Professional Documents
Culture Documents
z axis, and carries a surface charge density of ρ
z axis, and carries a surface charge density of ρ
Uploaded by
Muhammad RizwanOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
z axis, and carries a surface charge density of ρ
z axis, and carries a surface charge density of ρ
Uploaded by
Muhammad RizwanCopyright:
Available Formats
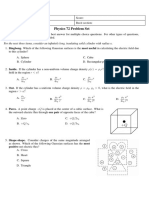
Problem 1.
(35 points) A perfectly-conducting cylinder having radius a, and of innite length, lies with its axis along the z axis, and carries a surface charge density of s C/m2 . A second perfectly-conducting cylindrical shell, whose axis is also the z axis, surrounds the rst conductor. The cylinder (of radius b), is at ground potential. The medium everywhere is free space. Under these conditions, the potential function between cylinders (a < < b) is given by V () = k where k is a constant to be determined. a. Find k in terms of given or known parameters. as ln() 0
b. Find the potential, V0 , on the inner conductor (radius a) in terms of given or known parameters.
b. Find the electric eld strength, E, for a < < b.
c. Find the electric eld strength, E, for > b.
d. Find the stored energy in the electric eld per unit length in the z direction within the volume dened by a < < b. Or, for partial credit, show how you would determine the energy.
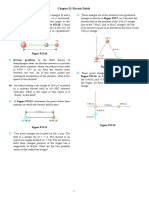
Problem 1. (30 points) A radial electric eld distribution in free space is given in spherical coordinates as: E= D0 ar 0 V/m
where D0 is a constant, and where 0 is the free space permittivity. a. Find, in terms of given parameters, the volume charge density, v , that would produce this eld. Note that in the present case of a radial component only, the divergence in spherical coordinates becomes 1 d D = 2 (r2 Dr ) r dr
b. Find, in terms of given parameters, the total charge, Q, within a sphere of radius r using Gauss Law.
c. Find, in terms of given parameters, the potential dierence between the points (r = 1, = 45 , = 80 ) and (r = 5, = 60 , = 90 ).
You might also like
- Quantum Mechanics 6th Rae Solution ManualDocument13 pagesQuantum Mechanics 6th Rae Solution ManualJustine Lotthammer98% (47)
- ODE Cheat SheetDocument2 pagesODE Cheat SheetMuhammad Rizwan88% (8)
- HW 1Document3 pagesHW 1Cenkay ÇelikliNo ratings yet
- Prob Extras f502 PDFDocument7 pagesProb Extras f502 PDFLuis Daniel RuizNo ratings yet
- LA Cheat SheetDocument1 pageLA Cheat SheetMuhammad RizwanNo ratings yet
- Exercises Set 3Document2 pagesExercises Set 3hatceNo ratings yet
- Classical ElectromanDocument1 pageClassical Electromanayush kumarNo ratings yet
- EM1 Final 2018SprDocument6 pagesEM1 Final 2018Spr홍윤제No ratings yet
- 2013 EM Assignment 2Document2 pages2013 EM Assignment 2Marcos Aaron Therthens0% (1)
- NTHU Electrical Engineering Department EE2140 Electromagnetics Spring 2024 HW #3Document1 pageNTHU Electrical Engineering Department EE2140 Electromagnetics Spring 2024 HW #3superhense55123No ratings yet
- Em Bank10 16 0Document20 pagesEm Bank10 16 0ArUn KuMarNo ratings yet
- Gauss - (1 To 50)Document6 pagesGauss - (1 To 50)holaheg352No ratings yet
- Electromagnetic Theory I (PH-424) Problem Set 1Document2 pagesElectromagnetic Theory I (PH-424) Problem Set 1DEBANJAN ADHIKARINo ratings yet
- 102 Recitation 2Document2 pages102 Recitation 2omar msmqNo ratings yet
- Applied Physics Notes For Computer, Electrical, Electronics Branch by Prof. Atul Waghmare 9657824223Document48 pagesApplied Physics Notes For Computer, Electrical, Electronics Branch by Prof. Atul Waghmare 9657824223AtulWaghmareNo ratings yet
- Tutorial EMDocument3 pagesTutorial EMMaheshree GohilNo ratings yet
- Sol 2Document9 pagesSol 2Saif IshtiaqueNo ratings yet
- Electromagnetism: Example Sheet 1Document3 pagesElectromagnetism: Example Sheet 1Fulgen VillegasNo ratings yet
- PH 531: Electromagnetic Theory IDocument1 pagePH 531: Electromagnetic Theory ISaif IshtiaqueNo ratings yet
- Em Questions 2019Document20 pagesEm Questions 2019MartinaGmizaNo ratings yet
- 02 Tutorial Vectors+ElectrostaticsDocument2 pages02 Tutorial Vectors+ElectrostaticsmukeshNo ratings yet
- Midsem 2Document1 pageMidsem 2pankajNo ratings yet
- AP Physics C - 2021 HW 12 Potential & CapacitanceDocument3 pagesAP Physics C - 2021 HW 12 Potential & CapacitanceRegina LinNo ratings yet
- Divr Rotr Gradr Rotfrrgradfr Divar Rotargradar PR M R M R PR Grad R MR Rot R M Ab Ambbma Abrotc Bacab CDocument2 pagesDivr Rotr Gradr Rotfrrgradfr Divar Rotargradar PR M R M R PR Grad R MR Rot R M Ab Ambbma Abrotc Bacab CDuong PhamNo ratings yet
- Physics: Electromagnetism Spring 2007 PROBLEM SET 7 SolutionsDocument7 pagesPhysics: Electromagnetism Spring 2007 PROBLEM SET 7 SolutionsByron AlvaradoNo ratings yet
- Electromagnetism Practice Problems 1 4Document18 pagesElectromagnetism Practice Problems 1 4Minh Trương PhúcNo ratings yet
- EM1 - Final - 2019Spr 2Document5 pagesEM1 - Final - 2019Spr 2홍윤제No ratings yet
- Physics II ProblemsDocument1 pagePhysics II ProblemsBOSS BOSSNo ratings yet
- Physics II Problems PDFDocument1 pagePhysics II Problems PDFBOSS BOSSNo ratings yet
- Dielectric Image MethodDocument7 pagesDielectric Image MethodvanalexbluesNo ratings yet
- SC 4Document6 pagesSC 4jspammail2306No ratings yet
- Homework Problem 1Document2 pagesHomework Problem 1Daniela Benavides RubioNo ratings yet
- Null 2Document7 pagesNull 2Sourav SahaNo ratings yet
- PHY 103 Problem Set - 5 IITK /ynm 21 August 2013: DIPA: Discussion of Illustrative Problems and AssignmentsDocument1 pagePHY 103 Problem Set - 5 IITK /ynm 21 August 2013: DIPA: Discussion of Illustrative Problems and AssignmentsPiyush PatelNo ratings yet
- Important Questions - EMWDocument2 pagesImportant Questions - EMWSandeep KumarNo ratings yet
- Ch-2 Holiday AssignmentDocument12 pagesCh-2 Holiday Assignmentsuryansu2006No ratings yet
- Electromagnetics Endterm 1Document13 pagesElectromagnetics Endterm 1dolarmarizninaNo ratings yet
- 02 - Potential & Cap - AssignmentDocument3 pages02 - Potential & Cap - AssignmentcaceyNo ratings yet
- ED-I Internal Test 04.08.2021Document2 pagesED-I Internal Test 04.08.2021Sandesh KaradNo ratings yet
- Unit 1Document5 pagesUnit 1Sapata KumarNo ratings yet
- First-Year Electromagnetism: Problem Set 2: Hilary Term 2018, Prof LM Herz B. The Method of Image ChargesDocument2 pagesFirst-Year Electromagnetism: Problem Set 2: Hilary Term 2018, Prof LM Herz B. The Method of Image Chargeswilmer benavidesNo ratings yet
- Full Download Quantum Mechanics 6th Rae Solution Manual PDF Full ChapterDocument36 pagesFull Download Quantum Mechanics 6th Rae Solution Manual PDF Full Chaptertortuous.osmiousr3v45i100% (24)
- MHD Ps PDFDocument5 pagesMHD Ps PDFkarishma kumarNo ratings yet
- Physics 72 Problem SetDocument3 pagesPhysics 72 Problem SetJazzverNo ratings yet
- 2023 EM1 hw3Document3 pages2023 EM1 hw3810003No ratings yet
- Electromagnetic Tutorial 5Document2 pagesElectromagnetic Tutorial 5everlovingmansiNo ratings yet
- FISI - 6431: Problem Set 2Document2 pagesFISI - 6431: Problem Set 2Jose D Sanchez BurgosNo ratings yet
- Tute Sheet Emt Non CitDocument15 pagesTute Sheet Emt Non CitSonu Patel0% (1)
- PHYF125 Tutorial Questions T2 2122Document11 pagesPHYF125 Tutorial Questions T2 2122Agag HsgsNo ratings yet
- Electromagnetic Theory I (PH-424) Problem Set 4Document2 pagesElectromagnetic Theory I (PH-424) Problem Set 4DEBANJAN ADHIKARINo ratings yet
- Paper - 1 (Question Paper) - 6Document17 pagesPaper - 1 (Question Paper) - 6Saumya MundraNo ratings yet
- Electricity and Magnetism Test 2020Document4 pagesElectricity and Magnetism Test 2020Anuja ojhaNo ratings yet
- Electrostatics - JEE Main 2020-22 PYQDocument255 pagesElectrostatics - JEE Main 2020-22 PYQfsqf41No ratings yet
- Electric and Magnetic Fields Assignment 7: Questions 1-4 Count For 95% of The Marks and Question 5 For 5% Q1Document2 pagesElectric and Magnetic Fields Assignment 7: Questions 1-4 Count For 95% of The Marks and Question 5 For 5% Q1ShootingStarPhotonsNo ratings yet
- Problems & QuestionsDocument3 pagesProblems & QuestionsRanko KamilNo ratings yet
- Xii Phy Holidayhomework 2Document13 pagesXii Phy Holidayhomework 2Amar Prasad DashNo ratings yet
- CapacitanceDocument71 pagesCapacitanceTharaj ThajNo ratings yet
- 6 Lecture 5 Gauss Capacitor DielectricDocument27 pages6 Lecture 5 Gauss Capacitor DielectricDaniel NegutNo ratings yet
- Problems On ElectrostaticsDocument3 pagesProblems On ElectrostaticsBen QuachtranNo ratings yet
- CLASS XII - CH - 2 - ELECTROSTATIC POTENTIAlAND CAPACITANCE (COMPETENCY - BASED TEST ITEMS) MARKS WISEDocument32 pagesCLASS XII - CH - 2 - ELECTROSTATIC POTENTIAlAND CAPACITANCE (COMPETENCY - BASED TEST ITEMS) MARKS WISERohan SNo ratings yet
- Problems in Quantum Mechanics: Third EditionFrom EverandProblems in Quantum Mechanics: Third EditionRating: 3 out of 5 stars3/5 (2)
- 07 Deep Reinforcement Learning (John)Document52 pages07 Deep Reinforcement Learning (John)Muhammad RizwanNo ratings yet
- 01 Introduction To Feedforward Neural Networks (Hugo)Document78 pages01 Introduction To Feedforward Neural Networks (Hugo)Muhammad RizwanNo ratings yet
- On The Move - Dynamical Systems For Modeling, Measurement and Inference in Low Dimensional Signal ModelsDocument50 pagesOn The Move - Dynamical Systems For Modeling, Measurement and Inference in Low Dimensional Signal ModelsMuhammad RizwanNo ratings yet
- Automated Low-Level Analysis and Description of Diverse Intelligence (Aladdin) VideoDocument11 pagesAutomated Low-Level Analysis and Description of Diverse Intelligence (Aladdin) VideoMuhammad RizwanNo ratings yet
- Convolutional Neural Network: From Theory To ImplementationDocument5 pagesConvolutional Neural Network: From Theory To ImplementationMuhammad RizwanNo ratings yet
- Linear Factor Models and Auto-EncodersDocument28 pagesLinear Factor Models and Auto-EncodersMuhammad RizwanNo ratings yet
- NMF TutorialDocument189 pagesNMF TutorialMuhammad RizwanNo ratings yet
- Sidebar 1Document4 pagesSidebar 1Muhammad RizwanNo ratings yet
- Bare Demo of Ieeetran - Cls For T M: Ransactions On AgneticsDocument1 pageBare Demo of Ieeetran - Cls For T M: Ransactions On AgneticsMuhammad RizwanNo ratings yet
- Example ThesisDocument17 pagesExample ThesisMuhammad RizwanNo ratings yet
- The cornell document class for L TEX 2εDocument20 pagesThe cornell document class for L TEX 2εMuhammad RizwanNo ratings yet
- 1 Example 1: This Is The Text in Example OneDocument1 page1 Example 1: This Is The Text in Example OneMuhammad RizwanNo ratings yet
- Thesis PDFDocument25 pagesThesis PDFMuhammad RizwanNo ratings yet
- English Cheat Sheet 1 (05/10/2015) : Types of Sentences VerbsDocument1 pageEnglish Cheat Sheet 1 (05/10/2015) : Types of Sentences VerbsMuhammad RizwanNo ratings yet
- Title: Section 3Document1 pageTitle: Section 3Muhammad RizwanNo ratings yet
- L Texcheatsheet: 1 What Is L Tex?Document4 pagesL Texcheatsheet: 1 What Is L Tex?Muhammad RizwanNo ratings yet
- L TEX 2ε Cheat Sheet: Document classesDocument2 pagesL TEX 2ε Cheat Sheet: Document classesMuhammad RizwanNo ratings yet
- Complex Cheat SheetDocument1 pageComplex Cheat SheetMuhammad RizwanNo ratings yet