Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Table of Ions
Table of Ions
Uploaded by
api-2185117410 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
522 views1 pageOriginal Title
table of ions
Copyright
© Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pdf or txt
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
522 views1 pageTable of Ions
Table of Ions
Uploaded by
api-218511741Copyright:
Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pdf or txt
You are on page 1of 1
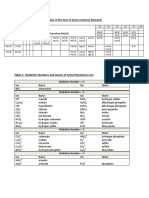
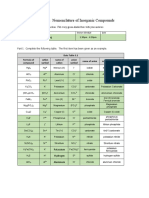
A TABLE OF IONS
NEGATIVE IONS (ANIONS) 3
P3 phosphide PO4 phosphate
3
POSITIVE IONS (CATIONS) +1
H+ hydrogen Li lithium Na+ sodium K+ potassium NH4 ammonium Ag+ silver
+ +
2
O2 oxide S sulfide SO42 sulfate CO32 carbonate Cr2O7 dichromate CrO42 chromate
2 2
1
F fluoride Cl chloride Br bromide I iodide OH hydroxide NO3 nitrate HCO3 bicarbonate MnO4
permanganate
+2
Ba2+ barium Cu2+ copper(II) (cupric) Zn2+ zinc Ca2+ calcium Fe2+ iron(II) (ferrous) Pb2+ lead Mg2+ magnesium
+3
Al3+ aluminium Fe3+ iron(III) (ferric)
Note: Some metals (eg iron) can have two possible valencies. To distinguish these, the valency is put in brackets after the name - such as iron(II) and iron(III). The older method, still in common use, is to use the suffix ous for the lower valency and ic for the higher valency. Hence ferrous and ferric.
You might also like
- documentDocument4 pagesdocumenterror.sutNo ratings yet
- Common Ions and Their ChargesDocument2 pagesCommon Ions and Their ChargesDip MajumderNo ratings yet
- Valency and Formulae-HandoutDocument3 pagesValency and Formulae-HandoutABHAVYA RAJNo ratings yet
- NomenclatureDocument68 pagesNomenclatureel tetraNo ratings yet
- QC1 - Naming Covalent Compounds and Ionic FormulaeDocument5 pagesQC1 - Naming Covalent Compounds and Ionic Formulaeykame4096No ratings yet
- Complete NomenclatureDocument10 pagesComplete NomenclaturezainalexanderaliNo ratings yet
- Ion Reference Updated 19-20Document2 pagesIon Reference Updated 19-20waxove1775No ratings yet
- Ion ReferenceDocument2 pagesIon Referenceapi-254514513No ratings yet
- ChemistryDocument2 pagesChemistryDimitri BlackwoodNo ratings yet
- Symbols and Charges For Monoatomic IonsDocument2 pagesSymbols and Charges For Monoatomic IonsaNo ratings yet
- Ammonium NH: List of Common IonsDocument2 pagesAmmonium NH: List of Common IonsCrispy ChickenNo ratings yet
- Write The Formulas For The Following Ionic Compounds:: Bonding and Naming WS 4Document2 pagesWrite The Formulas For The Following Ionic Compounds:: Bonding and Naming WS 4Bea Lha Zandra BesingaNo ratings yet
- General Chemistry 2 Module 3Document6 pagesGeneral Chemistry 2 Module 3Jason Vinluan CarinanNo ratings yet
- Chemical Formula Work Sheet 3Document3 pagesChemical Formula Work Sheet 3shayonninanNo ratings yet
- Common Cations:: Simple IonsDocument2 pagesCommon Cations:: Simple IonsElmer CarterNo ratings yet
- Naming CompoundsDocument2 pagesNaming CompoundsTeresa Marie CorderoNo ratings yet
- Common IonsDocument3 pagesCommon IonsabdallaaNo ratings yet
- W3 02 Naming Chemical Formulas of CompoundsDocument20 pagesW3 02 Naming Chemical Formulas of CompoundsResmiel IrishNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1, Naming CompoundsDocument19 pagesChapter 1, Naming CompoundsKurdishNo ratings yet
- 3-4 Polyatomic and Transition Ions SlidesDocument12 pages3-4 Polyatomic and Transition Ions Slidesapi-240915238No ratings yet
- Symbols and Charges-Monoatomic IonsDocument20 pagesSymbols and Charges-Monoatomic Ionsjon_kasilagNo ratings yet
- Chemical Nomenclature: Experiment #3Document27 pagesChemical Nomenclature: Experiment #3Ayi PunsalanNo ratings yet
- Ions and Their Common NamesDocument1 pageIons and Their Common NamesAnaya ChNo ratings yet
- CHEMISTRYDocument9 pagesCHEMISTRYXyiee ViorNo ratings yet
- Table For Urry Q3Document1 pageTable For Urry Q3andyNo ratings yet
- NamingDocument8 pagesNamingMADAYAG, RUTH L.No ratings yet
- 5.9 Polyatomic CompoundsDocument3 pages5.9 Polyatomic Compoundsmichael.delaney8541No ratings yet
- Polyatomic Ions ListDocument2 pagesPolyatomic Ions Listapi-256236481No ratings yet
- Cations: Al Aluminium Fe Iron (III) CR Chromium (III)Document2 pagesCations: Al Aluminium Fe Iron (III) CR Chromium (III)NPNo ratings yet
- Asm 33333333333Document2 pagesAsm 33333333333p5jp29697cNo ratings yet
- Stoichiometry-1: Chemical Nomenclature (Iupac)Document39 pagesStoichiometry-1: Chemical Nomenclature (Iupac)Vimanan A/L S. VelangganiNo ratings yet
- Chemical Nomenclature: (Naming Compounds)Document38 pagesChemical Nomenclature: (Naming Compounds)AhadSamiNo ratings yet
- Symbols and Names For Common Polyatomic IonsDocument1 pageSymbols and Names For Common Polyatomic IonsElixirNo ratings yet
- MODULE 2tables As ReferencesDocument10 pagesMODULE 2tables As ReferencesJuneyale Padilla100% (1)
- Common Cations & AnionsDocument2 pagesCommon Cations & AnionsDrew KlineNo ratings yet
- Unit 5 - Notes Nomenclature DLB Key Pages 1-7Document9 pagesUnit 5 - Notes Nomenclature DLB Key Pages 1-7Alea PrillyNo ratings yet
- Review #3 NomenclatureDocument1 pageReview #3 NomenclatureCassandra MachadoNo ratings yet
- Formulae of Some Common CationsDocument1 pageFormulae of Some Common CationsKhairul HakiminNo ratings yet
- Table 1: Usual Oxidation Number of The Ions of Some Common ElementsDocument1 pageTable 1: Usual Oxidation Number of The Ions of Some Common Elementsliam leeNo ratings yet
- Naming FormulasDocument3 pagesNaming Formulasilikegay2dmensNo ratings yet
- Chemical Formula Writing Worksheet PDFDocument4 pagesChemical Formula Writing Worksheet PDFkezia0% (1)
- Naming and Writing Ionic CompoundsDocument40 pagesNaming and Writing Ionic CompoundsJPHijastro15No ratings yet
- Chemical NomenclatureDocument7 pagesChemical NomenclatureKeith Lavin100% (1)
- Common Ion NamesDocument1 pageCommon Ion NamesRiemann100% (1)
- List of Catios and AnionsDocument7 pagesList of Catios and AnionsrituNo ratings yet
- Valency SheetDocument3 pagesValency SheetBex JacobsNo ratings yet
- Common Ions and Their ChargesDocument1 pageCommon Ions and Their ChargesChung Chee YuenNo ratings yet
- Element Group Cation Element Group AnionsDocument3 pagesElement Group Cation Element Group AnionsCharlotte TanNo ratings yet
- ApsummerDocument5 pagesApsummerLayleeNo ratings yet
- Common Ions and Their ChargesDocument2 pagesCommon Ions and Their ChargesSJ SuingNo ratings yet
- Common IonsDocument1 pageCommon IonsKah JunNo ratings yet
- NomenclatureDocument28 pagesNomenclatureJhayce Christian S. CapanayanNo ratings yet
- Lecture 1 EquationsDocument11 pagesLecture 1 Equationsmerabamoding11No ratings yet
- Ion Memorization ListDocument2 pagesIon Memorization Listdchao94No ratings yet
- 2.10 Naming Binary Nonmetal CompoundsDocument6 pages2.10 Naming Binary Nonmetal Compoundsmqdzpmjp2rNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2 StoichiometryDocument111 pagesChapter 2 StoichiometryNORMASLAILA JAAFARNo ratings yet
- Symbols and Names of Common Metal Ions With More Than One Ionic Charge Symbol Stock Name Classical NameDocument2 pagesSymbols and Names of Common Metal Ions With More Than One Ionic Charge Symbol Stock Name Classical NameLilyNo ratings yet
- Nomenclature of Inorganic Compounds: Report SheetDocument3 pagesNomenclature of Inorganic Compounds: Report SheetAEsmilingNo ratings yet
- Chapter 5 Coordination CompoundDocument36 pagesChapter 5 Coordination Compoundammar zakariaNo ratings yet
- Chemical Elements Pocket Guide: Detailed Summary of the Periodic TableFrom EverandChemical Elements Pocket Guide: Detailed Summary of the Periodic TableNo ratings yet
- Chemistry Research TaskDocument4 pagesChemistry Research Taskapi-218511741No ratings yet
- Eslwriting Video Worksheet CosmeticsDocument5 pagesEslwriting Video Worksheet Cosmeticsapi-2185117410% (1)
- 2 5 Marking ScheduleDocument6 pages2 5 Marking Scheduleapi-218511741No ratings yet
- First Spontaneous Reactions WorksheetDocument2 pagesFirst Spontaneous Reactions Worksheetapi-2185117410% (1)
- Entropy Notes and Exam QuestionsDocument3 pagesEntropy Notes and Exam Questionsapi-218511741100% (1)
- IUPAC HandoutDocument9 pagesIUPAC HandoutjanellamaikaNo ratings yet
- Esterification ExperimentDocument2 pagesEsterification Experimentapi-218511741No ratings yet
- On WorksheetDocument2 pagesOn Worksheetapi-218511741No ratings yet
- Quantitative Chem Notes Titrations OnlyDocument18 pagesQuantitative Chem Notes Titrations Onlyapi-218511741No ratings yet
- Level 2 Basic Facts Worksheet AnswersDocument9 pagesLevel 2 Basic Facts Worksheet Answersapi-218511741No ratings yet
- Oxidation of Organic Compounds WorksheetDocument3 pagesOxidation of Organic Compounds Worksheetapi-218511741No ratings yet
- Iron - Thiocyanate EquilibriumDocument7 pagesIron - Thiocyanate Equilibriumapi-218511741No ratings yet
- Opticalisomerism 09Document2 pagesOpticalisomerism 09api-218511741No ratings yet
- Fats and Oils NotesDocument1 pageFats and Oils Notesapi-218511741No ratings yet
- Substitution Notes For StudentsDocument2 pagesSubstitution Notes For Studentsapi-218511741No ratings yet
- Aldehydes and Ketones ExperimentDocument2 pagesAldehydes and Ketones Experimentapi-218511741No ratings yet
- Organic Names and Formula Answers OnlyDocument1 pageOrganic Names and Formula Answers Onlyapi-218511741No ratings yet
- Names and Structures Small Test 2Document1 pageNames and Structures Small Test 2api-218511741No ratings yet
- Organic Names and Formula QuestionsDocument1 pageOrganic Names and Formula Questionsapi-218511741No ratings yet