Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Chest Tube Insertion
Chest Tube Insertion
Uploaded by
feva550 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
79 views6 pagesThis document discusses chest tube insertion procedures. It lists indications for posterior and anterior chest tubes such as hemothorax, pneumothorax, and empyema. It describes how to identify the insertion site and describes potential complications including poor positioning, persistent pneumothorax, hemorrhage, lung injury, and cardiac dysrhythmias. Emergent thoracotomy is indicated if output is over 200ml/hr or 1.5L total or the patient is unstable.
Original Description:
ctt
Copyright
© Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Available Formats
PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentThis document discusses chest tube insertion procedures. It lists indications for posterior and anterior chest tubes such as hemothorax, pneumothorax, and empyema. It describes how to identify the insertion site and describes potential complications including poor positioning, persistent pneumothorax, hemorrhage, lung injury, and cardiac dysrhythmias. Emergent thoracotomy is indicated if output is over 200ml/hr or 1.5L total or the patient is unstable.
Copyright:
Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pptx, pdf, or txt
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
79 views6 pagesChest Tube Insertion
Chest Tube Insertion
Uploaded by
feva55This document discusses chest tube insertion procedures. It lists indications for posterior and anterior chest tubes such as hemothorax, pneumothorax, and empyema. It describes how to identify the insertion site and describes potential complications including poor positioning, persistent pneumothorax, hemorrhage, lung injury, and cardiac dysrhythmias. Emergent thoracotomy is indicated if output is over 200ml/hr or 1.5L total or the patient is unstable.
Copyright:
Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pptx, pdf, or txt
You are on page 1of 6
Performed to evacuate an ongoing production of air/fluid into the pleural space or fluid that is too viscous to be aspirated by thoracentesis
Indications:
Posterior chest tube
Hemothorax Pneumothorax (> 15%) Symptomatic pneumothorax of any size Persistent pleural effusion Empyema
Anterior chest tube
Pneumothorax (> 15%)
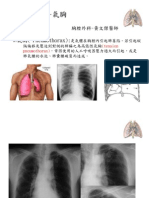
Identify the fifth intercostal space in the anterior axillary line this is where the tube will enter the pleural space; the incision is made at the level of the sixth intercostal space lateral to the nipple but medial to the edge of the latissimus dorsi.or Identify the second intercostal space lateral to the sternal angle of Louie in the midclavicular line (if pneumothorax)
Poor positioning Persistent pneumothorax
Hemorrhage or lung injury
If output is > 200 ml/hr or 1.5 L total or patient is
unstable, then emergent thoracotomy is indicated.
Cardiac dysrhythmias
You might also like
- Burn PPT VCMC 1Document70 pagesBurn PPT VCMC 1feva55100% (2)
- Schizophreniform DisorderDocument16 pagesSchizophreniform Disorderfeva55No ratings yet
- Care of Patient On I C DDocument15 pagesCare of Patient On I C DGeorge John Jeelu SusanNo ratings yet
- 6.1 ChestTraumaDocument79 pages6.1 ChestTraumasiti aminahNo ratings yet
- Pneumothorax & Hemothorax: Farshid MokhberiDocument32 pagesPneumothorax & Hemothorax: Farshid MokhberiYan Sheng HoNo ratings yet
- Pulmonary ThromoboembolismDocument24 pagesPulmonary ThromoboembolismIraj KhanNo ratings yet
- Chest Trauma FinishDocument76 pagesChest Trauma FinishSrix KurniawatiNo ratings yet
- Pneumothorax-Hemopneumothorax Needle DecompressionDocument30 pagesPneumothorax-Hemopneumothorax Needle DecompressionAlvin BernardNo ratings yet
- CTTDocument47 pagesCTTleizelgalvezNo ratings yet
- 2 5215416471575865318Document5 pages2 5215416471575865318b5mkn9h6pkNo ratings yet
- Trauma Dada RDocument94 pagesTrauma Dada RVivi AnggrainyNo ratings yet
- ThoracentesisDocument9 pagesThoracentesisPatricia G ChiuNo ratings yet
- Chest Drains and ThoracotomyDocument5 pagesChest Drains and ThoracotomyYanuar Rifqi AmrullohNo ratings yet
- Chest Trauma AMO1Document78 pagesChest Trauma AMO1HillaryNo ratings yet
- Chest Trauma: Prepared By: Bill Milan Nremt-P, Ccemt-PDocument79 pagesChest Trauma: Prepared By: Bill Milan Nremt-P, Ccemt-PEryanda DinataNo ratings yet
- Tension Pneumothorax by AnkurDocument30 pagesTension Pneumothorax by AnkurAnkur AgrawalNo ratings yet
- Pulmonary EmbolismDocument2 pagesPulmonary EmbolismMariya DantisNo ratings yet
- Pleural Anatomy 1st Year Clinical by DR MuzaffarDocument22 pagesPleural Anatomy 1st Year Clinical by DR MuzaffarKashar SaeedNo ratings yet
- Chest Tube TherapyDocument5 pagesChest Tube Therapye항해No ratings yet
- WSDDocument59 pagesWSDdiandrasafirinaNo ratings yet
- HemothoraxDocument3 pagesHemothoraxkrz05No ratings yet
- Thoracic TraumaDocument63 pagesThoracic Traumaheny seri meritaNo ratings yet
- Chest Trauma FinalDocument50 pagesChest Trauma FinalAsim Siddiq VineNo ratings yet
- Pleural EffusionDocument1 pagePleural EffusionElyas MehdarNo ratings yet
- Chest Trauma: DR - Seyed Mostafa Shiryadi Associate Professor of Surgery Shahid Sadoghi University Yazd-IranDocument79 pagesChest Trauma: DR - Seyed Mostafa Shiryadi Associate Professor of Surgery Shahid Sadoghi University Yazd-IranMuhidin Ae100% (1)
- Chest TraumaDocument26 pagesChest TraumaNader SaadNo ratings yet
- Chest X-Ray ReviewDocument145 pagesChest X-Ray ReviewHamid ShaalanNo ratings yet
- Pleura 1Document37 pagesPleura 1Praneetha NouduriNo ratings yet
- Hemothorax: BackgroundDocument6 pagesHemothorax: BackgroundTruly GracevaNo ratings yet
- Tension PneumothoraxDocument5 pagesTension PneumothoraxKay BristolNo ratings yet
- Pneumothorax: Disturbance in OxygenationDocument27 pagesPneumothorax: Disturbance in Oxygenationamier90No ratings yet
- Pleural EffusionsDocument49 pagesPleural Effusionsdale 99No ratings yet
- Understanding Chest Tube UseDocument4 pagesUnderstanding Chest Tube UseHarry Lingcopines WilliamsNo ratings yet
- Oxygenation 3.0Document14 pagesOxygenation 3.0Jake Yvan DizonNo ratings yet
- Torso TraumaDocument58 pagesTorso TraumaAbidisHereNo ratings yet
- Chest Tube Placement (Perform)Document14 pagesChest Tube Placement (Perform)ydtrgnNo ratings yet
- Tension Pneumoth Orax: Presented By: Juhara, Amroussie M. BSN 3 - DDocument13 pagesTension Pneumoth Orax: Presented By: Juhara, Amroussie M. BSN 3 - Dlea jumawanNo ratings yet
- Pneumothorax FinalDocument62 pagesPneumothorax FinalmithramuruganNo ratings yet
- Pneumothorax, COPD, CVDsDocument156 pagesPneumothorax, COPD, CVDsakoeljames8543No ratings yet
- Chest Tubes and ThoracentesisDocument18 pagesChest Tubes and ThoracentesisecleptosNo ratings yet
- Pneumothorax, Tension and TraumaticDocument24 pagesPneumothorax, Tension and TraumaticSatria WibawaNo ratings yet
- Tension Pneumothorax: Anak Agung Istri Intan YuniariDocument19 pagesTension Pneumothorax: Anak Agung Istri Intan Yuniarifaris nagibNo ratings yet
- Chest Tube TherapysDocument2 pagesChest Tube TherapysBobby ParksNo ratings yet
- PNEUMOTHORAXDocument3 pagesPNEUMOTHORAXbelleNo ratings yet
- Blunt Chest TraumaDocument10 pagesBlunt Chest TraumaFortune RubengoNo ratings yet
- Alok Sinha Department of Medicine Manipal College of Medical Sciences Pokhara, NepalDocument46 pagesAlok Sinha Department of Medicine Manipal College of Medical Sciences Pokhara, NepalAnnushika PalanichamyNo ratings yet
- Purpose of Chest TubesDocument2 pagesPurpose of Chest TubesCathrine Mae RamilNo ratings yet
- Tracheostomy EmergenciesDocument8 pagesTracheostomy Emergenciessabahat.husainNo ratings yet
- Chest Tubes and Drainage Systems: Deb Updegraff RN, CNS Picu LPCHDocument28 pagesChest Tubes and Drainage Systems: Deb Updegraff RN, CNS Picu LPCHLucila LugoNo ratings yet
- PleuraDocument23 pagesPleuraulerc1No ratings yet
- HemothoraxDocument13 pagesHemothoraxسما كركوكليNo ratings yet
- Chest Trauma and Diseases: Mexigin Gayatri Akash JohannaDocument80 pagesChest Trauma and Diseases: Mexigin Gayatri Akash JohannadidiNo ratings yet
- NursingBulletin Notes On PneumothoraxDocument27 pagesNursingBulletin Notes On Pneumothoraxseigelystic100% (11)
- Chest TubeDocument3 pagesChest TubeJohn Michael SalinasNo ratings yet
- Pleural Effusions: Professor Dr. Sameena AkramDocument20 pagesPleural Effusions: Professor Dr. Sameena AkramSadia Gulraiz100% (1)
- Assisting in Thoracostomy Tube InsertionDocument54 pagesAssisting in Thoracostomy Tube Insertioncoosa liquorsNo ratings yet
- 4.pleural EffusionDocument27 pages4.pleural Effusionachmad rizkiNo ratings yet
- PneumothoraxDocument24 pagesPneumothoraxItharshan IndreswaranNo ratings yet
- Tension Pneumothorax: History and PhysicalDocument5 pagesTension Pneumothorax: History and PhysicalKenneth AndayaNo ratings yet
- Approach To Pleura LeffusionDocument91 pagesApproach To Pleura Leffusionrodie1050% (1)
- Pneumoniae, Haemophilus Influenzae, or Moraxella Catarrhalis, IncreasingDocument4 pagesPneumoniae, Haemophilus Influenzae, or Moraxella Catarrhalis, IncreasingParth BhayanaNo ratings yet
- Reflection Paper PCMDocument5 pagesReflection Paper PCMfeva55100% (2)
- Treatment and Management Hep BDocument10 pagesTreatment and Management Hep Bfeva55No ratings yet
- Bone Marrow AspirationDocument12 pagesBone Marrow Aspirationfeva55No ratings yet
- Z ScoreDocument10 pagesZ Scorefeva55No ratings yet
- Unicystic AmeloblastomaDocument14 pagesUnicystic Ameloblastomafeva55No ratings yet
- Newborn ScreeningDocument20 pagesNewborn Screeningfeva55No ratings yet
- Food, Drug, and Cosmetics Act 2013Document17 pagesFood, Drug, and Cosmetics Act 2013feva55No ratings yet