Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Magnesium Sulfate Drug Study
Magnesium Sulfate Drug Study
Uploaded by
Monica Lyka BancaleOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Magnesium Sulfate Drug Study
Magnesium Sulfate Drug Study
Uploaded by
Monica Lyka BancaleCopyright:
Available Formats
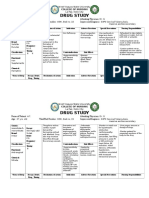
Name of Drug Brand name: magnesium sulfate Dosage/Route/ Frequency 2.
5g through IV 5g through IM at each buttocks q6o Classification Anticonvulsant Mechanism of Actions Cofactor of many enzyme systems involved in neurochemical transmission and muscu lar excitability; prevents or controls seizures by blocking neuromuscular transm ission; attracts and retains water in the intestinal lumen and distends bowel to promote mass movement and relieve constipation y Indications IV or IM: preeclampsia or eclampsia To correct or prevent hypomagnese mia in pat ients or parenteral nutrition y Contraindications Contraindicated with allergy to magnesium products; heart block, myocardial dama ge; fecal impaction, intestinal and biliary tract obstruction, Do not give durin g 2 hours preceding delivery because of risk of magnesium toxicity to the neonat e y Adverse Effects / Side Effects SLE: syndrome joint-swelling, fever) reaction, anemia, agranulocytosis, hepatiti s, glomerulonephriti s, acute renal failure. Nursing Responsibility Assess possibility for interactions w/ other drugs or herbal products the patien t may be taking especially anything that may impact blood pressure before start treatment. y Monitor patients closely during and following infusions. Observe or thostatic precautions. y y
Name of Drug Generic name: hydralazine Brand name: Apresoline Dosage: 5mg Frequency: prn Rout e of administration: Iv-infusion Classification Antihypertensive Mechanism of Actions Direct acting peripheral vasodilator w/c relaxes smooth muscles, reduces blood p ressure w/ reflex increase in heart rate, stroke volume, cardiac output. Indications Essential hypertension, severe essential hypertension, preeclampsia, eclampsia a nd heart failure. Contraindications Hypersensitivity idiopathic system lupus erythematosus and related disease. Seve re tachycardia and heart failure w/ a high cardiac output. y y y y Adverse Effects / Side Effects CNS: weakness, dizziness, fainting CV: palpitations GI: excessive bowel activity Metabolic: Magnesium intoxication; hypocalcemia with tetany y Nursing Responsibility SLE: syndrome joint-swelling, fever) reaction, anemia, agranulocytosis, hepatiti s, glomerulonephritis, acute renal failure.
You might also like
- HydroxyzineDocument3 pagesHydroxyzineapi-3797941100% (2)
- Magnesium Sulfate Drug StudyDocument2 pagesMagnesium Sulfate Drug StudyMaan Molinyawe82% (17)
- PATHOPHYSIOLOGY HmoleDocument4 pagesPATHOPHYSIOLOGY HmoleMonica Lyka Bancale100% (3)
- DRUG STUDY Magnesium SulfateDocument4 pagesDRUG STUDY Magnesium SulfateTempoNo ratings yet
- OB Drug StudyDocument12 pagesOB Drug StudyCj AttoNo ratings yet
- MethergineDocument2 pagesMetherginebdumaranNo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument6 pagesDrug StudyMiru มิริวNo ratings yet
- Magnesium SulfateDocument2 pagesMagnesium SulfateKarla Karina Dela CruzNo ratings yet
- Drug Study DRDocument6 pagesDrug Study DRBheigh Lomitao AlbueraNo ratings yet
- MisoprostolDocument3 pagesMisoprostolMichael Aditya LesmanaNo ratings yet
- Drug Study - Magnesium SulfateDocument6 pagesDrug Study - Magnesium SulfatePrincess Alane MorenoNo ratings yet
- Drug Study...Document5 pagesDrug Study...Ezra Dizon ManzanoNo ratings yet
- Gentamicin Pedia Drug StudyDocument3 pagesGentamicin Pedia Drug StudyGong AllenaNo ratings yet
- LidocaineDocument2 pagesLidocaineAhprelle Quiring Rodiel100% (1)
- AcyclovirDocument1 pageAcyclovirMuhammad ArsalanNo ratings yet
- Phenergan (Promethazine)Document1 pagePhenergan (Promethazine)E100% (1)
- Methyldopa, Losartan K, Ascorbic AcidDocument4 pagesMethyldopa, Losartan K, Ascorbic AcidRico Mae ValenciaNo ratings yet
- Cefoxitin Sodium MefoxinDocument3 pagesCefoxitin Sodium MefoxinKristi WrayNo ratings yet
- ParacetamolDocument2 pagesParacetamolBlesyl Sison Mabano100% (1)
- Drug StudyDocument11 pagesDrug StudyNedemar OcampoNo ratings yet
- Learning Derived (Lysha)Document1 pageLearning Derived (Lysha)Choy DavidNo ratings yet
- KamanJan ChloroquineDocument3 pagesKamanJan Chloroquinekimberly_caberteNo ratings yet
- MetoclopramideDocument3 pagesMetoclopramideapi-3797941100% (1)
- AmbroxolDocument1 pageAmbroxolPrecious CarmelaNo ratings yet
- Drug Study MgSO4Document1 pageDrug Study MgSO4Brigette Quirante100% (1)
- Meclizine Hydro ChlorideDocument3 pagesMeclizine Hydro Chlorideapi-3797941100% (1)
- Dextrose 50 InjectionDocument6 pagesDextrose 50 InjectionLip StickNo ratings yet
- Pseudoephedrine HydrochlorideDocument6 pagesPseudoephedrine HydrochlorideAbdelrhman AboodaNo ratings yet
- NifedipineDocument2 pagesNifedipineapi-3797941100% (3)
- PiroxicamDocument2 pagesPiroxicamVirginia Aira Lara MarquezNo ratings yet
- Drug Study For FractureDocument4 pagesDrug Study For FractureitsmeayaNo ratings yet
- OxytocinDocument1 pageOxytocinAudrey Martin RañisesNo ratings yet
- BuscopanDocument2 pagesBuscopancen janber cabrillosNo ratings yet
- DrugsDocument10 pagesDrugsRebecca JolieNo ratings yet
- Drug Name Mechanism of Action Administration Indications Contraindications Adverse Reactions Nursing ResponsibilitiesDocument1 pageDrug Name Mechanism of Action Administration Indications Contraindications Adverse Reactions Nursing ResponsibilitiesIvan Liquiran AvenadoNo ratings yet
- Postop Drug2Document3 pagesPostop Drug2zbestgurlNo ratings yet
- Drug Study HepatitisDocument7 pagesDrug Study HepatitisKateLayaogNo ratings yet
- NystatinDocument3 pagesNystatinapi-3797941100% (3)
- Drug StudyDocument9 pagesDrug StudyVicenia BalloganNo ratings yet
- Drug Study Delivery RoomDocument7 pagesDrug Study Delivery RoomkhleeoNo ratings yet
- Lansoprazole (Prevacid)Document3 pagesLansoprazole (Prevacid)tripj33No ratings yet
- Pilocarpine (Drug Monograph)Document1 pagePilocarpine (Drug Monograph)Muhammad ArsalanNo ratings yet
- Drug Name Mechanism of Action Administration Indication Contraindication Adverse Effects Nursing ResponsibilitiesDocument1 pageDrug Name Mechanism of Action Administration Indication Contraindication Adverse Effects Nursing ResponsibilitiesIvan Liquiran AvenadoNo ratings yet
- Nalbuphine HydrochlorideDocument6 pagesNalbuphine HydrochlorideMarie Therese Montaño Subong100% (1)
- Drug StudyDocument2 pagesDrug Studymegreen GamingNo ratings yet
- Folic AcidDocument3 pagesFolic Acidapi-37979410% (1)
- Drug StudyDocument4 pagesDrug StudyLene ThereseNo ratings yet
- Drug AnalysisDocument3 pagesDrug AnalysisAbby BorabienNo ratings yet
- CefuroximeDocument11 pagesCefuroximeAlmira Ballesteros CestonaNo ratings yet
- Terbutaline SulfateDocument2 pagesTerbutaline SulfateRhoellet VenzonNo ratings yet
- HNBBDocument3 pagesHNBBManelle SingzonNo ratings yet
- NifedipineDocument3 pagesNifedipineNovi YulianaNo ratings yet
- Ditropan Drug CardDocument2 pagesDitropan Drug CardBenNo ratings yet
- Amoxicillin Tri Hydrate Table FormatDocument3 pagesAmoxicillin Tri Hydrate Table FormatNico DonatoNo ratings yet
- DORMICUMDocument1 pageDORMICUMArian Rose100% (1)
- MethergineDocument3 pagesMethergineJohn AlanoNo ratings yet
- Lui Sh-Colored Lips and Finger Nails Blur Red VisionDocument1 pageLui Sh-Colored Lips and Finger Nails Blur Red VisionMagdayao Romamea100% (1)
- Drug Study and Mental Health AssessmentDocument8 pagesDrug Study and Mental Health AssessmentVincent Quitoriano100% (1)
- Folic AcidDocument1 pageFolic AcidCassie100% (2)
- Lyrica (Pregabalin)Document2 pagesLyrica (Pregabalin)Laromac RolandNo ratings yet
- The Ride of Your Life: What I Learned about God, Love, and Adventure by Teaching My Son to Ride a BikeFrom EverandThe Ride of Your Life: What I Learned about God, Love, and Adventure by Teaching My Son to Ride a BikeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (2)
- Conjunctions: Coordinating ConjunctionDocument2 pagesConjunctions: Coordinating ConjunctionMonica Lyka BancaleNo ratings yet
- Ampicillin Sulbactam SodiumDocument2 pagesAmpicillin Sulbactam SodiumMonica Lyka BancaleNo ratings yet
- AppendicesDocument18 pagesAppendicesMonica Lyka BancaleNo ratings yet
- SalbutamolDocument1 pageSalbutamolMonica Lyka BancaleNo ratings yet
- Monica Lyka Bancale BSN 3A: Microliter (MCL)Document3 pagesMonica Lyka Bancale BSN 3A: Microliter (MCL)Monica Lyka BancaleNo ratings yet
- Patho CrohnsDocument1 pagePatho CrohnsMonica Lyka BancaleNo ratings yet