Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Wave Particle Duality
Wave Particle Duality
Uploaded by
MCopyright:
Available Formats
You might also like
- Dual Nature ExplanationDocument9 pagesDual Nature ExplanationDaisy Rizza AgnesNo ratings yet
- Types of Waves EnergyDocument4 pagesTypes of Waves Energyjayson pintorNo ratings yet
- This Article Is About Waves in The Scientific Sense. For Waves On The Surface of The Ocean or Lakes, See - For Other Uses, SeeDocument1 pageThis Article Is About Waves in The Scientific Sense. For Waves On The Surface of The Ocean or Lakes, See - For Other Uses, SeeANMOLNo ratings yet
- Wave HandoutDocument2 pagesWave HandoutBridget CumlatNo ratings yet
- Salas PSQ4W4L1-2Document11 pagesSalas PSQ4W4L1-2riaNo ratings yet
- Waves and OpticsDocument2 pagesWaves and Opticsaligwilfredo08No ratings yet
- Unit 1 LESSON 1 2Document8 pagesUnit 1 LESSON 1 2kachechiekurosakiNo ratings yet
- NsokwjkkkDocument2 pagesNsokwjkkkCitruss TvNo ratings yet
- Radiation: Information From The CosmosDocument56 pagesRadiation: Information From The Cosmosglydel fedelicioNo ratings yet
- WaveDocument1 pageWaveTrideep BanerjeeNo ratings yet
- 4.2 DraftDocument5 pages4.2 DraftCarlos MendozaNo ratings yet
- Dual Nature of LightDocument15 pagesDual Nature of LightUriahs Victor75% (4)
- WaveDocument1 pageWaveAngelo John R. JavinezNo ratings yet
- Behaviors of LightDocument102 pagesBehaviors of Lightemil_masagca1467No ratings yet
- Reflection of Myna RafananDocument2 pagesReflection of Myna Rafananapi-260591778No ratings yet
- Unidad 3 - Espectro Electromagnético (Inglés)Document32 pagesUnidad 3 - Espectro Electromagnético (Inglés)bemdasNo ratings yet
- Factsheet No WaveDocument6 pagesFactsheet No WaveJohn Van Dave TaturoNo ratings yet
- PM289 ch1Document35 pagesPM289 ch1naveedabc986No ratings yet
- Investigation 2.0Document12 pagesInvestigation 2.0GnalixNo ratings yet
- Electromagnetic SpectrumDocument17 pagesElectromagnetic SpectrumAviation/Space History Library100% (4)
- Keph 207Document28 pagesKeph 207Abhinav ScientistNo ratings yet
- Superposition Principle of WavesDocument4 pagesSuperposition Principle of WavesHammad MalikNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Micro-World: Quantum TheoryDocument13 pagesIntroduction To Micro-World: Quantum TheoryTohin MiahNo ratings yet
- CBSE Class 11 Physics Chapter 15 Waves Revision Notes - PDFDocument53 pagesCBSE Class 11 Physics Chapter 15 Waves Revision Notes - PDFrazi sharifNo ratings yet
- Wavelike Behaviors of LightDocument3 pagesWavelike Behaviors of LightLeon MathaiosNo ratings yet
- Quantum Physics: Dan Hooper Fermilab Saturday Morning PhysicsDocument63 pagesQuantum Physics: Dan Hooper Fermilab Saturday Morning Physicsgracc mcdedeNo ratings yet
- Quantum Physics Paper, Intro To Quantum MechanicsDocument4 pagesQuantum Physics Paper, Intro To Quantum MechanicsJuliana YORDANOVA (10F)No ratings yet
- Articulo IeeeDocument5 pagesArticulo IeeeFajardo Acosta Julian CamiloNo ratings yet
- Unit 2 Part 1illumination and General Lighting SystemDocument7 pagesUnit 2 Part 1illumination and General Lighting Systemmahato4120No ratings yet
- Waves and The Wave Motion How Are Waves Produced?Document4 pagesWaves and The Wave Motion How Are Waves Produced?Kevin Felipe Carrillo EspinosaNo ratings yet
- FORCESDocument5 pagesFORCESSohid BacusNo ratings yet
- Different Types of WavesDocument4 pagesDifferent Types of Waveselladionisio01No ratings yet
- Categories of WaveDocument1 pageCategories of WaveMike PicheNo ratings yet
- Lesson 5 Wave Properties of LightDocument6 pagesLesson 5 Wave Properties of LightSherrie CasiaNo ratings yet
- PhysicDocument2 pagesPhysicWan ShamNo ratings yet
- CHP 15-1 IG Types of WavesDocument8 pagesCHP 15-1 IG Types of WavesnoteelleNo ratings yet
- Torsion WavesDocument6 pagesTorsion WavesSamscribding100% (5)
- Wave Theory1Document30 pagesWave Theory1refoyak828No ratings yet
- Light NotesDocument11 pagesLight NotesNaveed IqbalNo ratings yet
- Chem Discussion 2 RepliesDocument2 pagesChem Discussion 2 RepliesBenedict OnyangoNo ratings yet
- Actvivdidad Pre-saberes-Teoría de OndaDocument3 pagesActvivdidad Pre-saberes-Teoría de OndaCarlos BonetNo ratings yet
- MotionDocument15 pagesMotionSherilyn ApostolNo ratings yet
- Physics II - WavesDocument15 pagesPhysics II - WavesVicky Waran RajNo ratings yet
- An Introduction To WaveDocument9 pagesAn Introduction To WaveOyeladun IdrisNo ratings yet
- Physics AssignmentDocument32 pagesPhysics Assignmentkabeer rehmanNo ratings yet
- Waves:: Wave Disturbance Medium or Space Accompanied by A Transfer of EnergyDocument4 pagesWaves:: Wave Disturbance Medium or Space Accompanied by A Transfer of EnergyAriyan Abrar SaifNo ratings yet
- Module 2 Week 3 4Document9 pagesModule 2 Week 3 4LeiRne Jo KBahingawan TanGuidNo ratings yet
- Keph 207Document22 pagesKeph 207ysujeet074No ratings yet
- ThoughtsonEnergyinOscillations ThreetypesDocument3 pagesThoughtsonEnergyinOscillations ThreetypesTito CarloNo ratings yet
- Wave Sound WaveDocument48 pagesWave Sound WaveShiQah EbrAhimNo ratings yet
- " Wave Motion": Ma. Clarissa Cantos - G6 Innah Denyse Almarez - G2 IV - St. Stephen Mrs. Viola AbratiqueDocument12 pages" Wave Motion": Ma. Clarissa Cantos - G6 Innah Denyse Almarez - G2 IV - St. Stephen Mrs. Viola AbratiqueMaria ClarissaNo ratings yet
- Different Types of Wave1Document5 pagesDifferent Types of Wave1Patrick Joshua ZacariasNo ratings yet
- Group 2 Mark Chap 3 Lesson 7 To 12Document30 pagesGroup 2 Mark Chap 3 Lesson 7 To 12allanrnmanalotoNo ratings yet
- Anatomy of An Electromagnetic Wave - Science Mission DirectorateDocument8 pagesAnatomy of An Electromagnetic Wave - Science Mission DirectorateBhaskarKhersaNo ratings yet
- Keph 207Document22 pagesKeph 207Kushal GuptaNo ratings yet
- Investigation Project PhysicsDocument16 pagesInvestigation Project Physicskartikdutt.08No ratings yet
- What Is Electromagnetic Energy: Study of ElectromagnetismDocument23 pagesWhat Is Electromagnetic Energy: Study of ElectromagnetismUma Venkata SumanthNo ratings yet
- Propagation of WaveDocument18 pagesPropagation of WaveVipul KhandelwalNo ratings yet
- The Effects of a Magnetic Field on Radiation -Memoirs by Faraday Kerr and ZeemanFrom EverandThe Effects of a Magnetic Field on Radiation -Memoirs by Faraday Kerr and ZeemanNo ratings yet
Wave Particle Duality
Wave Particle Duality
Uploaded by
MOriginal Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Wave Particle Duality
Wave Particle Duality
Uploaded by
MCopyright:
Available Formats
Wave-Particle Duality
What is wave-particle duality?
Waveparticle duality is a theory that proposes that all matter exhibits the properties of not only particles, which have mass, but also waves, which transfer energy. However, they never act as both a particle and wave at the same time, it depends on how its being observed (the experimental set up). However, this was only fully accepted at the end of the 19th century, when the study of atomic systems required a fundamental revision of the classical ideas about physical objects.
How does a wave behave?
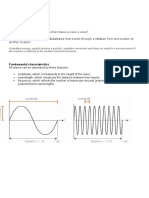
Common types of waves: ripples, surf, ocean
waves, sound waves, radio waves. Waves are oscillations in space and time.
Direction of travel, velocity Displacement
Wavelength ,frequency, velocity and oscillation size defines waves.
How does a particle behave?
Material Objects:
Ball, Car, person, or point like objects called particles. They can be located at a space point at a given time. They can be at rest, moving or accelerating.
Falling Ball
Ground level
The difference in behaviour of waves and particles
When particles collide they cannot pass through each other. They only collide. .
Before collision After collision
Another after collision state shatter
The difference in behaviour of waves and particles
Waves can pass through each other they can superpose (constructive interference) or cancel each other (destructive inference).
Light exhibits wave particle duality as it can refract like a wave, but it can also cause emission of electrons from metal surfaces by having discrete pockets of energy, known as photons. This effect is known as the photoelectric effect. Another example is electrons. Electron beams can be moved to higher energy levels via energy level transitions, but can also be diffracted or bent as they passed through a slit, much like a wave. So, the waves produced by an electron confined in its orbit about the nucleus sets up a standing wave of specific wavelength, energy and frequency like a guitar string sets up a standing wave when plucked.
Examples
www.youtube.com/watch?v=zKdoE1vX7k4
You might also like
- Dual Nature ExplanationDocument9 pagesDual Nature ExplanationDaisy Rizza AgnesNo ratings yet
- Types of Waves EnergyDocument4 pagesTypes of Waves Energyjayson pintorNo ratings yet
- This Article Is About Waves in The Scientific Sense. For Waves On The Surface of The Ocean or Lakes, See - For Other Uses, SeeDocument1 pageThis Article Is About Waves in The Scientific Sense. For Waves On The Surface of The Ocean or Lakes, See - For Other Uses, SeeANMOLNo ratings yet
- Wave HandoutDocument2 pagesWave HandoutBridget CumlatNo ratings yet
- Salas PSQ4W4L1-2Document11 pagesSalas PSQ4W4L1-2riaNo ratings yet
- Waves and OpticsDocument2 pagesWaves and Opticsaligwilfredo08No ratings yet
- Unit 1 LESSON 1 2Document8 pagesUnit 1 LESSON 1 2kachechiekurosakiNo ratings yet
- NsokwjkkkDocument2 pagesNsokwjkkkCitruss TvNo ratings yet
- Radiation: Information From The CosmosDocument56 pagesRadiation: Information From The Cosmosglydel fedelicioNo ratings yet
- WaveDocument1 pageWaveTrideep BanerjeeNo ratings yet
- 4.2 DraftDocument5 pages4.2 DraftCarlos MendozaNo ratings yet
- Dual Nature of LightDocument15 pagesDual Nature of LightUriahs Victor75% (4)
- WaveDocument1 pageWaveAngelo John R. JavinezNo ratings yet
- Behaviors of LightDocument102 pagesBehaviors of Lightemil_masagca1467No ratings yet
- Reflection of Myna RafananDocument2 pagesReflection of Myna Rafananapi-260591778No ratings yet
- Unidad 3 - Espectro Electromagnético (Inglés)Document32 pagesUnidad 3 - Espectro Electromagnético (Inglés)bemdasNo ratings yet
- Factsheet No WaveDocument6 pagesFactsheet No WaveJohn Van Dave TaturoNo ratings yet
- PM289 ch1Document35 pagesPM289 ch1naveedabc986No ratings yet
- Investigation 2.0Document12 pagesInvestigation 2.0GnalixNo ratings yet
- Electromagnetic SpectrumDocument17 pagesElectromagnetic SpectrumAviation/Space History Library100% (4)
- Keph 207Document28 pagesKeph 207Abhinav ScientistNo ratings yet
- Superposition Principle of WavesDocument4 pagesSuperposition Principle of WavesHammad MalikNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Micro-World: Quantum TheoryDocument13 pagesIntroduction To Micro-World: Quantum TheoryTohin MiahNo ratings yet
- CBSE Class 11 Physics Chapter 15 Waves Revision Notes - PDFDocument53 pagesCBSE Class 11 Physics Chapter 15 Waves Revision Notes - PDFrazi sharifNo ratings yet
- Wavelike Behaviors of LightDocument3 pagesWavelike Behaviors of LightLeon MathaiosNo ratings yet
- Quantum Physics: Dan Hooper Fermilab Saturday Morning PhysicsDocument63 pagesQuantum Physics: Dan Hooper Fermilab Saturday Morning Physicsgracc mcdedeNo ratings yet
- Quantum Physics Paper, Intro To Quantum MechanicsDocument4 pagesQuantum Physics Paper, Intro To Quantum MechanicsJuliana YORDANOVA (10F)No ratings yet
- Articulo IeeeDocument5 pagesArticulo IeeeFajardo Acosta Julian CamiloNo ratings yet
- Unit 2 Part 1illumination and General Lighting SystemDocument7 pagesUnit 2 Part 1illumination and General Lighting Systemmahato4120No ratings yet
- Waves and The Wave Motion How Are Waves Produced?Document4 pagesWaves and The Wave Motion How Are Waves Produced?Kevin Felipe Carrillo EspinosaNo ratings yet
- FORCESDocument5 pagesFORCESSohid BacusNo ratings yet
- Different Types of WavesDocument4 pagesDifferent Types of Waveselladionisio01No ratings yet
- Categories of WaveDocument1 pageCategories of WaveMike PicheNo ratings yet
- Lesson 5 Wave Properties of LightDocument6 pagesLesson 5 Wave Properties of LightSherrie CasiaNo ratings yet
- PhysicDocument2 pagesPhysicWan ShamNo ratings yet
- CHP 15-1 IG Types of WavesDocument8 pagesCHP 15-1 IG Types of WavesnoteelleNo ratings yet
- Torsion WavesDocument6 pagesTorsion WavesSamscribding100% (5)
- Wave Theory1Document30 pagesWave Theory1refoyak828No ratings yet
- Light NotesDocument11 pagesLight NotesNaveed IqbalNo ratings yet
- Chem Discussion 2 RepliesDocument2 pagesChem Discussion 2 RepliesBenedict OnyangoNo ratings yet
- Actvivdidad Pre-saberes-Teoría de OndaDocument3 pagesActvivdidad Pre-saberes-Teoría de OndaCarlos BonetNo ratings yet
- MotionDocument15 pagesMotionSherilyn ApostolNo ratings yet
- Physics II - WavesDocument15 pagesPhysics II - WavesVicky Waran RajNo ratings yet
- An Introduction To WaveDocument9 pagesAn Introduction To WaveOyeladun IdrisNo ratings yet
- Physics AssignmentDocument32 pagesPhysics Assignmentkabeer rehmanNo ratings yet
- Waves:: Wave Disturbance Medium or Space Accompanied by A Transfer of EnergyDocument4 pagesWaves:: Wave Disturbance Medium or Space Accompanied by A Transfer of EnergyAriyan Abrar SaifNo ratings yet
- Module 2 Week 3 4Document9 pagesModule 2 Week 3 4LeiRne Jo KBahingawan TanGuidNo ratings yet
- Keph 207Document22 pagesKeph 207ysujeet074No ratings yet
- ThoughtsonEnergyinOscillations ThreetypesDocument3 pagesThoughtsonEnergyinOscillations ThreetypesTito CarloNo ratings yet
- Wave Sound WaveDocument48 pagesWave Sound WaveShiQah EbrAhimNo ratings yet
- " Wave Motion": Ma. Clarissa Cantos - G6 Innah Denyse Almarez - G2 IV - St. Stephen Mrs. Viola AbratiqueDocument12 pages" Wave Motion": Ma. Clarissa Cantos - G6 Innah Denyse Almarez - G2 IV - St. Stephen Mrs. Viola AbratiqueMaria ClarissaNo ratings yet
- Different Types of Wave1Document5 pagesDifferent Types of Wave1Patrick Joshua ZacariasNo ratings yet
- Group 2 Mark Chap 3 Lesson 7 To 12Document30 pagesGroup 2 Mark Chap 3 Lesson 7 To 12allanrnmanalotoNo ratings yet
- Anatomy of An Electromagnetic Wave - Science Mission DirectorateDocument8 pagesAnatomy of An Electromagnetic Wave - Science Mission DirectorateBhaskarKhersaNo ratings yet
- Keph 207Document22 pagesKeph 207Kushal GuptaNo ratings yet
- Investigation Project PhysicsDocument16 pagesInvestigation Project Physicskartikdutt.08No ratings yet
- What Is Electromagnetic Energy: Study of ElectromagnetismDocument23 pagesWhat Is Electromagnetic Energy: Study of ElectromagnetismUma Venkata SumanthNo ratings yet
- Propagation of WaveDocument18 pagesPropagation of WaveVipul KhandelwalNo ratings yet
- The Effects of a Magnetic Field on Radiation -Memoirs by Faraday Kerr and ZeemanFrom EverandThe Effects of a Magnetic Field on Radiation -Memoirs by Faraday Kerr and ZeemanNo ratings yet