Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Finite Difference Method
Finite Difference Method
Uploaded by
sanketdange2007Copyright:
Available Formats
You might also like
- Fluid Mechanics 4e Solutions - Kundu CohenDocument155 pagesFluid Mechanics 4e Solutions - Kundu CohenJoge Caracol93% (43)
- AP Calc AB/BC Review SheetDocument2 pagesAP Calc AB/BC Review Sheetmhayolo69100% (1)
- Math102 Equation SheetDocument0 pagesMath102 Equation SheetMaureen LaiNo ratings yet
- Numerical Methods For Parabolic Equations-IDocument11 pagesNumerical Methods For Parabolic Equations-IPrasad BairyNo ratings yet
- 2010 TJC SolDocument12 pages2010 TJC SolPooja KapurNo ratings yet
- Blasius EquationDocument2 pagesBlasius Equationsanketdange2007No ratings yet
- Dance Drama Lesson Plan TemplateDocument4 pagesDance Drama Lesson Plan Templateapi-293674497No ratings yet
- CFD Lecture 3: Dr. Thomas J. BarberDocument24 pagesCFD Lecture 3: Dr. Thomas J. BarberTareq DahbNo ratings yet
- Calc 1 Lecture Notes Section 4.7 1 of 8: FXDXM FC X Ba X N C A XiDocument8 pagesCalc 1 Lecture Notes Section 4.7 1 of 8: FXDXM FC X Ba X N C A Ximasyuki1979No ratings yet
- Calc 1 Lecture Notes Section 4.5 1 of 4Document4 pagesCalc 1 Lecture Notes Section 4.5 1 of 4masyuki1979No ratings yet
- Class 9Document13 pagesClass 9tneshoeNo ratings yet
- Crack Propagation Methods in LS DYNADocument24 pagesCrack Propagation Methods in LS DYNAm085No ratings yet
- Integrals FormulasDocument10 pagesIntegrals Formulas007phantomNo ratings yet
- Numerical Integration of 3D Reaction-Diffusion Equations (Difference Methods For Parabolic Pdes, Boundary Value Problem)Document13 pagesNumerical Integration of 3D Reaction-Diffusion Equations (Difference Methods For Parabolic Pdes, Boundary Value Problem)Shalini JagtianiNo ratings yet
- Properties of Numerical MethodsDocument19 pagesProperties of Numerical MethodsSsheshan PugazhendhiNo ratings yet
- CFDDocument22 pagesCFDGoogle DocsNo ratings yet
- Load Flow - 3 - 2Document13 pagesLoad Flow - 3 - 2rauf2063036No ratings yet
- Formule Ploce I LjuskeDocument18 pagesFormule Ploce I LjuskeAmar MušovićNo ratings yet
- Chew 1505 CH2Document66 pagesChew 1505 CH2lzyabc597No ratings yet
- Moving Coil GalvonometerDocument27 pagesMoving Coil GalvonometerSani SweetuNo ratings yet
- Whole Digital Communication PPT-libreDocument319 pagesWhole Digital Communication PPT-librePiyush GuptaNo ratings yet
- Implicit MethodDocument30 pagesImplicit MethodshekhadaaNo ratings yet
- 05 FiniteElementMethodDocument83 pages05 FiniteElementMethodmileNo ratings yet
- Calculus SummaryDocument3 pagesCalculus SummaryJay JayNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 SolutionDocument5 pagesChapter 1 SolutionFaraa BellaNo ratings yet
- Estabilidad Interna y Entrada-Salida de Sistemas Continuos: Udec - DieDocument10 pagesEstabilidad Interna y Entrada-Salida de Sistemas Continuos: Udec - DieagustinpinochetNo ratings yet
- Groundwater Modeling: Finite Element MethodDocument32 pagesGroundwater Modeling: Finite Element Methodmaribo2005No ratings yet
- Financial Mathematics Course FIN 118 Unit Course 4 Number Unit Integral Calculus Unit SubjectDocument17 pagesFinancial Mathematics Course FIN 118 Unit Course 4 Number Unit Integral Calculus Unit Subjectayadi_ezer6795No ratings yet
- Rss Grad Diploma Module3 Solutions Specimen B PDFDocument10 pagesRss Grad Diploma Module3 Solutions Specimen B PDFA PirzadaNo ratings yet
- UNIT-III The Normal DensityDocument29 pagesUNIT-III The Normal DensityJoyce GeorgeNo ratings yet
- m820 Sol 2011Document234 pagesm820 Sol 2011Tom DavisNo ratings yet
- Differentiation Definition: Let: y FX Ab FXDocument25 pagesDifferentiation Definition: Let: y FX Ab FXRazvan Gabriel RizeaNo ratings yet
- Solutions To Home Practice Test/Mathematics: Differential Equation HWT - 1Document7 pagesSolutions To Home Practice Test/Mathematics: Differential Equation HWT - 1varunkohliinNo ratings yet
- Surface IntegralsDocument18 pagesSurface Integralsmasyuki1979No ratings yet
- Basic Aspects of DiscretizationDocument56 pagesBasic Aspects of DiscretizationSuta VijayaNo ratings yet
- Homework 4: Benjamin StahlDocument9 pagesHomework 4: Benjamin StahlReza AhmedNo ratings yet
- (V) ParabolicDocument21 pages(V) ParabolicM Haroon SheikhNo ratings yet
- A. Two-Variable Linear Regression Model:: X Y ε β α X X x Y Y y i = 1, 2, …, NDocument21 pagesA. Two-Variable Linear Regression Model:: X Y ε β α X X x Y Y y i = 1, 2, …, NBabagbéto YanNo ratings yet
- Discretization-Finite Difference, Finite Element Methods: D Dy Ax BX DX DX Dy DX Dy Ax A DXDocument6 pagesDiscretization-Finite Difference, Finite Element Methods: D Dy Ax BX DX DX Dy DX Dy Ax A DXratchagar aNo ratings yet
- Exam Formulas For CALCULUSDocument3 pagesExam Formulas For CALCULUSWendy HuynhNo ratings yet
- AJC JC 2 H2 Maths 2011 Mid Year Exam Solutions Paper 1Document12 pagesAJC JC 2 H2 Maths 2011 Mid Year Exam Solutions Paper 1jimmytanlimlongNo ratings yet
- 7A Definite IntegrationDocument51 pages7A Definite IntegrationSri DNo ratings yet
- Chap 8Document17 pagesChap 8Aryce_No ratings yet
- Formule ZavršneDocument4 pagesFormule ZavršnestudentftnNo ratings yet
- Summary 6-Green's TheoremDocument6 pagesSummary 6-Green's TheoremAjith KrishnanNo ratings yet
- Calc 2 Lecture Notes Section 7.2 1 of 8: Yx UxvyDocument8 pagesCalc 2 Lecture Notes Section 7.2 1 of 8: Yx Uxvymasyuki1979No ratings yet
- Math ReferenceDocument24 pagesMath ReferenceSujib BarmanNo ratings yet
- Get Full PointsDocument6 pagesGet Full PointsChing-Ting WuNo ratings yet
- Techniques of IntegrationDocument61 pagesTechniques of IntegrationAma PredaNo ratings yet
- The Handbook of Formulas and Tables For Signal ProcessingDocument17 pagesThe Handbook of Formulas and Tables For Signal ProcessingmadhurocksktmNo ratings yet
- Maths FormulaDocument4 pagesMaths Formulamickey_disney93No ratings yet
- Robust Control Design Via Feedback Linearization: Harry G. KwatnyDocument22 pagesRobust Control Design Via Feedback Linearization: Harry G. KwatnyChernet TugeNo ratings yet
- Chapter5 Calculus of VariationsDocument30 pagesChapter5 Calculus of VariationsRaja RamachandranNo ratings yet
- Analytic Geometry: Graphic Solutions Using Matlab LanguageFrom EverandAnalytic Geometry: Graphic Solutions Using Matlab LanguageNo ratings yet
- Trigonometric Ratios to Transformations (Trigonometry) Mathematics E-Book For Public ExamsFrom EverandTrigonometric Ratios to Transformations (Trigonometry) Mathematics E-Book For Public ExamsRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Mathematics 1St First Order Linear Differential Equations 2Nd Second Order Linear Differential Equations Laplace Fourier Bessel MathematicsFrom EverandMathematics 1St First Order Linear Differential Equations 2Nd Second Order Linear Differential Equations Laplace Fourier Bessel MathematicsNo ratings yet
- Wright Turn - Flying ArenaDocument4 pagesWright Turn - Flying Arenasanketdange2007No ratings yet
- Action Carv 5Document36 pagesAction Carv 5sanketdange2007No ratings yet
- Thermal Guidelines For Data Processing Environments, Second EditionDocument1 pageThermal Guidelines For Data Processing Environments, Second Editionsanketdange2007No ratings yet
- Cooling Tower DesingnDocument4 pagesCooling Tower Desingnsanketdange2007No ratings yet
- Thinking Outside The BoxDocument9 pagesThinking Outside The Boxsanketdange2007No ratings yet
- Thermal Guidelines For Data Processing Environments, Second EditionDocument1 pageThermal Guidelines For Data Processing Environments, Second Editionsanketdange2007No ratings yet
- Blasius PDFDocument2 pagesBlasius PDFsanketdange2007No ratings yet
- Comparing Data Center & Computer Thermal DesignDocument5 pagesComparing Data Center & Computer Thermal Designsanketdange2007No ratings yet
- Unix Shells Bash Fish KSH TCSH Zsh-HyperpolyglotDocument23 pagesUnix Shells Bash Fish KSH TCSH Zsh-Hyperpolyglotsanketdange2007No ratings yet
- CPP Crash Intro PDFDocument105 pagesCPP Crash Intro PDFsanketdange2007No ratings yet
- Duct Optimization Using Fluent Adjoint SolverDocument42 pagesDuct Optimization Using Fluent Adjoint Solversanketdange2007No ratings yet
- Linux CommandsDocument2,054 pagesLinux Commandssanketdange2007No ratings yet
- Heat & Mass Transfer JournalDocument7 pagesHeat & Mass Transfer Journalsanketdange2007No ratings yet
- B e (M) I & II 2008 CourseDocument43 pagesB e (M) I & II 2008 Coursenutanc2010No ratings yet
- CFD Simulation in Town Planning Case StudyDocument8 pagesCFD Simulation in Town Planning Case Studysanketdange2007No ratings yet
- Steam Path Analysis: A Tool To Monitor The Health of A Steam TurbineDocument30 pagesSteam Path Analysis: A Tool To Monitor The Health of A Steam Turbinesanketdange2007No ratings yet
- BuoyancyDocument8 pagesBuoyancysanketdange2007No ratings yet
- Solar PWR SatelliteDocument19 pagesSolar PWR Satellitesanketdange2007No ratings yet
- Boulanger and BeatyDocument13 pagesBoulanger and BeatySarah WilliamsNo ratings yet
- SUSTECH MathDocument24 pagesSUSTECH Matht0xic.369xNo ratings yet
- FaustinoDocument1 pageFaustinoEzra Orita CeletariaNo ratings yet
- RedoDocument1 pageRedogmpzgamerNo ratings yet
- Siemens Brazil enDocument5 pagesSiemens Brazil ensterilemovieNo ratings yet
- Closed Loop Control SystemDocument5 pagesClosed Loop Control Systembaswa vamsi krishnaNo ratings yet
- What Is New in SolidCAM GPPTool 2011Document37 pagesWhat Is New in SolidCAM GPPTool 2011pannickNo ratings yet
- A LatheDocument3 pagesA LatheDReena JoyceNo ratings yet
- Knife Gate Valve: Product DescriptionDocument2 pagesKnife Gate Valve: Product DescriptionTamil SelvanNo ratings yet
- Advanced Earthquake Resistant DesignDocument17 pagesAdvanced Earthquake Resistant Designraju619No ratings yet
- Digital VocabDocument2 pagesDigital Vocabdesikudi9000No ratings yet
- c5 Conc1 EnergeticsDocument7 pagesc5 Conc1 EnergeticsAlexandra AlexandraNo ratings yet
- Mathematics HL - Practice QuestionsDocument152 pagesMathematics HL - Practice QuestionsPyjama ManNo ratings yet
- 5085DL / 5055DL SeriesDocument2 pages5085DL / 5055DL SeriesMinh TranNo ratings yet
- RPP in EnglishDocument12 pagesRPP in EnglishAnggi MijayaNo ratings yet
- Water ConingDocument96 pagesWater ConingMubin Ashraf Sheikh100% (1)
- ΕΓΧΕΙΡΙΔΙΟ ΠΛΥΝΤΗΡΙΟΥ ΠΙΑΤΩΝ - ΑΝΤΑΛΛΑΚΤΙΚΑDocument16 pagesΕΓΧΕΙΡΙΔΙΟ ΠΛΥΝΤΗΡΙΟΥ ΠΙΑΤΩΝ - ΑΝΤΑΛΛΑΚΤΙΚΑΤΣΙΜΠΙΔΗΣ ΠΑΝΑΓΙΩΤΗΣNo ratings yet
- FuturaPC EngDocument36 pagesFuturaPC EngRashika SharmaNo ratings yet
- 1976 Melling Turbulent Flow in A Rectangular DuctDocument27 pages1976 Melling Turbulent Flow in A Rectangular Ductedward agimNo ratings yet
- Bahawalpur District Profile 2013Document138 pagesBahawalpur District Profile 2013Shaheer Rizvi100% (1)
- Demand Forecasting and Estimating Methods ProblemsDocument22 pagesDemand Forecasting and Estimating Methods ProblemsNagarjuna ReddyNo ratings yet
- An Efficient Bi-Layer Intumescent Paint Metal Laminate Fire Barrier For Various Substrates: Extension To Other ApplicationDocument16 pagesAn Efficient Bi-Layer Intumescent Paint Metal Laminate Fire Barrier For Various Substrates: Extension To Other ApplicationTan Keng ChowNo ratings yet
- SumanthDocument7 pagesSumanthSumanth ITonNo ratings yet
- Gnosis Issue 30Document0 pagesGnosis Issue 30utoob365100% (5)
- 205-03 Front Drive Axle and Differential - Diagnosis and TestingDocument6 pages205-03 Front Drive Axle and Differential - Diagnosis and TestingCARLOS LIMADANo ratings yet
- SelectaDocument55 pagesSelectaHuong Cam ThuyNo ratings yet
- Chapter 5 - Introduction To Differential Analysis of Fluid MotionDocument4 pagesChapter 5 - Introduction To Differential Analysis of Fluid MotionBin RenNo ratings yet
- Introductory Botulinum PresentationDocument113 pagesIntroductory Botulinum Presentationprontaprintpottersbar100% (5)
- Ralph Menikoff and Thomas D Sewell - Constituent Properties of HMX Needed For Mesoscale SimulationsDocument23 pagesRalph Menikoff and Thomas D Sewell - Constituent Properties of HMX Needed For Mesoscale SimulationsKommissar1981No ratings yet
Finite Difference Method
Finite Difference Method
Uploaded by
sanketdange2007Original Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Finite Difference Method
Finite Difference Method
Uploaded by
sanketdange2007Copyright:
Available Formats
1
Discretization
What?
Analytical Solution : Continuous
Numerical Solution : Discrete
Types of Discretization Technique
FDM (Finite Difference Method): Most popular
during the early days of CFD
FVM (Finite Volume Method): Gives greater
flexibility in handling complex geometry
FEM (Finite Element Method): More commonly
used in Solid Mechanics rather than Fluid
Mechanics
2
FDM: Discrete Grid Points
(i,j)
P
P
(i,j) (i+1,j) (i-1,j)
(i,j+1) (i+1,j+1) (i-1,j+1)
(i,j-1) (i+1,j-1) (i-1,j-1)
i
j
3
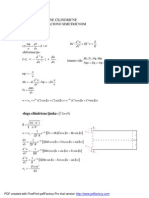
FDM: Finite Difference Quotient
Taylor Series Expansion
Example :
2 2
2
2 1
3
4
( ) sin 2
0.2, 0.02 ( ) 0.9511
( ) ( )
( ) ( )
2
0.9823 3.176%
0.9899 %
0.9824 %
f x x
x x f x x
f x f x x
f x x f x x
x x
f f
f
f
=
= = + =
+ = + + +
= =
=
=
( Error)
(0.775 Error)
(0.01 Error)
I Guess Add to
Capture Slope
Add to account
for Curvature
1 2
3
4
x
f(x)
4
FDM: Finite Difference Quotient
Taylor Series Expansion
I Order Forward Difference
2 2 3 3
1 , ,
2 3
,
, ,
2 2 3 3
1 , ,
2 3
,
, ,
2 3
1 , ,
2 3
,
,
2 3
2 3
2
i j i j
i j
i j i j
i j i j
i j
i j i j
i j i j
i j
i j
x x
x
x x x
x x
x
x x x
x
x x x x
+
+
| | | |
| |
= + + + +
| | |
\ .
\ . \ .
| | | |
| |
= + +
| | |
\ .
\ . \ .
| | |
| |
= +
`
| |
\ .
) \ . \
( )
2
,
1 , ,
,
3
i j
i j i j
i j
x
x
x x
+
(
|
+ (
|
( .
| |
= +
`
|
\ .
)
O
Finite Difference Quotient
T.E (Truncation Error)
I Order Accurate
(i+1,j)
(i,j)
(+)
(-)
x
5
FDM: Finite Difference Quotient
I Order Backward Difference
II Order Central Difference
( )
2 3 2
, 1,
2 3
,
, ,
, 1,
,
3 2 5 4
1, 1,
3 5
,
, ,
2 3
2 3 5
i j i j
i j
i j i j
i j i j
i j
i j i j
i j
i j i j
x x
x x x x
x
x x
x x
x x x x
+
(
| | | |
| |
= + + (
`
| | |
\ .
( ) \ . \ .
| |
= +
`
|
\ .
)
| | | |
| |
= +
`
| | |
\ .
) \ . \ .
( )
1, 1,
2
,
2
i j i j
i j
x
x x
+
(
(
(
| |
= +
`
|
\ .
)
O II Order Accurate
(i-1,j)
(i,j)
(+)
(-)
x
(i-1,j)
(+)
(-)
x
x
(i+1,j)
6
FDM: Finite Difference Quotient
II Order Central Second Difference
IV Order Second Difference
( )
2 4 2 6 4
1, , 1,
2 2 4 6
, , ,
2
1, , 1,
2
2 2
,
2
2, 1, , 1, 1,
2
,
2
2
4 6
2
16 30 16
1
i j i j i j
i j i j i j
i j i j i j
i j
i j i j i j i j i j
i j
x x
x x x x
x
x x
x
+
+
+ +
(
+
| | | | | |
= + +
(
`
| | |
( ) \ . \ . \ .
+
| |
= +
`
|
) \ .
+ +
| |
=
|
\ .
O
( )
( )
4
2
2
x
x
+
`
)
O
II Order Accurate
(+)
(+)
x
x (-2)
(i-1,j) (i,j) (i+1,j)
7
FDM: Finite Difference Quotient
Higher Order Accurate Difference
Quotients
Disadvantage : By requiring more
neighboring grid points, results in more
computational time for each grid point
computation
Advantage : Smaller number of total grid
points in a flow solution to obtain
comparable overall accuracy
II Order accuracy has been accepted in
the vast majority of CFD applications
8
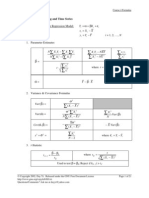
FDM: Finite Difference Equation
and Solution Methodology
1-D Steady State Conduction
G.E:
B,Cs:
F.D.Eq. :
Tridiagonal Matrix:
Solver
Jacobi
Gauss-Seidel
2
2
1 2
1 1 1 1
2
2 1
3
4
5
6 2
0
At 0, ; ,
2
0
2
2 1 0 0 0
0 1 2 1 0 0
0 0 1 2 1 0
0 0 0 1 2 1
0 0 0 1 2
b b
i i i i i
i
b
b
T
x
x T T x L T T
T T T T T
T
x
T T
T
T
T
T T
+ +
= = = =
+ +
= =
( ( (
( ( (
( ( (
( ( ( =
( ( (
( ( (
( ( (
L
T
b1 T
b2
i=1 2 3 4 5 6 7
9
FDM: Finite Difference Equation
and Solution Methodology
1-D Unsteady State Conduction
G.E:
I.C & B.Cs:
F.D.Eq. :
Reliability of num. results (within T.E.) Vs analytical
results
If the difference equation is consistent
If the numerical algorithm is stable
If the B.Cs are handled properly
{ }
2
2
0
1
2
1 1
2
At t 0;
2
T.E=O( t, x )
As t 0 & x 0 T.E 0 F.D.Eq. is Consistent
n n n n n
i i i i i
T T
t x
T T
T T T T T
t x
+
+
=
= =
+
=
T
b1 T
b2
i=1 2 3 4 5 6 7
T
b1 T
b2
T
b1 T
b2
n+1
n
n-1
10
FDM: Finite Difference Equation
and Solution Methodology
1-D Steady State Convection-Diffusion
( )
( )
2
2
0
/
0 0
1 1
B. C : at 0, at
1
E x act S o lu t i o n :
1
W h ere /
Alg eb rai c E q u at i o n : 0
L
xP e L
L
P e
i i i
E i P i W i
u
x x
x x L
e
e
P e u L
A A A
=
= = = =
= +
=
+ + =
F i n i te D i f f eren ce Q u o ti en t
2
1 1
2 2
2
2
:
/ ; ( )
i i i
i
d i d i d i d i d i
E W P E W
x x
A x A A A A
+
| |
+
|
\ .
= = = +
:
D i f f u s i o n
x
L
0
Pe=0
Pe>0
Pe<0
11
FDM: Finite Difference Equation
and Solution Methodology
1-D Steady State Convection-Diffusion
( )
( )
1
1
1 1
, 0
, 0
min( , 0) / ; max( , 0) / ; ( )
2
/ 2
i i
i i
i
ci ci ci ci ci
E W P E W
i i
i
ci ci
E W
u u
u
x
x
u u
x
A u x A u x A A A
u
u
x x
A u x A
+
+
>
<
= = = +
(
(
= =
if
Convection: UDS
if
CDS
0
; ( ) 0
1.0, 1.0, 1.0, 0.02,
0 1.0; 11 11 51 51
ci ci ci
P E W
L
A A A
L u
= + =
= = = =
= = =
Example Prob. :
and Gridsize and
12
FDM: Finite Difference Equation
and Solution Methodology
1-D Unsteady State Convection-Diffusion
( )
2
2
1
1 1 1 1
2
1
1 1 1 1
2
2
2
2
2
min( , 0) / ; max( , 0) / ; (
n n n n n n n
i i i i i i i
n n ci n ci n ci n n n n
i i E i P i W i i i i
ci ci ci ci
E W P E W
u
t x x
u
t x x
A A A
u
t x x
A u x A u x A A A
+
+ +
+
+ +
+ =
+
+ =
+ + +
+ =
= = = +
F.D.Eq.:
CDS
UDS
)
ci
You might also like
- Fluid Mechanics 4e Solutions - Kundu CohenDocument155 pagesFluid Mechanics 4e Solutions - Kundu CohenJoge Caracol93% (43)
- AP Calc AB/BC Review SheetDocument2 pagesAP Calc AB/BC Review Sheetmhayolo69100% (1)
- Math102 Equation SheetDocument0 pagesMath102 Equation SheetMaureen LaiNo ratings yet
- Numerical Methods For Parabolic Equations-IDocument11 pagesNumerical Methods For Parabolic Equations-IPrasad BairyNo ratings yet
- 2010 TJC SolDocument12 pages2010 TJC SolPooja KapurNo ratings yet
- Blasius EquationDocument2 pagesBlasius Equationsanketdange2007No ratings yet
- Dance Drama Lesson Plan TemplateDocument4 pagesDance Drama Lesson Plan Templateapi-293674497No ratings yet
- CFD Lecture 3: Dr. Thomas J. BarberDocument24 pagesCFD Lecture 3: Dr. Thomas J. BarberTareq DahbNo ratings yet
- Calc 1 Lecture Notes Section 4.7 1 of 8: FXDXM FC X Ba X N C A XiDocument8 pagesCalc 1 Lecture Notes Section 4.7 1 of 8: FXDXM FC X Ba X N C A Ximasyuki1979No ratings yet
- Calc 1 Lecture Notes Section 4.5 1 of 4Document4 pagesCalc 1 Lecture Notes Section 4.5 1 of 4masyuki1979No ratings yet
- Class 9Document13 pagesClass 9tneshoeNo ratings yet
- Crack Propagation Methods in LS DYNADocument24 pagesCrack Propagation Methods in LS DYNAm085No ratings yet
- Integrals FormulasDocument10 pagesIntegrals Formulas007phantomNo ratings yet
- Numerical Integration of 3D Reaction-Diffusion Equations (Difference Methods For Parabolic Pdes, Boundary Value Problem)Document13 pagesNumerical Integration of 3D Reaction-Diffusion Equations (Difference Methods For Parabolic Pdes, Boundary Value Problem)Shalini JagtianiNo ratings yet
- Properties of Numerical MethodsDocument19 pagesProperties of Numerical MethodsSsheshan PugazhendhiNo ratings yet
- CFDDocument22 pagesCFDGoogle DocsNo ratings yet
- Load Flow - 3 - 2Document13 pagesLoad Flow - 3 - 2rauf2063036No ratings yet
- Formule Ploce I LjuskeDocument18 pagesFormule Ploce I LjuskeAmar MušovićNo ratings yet
- Chew 1505 CH2Document66 pagesChew 1505 CH2lzyabc597No ratings yet
- Moving Coil GalvonometerDocument27 pagesMoving Coil GalvonometerSani SweetuNo ratings yet
- Whole Digital Communication PPT-libreDocument319 pagesWhole Digital Communication PPT-librePiyush GuptaNo ratings yet
- Implicit MethodDocument30 pagesImplicit MethodshekhadaaNo ratings yet
- 05 FiniteElementMethodDocument83 pages05 FiniteElementMethodmileNo ratings yet
- Calculus SummaryDocument3 pagesCalculus SummaryJay JayNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 SolutionDocument5 pagesChapter 1 SolutionFaraa BellaNo ratings yet
- Estabilidad Interna y Entrada-Salida de Sistemas Continuos: Udec - DieDocument10 pagesEstabilidad Interna y Entrada-Salida de Sistemas Continuos: Udec - DieagustinpinochetNo ratings yet
- Groundwater Modeling: Finite Element MethodDocument32 pagesGroundwater Modeling: Finite Element Methodmaribo2005No ratings yet
- Financial Mathematics Course FIN 118 Unit Course 4 Number Unit Integral Calculus Unit SubjectDocument17 pagesFinancial Mathematics Course FIN 118 Unit Course 4 Number Unit Integral Calculus Unit Subjectayadi_ezer6795No ratings yet
- Rss Grad Diploma Module3 Solutions Specimen B PDFDocument10 pagesRss Grad Diploma Module3 Solutions Specimen B PDFA PirzadaNo ratings yet
- UNIT-III The Normal DensityDocument29 pagesUNIT-III The Normal DensityJoyce GeorgeNo ratings yet
- m820 Sol 2011Document234 pagesm820 Sol 2011Tom DavisNo ratings yet
- Differentiation Definition: Let: y FX Ab FXDocument25 pagesDifferentiation Definition: Let: y FX Ab FXRazvan Gabriel RizeaNo ratings yet
- Solutions To Home Practice Test/Mathematics: Differential Equation HWT - 1Document7 pagesSolutions To Home Practice Test/Mathematics: Differential Equation HWT - 1varunkohliinNo ratings yet
- Surface IntegralsDocument18 pagesSurface Integralsmasyuki1979No ratings yet
- Basic Aspects of DiscretizationDocument56 pagesBasic Aspects of DiscretizationSuta VijayaNo ratings yet
- Homework 4: Benjamin StahlDocument9 pagesHomework 4: Benjamin StahlReza AhmedNo ratings yet
- (V) ParabolicDocument21 pages(V) ParabolicM Haroon SheikhNo ratings yet
- A. Two-Variable Linear Regression Model:: X Y ε β α X X x Y Y y i = 1, 2, …, NDocument21 pagesA. Two-Variable Linear Regression Model:: X Y ε β α X X x Y Y y i = 1, 2, …, NBabagbéto YanNo ratings yet
- Discretization-Finite Difference, Finite Element Methods: D Dy Ax BX DX DX Dy DX Dy Ax A DXDocument6 pagesDiscretization-Finite Difference, Finite Element Methods: D Dy Ax BX DX DX Dy DX Dy Ax A DXratchagar aNo ratings yet
- Exam Formulas For CALCULUSDocument3 pagesExam Formulas For CALCULUSWendy HuynhNo ratings yet
- AJC JC 2 H2 Maths 2011 Mid Year Exam Solutions Paper 1Document12 pagesAJC JC 2 H2 Maths 2011 Mid Year Exam Solutions Paper 1jimmytanlimlongNo ratings yet
- 7A Definite IntegrationDocument51 pages7A Definite IntegrationSri DNo ratings yet
- Chap 8Document17 pagesChap 8Aryce_No ratings yet
- Formule ZavršneDocument4 pagesFormule ZavršnestudentftnNo ratings yet
- Summary 6-Green's TheoremDocument6 pagesSummary 6-Green's TheoremAjith KrishnanNo ratings yet
- Calc 2 Lecture Notes Section 7.2 1 of 8: Yx UxvyDocument8 pagesCalc 2 Lecture Notes Section 7.2 1 of 8: Yx Uxvymasyuki1979No ratings yet
- Math ReferenceDocument24 pagesMath ReferenceSujib BarmanNo ratings yet
- Get Full PointsDocument6 pagesGet Full PointsChing-Ting WuNo ratings yet
- Techniques of IntegrationDocument61 pagesTechniques of IntegrationAma PredaNo ratings yet
- The Handbook of Formulas and Tables For Signal ProcessingDocument17 pagesThe Handbook of Formulas and Tables For Signal ProcessingmadhurocksktmNo ratings yet
- Maths FormulaDocument4 pagesMaths Formulamickey_disney93No ratings yet
- Robust Control Design Via Feedback Linearization: Harry G. KwatnyDocument22 pagesRobust Control Design Via Feedback Linearization: Harry G. KwatnyChernet TugeNo ratings yet
- Chapter5 Calculus of VariationsDocument30 pagesChapter5 Calculus of VariationsRaja RamachandranNo ratings yet
- Analytic Geometry: Graphic Solutions Using Matlab LanguageFrom EverandAnalytic Geometry: Graphic Solutions Using Matlab LanguageNo ratings yet
- Trigonometric Ratios to Transformations (Trigonometry) Mathematics E-Book For Public ExamsFrom EverandTrigonometric Ratios to Transformations (Trigonometry) Mathematics E-Book For Public ExamsRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Mathematics 1St First Order Linear Differential Equations 2Nd Second Order Linear Differential Equations Laplace Fourier Bessel MathematicsFrom EverandMathematics 1St First Order Linear Differential Equations 2Nd Second Order Linear Differential Equations Laplace Fourier Bessel MathematicsNo ratings yet
- Wright Turn - Flying ArenaDocument4 pagesWright Turn - Flying Arenasanketdange2007No ratings yet
- Action Carv 5Document36 pagesAction Carv 5sanketdange2007No ratings yet
- Thermal Guidelines For Data Processing Environments, Second EditionDocument1 pageThermal Guidelines For Data Processing Environments, Second Editionsanketdange2007No ratings yet
- Cooling Tower DesingnDocument4 pagesCooling Tower Desingnsanketdange2007No ratings yet
- Thinking Outside The BoxDocument9 pagesThinking Outside The Boxsanketdange2007No ratings yet
- Thermal Guidelines For Data Processing Environments, Second EditionDocument1 pageThermal Guidelines For Data Processing Environments, Second Editionsanketdange2007No ratings yet
- Blasius PDFDocument2 pagesBlasius PDFsanketdange2007No ratings yet
- Comparing Data Center & Computer Thermal DesignDocument5 pagesComparing Data Center & Computer Thermal Designsanketdange2007No ratings yet
- Unix Shells Bash Fish KSH TCSH Zsh-HyperpolyglotDocument23 pagesUnix Shells Bash Fish KSH TCSH Zsh-Hyperpolyglotsanketdange2007No ratings yet
- CPP Crash Intro PDFDocument105 pagesCPP Crash Intro PDFsanketdange2007No ratings yet
- Duct Optimization Using Fluent Adjoint SolverDocument42 pagesDuct Optimization Using Fluent Adjoint Solversanketdange2007No ratings yet
- Linux CommandsDocument2,054 pagesLinux Commandssanketdange2007No ratings yet
- Heat & Mass Transfer JournalDocument7 pagesHeat & Mass Transfer Journalsanketdange2007No ratings yet
- B e (M) I & II 2008 CourseDocument43 pagesB e (M) I & II 2008 Coursenutanc2010No ratings yet
- CFD Simulation in Town Planning Case StudyDocument8 pagesCFD Simulation in Town Planning Case Studysanketdange2007No ratings yet
- Steam Path Analysis: A Tool To Monitor The Health of A Steam TurbineDocument30 pagesSteam Path Analysis: A Tool To Monitor The Health of A Steam Turbinesanketdange2007No ratings yet
- BuoyancyDocument8 pagesBuoyancysanketdange2007No ratings yet
- Solar PWR SatelliteDocument19 pagesSolar PWR Satellitesanketdange2007No ratings yet
- Boulanger and BeatyDocument13 pagesBoulanger and BeatySarah WilliamsNo ratings yet
- SUSTECH MathDocument24 pagesSUSTECH Matht0xic.369xNo ratings yet
- FaustinoDocument1 pageFaustinoEzra Orita CeletariaNo ratings yet
- RedoDocument1 pageRedogmpzgamerNo ratings yet
- Siemens Brazil enDocument5 pagesSiemens Brazil ensterilemovieNo ratings yet
- Closed Loop Control SystemDocument5 pagesClosed Loop Control Systembaswa vamsi krishnaNo ratings yet
- What Is New in SolidCAM GPPTool 2011Document37 pagesWhat Is New in SolidCAM GPPTool 2011pannickNo ratings yet
- A LatheDocument3 pagesA LatheDReena JoyceNo ratings yet
- Knife Gate Valve: Product DescriptionDocument2 pagesKnife Gate Valve: Product DescriptionTamil SelvanNo ratings yet
- Advanced Earthquake Resistant DesignDocument17 pagesAdvanced Earthquake Resistant Designraju619No ratings yet
- Digital VocabDocument2 pagesDigital Vocabdesikudi9000No ratings yet
- c5 Conc1 EnergeticsDocument7 pagesc5 Conc1 EnergeticsAlexandra AlexandraNo ratings yet
- Mathematics HL - Practice QuestionsDocument152 pagesMathematics HL - Practice QuestionsPyjama ManNo ratings yet
- 5085DL / 5055DL SeriesDocument2 pages5085DL / 5055DL SeriesMinh TranNo ratings yet
- RPP in EnglishDocument12 pagesRPP in EnglishAnggi MijayaNo ratings yet
- Water ConingDocument96 pagesWater ConingMubin Ashraf Sheikh100% (1)
- ΕΓΧΕΙΡΙΔΙΟ ΠΛΥΝΤΗΡΙΟΥ ΠΙΑΤΩΝ - ΑΝΤΑΛΛΑΚΤΙΚΑDocument16 pagesΕΓΧΕΙΡΙΔΙΟ ΠΛΥΝΤΗΡΙΟΥ ΠΙΑΤΩΝ - ΑΝΤΑΛΛΑΚΤΙΚΑΤΣΙΜΠΙΔΗΣ ΠΑΝΑΓΙΩΤΗΣNo ratings yet
- FuturaPC EngDocument36 pagesFuturaPC EngRashika SharmaNo ratings yet
- 1976 Melling Turbulent Flow in A Rectangular DuctDocument27 pages1976 Melling Turbulent Flow in A Rectangular Ductedward agimNo ratings yet
- Bahawalpur District Profile 2013Document138 pagesBahawalpur District Profile 2013Shaheer Rizvi100% (1)
- Demand Forecasting and Estimating Methods ProblemsDocument22 pagesDemand Forecasting and Estimating Methods ProblemsNagarjuna ReddyNo ratings yet
- An Efficient Bi-Layer Intumescent Paint Metal Laminate Fire Barrier For Various Substrates: Extension To Other ApplicationDocument16 pagesAn Efficient Bi-Layer Intumescent Paint Metal Laminate Fire Barrier For Various Substrates: Extension To Other ApplicationTan Keng ChowNo ratings yet
- SumanthDocument7 pagesSumanthSumanth ITonNo ratings yet
- Gnosis Issue 30Document0 pagesGnosis Issue 30utoob365100% (5)
- 205-03 Front Drive Axle and Differential - Diagnosis and TestingDocument6 pages205-03 Front Drive Axle and Differential - Diagnosis and TestingCARLOS LIMADANo ratings yet
- SelectaDocument55 pagesSelectaHuong Cam ThuyNo ratings yet
- Chapter 5 - Introduction To Differential Analysis of Fluid MotionDocument4 pagesChapter 5 - Introduction To Differential Analysis of Fluid MotionBin RenNo ratings yet
- Introductory Botulinum PresentationDocument113 pagesIntroductory Botulinum Presentationprontaprintpottersbar100% (5)
- Ralph Menikoff and Thomas D Sewell - Constituent Properties of HMX Needed For Mesoscale SimulationsDocument23 pagesRalph Menikoff and Thomas D Sewell - Constituent Properties of HMX Needed For Mesoscale SimulationsKommissar1981No ratings yet