Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Cardiac Contraction: Transverse (T) Tubule: Enables Conduction of Action Potential To Interior of Muscle Cell
Cardiac Contraction: Transverse (T) Tubule: Enables Conduction of Action Potential To Interior of Muscle Cell
Uploaded by
Michael HiiOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Cardiac Contraction: Transverse (T) Tubule: Enables Conduction of Action Potential To Interior of Muscle Cell
Cardiac Contraction: Transverse (T) Tubule: Enables Conduction of Action Potential To Interior of Muscle Cell
Uploaded by
Michael HiiCopyright:
Available Formats
Cardiac Contraction
Monday, 19 March 2012 3:09 PM
Cardiac Co...
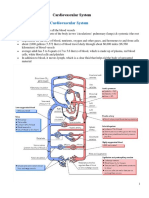
Contractions are caused by an influx of calcium to the interior of the cell The heart requires ionic calcium in the extracellular environment, in order to contract (in addition to calcium from internal stores). Calcium influx from the exterior of the cell causes calcium to be released from the interior of the cell (from the sarcoplasmic reticulum). Calcium enables myosin bind to actin (troponin and tropomyosin are detached). ATP is used to detach myosin from actin (hence lack of ATP, due to death, causes rigor mortis). Transverse (T) tubule: enables conduction of action potential to interior of muscle cell
Calcium-induced calcium release L-Type Calcium Channel
Calcium release channels
Stroke Volume: the volume of blood pumped in one beat The output of the heart from the left ventricle must match that of the right ventricle (output must match input). Frank-Starling Law Hence the force of contraction of the heart increases when end-diastolic pressure and volume is
Case Based Learning Page 1
Hence the force of contraction of the heart increases when end-diastolic pressure and volume is increased, i.e. muscle is stretched. (may be due to increased venous return to the heart) Types of Heart Failure: Systolic Diastolic
Sympathetic stimulation assists in maintaining proper cardiac function, however proper function is not completely attainable.
Case Based Learning Page 2
You might also like
- Resumen CardioDocument15 pagesResumen CardioSofia LacuadraNo ratings yet
- Cardiac L2Document18 pagesCardiac L2Qutaybah JahmanyNo ratings yet
- Pathophysiology On ArrhythmiaDocument34 pagesPathophysiology On ArrhythmiaYhr Yh100% (1)
- Cardiovascular Physiology: Clement Tettey, PHDDocument62 pagesCardiovascular Physiology: Clement Tettey, PHDRuhianat OsmanNo ratings yet
- Mechanical Function of The HeartDocument28 pagesMechanical Function of The HeartKarmilahNNo ratings yet
- 01 - Kontraksi Otot JantungDocument39 pages01 - Kontraksi Otot JantungNauval Zilal FananyNo ratings yet
- What Is Atrial DepolarizationDocument5 pagesWhat Is Atrial DepolarizationPrashant wadkarNo ratings yet
- Cardiovascular AssessmentDocument182 pagesCardiovascular AssessmentAbie Jean BalbontinNo ratings yet
- Functional Human Physiology: For The Exercise and Sport Sciences The Cardiovascular System: Cardiac FunctionDocument186 pagesFunctional Human Physiology: For The Exercise and Sport Sciences The Cardiovascular System: Cardiac FunctionBery Agana F. PurbaNo ratings yet
- Diagnostic Use of Radiopharmaceuticals in Nuclear Medicine (Heart)Document21 pagesDiagnostic Use of Radiopharmaceuticals in Nuclear Medicine (Heart)Orindia SuarminNo ratings yet
- Atrial Depolarization: The ST-segmentDocument2 pagesAtrial Depolarization: The ST-segmentbinukirubaNo ratings yet
- Cardiac Muscle NotesDocument17 pagesCardiac Muscle Notessandeepv08No ratings yet
- Cardiovascular DrugsDocument33 pagesCardiovascular DrugsKish Gabriel100% (1)
- Phys 4.1 CV Heart Electrical NOTESDocument5 pagesPhys 4.1 CV Heart Electrical NOTESEsther RaniNo ratings yet
- Pathophysiology of Cardiovascular System Feghiu I., Tacu L., Iarovoi ADocument25 pagesPathophysiology of Cardiovascular System Feghiu I., Tacu L., Iarovoi ALunguVictoriaNo ratings yet
- 3 - Cardiac Contractility - Ass. Prof. Doaa Abou-Bakr - 2020Document8 pages3 - Cardiac Contractility - Ass. Prof. Doaa Abou-Bakr - 2020Hossam BaniisNo ratings yet
- Components of The Cardiovascular SystemDocument23 pagesComponents of The Cardiovascular SystemMr. DummyNo ratings yet
- Exam 4 Study Guide (1386)Document11 pagesExam 4 Study Guide (1386)S. MartinezNo ratings yet
- L1 MCQsDocument5 pagesL1 MCQsmeqdadamr9No ratings yet
- Pages From Introductory Human Physiology by Emma Jakoi, Jennifer CarbreyDocument8 pagesPages From Introductory Human Physiology by Emma Jakoi, Jennifer CarbreyDuat NDNo ratings yet
- Chapter 4 - Cardiovascular SystemDocument8 pagesChapter 4 - Cardiovascular SystemPersonne AnonymeNo ratings yet
- CardioDocument40 pagesCardioOctavio González InversonNo ratings yet
- 38.17 Cardiac Pacing: Basic Concepts: Renato Pietro RicciDocument16 pages38.17 Cardiac Pacing: Basic Concepts: Renato Pietro RicciurtikikeNo ratings yet
- Iv. Review of Anatomy and PhysiologyDocument9 pagesIv. Review of Anatomy and PhysiologyDizerine Mirafuentes RolidaNo ratings yet
- Explanation of The Cardiac Conduction SystemDocument4 pagesExplanation of The Cardiac Conduction SystemCharli VilcanNo ratings yet
- BSA 1C 11-02-2021the Cardiovascular SystemDocument28 pagesBSA 1C 11-02-2021the Cardiovascular SystemAngelika ButaslacNo ratings yet
- Case 3Document4 pagesCase 3the urvashiNo ratings yet
- CirculationDocument11 pagesCirculationRishikaphriya RauichandranNo ratings yet
- Heart MuscleDocument10 pagesHeart Muscle22194No ratings yet
- The HeartDocument9 pagesThe HeartShiela Belandres MendozaNo ratings yet
- Human Circulatory SystemDocument8 pagesHuman Circulatory SystemChelsea EdwardsNo ratings yet
- 2015A&PIntro CardiovascularHandoutDocument16 pages2015A&PIntro CardiovascularHandoutMaggieHameedNo ratings yet
- Electrical Activity of Heart CellsDocument37 pagesElectrical Activity of Heart Cellsspdharanimaran001No ratings yet
- 3-CVS.new3Document16 pages3-CVS.new3Mariam WalyNo ratings yet
- Lecture 2: The Heart: Prof. Magidah Alaudi, M.SCDocument62 pagesLecture 2: The Heart: Prof. Magidah Alaudi, M.SCMonicaNo ratings yet
- Phase 2 Cardiac Muscle - 1Document30 pagesPhase 2 Cardiac Muscle - 1erenyorulmaz143No ratings yet
- Cardiovascular System: (Review)Document42 pagesCardiovascular System: (Review)Leichel AlbertoNo ratings yet
- CV Physio-IntroductionDocument33 pagesCV Physio-IntroductionHanaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 18 - The Heart Study Guide: Save Date: Wednesday, March 25, 2009 4:18:00 PMDocument7 pagesChapter 18 - The Heart Study Guide: Save Date: Wednesday, March 25, 2009 4:18:00 PMBettina RosuNo ratings yet
- Kitar KardiakDocument23 pagesKitar KardiakNur Azila ZabidiNo ratings yet
- 1st Year PhysiologyDocument15 pages1st Year PhysiologyMaheen AnwaarNo ratings yet
- ArrythmiasDocument26 pagesArrythmiasValeria MolinaNo ratings yet
- Sifat Dan Kerja Otot Jantung - CVS-K10Document21 pagesSifat Dan Kerja Otot Jantung - CVS-K10Suci Intan FatrisiaNo ratings yet
- Physiology Worksheet Chapter Five: Cardiovascular SystemDocument2 pagesPhysiology Worksheet Chapter Five: Cardiovascular SystemTalya DannawiNo ratings yet
- Blood Clotting Mechanisms and AtherosclesrosisDocument11 pagesBlood Clotting Mechanisms and AtherosclesrosisGizelle Iwo BatkoNo ratings yet
- CVS Physiology FinalDocument21 pagesCVS Physiology FinalVondNo ratings yet
- Physiology Chap9 (Cardiac Muscle)Document5 pagesPhysiology Chap9 (Cardiac Muscle)Man DejeloNo ratings yet
- 8 Coronary CirculationDocument31 pages8 Coronary CirculationAhmed AliNo ratings yet
- 565656Document61 pages565656Bashar AntriNo ratings yet
- Summary Vet Quiz (Cvs-Heart)Document3 pagesSummary Vet Quiz (Cvs-Heart)Deeza Joice CastañedaNo ratings yet
- CirculationDocument10 pagesCirculationKezia JenniferNo ratings yet
- Physiology of The Normal Heart: Key PointsDocument5 pagesPhysiology of The Normal Heart: Key PointsGustavo TejerinaNo ratings yet
- Heart Muscle: The Heart As A Pump and FunctionDocument4 pagesHeart Muscle: The Heart As A Pump and Functionmcwnotes100% (1)
- Coronary CirculationDocument4 pagesCoronary CirculationReena MathewNo ratings yet
- Kelainan Hemodinamik, Thromboemboli Dan SyokDocument82 pagesKelainan Hemodinamik, Thromboemboli Dan SyokwulanNo ratings yet
- The Cardiovascular System 2Document23 pagesThe Cardiovascular System 26rz5b6r9z2No ratings yet
- Cardiac Conduction System - WikipediaDocument32 pagesCardiac Conduction System - Wikipediakirubel demelashNo ratings yet
- Anatomy and Physiology of Heart and Rhd.Document11 pagesAnatomy and Physiology of Heart and Rhd.galangpatrick100% (4)
- Human Body Book | Introduction to the Vascular System | Children's Anatomy & Physiology EditionFrom EverandHuman Body Book | Introduction to the Vascular System | Children's Anatomy & Physiology EditionNo ratings yet
- Dancing in The MoonlightDocument1 pageDancing in The MoonlightMichael HiiNo ratings yet
- Cosmic Girl - JamiroquaiDocument1 pageCosmic Girl - JamiroquaiMichael HiiNo ratings yet
- Liver Histology - Medicine 3Document12 pagesLiver Histology - Medicine 3Michael HiiNo ratings yet
- Game of Thrones - A Dance of Dragons House Card SheetDocument2 pagesGame of Thrones - A Dance of Dragons House Card SheetMichael HiiNo ratings yet
- L9 Trigeminal Nerve P1Document1 pageL9 Trigeminal Nerve P1Michael HiiNo ratings yet
- Copper Metabolism: Distribution of Copper in The BodyDocument4 pagesCopper Metabolism: Distribution of Copper in The BodyMichael HiiNo ratings yet
- Arthritis RobbinsDocument12 pagesArthritis RobbinsMichael HiiNo ratings yet