Professional Documents
Culture Documents
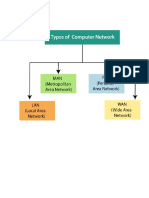
Local Area Network Wide Area Network Public Switched Telephone Network
Local Area Network Wide Area Network Public Switched Telephone Network
Uploaded by
76697669Original Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Local Area Network Wide Area Network Public Switched Telephone Network
Local Area Network Wide Area Network Public Switched Telephone Network
Uploaded by
76697669Copyright:
Available Formats
A near-me area network (NAN) is a logical communication network that focuses on communication among wireless devices in close proximity.
Unlike local area networks (LANs), in which the devices are in the same network segment and share the same broadcast domain, the devices in a NAN can belong to different proprietary network infrastructures (for example, different mobile carriers). So, even though two devices are geographically close, the communication path between them might, in fact, traverse a long distance, going from a LAN, through the Internet, and to another LAN. NAN applications focus on two-way communications among people within a certain proximity to each other, but don't generally concern themselves with those peoples exact locations.
An Internet area network (IAN) is a concept for a communications network that connects voice and data endpoints within a cloud environment over IP, replacing an existing Local Area Network (LAN), Wide Area Network (WAN) and/or Public switched telephone network (PSTN). Seen by proponents as the networking model of the future, an IAN securely connects endpoints through the public Web, so that they can communicate and exchange information and data without being tied to a physical location. Unlike a LAN, which interconnects computers in a limited area such as a home, school, computer laboratory or office building using network media, or a WAN, which is a network that covers a broad area (i.e., any telecommunications network that links across metropolitan, regional or national boundaries) using private or public network transports, the IAN eliminates a geographic profile for the network entirely because the applications and communications services have become virtualized. Endpoints need only be connected over a broadband connection to the Internet.
[2]
[1]
You might also like
- Sir Kyle Perez 3Document2 pagesSir Kyle Perez 3Paulo CelisNo ratings yet
- Types of NetworksDocument5 pagesTypes of NetworksmmrmadhuNo ratings yet
- 1 What Is A Computer NetworkDocument4 pages1 What Is A Computer NetworkMd. Abdullah ZishanNo ratings yet
- Diff Types of Comp NetworksDocument3 pagesDiff Types of Comp NetworkssuzettNo ratings yet
- Types of NetworkDocument15 pagesTypes of NetworkTito Cadizal Jr.No ratings yet
- Tech Support QuestiondDocument1 pageTech Support QuestiondLeroy LeoNo ratings yet
- Zachie V2Document1 pageZachie V2Joseph LapsoNo ratings yet
- Types of NetworksDocument3 pagesTypes of NetworksOsmanicNo ratings yet
- Mobile Devices: Local Area NetworkDocument19 pagesMobile Devices: Local Area NetworkTushar KhandelwalNo ratings yet
- NetworkDocument11 pagesNetworkkhushi birlaNo ratings yet
- Mba AssignmentDocument17 pagesMba AssignmentFatima AliNo ratings yet
- Art IntegrationDocument5 pagesArt IntegrationHargun MakkarNo ratings yet
- Computer Networks: by Tilak.k & AbhishekDocument10 pagesComputer Networks: by Tilak.k & Abhishektilak101No ratings yet
- Computer NetworkDocument4 pagesComputer NetworkFejiro AbirhireNo ratings yet
- Inbound 227821031997857446Document2 pagesInbound 227821031997857446Aidin JumadNo ratings yet
- History of InternetDocument1 pageHistory of InternetTushar ShahNo ratings yet
- Presentation 1Document8 pagesPresentation 1lanaabas429No ratings yet
- Teal Futuristic Technology Facebook CoverDocument24 pagesTeal Futuristic Technology Facebook CoverGarrette ValenciaNo ratings yet
- Types of Computer Networks Personal Area NetworkDocument3 pagesTypes of Computer Networks Personal Area Networkchapatatatenda_45863No ratings yet
- What Is The Computer Network and It Types MahmudDocument1 pageWhat Is The Computer Network and It Types MahmudMahmud MuseNo ratings yet
- Types of NetworkDocument3 pagesTypes of NetworkCaseelyn Joy NantizaNo ratings yet
- KJLKJKDocument29 pagesKJLKJKHamzaNoumanNo ratings yet
- Computer Networking ResearchDocument5 pagesComputer Networking ResearchCheina Ann OrpillaNo ratings yet
- What Is NetworkDocument25 pagesWhat Is Networkshreya100% (1)
- Types of Network 1yvycyDocument3 pagesTypes of Network 1yvycy1I Delatorre NoliboyNo ratings yet
- 1.3. Types of Computer NetworksDocument10 pages1.3. Types of Computer NetworksJUGRAJ SINGHNo ratings yet
- Types of NetworkDocument2 pagesTypes of NetworkAMIT KUMARNo ratings yet
- Personal Area Network (PAN) : NetworksDocument3 pagesPersonal Area Network (PAN) : NetworksShirlyn PerezNo ratings yet
- PDF DocumentDocument20 pagesPDF DocumentSheila PadinNo ratings yet
- Types of NetworksDocument13 pagesTypes of NetworksharmangahirNo ratings yet
- Classification of NetworksDocument13 pagesClassification of NetworksJames MacalaladNo ratings yet
- Computer Network11Document10 pagesComputer Network11manjeetsingh90No ratings yet
- Types of NetworkDocument16 pagesTypes of NetworkRINA ARANIGONo ratings yet
- 11 Types of Networks in Use TodayDocument3 pages11 Types of Networks in Use TodaySaif ul HassanNo ratings yet
- Different Types of Network According To ScaleDocument15 pagesDifferent Types of Network According To ScaleJohn Lowell BejasaNo ratings yet
- 11 Types of Network: Jherrymie L. Galicia X-14 Mrs - ImperialDocument12 pages11 Types of Network: Jherrymie L. Galicia X-14 Mrs - ImperialEmil PerezNo ratings yet
- Communication Network: Let's Learn With Fun Together!Document10 pagesCommunication Network: Let's Learn With Fun Together!Shein RoseteNo ratings yet
- Types of Computer NetworksDocument8 pagesTypes of Computer NetworksMia StocktonNo ratings yet
- Computer NetworkingDocument2 pagesComputer NetworkingDebabrata DuttaNo ratings yet
- Answer: - Difference Between The LAN and The WANDocument1 pageAnswer: - Difference Between The LAN and The WANherrajohnNo ratings yet
- PT Lesson2 CompNetworkDocument20 pagesPT Lesson2 CompNetworkbench SantosNo ratings yet
- (Network) Computer-NetworkDocument9 pages(Network) Computer-NetworkKaidyo ChiNo ratings yet
- Networks Geographical Area, Like A Home, Office, or Groups of Buildings E.G. ADocument5 pagesNetworks Geographical Area, Like A Home, Office, or Groups of Buildings E.G. ASourav BiswasNo ratings yet
- What Is A Local-Area Network (LAN) ?Document1 pageWhat Is A Local-Area Network (LAN) ?surajNo ratings yet
- NETWORK SYSTEM (Ga, Fernandez, Gio and Louis Gutierrez)Document11 pagesNETWORK SYSTEM (Ga, Fernandez, Gio and Louis Gutierrez)Ruby HermanoNo ratings yet
- ICT 8 - Q3 (Network and Network Devices)Document4 pagesICT 8 - Q3 (Network and Network Devices)Glaiza HigoNo ratings yet
- ICT Lec-7 Introduction To Computer NetworkDocument19 pagesICT Lec-7 Introduction To Computer NetworkShoaib KareemNo ratings yet
- Personal Area NetworkDocument5 pagesPersonal Area Networkshahed_mdbNo ratings yet
- Networking On HDFCDocument9 pagesNetworking On HDFCAbhishek SrivastavaNo ratings yet
- Network, WAN - Wide Area Network, WLAN - Wireless Local Area Network, MAN - Metropolitan Area Network and CAN - Campus Area NetworkDocument1 pageNetwork, WAN - Wide Area Network, WLAN - Wireless Local Area Network, MAN - Metropolitan Area Network and CAN - Campus Area NetworkPrasadaRaoNo ratings yet
- Unit 1 Overview of Internet and Network 1Document7 pagesUnit 1 Overview of Internet and Network 1Dudzayi KasiyoNo ratings yet
- Topic 8 Computer NetworksDocument4 pagesTopic 8 Computer NetworksOsii JuliusNo ratings yet
- 11 Types of Networks ExplainedDocument2 pages11 Types of Networks ExplainedDwin RoscoNo ratings yet
- Course Name It For Mangers Course CodeDocument19 pagesCourse Name It For Mangers Course CodesaadNo ratings yet
- Internet Technology:: Network Basics: Classification of NetworkDocument30 pagesInternet Technology:: Network Basics: Classification of NetworkAdibahNo ratings yet
- Pan Vs VanDocument1 pagePan Vs VanFahad AhmedNo ratings yet
- Personal Area Network (PAN)Document5 pagesPersonal Area Network (PAN)Garcia Justine RestarNo ratings yet
- 2nd Quarter TLE ICT 7 - Chapter 6Document11 pages2nd Quarter TLE ICT 7 - Chapter 6Raymond PunoNo ratings yet
- Trabalho Redes 2Document5 pagesTrabalho Redes 2Vinicius FreitasNo ratings yet
- (Advertising Set A) Q1) Answer The Following. (Any 2) 15Document2 pages(Advertising Set A) Q1) Answer The Following. (Any 2) 1576697669No ratings yet
- David M. JarzenDocument6 pagesDavid M. Jarzen76697669No ratings yet
- Iind Unit Test Examination, January 2016: Shoeb Junior CollegeDocument2 pagesIind Unit Test Examination, January 2016: Shoeb Junior College76697669No ratings yet
- HR Issues and Challenges in Indian Banking Sector: Research ScholarDocument17 pagesHR Issues and Challenges in Indian Banking Sector: Research ScholarsownikaNo ratings yet
- Admire Clases: Q.1. A) Fill in The BlanksDocument3 pagesAdmire Clases: Q.1. A) Fill in The Blanks76697669No ratings yet
- Index: SR .NO Topic Page NoDocument3 pagesIndex: SR .NO Topic Page No76697669No ratings yet
- A Bipolar Junction TransistorDocument29 pagesA Bipolar Junction Transistor76697669No ratings yet