8th Pillar: Tourism InfrastructureDocument2 pages8th Pillar: Tourism Infrastructureapi-25966334No ratings yet
- Sustainable Performance Analysis of Selected Smes For DigitalizationDocument24 pagesSustainable Performance Analysis of Selected Smes For DigitalizationKRISHNA PRASAD SAMUDRALANo ratings yet
- Cookbook Inside Final 7.15Document92 pagesCookbook Inside Final 7.15Fe Guerra QuanicoNo ratings yet
- PhilippinesDocument1 pagePhilippinesegghead2point0No ratings yet
- QMS RequirementsDocument60 pagesQMS Requirementsvishwas salunkheNo ratings yet
- Communication Strategy For InstitutionDocument124 pagesCommunication Strategy For InstitutionHPNo ratings yet
- EIC Work Programme 2022Document156 pagesEIC Work Programme 2022irinaNo ratings yet
- Vision 2030 - MTP 2008-2012 - First Annual Progress ReportDocument198 pagesVision 2030 - MTP 2008-2012 - First Annual Progress ReportRyan RoweNo ratings yet
- APA Guideline FinalDocument198 pagesAPA Guideline FinalsolomonNo ratings yet
- 0 DESI 2021 Thematic Chapters Full European Analysis DhhO6dGif25zTsq4LXZQCIrI 80563Document108 pages0 DESI 2021 Thematic Chapters Full European Analysis DhhO6dGif25zTsq4LXZQCIrI 80563Corina CosteaNo ratings yet
- EITM Call For Proposals Guidelines 23-25 - Final Version - Amended 01juneDocument51 pagesEITM Call For Proposals Guidelines 23-25 - Final Version - Amended 01juneIvo HaladinNo ratings yet
- 01 Beyond Strategic Kaizen - Performing Synchronous Profitable Operations - Alin Posteucă - Routledge - Productivity Press (2023)Document324 pages01 Beyond Strategic Kaizen - Performing Synchronous Profitable Operations - Alin Posteucă - Routledge - Productivity Press (2023)phuoc.daoduy1704No ratings yet
- Global Information Technology ReportDocument1 pageGlobal Information Technology Reportcocoy.dayao831100% (2)
- Perfilde Peru 2014Document2 pagesPerfilde Peru 2014Jorge RodríguezNo ratings yet
- Uribe PDFDocument225 pagesUribe PDFSzabó TamásNo ratings yet
- Cotton GinningDocument48 pagesCotton GinningTariq ShafiNo ratings yet
- IbmDocument59 pagesIbmDarren_Fung_8729No ratings yet
- Innovation and Industrial Policies Deschamps Full Chapter PDFDocument61 pagesInnovation and Industrial Policies Deschamps Full Chapter PDFripperblowes100% (6)
- UNIDO IndustrialStatistics Yearbook 2023Document162 pagesUNIDO IndustrialStatistics Yearbook 2023Uzair Khaleeq uz ZamanNo ratings yet
- Microsoft Yahoo! Merger: Novel Innovative Businessmodel of ADocument38 pagesMicrosoft Yahoo! Merger: Novel Innovative Businessmodel of APirmin HeinzerNo ratings yet
- TM-Entrepreneurship and Employabilityskill - TwoDocument228 pagesTM-Entrepreneurship and Employabilityskill - TwoKiya Abdi100% (2)
- Lecture - Notes in Open Economy MacroDocument183 pagesLecture - Notes in Open Economy MacroMadMinarchNo ratings yet
- UNIDO IndustrialStatistics Yearbook 2022Document138 pagesUNIDO IndustrialStatistics Yearbook 2022Miền ĐinhNo ratings yet
- Study Eu Cosmetics Industry PDFDocument165 pagesStudy Eu Cosmetics Industry PDFJa JUOINo ratings yet
- Barend Rogier Final ThesisDocument167 pagesBarend Rogier Final ThesisIrakli SheroziaNo ratings yet
- 88 - Evaluation of Phase 2 of The Commonwealth Private Investment Initia...Document81 pages88 - Evaluation of Phase 2 of The Commonwealth Private Investment Initia...B VNo ratings yet
- Project Report ON Pakistan Telecommunication Company Limited (PTCL)Document20 pagesProject Report ON Pakistan Telecommunication Company Limited (PTCL)Sumera Arif MalikNo ratings yet
- Tsirimpas 2015Document212 pagesTsirimpas 2015fantasy azerbaijanNo ratings yet
- TN Vision 2023 PDFDocument68 pagesTN Vision 2023 PDFRajanbabu100% (1)
- Level III - Cadastral Surveying and Mapping ServiceDocument267 pagesLevel III - Cadastral Surveying and Mapping Servicekenna abdetenNo ratings yet
- Next Generation Manufacturing Technology Initiative PDFDocument253 pagesNext Generation Manufacturing Technology Initiative PDFAndriya Narasimhulu100% (1)
- Convergence: User Expectations, Communications Enablers and Business OpportunitiesFrom EverandConvergence: User Expectations, Communications Enablers and Business OpportunitiesNo ratings yet
- Evaluation of the International Finance Corporation's Global Trade Finance Program, 2006-12From EverandEvaluation of the International Finance Corporation's Global Trade Finance Program, 2006-12No ratings yet
- The Strategy Gap: Leveraging Technology to Execute Winning StrategiesFrom EverandThe Strategy Gap: Leveraging Technology to Execute Winning StrategiesNo ratings yet
- Business Administration PapersDocument36 pagesBusiness Administration Papersinfiniti786No ratings yet
- SSCDocument67 pagesSSCSukanya Ray100% (1)
- Qatar Visa ProcedureDocument4 pagesQatar Visa ProcedureSeven Seas BPONo ratings yet
- Webinar - CPR SAVES TRADES - A MULTI-TIMEFRAME APPROACH - ELMDocument5 pagesWebinar - CPR SAVES TRADES - A MULTI-TIMEFRAME APPROACH - ELMParminder Singh MatharuNo ratings yet
- Micros CoffeeDocument7 pagesMicros CoffeeBlessy LapinaNo ratings yet
- Είδη Μεταφοράς ή Συσκευασίας Από Πλαστικές Ύλες.2016714104726Document959 pagesΕίδη Μεταφοράς ή Συσκευασίας Από Πλαστικές Ύλες.2016714104726traceNo ratings yet
- FirmsDocument5 pagesFirmsl.mufaddalNo ratings yet
- Shy Chapter 7Document18 pagesShy Chapter 7Prinny ThomasNo ratings yet
- Lección 1 / Actividad 1Document2 pagesLección 1 / Actividad 1Marina D'AnconiaNo ratings yet
- James Cantorne Corporation Liquidation and ReorganizationDocument8 pagesJames Cantorne Corporation Liquidation and ReorganizationJames CantorneNo ratings yet
- About CIPETDocument37 pagesAbout CIPETTool Room CIPET VijayawadaNo ratings yet
- Netvault Backup Compatibility Guide For Hardware and Software TechnicalDocument71 pagesNetvault Backup Compatibility Guide For Hardware and Software TechnicalArunmurNo ratings yet
- IFRS 5, Non-Current Assets Held For Sale and Discontinued Operations: Practical Guide To Application and Expected ChangesDocument42 pagesIFRS 5, Non-Current Assets Held For Sale and Discontinued Operations: Practical Guide To Application and Expected ChangesJahidul ShahNo ratings yet
- E Book On ADC ProductsDocument29 pagesE Book On ADC ProductsSudharani YellapragadaNo ratings yet
- Health IQ A - Q-246847 - v1Document3 pagesHealth IQ A - Q-246847 - v1racrabeNo ratings yet
- The Link Between SD and MMDocument3 pagesThe Link Between SD and MMSuneetha MathukumalliNo ratings yet
- Chik-Shampoo Sachet: DR Amit RangnekarDocument46 pagesChik-Shampoo Sachet: DR Amit RangnekarDr Amit Rangnekar67% (3)
- Anmol Setia Project On New Scheme Launch by Present Govement Like Jhan Dhan and Bima Yojana - Undertaken in Oriental Bank of Commerce .Document87 pagesAnmol Setia Project On New Scheme Launch by Present Govement Like Jhan Dhan and Bima Yojana - Undertaken in Oriental Bank of Commerce .ANMOLNo ratings yet
- Securing AnexgateDocument2 pagesSecuring Anexgatebsatish_70No ratings yet
- Class Exercise 1Document2 pagesClass Exercise 1KenWuNo ratings yet
- Doc. 153-1 - Affidavit of R. Lance FloresDocument13 pagesDoc. 153-1 - Affidavit of R. Lance FloresR. Lance FloresNo ratings yet
- Client Feedback FormDocument3 pagesClient Feedback FormnissreenbarakatNo ratings yet
- Sub Topic 2: Approaches To The Study of Agricultural MarketingDocument23 pagesSub Topic 2: Approaches To The Study of Agricultural MarketingRoberto GarciaNo ratings yet
- Dela Rama Et Al Vs Mao - Ao Sugar - CentralDocument2 pagesDela Rama Et Al Vs Mao - Ao Sugar - CentralJude MaiquezNo ratings yet
- Dosti Codename Dosti Group Thane Archstones ASPS Bhavik BhattDocument11 pagesDosti Codename Dosti Group Thane Archstones ASPS Bhavik BhattArchstones Property SolutionsNo ratings yet
- Alur Kerja Erp: Pemasaran Rendal Produksi Logistik & Ekspedisi Supply Chain Finance Accounting Asset QuaryDocument1 pageAlur Kerja Erp: Pemasaran Rendal Produksi Logistik & Ekspedisi Supply Chain Finance Accounting Asset QuaryMuhammad FairusNo ratings yet
- 02 WholeDocument230 pages02 WholeAgnes LiewNo ratings yet