Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Useful Formulas: A 0 A 2 A 0 A 2 A 0
Useful Formulas: A 0 A 2 A 0 A 2 A 0
Uploaded by
nh16888Copyright:
Available Formats
You might also like
- Math 257-316 PDE Formula Sheet - Final Exam: M It It M It ItDocument3 pagesMath 257-316 PDE Formula Sheet - Final Exam: M It It M It ItHari KrishnaNo ratings yet
- Final FormulasDocument2 pagesFinal FormulasVasil GorgievNo ratings yet
- Seminar in Large Deviations and ApplicationsDocument14 pagesSeminar in Large Deviations and ApplicationsDomenique SchwestermannNo ratings yet
- M340project Sacco MaddenDocument6 pagesM340project Sacco MaddenDavid SaccoNo ratings yet
- Outline CD 2Document9 pagesOutline CD 2Imdadul HaqueNo ratings yet
- Exam - 2013 10 30Document5 pagesExam - 2013 10 30lieth-4No ratings yet
- Exam - 2011 10 28Document5 pagesExam - 2011 10 28lieth-4No ratings yet
- Final Exam Formula SheetDocument3 pagesFinal Exam Formula SheetYuhao ChenNo ratings yet
- 15 Spherical CoordinatesDocument17 pages15 Spherical CoordinatesRaul FraulNo ratings yet
- Laplace'S and Poisson'S EquationsDocument16 pagesLaplace'S and Poisson'S EquationsOBStaffNo ratings yet
- Exam - 2012 10 30Document5 pagesExam - 2012 10 30lieth-4No ratings yet
- Burkholder Integrals, Holomorphic Motions and Quasiconformal MappingsDocument28 pagesBurkholder Integrals, Holomorphic Motions and Quasiconformal Mappingsmez00No ratings yet
- FormulaeDocument2 pagesFormulaeMahatama Sharan PandeyNo ratings yet
- A Functional Determinant Expression For The Riemann Xi FunctionDocument13 pagesA Functional Determinant Expression For The Riemann Xi FunctionJose Javier Garcia MoretaNo ratings yet
- Notas Matematicas para Electronica de PotenciaDocument10 pagesNotas Matematicas para Electronica de PotenciaAndrés David Martínez MarteloNo ratings yet
- Niu Physics PHD Candidacy Exam - Standard Formula SheetDocument3 pagesNiu Physics PHD Candidacy Exam - Standard Formula SheetMiguel AngelNo ratings yet
- Advanced Calculus FormulasDocument13 pagesAdvanced Calculus Formulasvignes011No ratings yet
- Multivariable Calculus, 2009-10-30. Per-Sverre Svendsen, Tel.035 - 167 615/0709 - 398 526Document5 pagesMultivariable Calculus, 2009-10-30. Per-Sverre Svendsen, Tel.035 - 167 615/0709 - 398 526lieth-4No ratings yet
- Calculus FormulaDocument2 pagesCalculus FormulaleeshiNo ratings yet
- 10.Error-Evaluator: The Syndrome ComponentsDocument14 pages10.Error-Evaluator: The Syndrome Componentsisrael_zamora6389No ratings yet
- Fourier Finite TransformsDocument8 pagesFourier Finite Transformserev_20No ratings yet
- Parte 10Document7 pagesParte 10Elohim Ortiz CaballeroNo ratings yet
- Multivariable Calculus, 2007-03-15. Per-Sverre Svendsen, Tel.035 - 167 615/0709 - 398 526Document5 pagesMultivariable Calculus, 2007-03-15. Per-Sverre Svendsen, Tel.035 - 167 615/0709 - 398 526lieth-4No ratings yet
- Ch. 1: Review of ProbabilityDocument19 pagesCh. 1: Review of ProbabilityKyusang ParkNo ratings yet
- Tcu12 CRC SinglegDocument2 pagesTcu12 CRC SinglegTyler BienhoffNo ratings yet
- Stuff Must Know Cold NewDocument3 pagesStuff Must Know Cold NewZach FergerNo ratings yet
- Multivariable Calculus, 2007-10-26. Per-Sverre Svendsen, Tel.035 - 167 615/0709 - 398 526Document5 pagesMultivariable Calculus, 2007-10-26. Per-Sverre Svendsen, Tel.035 - 167 615/0709 - 398 526lieth-4No ratings yet
- Vector FormulaeDocument16 pagesVector FormulaeahsbonNo ratings yet
- Quantum Mechanics Course ZeemansplittingDocument29 pagesQuantum Mechanics Course ZeemansplittingjlbalbNo ratings yet
- 241 Testsol 2Document5 pages241 Testsol 2كاظم طارقNo ratings yet
- PHYS3051 Methods in Theoretical Physics I (2016-17) : XX Yy ZZDocument2 pagesPHYS3051 Methods in Theoretical Physics I (2016-17) : XX Yy ZZKwong DavidNo ratings yet
- E e e E: Departamento de Matem Atica Escola Superior de Tecnologia de ViseuDocument8 pagesE e e E: Departamento de Matem Atica Escola Superior de Tecnologia de ViseuNelly EspinosaNo ratings yet
- Formula For SOA MFEDocument4 pagesFormula For SOA MFEferferNo ratings yet
- Solutions of Higher Order Constant Coefficient Linear Odes: Homogeneous CaseDocument9 pagesSolutions of Higher Order Constant Coefficient Linear Odes: Homogeneous CaseakshayNo ratings yet
- Communication Systems Solutions RDocument48 pagesCommunication Systems Solutions RvikaschawlavcNo ratings yet
- Assignment 13 - SolutionsDocument2 pagesAssignment 13 - SolutionsGayatri Govind NairNo ratings yet
- Polar and Parametric Equations: Sanaa Charania, Hanna Park, and Danielle ChowDocument18 pagesPolar and Parametric Equations: Sanaa Charania, Hanna Park, and Danielle ChowgulzchrnNo ratings yet
- Differential EquationsDocument11 pagesDifferential EquationssivamadhaviyamNo ratings yet
- Numerical Methods For Systems of Nonlinear Differential Functional EquationsDocument14 pagesNumerical Methods For Systems of Nonlinear Differential Functional EquationsMaz AmininNo ratings yet
- 221B Lecture Notes: Notes On Spherical Bessel Functions 1 DefinitionsDocument5 pages221B Lecture Notes: Notes On Spherical Bessel Functions 1 DefinitionsKhem UpathambhakulNo ratings yet
- Modeling: ∞ −st 1 s 1 s n n! s −at 1 s+a ω s +ω s s +ωDocument4 pagesModeling: ∞ −st 1 s 1 s n n! s −at 1 s+a ω s +ω s s +ωjameelahmadNo ratings yet
- Calculus BookletDocument6 pagesCalculus Bookletangie81No ratings yet
- Chapter 5: Laplace Transform and Its ApplicationsDocument23 pagesChapter 5: Laplace Transform and Its ApplicationsEECS7No ratings yet
- Homework 9. Solutions. 1. Find Coordinate Basis Vectors, First Quadratic Form, Unit Normal Vector Field, Shape Operator and GaussianDocument8 pagesHomework 9. Solutions. 1. Find Coordinate Basis Vectors, First Quadratic Form, Unit Normal Vector Field, Shape Operator and GaussianKiprop VentureNo ratings yet
- Depi 9Document7 pagesDepi 9AndreiSanduNo ratings yet
- Otakar Svítek and Tayebeh Tahamtan: Institute of Theoretical Physics Charles University in PragueDocument17 pagesOtakar Svítek and Tayebeh Tahamtan: Institute of Theoretical Physics Charles University in PraguespinfoamNo ratings yet
- Enhanced Eudml Content Accessible Layered PDF Eudml 49037 0Document12 pagesEnhanced Eudml Content Accessible Layered PDF Eudml 49037 0Youssef S. DablizNo ratings yet
- Psaromhligkos Master ThesisDocument41 pagesPsaromhligkos Master ThesishhhybpmdqzNo ratings yet
- Problem Set 1Document9 pagesProblem Set 1belderandover09No ratings yet
- 200b Midterm FormulaeDocument1 page200b Midterm FormulaeKaren NgNo ratings yet
- Semi Classic A Electron OpticsDocument15 pagesSemi Classic A Electron Opticslenc46No ratings yet
- Examples 1: Fourier Series: F1.3YF2 Mathematical Techniques 1Document8 pagesExamples 1: Fourier Series: F1.3YF2 Mathematical Techniques 1Shaibal AhmedNo ratings yet
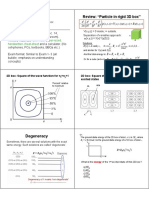
- DegeneracyDocument4 pagesDegeneracypradeep khannaNo ratings yet
- Formula Sheet For MathsDocument5 pagesFormula Sheet For Mathsbobd123No ratings yet
- Legendre FunctionsDocument16 pagesLegendre FunctionsBlind RodroNo ratings yet
- Fourier Electrical Circuits PDFDocument18 pagesFourier Electrical Circuits PDFCharmaine CuynoNo ratings yet
- Tables of the Function w (z)- e-z2 ? ex2 dx: Mathematical Tables Series, Vol. 27From EverandTables of the Function w (z)- e-z2 ? ex2 dx: Mathematical Tables Series, Vol. 27No ratings yet
- Green's Function Estimates for Lattice Schrödinger Operators and Applications. (AM-158)From EverandGreen's Function Estimates for Lattice Schrödinger Operators and Applications. (AM-158)No ratings yet
- Tables of Laguerre Polynomials and Functions: Mathematical Tables Series, Vol. 39From EverandTables of Laguerre Polynomials and Functions: Mathematical Tables Series, Vol. 39No ratings yet
Useful Formulas: A 0 A 2 A 0 A 2 A 0
Useful Formulas: A 0 A 2 A 0 A 2 A 0
Uploaded by
nh16888Original Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Useful Formulas: A 0 A 2 A 0 A 2 A 0
Useful Formulas: A 0 A 2 A 0 A 2 A 0
Uploaded by
nh16888Copyright:
Available Formats
Useful Formulas
Orthogonality relations for trig functions (for m and n positive integers):
a
cos
0 a
mx nx cos a a mx nx sin a a nx mx sin a a
dx = dx = dx = 0,
0, if m = n a 2 , if m = n 0, if m = n a 2 , if m = n for all m, n
sin
0 a
cos
0
Bessel equation of order m (for m integer): r(rR ) + (2 r2 m2 )R = 0, for 0 < r < a Eigenfunctions: Eigenvalues: R(r) = AJm (r) + BYm (r) mn =
jmn a
where Jm (jmn ) = 0
for m = 0, 1, 2, . . . and n = 1, 2, 3, . . . Orthogonality:
a 0
Jm (mn r) Jm (mq r) r dr = 0
when n = q
Legendre equation: (sin() ) + 2 sin() = 0, for 0 < < OR (1 x2 )y 2xy + 2 y = 0, for 1 < x < 1 (and x = cos ) Eigenfunctions: () = Pn (cos ) OR y (x) = Pn (x), where P0 (x) = 1, P1 (x) = x,
1 2 P2 (x) = 3 2x 2, . . .
(n + 1)Pn+1 (x) = (2n + 1)xPn (x) nPn1 (x) Eigenvalues: Orthogonality:
1
2 = 2 n = n(n + 1), n = 0, 1, 2, . . .
Pn (cos )Pm (cos ) sin d =
0 1
Pn (x) Pm (x) dx 0,
2 2n+1 ,
if m = n if m = n
Laplacian in cylindrical polar coordinates: u(r, ) = 1 r r r u r + 1 2u r2 2
Laplacian in spherical polar coordinates: u(r, , ) = 1 r2 r r2 u r + r2 1 sin sin u + r2 2u 1 2 sin 2
13
Useful Formulas (contd)
Some integral identities: x sin(kx) dx = x cos(kx) dx = x2 sin(kx) dx = x2 cos(kx) dx = eax sin(kx) dx = eax cos(kx) dx = sin(kx) x cos(kx) k2 k cos(kx) x sin(kx) + k2 k 2x sin(kx) (2 k 2 x2 ) cos(kx) + k2 k3 2x cos(kx) (k 2 x2 2) sin(kx) + k2 k3 eax (a sin(kx) k cos(kx)) a2 + k 2 eax (a cos(kx) + k sin(kx)) a2 + k 2
Hyperbolic trig identities: sinh x = 1 x (e ex ) 2 cosh x = 1 x (e + ex ) 2
cosh2 x sinh2 x = 1 d sinh x = cosh x dx d cosh x = sinh x dx
14
Useful Formulas (contd)
Laplace transform properties:
Denition: Linearity:
L (f (t)) = F (s) =
0
est f (t) dt
L (cf (t)) = cF (s) L (f (t) + g (t)) = L (f (t)) + L (g (t))
Derivatives:
L (f (t)) = f (0) + sF (s) L (f (t)) = f (0) sf (0) + s2 F (s) L (f (n) (t)) = f (n1) (0) sf (n2) (0) sn1 f (0) + sn F (s)
Shift: Heaviside:
L (eat f (t)) = F (s a) L (Hc (t)) =
ecs s
L (Hc (t)f (t)) = ecs F (s) Convolution: L
t 0
f (t t )g (t ) dt = F (s) G(s)
Common Laplace transforms:
f (t) 0 1 eat cosh(bt) sinh(bt) cos(bt) sin(bt)
F (s) 0 1 s 1 sa s s2 b 2 b s2 b 2 s s2 + b 2 b s2 + b 2
f (t) t tk eat cos(bt) eat sin(bt) eat tk
F (s) 1 s2 k! sk+1 sa s2 2as + a2 + b2 b s2 2as + a2 + b2 k! (s a)k+1
15
You might also like
- Math 257-316 PDE Formula Sheet - Final Exam: M It It M It ItDocument3 pagesMath 257-316 PDE Formula Sheet - Final Exam: M It It M It ItHari KrishnaNo ratings yet
- Final FormulasDocument2 pagesFinal FormulasVasil GorgievNo ratings yet
- Seminar in Large Deviations and ApplicationsDocument14 pagesSeminar in Large Deviations and ApplicationsDomenique SchwestermannNo ratings yet
- M340project Sacco MaddenDocument6 pagesM340project Sacco MaddenDavid SaccoNo ratings yet
- Outline CD 2Document9 pagesOutline CD 2Imdadul HaqueNo ratings yet
- Exam - 2013 10 30Document5 pagesExam - 2013 10 30lieth-4No ratings yet
- Exam - 2011 10 28Document5 pagesExam - 2011 10 28lieth-4No ratings yet
- Final Exam Formula SheetDocument3 pagesFinal Exam Formula SheetYuhao ChenNo ratings yet
- 15 Spherical CoordinatesDocument17 pages15 Spherical CoordinatesRaul FraulNo ratings yet
- Laplace'S and Poisson'S EquationsDocument16 pagesLaplace'S and Poisson'S EquationsOBStaffNo ratings yet
- Exam - 2012 10 30Document5 pagesExam - 2012 10 30lieth-4No ratings yet
- Burkholder Integrals, Holomorphic Motions and Quasiconformal MappingsDocument28 pagesBurkholder Integrals, Holomorphic Motions and Quasiconformal Mappingsmez00No ratings yet
- FormulaeDocument2 pagesFormulaeMahatama Sharan PandeyNo ratings yet
- A Functional Determinant Expression For The Riemann Xi FunctionDocument13 pagesA Functional Determinant Expression For The Riemann Xi FunctionJose Javier Garcia MoretaNo ratings yet
- Notas Matematicas para Electronica de PotenciaDocument10 pagesNotas Matematicas para Electronica de PotenciaAndrés David Martínez MarteloNo ratings yet
- Niu Physics PHD Candidacy Exam - Standard Formula SheetDocument3 pagesNiu Physics PHD Candidacy Exam - Standard Formula SheetMiguel AngelNo ratings yet
- Advanced Calculus FormulasDocument13 pagesAdvanced Calculus Formulasvignes011No ratings yet
- Multivariable Calculus, 2009-10-30. Per-Sverre Svendsen, Tel.035 - 167 615/0709 - 398 526Document5 pagesMultivariable Calculus, 2009-10-30. Per-Sverre Svendsen, Tel.035 - 167 615/0709 - 398 526lieth-4No ratings yet
- Calculus FormulaDocument2 pagesCalculus FormulaleeshiNo ratings yet
- 10.Error-Evaluator: The Syndrome ComponentsDocument14 pages10.Error-Evaluator: The Syndrome Componentsisrael_zamora6389No ratings yet
- Fourier Finite TransformsDocument8 pagesFourier Finite Transformserev_20No ratings yet
- Parte 10Document7 pagesParte 10Elohim Ortiz CaballeroNo ratings yet
- Multivariable Calculus, 2007-03-15. Per-Sverre Svendsen, Tel.035 - 167 615/0709 - 398 526Document5 pagesMultivariable Calculus, 2007-03-15. Per-Sverre Svendsen, Tel.035 - 167 615/0709 - 398 526lieth-4No ratings yet
- Ch. 1: Review of ProbabilityDocument19 pagesCh. 1: Review of ProbabilityKyusang ParkNo ratings yet
- Tcu12 CRC SinglegDocument2 pagesTcu12 CRC SinglegTyler BienhoffNo ratings yet
- Stuff Must Know Cold NewDocument3 pagesStuff Must Know Cold NewZach FergerNo ratings yet
- Multivariable Calculus, 2007-10-26. Per-Sverre Svendsen, Tel.035 - 167 615/0709 - 398 526Document5 pagesMultivariable Calculus, 2007-10-26. Per-Sverre Svendsen, Tel.035 - 167 615/0709 - 398 526lieth-4No ratings yet
- Vector FormulaeDocument16 pagesVector FormulaeahsbonNo ratings yet
- Quantum Mechanics Course ZeemansplittingDocument29 pagesQuantum Mechanics Course ZeemansplittingjlbalbNo ratings yet
- 241 Testsol 2Document5 pages241 Testsol 2كاظم طارقNo ratings yet
- PHYS3051 Methods in Theoretical Physics I (2016-17) : XX Yy ZZDocument2 pagesPHYS3051 Methods in Theoretical Physics I (2016-17) : XX Yy ZZKwong DavidNo ratings yet
- E e e E: Departamento de Matem Atica Escola Superior de Tecnologia de ViseuDocument8 pagesE e e E: Departamento de Matem Atica Escola Superior de Tecnologia de ViseuNelly EspinosaNo ratings yet
- Formula For SOA MFEDocument4 pagesFormula For SOA MFEferferNo ratings yet
- Solutions of Higher Order Constant Coefficient Linear Odes: Homogeneous CaseDocument9 pagesSolutions of Higher Order Constant Coefficient Linear Odes: Homogeneous CaseakshayNo ratings yet
- Communication Systems Solutions RDocument48 pagesCommunication Systems Solutions RvikaschawlavcNo ratings yet
- Assignment 13 - SolutionsDocument2 pagesAssignment 13 - SolutionsGayatri Govind NairNo ratings yet
- Polar and Parametric Equations: Sanaa Charania, Hanna Park, and Danielle ChowDocument18 pagesPolar and Parametric Equations: Sanaa Charania, Hanna Park, and Danielle ChowgulzchrnNo ratings yet
- Differential EquationsDocument11 pagesDifferential EquationssivamadhaviyamNo ratings yet
- Numerical Methods For Systems of Nonlinear Differential Functional EquationsDocument14 pagesNumerical Methods For Systems of Nonlinear Differential Functional EquationsMaz AmininNo ratings yet
- 221B Lecture Notes: Notes On Spherical Bessel Functions 1 DefinitionsDocument5 pages221B Lecture Notes: Notes On Spherical Bessel Functions 1 DefinitionsKhem UpathambhakulNo ratings yet
- Modeling: ∞ −st 1 s 1 s n n! s −at 1 s+a ω s +ω s s +ωDocument4 pagesModeling: ∞ −st 1 s 1 s n n! s −at 1 s+a ω s +ω s s +ωjameelahmadNo ratings yet
- Calculus BookletDocument6 pagesCalculus Bookletangie81No ratings yet
- Chapter 5: Laplace Transform and Its ApplicationsDocument23 pagesChapter 5: Laplace Transform and Its ApplicationsEECS7No ratings yet
- Homework 9. Solutions. 1. Find Coordinate Basis Vectors, First Quadratic Form, Unit Normal Vector Field, Shape Operator and GaussianDocument8 pagesHomework 9. Solutions. 1. Find Coordinate Basis Vectors, First Quadratic Form, Unit Normal Vector Field, Shape Operator and GaussianKiprop VentureNo ratings yet
- Depi 9Document7 pagesDepi 9AndreiSanduNo ratings yet
- Otakar Svítek and Tayebeh Tahamtan: Institute of Theoretical Physics Charles University in PragueDocument17 pagesOtakar Svítek and Tayebeh Tahamtan: Institute of Theoretical Physics Charles University in PraguespinfoamNo ratings yet
- Enhanced Eudml Content Accessible Layered PDF Eudml 49037 0Document12 pagesEnhanced Eudml Content Accessible Layered PDF Eudml 49037 0Youssef S. DablizNo ratings yet
- Psaromhligkos Master ThesisDocument41 pagesPsaromhligkos Master ThesishhhybpmdqzNo ratings yet
- Problem Set 1Document9 pagesProblem Set 1belderandover09No ratings yet
- 200b Midterm FormulaeDocument1 page200b Midterm FormulaeKaren NgNo ratings yet
- Semi Classic A Electron OpticsDocument15 pagesSemi Classic A Electron Opticslenc46No ratings yet
- Examples 1: Fourier Series: F1.3YF2 Mathematical Techniques 1Document8 pagesExamples 1: Fourier Series: F1.3YF2 Mathematical Techniques 1Shaibal AhmedNo ratings yet
- DegeneracyDocument4 pagesDegeneracypradeep khannaNo ratings yet
- Formula Sheet For MathsDocument5 pagesFormula Sheet For Mathsbobd123No ratings yet
- Legendre FunctionsDocument16 pagesLegendre FunctionsBlind RodroNo ratings yet
- Fourier Electrical Circuits PDFDocument18 pagesFourier Electrical Circuits PDFCharmaine CuynoNo ratings yet
- Tables of the Function w (z)- e-z2 ? ex2 dx: Mathematical Tables Series, Vol. 27From EverandTables of the Function w (z)- e-z2 ? ex2 dx: Mathematical Tables Series, Vol. 27No ratings yet
- Green's Function Estimates for Lattice Schrödinger Operators and Applications. (AM-158)From EverandGreen's Function Estimates for Lattice Schrödinger Operators and Applications. (AM-158)No ratings yet
- Tables of Laguerre Polynomials and Functions: Mathematical Tables Series, Vol. 39From EverandTables of Laguerre Polynomials and Functions: Mathematical Tables Series, Vol. 39No ratings yet

























































![Mathematical Tables: Tables of in G [z] for Complex Argument](https://imgv2-2-f.scribdassets.com/img/word_document/282615796/149x198/febb728e8d/1714993295?v=1)