Professional Documents
Culture Documents
3.14 Mutual Inductance: Ne RR Theory ' Rric NF TW RKS
3.14 Mutual Inductance: Ne RR Theory ' Rric NF TW RKS
Uploaded by
vind_hya1Copyright:
Available Formats
You might also like
- Handbook of Microwave MeasurementsDocument169 pagesHandbook of Microwave Measurementselect222No ratings yet
- ELECTROMAGNETIC THEORY - Two Mark Questions and AnswersDocument12 pagesELECTROMAGNETIC THEORY - Two Mark Questions and AnswersRavi Kannappan80% (5)
- Hindusthan College of Engineering and TechnologyDocument17 pagesHindusthan College of Engineering and TechnologyDei PehNo ratings yet
- Lecture 09 - Transmission LinesDocument55 pagesLecture 09 - Transmission LinesDorcas Jay B. RegaladoNo ratings yet
- EEE 1002 Module 8 Self and Mutual InductanceDocument37 pagesEEE 1002 Module 8 Self and Mutual InductanceGnanavignesh RNo ratings yet
- Transmission LinesDocument55 pagesTransmission LinesPavan KhetrapalNo ratings yet
- Resonant Circuits and Mutual Inductances: + V R L CDocument5 pagesResonant Circuits and Mutual Inductances: + V R L CKodali JayachandraNo ratings yet
- Rana Abubakar Khan: Join FB Group For Vu HelpDocument5 pagesRana Abubakar Khan: Join FB Group For Vu HelpYasir WaseemNo ratings yet
- Syllabus:Network Theory (3-1-0)Document82 pagesSyllabus:Network Theory (3-1-0)Hassan SayedNo ratings yet
- Wide Band RF TransformersDocument13 pagesWide Band RF Transformerskbdstl1No ratings yet
- ECA Unit 5Document37 pagesECA Unit 5Komalaselvan VNo ratings yet
- Chapter 13 - Magnetically Coupled CircuitsDocument45 pagesChapter 13 - Magnetically Coupled CircuitsHayan BaigNo ratings yet
- 2 MarkscseDocument23 pages2 MarkscsetrpratapNo ratings yet
- Two Inductively Coupled RLC CircuitsDocument4 pagesTwo Inductively Coupled RLC CircuitsAshutoshMishraNo ratings yet
- Inductance: 1 Circuit AnalysisDocument9 pagesInductance: 1 Circuit Analysisferdinando16No ratings yet
- Final Key: Electrical Engineering - Paper-IIDocument25 pagesFinal Key: Electrical Engineering - Paper-IISuryaCharanPaidipalliNo ratings yet
- Appsc Aee Mains 2019 Electrical Engineering Paper II 0ec6f9c2Document25 pagesAppsc Aee Mains 2019 Electrical Engineering Paper II 0ec6f9c2SURYA PRAKASHNo ratings yet
- Boost Converter ConfigurationDocument7 pagesBoost Converter Configurationultrakill rampageNo ratings yet
- Electric CircuitsDocument15 pagesElectric CircuitsArpit RajpootNo ratings yet
- Electrical Engineering Question Paper-II: - Kirchoff's LossDocument25 pagesElectrical Engineering Question Paper-II: - Kirchoff's LossbasavarajNo ratings yet
- Electro Magnetic InductionDocument3 pagesElectro Magnetic Inductionadnankhannomanpathan100No ratings yet
- Ec2151 2 Marks With AnswersDocument19 pagesEc2151 2 Marks With AnswersRaji SharmiNo ratings yet
- 972 12 Physics 3 Marks em Questions and AnswersDocument14 pages972 12 Physics 3 Marks em Questions and AnswersJai Ram100% (1)
- Electrode Contact ResistanceDocument8 pagesElectrode Contact Resistancejavicol70No ratings yet
- EC&ED QB For CIE2Document10 pagesEC&ED QB For CIE2bhardamuNo ratings yet
- Lecture 09 - Transmission LinesDocument28 pagesLecture 09 - Transmission LinesPinku MeenaNo ratings yet
- TLWDocument15 pagesTLWanon_846897733No ratings yet
- 1 Theory: 1.1 Coplanar 2d-Waveguide StructuresDocument9 pages1 Theory: 1.1 Coplanar 2d-Waveguide StructuresSebastianMeierNo ratings yet
- Magnetically Coupled CircuitsDocument22 pagesMagnetically Coupled CircuitsMohammed MaherNo ratings yet
- Mag 704Document144 pagesMag 704jeffd1787No ratings yet
- Faculty of Engineerin1Document13 pagesFaculty of Engineerin1maged mohamedNo ratings yet
- Transmission Line Transformers: Theory, Design and ApplicationsDocument5 pagesTransmission Line Transformers: Theory, Design and ApplicationsEm Gomez100% (1)
- Linear Transformer Mago UlatDocument26 pagesLinear Transformer Mago UlatniggNo ratings yet
- Class19 Crosstalk OverviewDocument32 pagesClass19 Crosstalk OverviewNag ArjunNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1Document11 pagesChapter 1Dhanashree ParanjapeNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 (A) DC Circuits Class 2: Ohm'S LawDocument11 pagesChapter 1 (A) DC Circuits Class 2: Ohm'S LawDhanashree ParanjapeNo ratings yet
- University of Tripoli: Properties of Microwave DevicesDocument7 pagesUniversity of Tripoli: Properties of Microwave DevicesSalem AllamNo ratings yet
- Lecture 1-3Document43 pagesLecture 1-3JaleesNo ratings yet
- Measurement of High D.C., A.C. and Impulse CurrentsDocument18 pagesMeasurement of High D.C., A.C. and Impulse CurrentsSumaira SaifNo ratings yet
- Lecture 2 - Transmission Line Parameters and PerformanceDocument18 pagesLecture 2 - Transmission Line Parameters and Performancekiprotich allanNo ratings yet
- Circuit TheoryDocument33 pagesCircuit Theoryavi713331No ratings yet
- Current: Unit: The Appropriate MKS Unit of Current Is AmpereDocument13 pagesCurrent: Unit: The Appropriate MKS Unit of Current Is AmpereNaymur RahmanNo ratings yet
- Unit-I Resonance: 2 Marks Questions and AnswersDocument14 pagesUnit-I Resonance: 2 Marks Questions and AnswersyaminiNo ratings yet
- Part BDocument9 pagesPart Bsramalingam288953No ratings yet
- Impact of Circuit Impedance On Signal Crosstalk: January 2015Document7 pagesImpact of Circuit Impedance On Signal Crosstalk: January 2015Imane MassaoudiNo ratings yet
- Ece 3323 Experiment 1Document11 pagesEce 3323 Experiment 1TANQUERO_WW20% (1)
- Term Paper Topic: Magnetic CouplingDocument13 pagesTerm Paper Topic: Magnetic Couplingshailesh singhNo ratings yet
- Circuit Analysis II. 5. Magnetically Coupled CircuitsDocument48 pagesCircuit Analysis II. 5. Magnetically Coupled Circuits10mq33No ratings yet
- Anna University Transmission Lines and Wave Guide Lecture NotesDocument64 pagesAnna University Transmission Lines and Wave Guide Lecture NotesHammad HassanNo ratings yet
- OHMs Law & CircuitsDocument18 pagesOHMs Law & CircuitsYugandhar Veeramachaneni100% (2)
- Feynman Lectures Simplified 2C: Electromagnetism: in Relativity & in Dense MatterFrom EverandFeynman Lectures Simplified 2C: Electromagnetism: in Relativity & in Dense MatterNo ratings yet
- Analysis and Design of Multicell DC/DC Converters Using Vectorized ModelsFrom EverandAnalysis and Design of Multicell DC/DC Converters Using Vectorized ModelsNo ratings yet
- Principles and Practices of Molecular Properties: Theory, Modeling, and SimulationsFrom EverandPrinciples and Practices of Molecular Properties: Theory, Modeling, and SimulationsNo ratings yet
- Reference Guide To Useful Electronic Circuits And Circuit Design Techniques - Part 2From EverandReference Guide To Useful Electronic Circuits And Circuit Design Techniques - Part 2No ratings yet
- Reference Guide To Useful Electronic Circuits And Circuit Design Techniques - Part 1From EverandReference Guide To Useful Electronic Circuits And Circuit Design Techniques - Part 1Rating: 2.5 out of 5 stars2.5/5 (3)
- Basic Electronics QuestionsDocument7 pagesBasic Electronics Questionsvind_hya1No ratings yet
- Once Student Asked His GuruDocument3 pagesOnce Student Asked His Guruvind_hya1No ratings yet
- Sliding Gates: Self-Supporting Construction, High Security Standards, Completely Pre-AssembledDocument16 pagesSliding Gates: Self-Supporting Construction, High Security Standards, Completely Pre-Assembledvind_hya1100% (1)
- Scan Doc0081Document1 pageScan Doc0081vind_hya1No ratings yet
- D) C Z. (, A (: Klystron Mustbe 3 4Document1 pageD) C Z. (, A (: Klystron Mustbe 3 4vind_hya1No ratings yet
- Scan Doc0055Document1 pageScan Doc0055vind_hya1No ratings yet
- Electromagnetic Fields AND WaveguidesDocument1 pageElectromagnetic Fields AND Waveguidesvind_hya1No ratings yet
- Circuit Theory and Electric NetworksDocument2 pagesCircuit Theory and Electric Networksvind_hya1No ratings yet
- Scan Doc0072Document2 pagesScan Doc0072vind_hya1No ratings yet
- MH MHZ GHZ: Can Not NotDocument1 pageMH MHZ GHZ: Can Not Notvind_hya1No ratings yet
- Scan Doc0109Document1 pageScan Doc0109vind_hya1No ratings yet
- Scan Doc0020Document1 pageScan Doc0020vind_hya1No ratings yet
- Scan Doc0124Document1 pageScan Doc0124vind_hya1No ratings yet
- Scan Doc0110Document1 pageScan Doc0110vind_hya1No ratings yet
- Scan Doc0106Document1 pageScan Doc0106vind_hya1No ratings yet
- Nha Ass Fi, Es e e E: Cap Cit Ve: A System Is Initially at Rest. The Respons ToaDocument1 pageNha Ass Fi, Es e e E: Cap Cit Ve: A System Is Initially at Rest. The Respons Toavind_hya1No ratings yet
- Scan Doc0126Document2 pagesScan Doc0126vind_hya1No ratings yet
- Scan Doc0113Document1 pageScan Doc0113vind_hya1No ratings yet
- Scan Doc0123Document3 pagesScan Doc0123vind_hya1No ratings yet
- Scan Doc0068Document2 pagesScan Doc0068vind_hya1No ratings yet
- Scan Doc0122Document1 pageScan Doc0122vind_hya1No ratings yet
- Scan Doc0108Document1 pageScan Doc0108vind_hya1No ratings yet
- Prop - Aga Tion An Lines: Question-Nkjan1 Ennas, L Ransmissio NDocument1 pageProp - Aga Tion An Lines: Question-Nkjan1 Ennas, L Ransmissio Nvind_hya1No ratings yet
- Scan Doc0086Document1 pageScan Doc0086vind_hya1No ratings yet
- Scan Doc0124Document1 pageScan Doc0124vind_hya1No ratings yet
3.14 Mutual Inductance: Ne RR Theory ' Rric NF TW RKS
3.14 Mutual Inductance: Ne RR Theory ' Rric NF TW RKS
Uploaded by
vind_hya1Original Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
3.14 Mutual Inductance: Ne RR Theory ' Rric NF TW RKS
3.14 Mutual Inductance: Ne RR Theory ' Rric NF TW RKS
Uploaded by
vind_hya1Copyright:
Available Formats
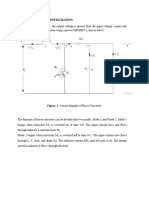
cnecurr THEORY I\NIl ~:U:C'rRIC Nf:TWORKS
-------.------
3.14 Mutual Inductance
When the interaction between two loops takes place through a magnetic field instead of through
COT!1I!lon elements, the loops are said to be mductivity or magnetically coupled: Mutual inductance IS
defined as
dt
Coefficient of coupling is given by
The dot convention states that
9.
When both assumed currents enter or leave a pair of coupled coils at the dotted terminals, the
signs of the M terms will be same as the signs of the L terms .
10.
If one current enters at a dotted terminal and one leaves by a dotted terminal, the signs of the
M terms are opposite to the signs of the L terms.
.
3.15 Parallel resonance and Series resonance
A network is said to be resonant when the voltage and current at the network input terminals are in
phase,
Frequency of resonance
fo =
2~
Qo = roo RC = R ~
Quality factor
roo
Bandwidth
~(O
Qo
=-
The resonant frequency is the geomatric mean of two cutoff frequencies (01 and 0>2. Thus
roo=~
For series resonance,
3.16 Network Theorems
11.
1.
Star-delta transformation:
star-to-delta
delta-to-star
ZI =
ZAZB.
ZA +Zs+Zc
You might also like
- Handbook of Microwave MeasurementsDocument169 pagesHandbook of Microwave Measurementselect222No ratings yet
- ELECTROMAGNETIC THEORY - Two Mark Questions and AnswersDocument12 pagesELECTROMAGNETIC THEORY - Two Mark Questions and AnswersRavi Kannappan80% (5)
- Hindusthan College of Engineering and TechnologyDocument17 pagesHindusthan College of Engineering and TechnologyDei PehNo ratings yet
- Lecture 09 - Transmission LinesDocument55 pagesLecture 09 - Transmission LinesDorcas Jay B. RegaladoNo ratings yet
- EEE 1002 Module 8 Self and Mutual InductanceDocument37 pagesEEE 1002 Module 8 Self and Mutual InductanceGnanavignesh RNo ratings yet
- Transmission LinesDocument55 pagesTransmission LinesPavan KhetrapalNo ratings yet
- Resonant Circuits and Mutual Inductances: + V R L CDocument5 pagesResonant Circuits and Mutual Inductances: + V R L CKodali JayachandraNo ratings yet
- Rana Abubakar Khan: Join FB Group For Vu HelpDocument5 pagesRana Abubakar Khan: Join FB Group For Vu HelpYasir WaseemNo ratings yet
- Syllabus:Network Theory (3-1-0)Document82 pagesSyllabus:Network Theory (3-1-0)Hassan SayedNo ratings yet
- Wide Band RF TransformersDocument13 pagesWide Band RF Transformerskbdstl1No ratings yet
- ECA Unit 5Document37 pagesECA Unit 5Komalaselvan VNo ratings yet
- Chapter 13 - Magnetically Coupled CircuitsDocument45 pagesChapter 13 - Magnetically Coupled CircuitsHayan BaigNo ratings yet
- 2 MarkscseDocument23 pages2 MarkscsetrpratapNo ratings yet
- Two Inductively Coupled RLC CircuitsDocument4 pagesTwo Inductively Coupled RLC CircuitsAshutoshMishraNo ratings yet
- Inductance: 1 Circuit AnalysisDocument9 pagesInductance: 1 Circuit Analysisferdinando16No ratings yet
- Final Key: Electrical Engineering - Paper-IIDocument25 pagesFinal Key: Electrical Engineering - Paper-IISuryaCharanPaidipalliNo ratings yet
- Appsc Aee Mains 2019 Electrical Engineering Paper II 0ec6f9c2Document25 pagesAppsc Aee Mains 2019 Electrical Engineering Paper II 0ec6f9c2SURYA PRAKASHNo ratings yet
- Boost Converter ConfigurationDocument7 pagesBoost Converter Configurationultrakill rampageNo ratings yet
- Electric CircuitsDocument15 pagesElectric CircuitsArpit RajpootNo ratings yet
- Electrical Engineering Question Paper-II: - Kirchoff's LossDocument25 pagesElectrical Engineering Question Paper-II: - Kirchoff's LossbasavarajNo ratings yet
- Electro Magnetic InductionDocument3 pagesElectro Magnetic Inductionadnankhannomanpathan100No ratings yet
- Ec2151 2 Marks With AnswersDocument19 pagesEc2151 2 Marks With AnswersRaji SharmiNo ratings yet
- 972 12 Physics 3 Marks em Questions and AnswersDocument14 pages972 12 Physics 3 Marks em Questions and AnswersJai Ram100% (1)
- Electrode Contact ResistanceDocument8 pagesElectrode Contact Resistancejavicol70No ratings yet
- EC&ED QB For CIE2Document10 pagesEC&ED QB For CIE2bhardamuNo ratings yet
- Lecture 09 - Transmission LinesDocument28 pagesLecture 09 - Transmission LinesPinku MeenaNo ratings yet
- TLWDocument15 pagesTLWanon_846897733No ratings yet
- 1 Theory: 1.1 Coplanar 2d-Waveguide StructuresDocument9 pages1 Theory: 1.1 Coplanar 2d-Waveguide StructuresSebastianMeierNo ratings yet
- Magnetically Coupled CircuitsDocument22 pagesMagnetically Coupled CircuitsMohammed MaherNo ratings yet
- Mag 704Document144 pagesMag 704jeffd1787No ratings yet
- Faculty of Engineerin1Document13 pagesFaculty of Engineerin1maged mohamedNo ratings yet
- Transmission Line Transformers: Theory, Design and ApplicationsDocument5 pagesTransmission Line Transformers: Theory, Design and ApplicationsEm Gomez100% (1)
- Linear Transformer Mago UlatDocument26 pagesLinear Transformer Mago UlatniggNo ratings yet
- Class19 Crosstalk OverviewDocument32 pagesClass19 Crosstalk OverviewNag ArjunNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1Document11 pagesChapter 1Dhanashree ParanjapeNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 (A) DC Circuits Class 2: Ohm'S LawDocument11 pagesChapter 1 (A) DC Circuits Class 2: Ohm'S LawDhanashree ParanjapeNo ratings yet
- University of Tripoli: Properties of Microwave DevicesDocument7 pagesUniversity of Tripoli: Properties of Microwave DevicesSalem AllamNo ratings yet
- Lecture 1-3Document43 pagesLecture 1-3JaleesNo ratings yet
- Measurement of High D.C., A.C. and Impulse CurrentsDocument18 pagesMeasurement of High D.C., A.C. and Impulse CurrentsSumaira SaifNo ratings yet
- Lecture 2 - Transmission Line Parameters and PerformanceDocument18 pagesLecture 2 - Transmission Line Parameters and Performancekiprotich allanNo ratings yet
- Circuit TheoryDocument33 pagesCircuit Theoryavi713331No ratings yet
- Current: Unit: The Appropriate MKS Unit of Current Is AmpereDocument13 pagesCurrent: Unit: The Appropriate MKS Unit of Current Is AmpereNaymur RahmanNo ratings yet
- Unit-I Resonance: 2 Marks Questions and AnswersDocument14 pagesUnit-I Resonance: 2 Marks Questions and AnswersyaminiNo ratings yet
- Part BDocument9 pagesPart Bsramalingam288953No ratings yet
- Impact of Circuit Impedance On Signal Crosstalk: January 2015Document7 pagesImpact of Circuit Impedance On Signal Crosstalk: January 2015Imane MassaoudiNo ratings yet
- Ece 3323 Experiment 1Document11 pagesEce 3323 Experiment 1TANQUERO_WW20% (1)
- Term Paper Topic: Magnetic CouplingDocument13 pagesTerm Paper Topic: Magnetic Couplingshailesh singhNo ratings yet
- Circuit Analysis II. 5. Magnetically Coupled CircuitsDocument48 pagesCircuit Analysis II. 5. Magnetically Coupled Circuits10mq33No ratings yet
- Anna University Transmission Lines and Wave Guide Lecture NotesDocument64 pagesAnna University Transmission Lines and Wave Guide Lecture NotesHammad HassanNo ratings yet
- OHMs Law & CircuitsDocument18 pagesOHMs Law & CircuitsYugandhar Veeramachaneni100% (2)
- Feynman Lectures Simplified 2C: Electromagnetism: in Relativity & in Dense MatterFrom EverandFeynman Lectures Simplified 2C: Electromagnetism: in Relativity & in Dense MatterNo ratings yet
- Analysis and Design of Multicell DC/DC Converters Using Vectorized ModelsFrom EverandAnalysis and Design of Multicell DC/DC Converters Using Vectorized ModelsNo ratings yet
- Principles and Practices of Molecular Properties: Theory, Modeling, and SimulationsFrom EverandPrinciples and Practices of Molecular Properties: Theory, Modeling, and SimulationsNo ratings yet
- Reference Guide To Useful Electronic Circuits And Circuit Design Techniques - Part 2From EverandReference Guide To Useful Electronic Circuits And Circuit Design Techniques - Part 2No ratings yet
- Reference Guide To Useful Electronic Circuits And Circuit Design Techniques - Part 1From EverandReference Guide To Useful Electronic Circuits And Circuit Design Techniques - Part 1Rating: 2.5 out of 5 stars2.5/5 (3)
- Basic Electronics QuestionsDocument7 pagesBasic Electronics Questionsvind_hya1No ratings yet
- Once Student Asked His GuruDocument3 pagesOnce Student Asked His Guruvind_hya1No ratings yet
- Sliding Gates: Self-Supporting Construction, High Security Standards, Completely Pre-AssembledDocument16 pagesSliding Gates: Self-Supporting Construction, High Security Standards, Completely Pre-Assembledvind_hya1100% (1)
- Scan Doc0081Document1 pageScan Doc0081vind_hya1No ratings yet
- D) C Z. (, A (: Klystron Mustbe 3 4Document1 pageD) C Z. (, A (: Klystron Mustbe 3 4vind_hya1No ratings yet
- Scan Doc0055Document1 pageScan Doc0055vind_hya1No ratings yet
- Electromagnetic Fields AND WaveguidesDocument1 pageElectromagnetic Fields AND Waveguidesvind_hya1No ratings yet
- Circuit Theory and Electric NetworksDocument2 pagesCircuit Theory and Electric Networksvind_hya1No ratings yet
- Scan Doc0072Document2 pagesScan Doc0072vind_hya1No ratings yet
- MH MHZ GHZ: Can Not NotDocument1 pageMH MHZ GHZ: Can Not Notvind_hya1No ratings yet
- Scan Doc0109Document1 pageScan Doc0109vind_hya1No ratings yet
- Scan Doc0020Document1 pageScan Doc0020vind_hya1No ratings yet
- Scan Doc0124Document1 pageScan Doc0124vind_hya1No ratings yet
- Scan Doc0110Document1 pageScan Doc0110vind_hya1No ratings yet
- Scan Doc0106Document1 pageScan Doc0106vind_hya1No ratings yet
- Nha Ass Fi, Es e e E: Cap Cit Ve: A System Is Initially at Rest. The Respons ToaDocument1 pageNha Ass Fi, Es e e E: Cap Cit Ve: A System Is Initially at Rest. The Respons Toavind_hya1No ratings yet
- Scan Doc0126Document2 pagesScan Doc0126vind_hya1No ratings yet
- Scan Doc0113Document1 pageScan Doc0113vind_hya1No ratings yet
- Scan Doc0123Document3 pagesScan Doc0123vind_hya1No ratings yet
- Scan Doc0068Document2 pagesScan Doc0068vind_hya1No ratings yet
- Scan Doc0122Document1 pageScan Doc0122vind_hya1No ratings yet
- Scan Doc0108Document1 pageScan Doc0108vind_hya1No ratings yet
- Prop - Aga Tion An Lines: Question-Nkjan1 Ennas, L Ransmissio NDocument1 pageProp - Aga Tion An Lines: Question-Nkjan1 Ennas, L Ransmissio Nvind_hya1No ratings yet
- Scan Doc0086Document1 pageScan Doc0086vind_hya1No ratings yet
- Scan Doc0124Document1 pageScan Doc0124vind_hya1No ratings yet