Professional Documents
Culture Documents
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
24 viewsLecture 04 of Solid State Physics
Lecture 04 of Solid State Physics
Uploaded by
Hena DianThe document discusses techniques for studying crystal structure using x-rays, neutrons, and electrons. It introduces diffraction as the constructive interference of scattering from periodic structures in crystals. The Bragg scattering law governs diffraction and scattering from different crystal planes in the lattice. Crystals can be probed by techniques that penetrate the material without strong interaction, allowing investigation of the periodic atomic structure.
Copyright:
Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Available Formats
Download as PPT, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You might also like
- Solid State Physics I - PPT (Repaired)Document159 pagesSolid State Physics I - PPT (Repaired)davididosa40No ratings yet
- Solid State Chapter 1Document38 pagesSolid State Chapter 1Abrish HaremNo ratings yet
- Today: - Chap 11, Atomic Nature of MatterDocument34 pagesToday: - Chap 11, Atomic Nature of Matterbaig79No ratings yet
- Reciprocal Lattice and Brillouin ZoneDocument5 pagesReciprocal Lattice and Brillouin ZoneanggasoedNo ratings yet
- Teori AtomDocument46 pagesTeori AtomWaskitaDwiNo ratings yet
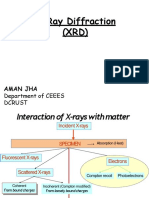
- X Ray DiffractionsDocument15 pagesX Ray DiffractionsAman JhaNo ratings yet
- Atoms and The Atomic TheoryDocument47 pagesAtoms and The Atomic TheoryEdgar PeninsulaNo ratings yet
- Wave Properties of ParticlesDocument14 pagesWave Properties of Particlescornel_24No ratings yet
- X-Ray Diffraction (XRD) : Ulrike TroitzschDocument38 pagesX-Ray Diffraction (XRD) : Ulrike TroitzschprianNo ratings yet
- X-Ray CrystallographyDocument30 pagesX-Ray Crystallographyariba khanNo ratings yet
- Atomic Structure Basic ConceptsDocument39 pagesAtomic Structure Basic ConceptsTithiparna SenguptaNo ratings yet
- Neutron Diffraction TechniquesDocument30 pagesNeutron Diffraction TechniquesAgnes maria maniNo ratings yet
- Class 11 Chapter 2 Structure of AtomDocument131 pagesClass 11 Chapter 2 Structure of Atomyasdin.ashiNo ratings yet
- LatticeDocument15 pagesLatticemisganawsimachew5No ratings yet
- Basic Science of MaterialsDocument208 pagesBasic Science of MaterialsJezzrel Xandy BalmesNo ratings yet
- Nucleus and Its Characterstics: Prof - Arun Bharti Department of Physics University of JammuDocument41 pagesNucleus and Its Characterstics: Prof - Arun Bharti Department of Physics University of JammuSurbhi guptaNo ratings yet
- Atomic Theories Quatum ModelDocument31 pagesAtomic Theories Quatum Modelerinallyson20No ratings yet
- First Year Chemistry 20-02Document100 pagesFirst Year Chemistry 20-02Ahmed Hassan Mina HamadNo ratings yet
- - N = 2 D Sinθ: Bragg EquationDocument35 pages- N = 2 D Sinθ: Bragg EquationdkaurNo ratings yet
- Solid State Part 1Document31 pagesSolid State Part 1fatmaehab.139No ratings yet
- 1.10. Atoms, Spectra and Quantum Nature of LightDocument21 pages1.10. Atoms, Spectra and Quantum Nature of Lightaevadf760No ratings yet
- Calicut University M.SC PHYSICS Experimental Techniques X-RAY DIFFRACTION TECHNIQUES JOYAL (STC)Document22 pagesCalicut University M.SC PHYSICS Experimental Techniques X-RAY DIFFRACTION TECHNIQUES JOYAL (STC)Joyal Jain100% (1)
- CrystalDiffraction Reciprocal Lattice DiffractionMethodsDocument153 pagesCrystalDiffraction Reciprocal Lattice DiffractionMethodsKRISHNA KUMAR GODARANo ratings yet
- Introduction To Particle PhysicsDocument61 pagesIntroduction To Particle PhysicsFrank LipskyNo ratings yet
- Ch. S4 PDFDocument56 pagesCh. S4 PDFlittleitaly5No ratings yet
- 1-Atom StructureDocument75 pages1-Atom Structurenirvanjain212007No ratings yet
- 18BPH62C U3Document63 pages18BPH62C U3moneymaker1906vNo ratings yet
- XRD ReportDocument13 pagesXRD ReportMukulNo ratings yet
- Report XRD 8153Document16 pagesReport XRD 8153Rishabh SoodNo ratings yet
- Formation of The Elements and Nuclear ReactionsDocument23 pagesFormation of The Elements and Nuclear ReactionsHIA GS AACNo ratings yet
- Solid State Chapter 2Document75 pagesSolid State Chapter 2Ambreen KhanNo ratings yet
- Atomic Structure Basic Information FullDocument45 pagesAtomic Structure Basic Information FullSai KrishnaNo ratings yet
- 1.atomic Structure 1-24Document16 pages1.atomic Structure 1-24eamcetmaterials67% (15)
- General Chemistry PresentationDocument45 pagesGeneral Chemistry PresentationJohn Adrian MalunesNo ratings yet
- Condensed Matter Physics - NotesDocument7 pagesCondensed Matter Physics - NotesBs PhysicsNo ratings yet
- HS Science Reviewer (Light and Electromagnetism, Atoms)Document11 pagesHS Science Reviewer (Light and Electromagnetism, Atoms)Halcyon Zenith DelosoNo ratings yet
- X-Ray Diffraction 7Document11 pagesX-Ray Diffraction 7alina.tlekkabylova270202No ratings yet
- Chemistry: Atoms, Molecules, & Chemical BondingDocument149 pagesChemistry: Atoms, Molecules, & Chemical BondingnadnotmeNo ratings yet
- Centre of Excellence of Solid State Physics: Paper: X-Ray DiffractionDocument32 pagesCentre of Excellence of Solid State Physics: Paper: X-Ray DiffractionamnaNo ratings yet
- BasicsDocument40 pagesBasicsVarun AkashNo ratings yet
- The Development of Atomic TheoryDocument23 pagesThe Development of Atomic TheoryAndreyan PoerwonegoroNo ratings yet
- The Crystalline Solid StateDocument58 pagesThe Crystalline Solid Stated-fbuser-65596417No ratings yet
- Semiconductor BasicsDocument94 pagesSemiconductor BasicsArindam SenNo ratings yet
- Concept+1+Notes+ +Structure+of+the+AtomDocument9 pagesConcept+1+Notes+ +Structure+of+the+AtomsanchezsolsalmaNo ratings yet
- QP 1Document36 pagesQP 1Project Chores to HomeNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3Document35 pagesChapter 3Peth alambatinNo ratings yet
- Crystal Blueprint Reconnect With Your Authentic Self Through The Ancient Wisdom and Modern Science of Quartz CrystalsDocument25 pagesCrystal Blueprint Reconnect With Your Authentic Self Through The Ancient Wisdom and Modern Science of Quartz CrystalsKaren LencinaNo ratings yet
- Atomic Structure: Vinay Desai M.SC Radiation Physics Kidwai Memorial Institute of OncologyDocument28 pagesAtomic Structure: Vinay Desai M.SC Radiation Physics Kidwai Memorial Institute of OncologyJerry De Leon LptNo ratings yet
- The Crystalline Solid StateDocument58 pagesThe Crystalline Solid Statearamki1No ratings yet
- XRD NotesDocument54 pagesXRD NotesBME62Thejeswar SeggamNo ratings yet
- 2020 - 2021 Atom and Subatomic ParticlesDocument37 pages2020 - 2021 Atom and Subatomic ParticlesGeraldine LatupeirissaNo ratings yet
- Inorganic Chem 1Document64 pagesInorganic Chem 1Habtamu mullu BiadgoNo ratings yet
- Formation of The Elements and Nuclear ReactionsDocument19 pagesFormation of The Elements and Nuclear Reactionsian josephNo ratings yet
- The Atom For AnatomyDocument106 pagesThe Atom For AnatomyAlexandra B. FloresNo ratings yet
- Nanotechnology: Suwarna Datar - Ap 608Document56 pagesNanotechnology: Suwarna Datar - Ap 608prakush01975225403No ratings yet
- Sir William Henry Bragg: Noble Prize 1915!Document53 pagesSir William Henry Bragg: Noble Prize 1915!Harneysia JaneNo ratings yet
- Astr. Phy4324Document38 pagesAstr. Phy4324Senait KetemaNo ratings yet
- General Relativity 3: Astrophysics with Tensor CalculusFrom EverandGeneral Relativity 3: Astrophysics with Tensor CalculusRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (4)
- Hameed2018 - Pathogenic BacteriaDocument41 pagesHameed2018 - Pathogenic BacteriaHena DianNo ratings yet
- Nanoparticles Synthesis: Teknologi Nano S3 Pendidikan IPA UNSDocument36 pagesNanoparticles Synthesis: Teknologi Nano S3 Pendidikan IPA UNSHena DianNo ratings yet
- Timms UsDocument216 pagesTimms UsHena DianNo ratings yet
- What Level Is YOUR Team?: EndressDocument1 pageWhat Level Is YOUR Team?: EndressHena DianNo ratings yet
- Where Models of Teaching Come From: Chapter OneDocument5 pagesWhere Models of Teaching Come From: Chapter OneHena DianNo ratings yet
- T15 International Results in Science PDFDocument392 pagesT15 International Results in Science PDFHena DianNo ratings yet
- 2406 Physics Paper With Answer EveningDocument4 pages2406 Physics Paper With Answer EveningASHWANINo ratings yet
- Infrared Spectroscopy - WikipediaDocument13 pagesInfrared Spectroscopy - WikipediaZärràr PáÃshäNo ratings yet
- The Tesla Beograd Wwii Nazi Bell Connection: Comments by Jack Sarfatti, PHD PhysicsDocument11 pagesThe Tesla Beograd Wwii Nazi Bell Connection: Comments by Jack Sarfatti, PHD PhysicsAlexandru DragomirNo ratings yet
- 24 - 400 - 220 - KV - SS HW PDFDocument28 pages24 - 400 - 220 - KV - SS HW PDFgaurang1111No ratings yet
- 60V, 3A, 150Khz, Step-Down Switching Regulator Lm2596HvDocument9 pages60V, 3A, 150Khz, Step-Down Switching Regulator Lm2596HvРуслан СаламовNo ratings yet
- Magneto Optics and Electro OpticsDocument2 pagesMagneto Optics and Electro Opticskanchankonwar100% (1)
- Model 2-Way, Direct-Acting, Solenoid-Operated Directional Blocking Poppet Valve (740 Series)Document3 pagesModel 2-Way, Direct-Acting, Solenoid-Operated Directional Blocking Poppet Valve (740 Series)Anurag JainNo ratings yet
- Midhuna Suresh - Ab20phy033Document36 pagesMidhuna Suresh - Ab20phy033devashishnaik35No ratings yet
- UCLA Mathematics of ComputationDocument2 pagesUCLA Mathematics of ComputationkensusantoNo ratings yet
- 1-PSAE Review 2021 Rural Electrification Part 1 - MKSODocument153 pages1-PSAE Review 2021 Rural Electrification Part 1 - MKSOFrances PasanaNo ratings yet
- Physics 1 (A) KifungiloDocument8 pagesPhysics 1 (A) KifungiloDaniel MapogoNo ratings yet
- NDB2 Series MCB Datasheet PDFDocument81 pagesNDB2 Series MCB Datasheet PDFjahabarsathickNo ratings yet
- Hilti Pd32Document34 pagesHilti Pd32DevetarCokulicNo ratings yet
- IMG - 0038 EE Preboard 2016bDocument1 pageIMG - 0038 EE Preboard 2016bMaster JaguarNo ratings yet
- Lesson Plan UPEMDocument2 pagesLesson Plan UPEMShraddha Suman MishraNo ratings yet
- Two-Hand Control Unit: P2HZ X1.10PDocument7 pagesTwo-Hand Control Unit: P2HZ X1.10PMeny LmlNo ratings yet
- Simulation Analysis of Inrush Current of Three Phase Transformer Based On MATLABDocument3 pagesSimulation Analysis of Inrush Current of Three Phase Transformer Based On MATLABDon NepalNo ratings yet
- Advanced Optical CommunicationsDocument138 pagesAdvanced Optical CommunicationsErasmo VizzaccaroNo ratings yet
- Static Worksheet AnswersDocument2 pagesStatic Worksheet AnswersSun RuangkajohnNo ratings yet
- 2023 08 24 X ICSE Phisics SolutionDocument8 pages2023 08 24 X ICSE Phisics Solution8A - Shynita Mukherjee - 41No ratings yet
- Module 4 Electrons Photons Waves DefitionsDocument5 pagesModule 4 Electrons Photons Waves DefitionsAbir MohammedNo ratings yet
- Bruce Depalma HistoryDocument44 pagesBruce Depalma HistoryFrancisco Luis Bocanegra SanchezNo ratings yet
- Maintenance and Repair ElectricalDocument43 pagesMaintenance and Repair ElectricalCisa Seaboy100% (1)
- Surface Integrals: Vector Calculus (MATH-243) Instructor: Dr. Naila AmirDocument35 pagesSurface Integrals: Vector Calculus (MATH-243) Instructor: Dr. Naila AmirRakhmeen GulNo ratings yet
- Fundamental ACDocument1 pageFundamental ACAaj AajNo ratings yet
- 31 Regelung EMV 03Document34 pages31 Regelung EMV 03alastairNo ratings yet
- HFIC Chapter 4 PassivesDocument65 pagesHFIC Chapter 4 PassivesNotoriety OrientedNo ratings yet
- 11 8 Fig. 8.1 Represents A Travelling Wave at An Instant in TimeDocument5 pages11 8 Fig. 8.1 Represents A Travelling Wave at An Instant in Timeffgfgfgffg100% (1)
- 2010 YJC H2 Phy - Paper3 - QNDocument20 pages2010 YJC H2 Phy - Paper3 - QNcjcsucksNo ratings yet
- Questions Based On Fleming'S Left Hand Rule - Youtube: Bijuaylara111Document9 pagesQuestions Based On Fleming'S Left Hand Rule - Youtube: Bijuaylara111Shamik GhoshNo ratings yet
Lecture 04 of Solid State Physics
Lecture 04 of Solid State Physics
Uploaded by
Hena Dian0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
24 views29 pagesThe document discusses techniques for studying crystal structure using x-rays, neutrons, and electrons. It introduces diffraction as the constructive interference of scattering from periodic structures in crystals. The Bragg scattering law governs diffraction and scattering from different crystal planes in the lattice. Crystals can be probed by techniques that penetrate the material without strong interaction, allowing investigation of the periodic atomic structure.
Original Description:
Copyright
© Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Available Formats
PPT, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentThe document discusses techniques for studying crystal structure using x-rays, neutrons, and electrons. It introduces diffraction as the constructive interference of scattering from periodic structures in crystals. The Bragg scattering law governs diffraction and scattering from different crystal planes in the lattice. Crystals can be probed by techniques that penetrate the material without strong interaction, allowing investigation of the periodic atomic structure.
Copyright:
Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Available Formats
Download as PPT, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as ppt, pdf, or txt
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
24 views29 pagesLecture 04 of Solid State Physics
Lecture 04 of Solid State Physics
Uploaded by
Hena DianThe document discusses techniques for studying crystal structure using x-rays, neutrons, and electrons. It introduces diffraction as the constructive interference of scattering from periodic structures in crystals. The Bragg scattering law governs diffraction and scattering from different crystal planes in the lattice. Crystals can be probed by techniques that penetrate the material without strong interaction, allowing investigation of the periodic atomic structure.
Copyright:
Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Available Formats
Download as PPT, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as ppt, pdf, or txt
You are on page 1of 29
Difraction and The Reciprocal Lattice
Crystals-recall from last time
A crystal is a repeated array of atoms
Crystal
Lattice
Basis
Latice of Points Bravais Lattice Crystal
Basic of Atoms
How Can We Study Crystal Structure ?
Need probe that can penetrate into crystal X-rays , neutrons, (high energy electrons)
X-rays discovered by Roentgen in 1895 instant sensation round the world-view of his wifes hand Neutron (discovered in 1932) penetrate with almost no interaction with most materials.
How can we srudy crystal structure ?
X-rays scatter from the electrons-intensity proportional to the density n - mainly the core electrons around the nucleus Similarly for high energy electrons Neutrons scatter from the nuclei (and electron magnetic moment).
In all cases the scattering is periodic-that is it is the same in each cell of the crystal Diffraction is the constructive interference of the scattering from the very large number of cells of the crystal.
The crystal can be viewed as made up of planes in different ways
Lattice
(01)
(14)
Different sets of parallel planes Low index planes : more dense, more widely spaced High index planes : less dense, more closely spaced.
Bragg Scattering Law
You might also like
- Solid State Physics I - PPT (Repaired)Document159 pagesSolid State Physics I - PPT (Repaired)davididosa40No ratings yet
- Solid State Chapter 1Document38 pagesSolid State Chapter 1Abrish HaremNo ratings yet
- Today: - Chap 11, Atomic Nature of MatterDocument34 pagesToday: - Chap 11, Atomic Nature of Matterbaig79No ratings yet
- Reciprocal Lattice and Brillouin ZoneDocument5 pagesReciprocal Lattice and Brillouin ZoneanggasoedNo ratings yet
- Teori AtomDocument46 pagesTeori AtomWaskitaDwiNo ratings yet
- X Ray DiffractionsDocument15 pagesX Ray DiffractionsAman JhaNo ratings yet
- Atoms and The Atomic TheoryDocument47 pagesAtoms and The Atomic TheoryEdgar PeninsulaNo ratings yet
- Wave Properties of ParticlesDocument14 pagesWave Properties of Particlescornel_24No ratings yet
- X-Ray Diffraction (XRD) : Ulrike TroitzschDocument38 pagesX-Ray Diffraction (XRD) : Ulrike TroitzschprianNo ratings yet
- X-Ray CrystallographyDocument30 pagesX-Ray Crystallographyariba khanNo ratings yet
- Atomic Structure Basic ConceptsDocument39 pagesAtomic Structure Basic ConceptsTithiparna SenguptaNo ratings yet
- Neutron Diffraction TechniquesDocument30 pagesNeutron Diffraction TechniquesAgnes maria maniNo ratings yet
- Class 11 Chapter 2 Structure of AtomDocument131 pagesClass 11 Chapter 2 Structure of Atomyasdin.ashiNo ratings yet
- LatticeDocument15 pagesLatticemisganawsimachew5No ratings yet
- Basic Science of MaterialsDocument208 pagesBasic Science of MaterialsJezzrel Xandy BalmesNo ratings yet
- Nucleus and Its Characterstics: Prof - Arun Bharti Department of Physics University of JammuDocument41 pagesNucleus and Its Characterstics: Prof - Arun Bharti Department of Physics University of JammuSurbhi guptaNo ratings yet
- Atomic Theories Quatum ModelDocument31 pagesAtomic Theories Quatum Modelerinallyson20No ratings yet
- First Year Chemistry 20-02Document100 pagesFirst Year Chemistry 20-02Ahmed Hassan Mina HamadNo ratings yet
- - N = 2 D Sinθ: Bragg EquationDocument35 pages- N = 2 D Sinθ: Bragg EquationdkaurNo ratings yet
- Solid State Part 1Document31 pagesSolid State Part 1fatmaehab.139No ratings yet
- 1.10. Atoms, Spectra and Quantum Nature of LightDocument21 pages1.10. Atoms, Spectra and Quantum Nature of Lightaevadf760No ratings yet
- Calicut University M.SC PHYSICS Experimental Techniques X-RAY DIFFRACTION TECHNIQUES JOYAL (STC)Document22 pagesCalicut University M.SC PHYSICS Experimental Techniques X-RAY DIFFRACTION TECHNIQUES JOYAL (STC)Joyal Jain100% (1)
- CrystalDiffraction Reciprocal Lattice DiffractionMethodsDocument153 pagesCrystalDiffraction Reciprocal Lattice DiffractionMethodsKRISHNA KUMAR GODARANo ratings yet
- Introduction To Particle PhysicsDocument61 pagesIntroduction To Particle PhysicsFrank LipskyNo ratings yet
- Ch. S4 PDFDocument56 pagesCh. S4 PDFlittleitaly5No ratings yet
- 1-Atom StructureDocument75 pages1-Atom Structurenirvanjain212007No ratings yet
- 18BPH62C U3Document63 pages18BPH62C U3moneymaker1906vNo ratings yet
- XRD ReportDocument13 pagesXRD ReportMukulNo ratings yet
- Report XRD 8153Document16 pagesReport XRD 8153Rishabh SoodNo ratings yet
- Formation of The Elements and Nuclear ReactionsDocument23 pagesFormation of The Elements and Nuclear ReactionsHIA GS AACNo ratings yet
- Solid State Chapter 2Document75 pagesSolid State Chapter 2Ambreen KhanNo ratings yet
- Atomic Structure Basic Information FullDocument45 pagesAtomic Structure Basic Information FullSai KrishnaNo ratings yet
- 1.atomic Structure 1-24Document16 pages1.atomic Structure 1-24eamcetmaterials67% (15)
- General Chemistry PresentationDocument45 pagesGeneral Chemistry PresentationJohn Adrian MalunesNo ratings yet
- Condensed Matter Physics - NotesDocument7 pagesCondensed Matter Physics - NotesBs PhysicsNo ratings yet
- HS Science Reviewer (Light and Electromagnetism, Atoms)Document11 pagesHS Science Reviewer (Light and Electromagnetism, Atoms)Halcyon Zenith DelosoNo ratings yet
- X-Ray Diffraction 7Document11 pagesX-Ray Diffraction 7alina.tlekkabylova270202No ratings yet
- Chemistry: Atoms, Molecules, & Chemical BondingDocument149 pagesChemistry: Atoms, Molecules, & Chemical BondingnadnotmeNo ratings yet
- Centre of Excellence of Solid State Physics: Paper: X-Ray DiffractionDocument32 pagesCentre of Excellence of Solid State Physics: Paper: X-Ray DiffractionamnaNo ratings yet
- BasicsDocument40 pagesBasicsVarun AkashNo ratings yet
- The Development of Atomic TheoryDocument23 pagesThe Development of Atomic TheoryAndreyan PoerwonegoroNo ratings yet
- The Crystalline Solid StateDocument58 pagesThe Crystalline Solid Stated-fbuser-65596417No ratings yet
- Semiconductor BasicsDocument94 pagesSemiconductor BasicsArindam SenNo ratings yet
- Concept+1+Notes+ +Structure+of+the+AtomDocument9 pagesConcept+1+Notes+ +Structure+of+the+AtomsanchezsolsalmaNo ratings yet
- QP 1Document36 pagesQP 1Project Chores to HomeNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3Document35 pagesChapter 3Peth alambatinNo ratings yet
- Crystal Blueprint Reconnect With Your Authentic Self Through The Ancient Wisdom and Modern Science of Quartz CrystalsDocument25 pagesCrystal Blueprint Reconnect With Your Authentic Self Through The Ancient Wisdom and Modern Science of Quartz CrystalsKaren LencinaNo ratings yet
- Atomic Structure: Vinay Desai M.SC Radiation Physics Kidwai Memorial Institute of OncologyDocument28 pagesAtomic Structure: Vinay Desai M.SC Radiation Physics Kidwai Memorial Institute of OncologyJerry De Leon LptNo ratings yet
- The Crystalline Solid StateDocument58 pagesThe Crystalline Solid Statearamki1No ratings yet
- XRD NotesDocument54 pagesXRD NotesBME62Thejeswar SeggamNo ratings yet
- 2020 - 2021 Atom and Subatomic ParticlesDocument37 pages2020 - 2021 Atom and Subatomic ParticlesGeraldine LatupeirissaNo ratings yet
- Inorganic Chem 1Document64 pagesInorganic Chem 1Habtamu mullu BiadgoNo ratings yet
- Formation of The Elements and Nuclear ReactionsDocument19 pagesFormation of The Elements and Nuclear Reactionsian josephNo ratings yet
- The Atom For AnatomyDocument106 pagesThe Atom For AnatomyAlexandra B. FloresNo ratings yet
- Nanotechnology: Suwarna Datar - Ap 608Document56 pagesNanotechnology: Suwarna Datar - Ap 608prakush01975225403No ratings yet
- Sir William Henry Bragg: Noble Prize 1915!Document53 pagesSir William Henry Bragg: Noble Prize 1915!Harneysia JaneNo ratings yet
- Astr. Phy4324Document38 pagesAstr. Phy4324Senait KetemaNo ratings yet
- General Relativity 3: Astrophysics with Tensor CalculusFrom EverandGeneral Relativity 3: Astrophysics with Tensor CalculusRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (4)
- Hameed2018 - Pathogenic BacteriaDocument41 pagesHameed2018 - Pathogenic BacteriaHena DianNo ratings yet
- Nanoparticles Synthesis: Teknologi Nano S3 Pendidikan IPA UNSDocument36 pagesNanoparticles Synthesis: Teknologi Nano S3 Pendidikan IPA UNSHena DianNo ratings yet
- Timms UsDocument216 pagesTimms UsHena DianNo ratings yet
- What Level Is YOUR Team?: EndressDocument1 pageWhat Level Is YOUR Team?: EndressHena DianNo ratings yet
- Where Models of Teaching Come From: Chapter OneDocument5 pagesWhere Models of Teaching Come From: Chapter OneHena DianNo ratings yet
- T15 International Results in Science PDFDocument392 pagesT15 International Results in Science PDFHena DianNo ratings yet
- 2406 Physics Paper With Answer EveningDocument4 pages2406 Physics Paper With Answer EveningASHWANINo ratings yet
- Infrared Spectroscopy - WikipediaDocument13 pagesInfrared Spectroscopy - WikipediaZärràr PáÃshäNo ratings yet
- The Tesla Beograd Wwii Nazi Bell Connection: Comments by Jack Sarfatti, PHD PhysicsDocument11 pagesThe Tesla Beograd Wwii Nazi Bell Connection: Comments by Jack Sarfatti, PHD PhysicsAlexandru DragomirNo ratings yet
- 24 - 400 - 220 - KV - SS HW PDFDocument28 pages24 - 400 - 220 - KV - SS HW PDFgaurang1111No ratings yet
- 60V, 3A, 150Khz, Step-Down Switching Regulator Lm2596HvDocument9 pages60V, 3A, 150Khz, Step-Down Switching Regulator Lm2596HvРуслан СаламовNo ratings yet
- Magneto Optics and Electro OpticsDocument2 pagesMagneto Optics and Electro Opticskanchankonwar100% (1)
- Model 2-Way, Direct-Acting, Solenoid-Operated Directional Blocking Poppet Valve (740 Series)Document3 pagesModel 2-Way, Direct-Acting, Solenoid-Operated Directional Blocking Poppet Valve (740 Series)Anurag JainNo ratings yet
- Midhuna Suresh - Ab20phy033Document36 pagesMidhuna Suresh - Ab20phy033devashishnaik35No ratings yet
- UCLA Mathematics of ComputationDocument2 pagesUCLA Mathematics of ComputationkensusantoNo ratings yet
- 1-PSAE Review 2021 Rural Electrification Part 1 - MKSODocument153 pages1-PSAE Review 2021 Rural Electrification Part 1 - MKSOFrances PasanaNo ratings yet
- Physics 1 (A) KifungiloDocument8 pagesPhysics 1 (A) KifungiloDaniel MapogoNo ratings yet
- NDB2 Series MCB Datasheet PDFDocument81 pagesNDB2 Series MCB Datasheet PDFjahabarsathickNo ratings yet
- Hilti Pd32Document34 pagesHilti Pd32DevetarCokulicNo ratings yet
- IMG - 0038 EE Preboard 2016bDocument1 pageIMG - 0038 EE Preboard 2016bMaster JaguarNo ratings yet
- Lesson Plan UPEMDocument2 pagesLesson Plan UPEMShraddha Suman MishraNo ratings yet
- Two-Hand Control Unit: P2HZ X1.10PDocument7 pagesTwo-Hand Control Unit: P2HZ X1.10PMeny LmlNo ratings yet
- Simulation Analysis of Inrush Current of Three Phase Transformer Based On MATLABDocument3 pagesSimulation Analysis of Inrush Current of Three Phase Transformer Based On MATLABDon NepalNo ratings yet
- Advanced Optical CommunicationsDocument138 pagesAdvanced Optical CommunicationsErasmo VizzaccaroNo ratings yet
- Static Worksheet AnswersDocument2 pagesStatic Worksheet AnswersSun RuangkajohnNo ratings yet
- 2023 08 24 X ICSE Phisics SolutionDocument8 pages2023 08 24 X ICSE Phisics Solution8A - Shynita Mukherjee - 41No ratings yet
- Module 4 Electrons Photons Waves DefitionsDocument5 pagesModule 4 Electrons Photons Waves DefitionsAbir MohammedNo ratings yet
- Bruce Depalma HistoryDocument44 pagesBruce Depalma HistoryFrancisco Luis Bocanegra SanchezNo ratings yet
- Maintenance and Repair ElectricalDocument43 pagesMaintenance and Repair ElectricalCisa Seaboy100% (1)
- Surface Integrals: Vector Calculus (MATH-243) Instructor: Dr. Naila AmirDocument35 pagesSurface Integrals: Vector Calculus (MATH-243) Instructor: Dr. Naila AmirRakhmeen GulNo ratings yet
- Fundamental ACDocument1 pageFundamental ACAaj AajNo ratings yet
- 31 Regelung EMV 03Document34 pages31 Regelung EMV 03alastairNo ratings yet
- HFIC Chapter 4 PassivesDocument65 pagesHFIC Chapter 4 PassivesNotoriety OrientedNo ratings yet
- 11 8 Fig. 8.1 Represents A Travelling Wave at An Instant in TimeDocument5 pages11 8 Fig. 8.1 Represents A Travelling Wave at An Instant in Timeffgfgfgffg100% (1)
- 2010 YJC H2 Phy - Paper3 - QNDocument20 pages2010 YJC H2 Phy - Paper3 - QNcjcsucksNo ratings yet
- Questions Based On Fleming'S Left Hand Rule - Youtube: Bijuaylara111Document9 pagesQuestions Based On Fleming'S Left Hand Rule - Youtube: Bijuaylara111Shamik GhoshNo ratings yet