Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Quantum Atomic Physics Eg Photoelectric Affect Formula Sheet Study Tool Physics A
Quantum Atomic Physics Eg Photoelectric Affect Formula Sheet Study Tool Physics A
Uploaded by
rohitpatyalCopyright:
Available Formats
You might also like
- Physics Final (Cheat Sheet) With ProblemsDocument2 pagesPhysics Final (Cheat Sheet) With ProblemsRSlipkov97% (97)
- Grade 11 Physics Study Guide / Notes For Final Exam SPH3U1Document23 pagesGrade 11 Physics Study Guide / Notes For Final Exam SPH3U1Niki79% (14)
- Ultimate Physics Cheat SheetDocument2 pagesUltimate Physics Cheat SheetNehal VoraNo ratings yet
- Physics I Final Cheat SheetDocument1 pagePhysics I Final Cheat SheetJsea2011100% (1)
- Optics Formula Sheet Study Sheet PhysicsA 2010Document1 pageOptics Formula Sheet Study Sheet PhysicsA 2010Mark Riley100% (1)
- Optics Formula Sheet Study Sheet PhysicsA 2010Document1 pageOptics Formula Sheet Study Sheet PhysicsA 2010Mark Riley100% (1)
- Physics Exam Cheat SheetDocument3 pagesPhysics Exam Cheat SheetJib Bros100% (4)
- Physics Formula SheetDocument12 pagesPhysics Formula SheetRohit Ghere100% (4)
- Physics2A CheatSheetDocument1 pagePhysics2A CheatSheetNastassja LopezNo ratings yet
- Physics EquationsDocument5 pagesPhysics Equationsanon-992211100% (64)
- Physics 1121 A Cheat SheetDocument8 pagesPhysics 1121 A Cheat SheetAmmar Tirmzey100% (1)
- Halzen and MartinDocument412 pagesHalzen and Martinapi-3797443100% (1)
- Fluids Dynamics Formula SheetDocument2 pagesFluids Dynamics Formula SheetMark Riley88% (8)
- Freshman Physics Formula SheetDocument6 pagesFreshman Physics Formula SheetMickey Boy83% (6)
- MCAT Physics Formula SheetDocument3 pagesMCAT Physics Formula Sheetemma_reese100% (2)
- Grade 11 Physics - Kinematics ReviewDocument2 pagesGrade 11 Physics - Kinematics Reviewfairwayhills70275% (12)
- Heat & Determining Enthalpy Change (Lab Assessment) Part I & Part 2Document8 pagesHeat & Determining Enthalpy Change (Lab Assessment) Part I & Part 2Mark Riley81% (16)
- Fluids Dynamics Formula SheetDocument2 pagesFluids Dynamics Formula SheetMark Riley88% (8)
- Subject Test - Advanced Physics - Chegg IndiaDocument2 pagesSubject Test - Advanced Physics - Chegg IndiaSanjeevkumarSingh50% (6)
- (Lauri H.J. Lajunen) Spectrochemical AnalysisDocument258 pages(Lauri H.J. Lajunen) Spectrochemical AnalysisAndrew CarrNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Quantum Computing - Quantum Circuit ElementsDocument13 pagesIntroduction To Quantum Computing - Quantum Circuit ElementsSaikiranKumarNo ratings yet
- Formula Sheet Physics 133Document12 pagesFormula Sheet Physics 133Muhammad IshtiaqNo ratings yet
- Formula Sheet For Grade 10 NewDocument4 pagesFormula Sheet For Grade 10 NewNo PainNo ratings yet
- Physics Formula SheetDocument4 pagesPhysics Formula SheetfabolaNo ratings yet
- Inorganic Memory Chart PDFDocument22 pagesInorganic Memory Chart PDFUtkarsh GuptaNo ratings yet
- Limits of FunctionsDocument11 pagesLimits of Functionsnormasulasa100% (1)
- Tau ThetaDocument3 pagesTau Thetapradeep reddy0% (1)
- SPH3U1 Exam Review NotesDocument26 pagesSPH3U1 Exam Review Notesrahihot100% (1)
- Formula Booklet Physics XIDocument35 pagesFormula Booklet Physics XIsreenatpppp84% (147)
- Mathematics Formula SheetDocument35 pagesMathematics Formula SheetChandra Kishore Paul67% (3)
- Optics Cheat SheetDocument1 pageOptics Cheat SheetAlex MuresanNo ratings yet
- Concentration Cheat Sheet PDFDocument2 pagesConcentration Cheat Sheet PDFimec_coordinator7353No ratings yet
- Unit III Quantum MechanicsDocument148 pagesUnit III Quantum MechanicsPrince JunejaNo ratings yet
- Evidence For Wave-Particle DualityDocument24 pagesEvidence For Wave-Particle DualitySudipta DasNo ratings yet
- Vce Unit 3 and 4 Physics Cheat SheetDocument2 pagesVce Unit 3 and 4 Physics Cheat SheetRameesha AizazNo ratings yet
- Day 31Document10 pagesDay 31g.sathyanarayanan252008No ratings yet
- Smart Revision Quantum PhysicsDocument18 pagesSmart Revision Quantum PhysicsZAIHASRA BINTI AHMAD KPM-GuruNo ratings yet
- Dual Nature NotesDocument4 pagesDual Nature Noteswifohiw819No ratings yet
- Modern PhysicsDocument11 pagesModern PhysicsPuja KumariNo ratings yet
- 2023 F5 UT MemoDocument2 pages2023 F5 UT Memo2B-11 HO HOI TINGNo ratings yet
- Particle Wave DualityDocument24 pagesParticle Wave DualityIsrael PopeNo ratings yet
- CHAPTER-1 SummaryDocument8 pagesCHAPTER-1 SummaryRaven John Yecyec RufinoNo ratings yet
- Optical Fiber Communications: Lecture 2: Physics of LightDocument15 pagesOptical Fiber Communications: Lecture 2: Physics of Lightjeddo2005No ratings yet
- Chapter II: Interaction of Electromagnetic Radiation With Atoms and MoleculesDocument14 pagesChapter II: Interaction of Electromagnetic Radiation With Atoms and Moleculeskiswah computersNo ratings yet
- Photoelectric Effect: Day Thirty TwoDocument9 pagesPhotoelectric Effect: Day Thirty TwoPrayas RaneNo ratings yet
- Kuliah-19 Dualisme Partikel GelombangDocument24 pagesKuliah-19 Dualisme Partikel GelombangNeni Fitria RahayuNo ratings yet
- LMR Final Physics 3.30 - RemovedDocument13 pagesLMR Final Physics 3.30 - RemovedEco DudeNo ratings yet
- 1237.quantum Mechanics 1Document94 pages1237.quantum Mechanics 1cattlNo ratings yet
- QM 2020-21 Sem1Document79 pagesQM 2020-21 Sem1wzardking69No ratings yet
- PYL101 QM Lecture 3Document16 pagesPYL101 QM Lecture 3mukeshNo ratings yet
- Morden PhysicsDocument37 pagesMorden PhysicsSimilinga MnyongeNo ratings yet
- 1.1.6 Einstein Coefficients - 1: Rate EquationDocument15 pages1.1.6 Einstein Coefficients - 1: Rate Equationshouravme2k11No ratings yet
- Short Notes - Modern Physics by Gulshan JhaDocument3 pagesShort Notes - Modern Physics by Gulshan JhaSHIVI DwivediNo ratings yet
- EP 1108 Photoelectric EffectDocument12 pagesEP 1108 Photoelectric EffectAryam SharmaNo ratings yet
- Light and Matter FormulaeDocument2 pagesLight and Matter FormulaefizzvineNo ratings yet
- TUNNELLINGDocument14 pagesTUNNELLINGkumarmanojod010215No ratings yet
- Physics - 1 - LESSON 1 (Final Term - Summer 23)Document18 pagesPhysics - 1 - LESSON 1 (Final Term - Summer 23)fardinmojumdar123No ratings yet
- Particle Nature of Light - Sunday 7 FebpptxDocument33 pagesParticle Nature of Light - Sunday 7 Febpptxtohfeh kassemNo ratings yet
- Efek Foto ListrikDocument38 pagesEfek Foto ListrikZAHWA RIZZI ANINo ratings yet
- Dual Nature of Matter and RadiationDocument14 pagesDual Nature of Matter and RadiationAmrit AnuragNo ratings yet
- SFI 5800 Spectroscopy General3Document10 pagesSFI 5800 Spectroscopy General3Alejandra Ayulo CumpalliNo ratings yet
- Quantum Mechanics and Atomic Theory: Chapter 12, J. Ren, 2021 1Document97 pagesQuantum Mechanics and Atomic Theory: Chapter 12, J. Ren, 2021 1Babeejay2No ratings yet
- Physics Module Three ReviewDocument22 pagesPhysics Module Three Reviewshan mackNo ratings yet
- Feynman Lectures Simplified 2B: Magnetism & ElectrodynamicsFrom EverandFeynman Lectures Simplified 2B: Magnetism & ElectrodynamicsNo ratings yet
- Feynman Lectures Simplified 2A: Maxwell's Equations & ElectrostaticsFrom EverandFeynman Lectures Simplified 2A: Maxwell's Equations & ElectrostaticsNo ratings yet
- Feynman Lectures Simplified 2C: Electromagnetism: in Relativity & in Dense MatterFrom EverandFeynman Lectures Simplified 2C: Electromagnetism: in Relativity & in Dense MatterNo ratings yet
- Unified Field Theory in a Nutshell1: The Quest for the Theory of EverythingFrom EverandUnified Field Theory in a Nutshell1: The Quest for the Theory of EverythingNo ratings yet
- Dimensional Analysis: A Simple ExampleDocument10 pagesDimensional Analysis: A Simple ExampleMark RileyNo ratings yet
- Physics - Relationships Between The Equations Linear and Angular Motion. Torque, Momentum, Angular Velocity EtcDocument2 pagesPhysics - Relationships Between The Equations Linear and Angular Motion. Torque, Momentum, Angular Velocity EtcMark Riley100% (2)
- Organic Chemistry - Esters Lab & Lab Report (Making Scents of Esters)Document7 pagesOrganic Chemistry - Esters Lab & Lab Report (Making Scents of Esters)Mark Riley86% (14)
- Senior Maths Formula SheetDocument2 pagesSenior Maths Formula SheetMark Riley100% (2)
- Maths Assignment - With Roller Coaster QuestionDocument12 pagesMaths Assignment - With Roller Coaster QuestionMark Riley100% (1)
- Physics Lab - Magnetic Field Strengths Practical Reports (REALLY BASIC)Document7 pagesPhysics Lab - Magnetic Field Strengths Practical Reports (REALLY BASIC)Mark Riley100% (2)
- Lab8 Part I (Major Assessment) Design A Flow Chart To Determine An Unknown Organic Compound - (BEST FLOW CHART EVER)Document1 pageLab8 Part I (Major Assessment) Design A Flow Chart To Determine An Unknown Organic Compound - (BEST FLOW CHART EVER)Mark Riley50% (2)
- Physics Lab Assessment 7 PARTA - The Conservation of Energy (Elastic Potential Energy) Practical ReportDocument8 pagesPhysics Lab Assessment 7 PARTA - The Conservation of Energy (Elastic Potential Energy) Practical ReportMark Riley67% (3)
- Missing Page From - Determining Unknown Organic Compound Lab ReportDocument1 pageMissing Page From - Determining Unknown Organic Compound Lab ReportMark RileyNo ratings yet
- Chemistry Lab Assessment - Oxidation & Reduction - Redox Reactions Lab ReportDocument5 pagesChemistry Lab Assessment - Oxidation & Reduction - Redox Reactions Lab ReportMark Riley100% (11)
- Chem - Redox Formula Sheet (Never Completely Finished), Electrolytic Cells, Voltaic Cells, Electric PotentialsDocument2 pagesChem - Redox Formula Sheet (Never Completely Finished), Electrolytic Cells, Voltaic Cells, Electric PotentialsMark Riley100% (2)
- String Theory Problem Set 1 HarvardDocument2 pagesString Theory Problem Set 1 Harvardbelderandover09No ratings yet
- Full Text 01Document128 pagesFull Text 01Renan Alves100% (1)
- MIT Quantum Therory NotesDocument40 pagesMIT Quantum Therory Notespck87No ratings yet
- Feynman Diagrams: Particle and Nuclear PhysicsDocument20 pagesFeynman Diagrams: Particle and Nuclear PhysicsAyushi ShumanNo ratings yet
- Rutu Gate PDFDocument2 pagesRutu Gate PDFRuturaj MendhegiriNo ratings yet
- Objective Type Questions Chapter # 1 The Scope of Physics: Compiled By: Faizan AhmedDocument2 pagesObjective Type Questions Chapter # 1 The Scope of Physics: Compiled By: Faizan AhmedHyder Ali RindNo ratings yet
- XXCVDocument26 pagesXXCVRevolution WorldNo ratings yet
- Deformations and Theoretical NuclearDocument28 pagesDeformations and Theoretical NuclearbinifsNo ratings yet
- Chapter 20 Exercise Short QuestionsDocument2 pagesChapter 20 Exercise Short Questionssaifullah629No ratings yet
- The Students' ProblemDocument21 pagesThe Students' ProblemAmairaNo ratings yet
- Electric Charge: - 1 Class 10 - ElectricityDocument4 pagesElectric Charge: - 1 Class 10 - ElectricityAaryanNo ratings yet
- 3 Quantum Mechanics IntroDocument79 pages3 Quantum Mechanics IntroShan Yu XuanNo ratings yet
- QuarksDocument243 pagesQuarksManfred Manfrito100% (1)
- Supersymmetric Hyperbolic Calogero-Sutherland Models by GaugingDocument18 pagesSupersymmetric Hyperbolic Calogero-Sutherland Models by GaugingSomanshu KumarNo ratings yet
- A Semi-Detailed Lesson Plan in TLE 7 (Productivity, Humility) Common Carpentry Tools January 25, 2017Document2 pagesA Semi-Detailed Lesson Plan in TLE 7 (Productivity, Humility) Common Carpentry Tools January 25, 2017gaea lou50% (4)
- An Interview With Alain Connes PDFDocument45 pagesAn Interview With Alain Connes PDFDhinakaran SampathNo ratings yet
- M103-Conducting - Quantum TheroyDocument13 pagesM103-Conducting - Quantum Theroymades samiNo ratings yet
- 2004 Ams Nim Paper DraftDocument254 pages2004 Ams Nim Paper DraftMarco IncagliNo ratings yet
- Curriculum Vitae: July 2010Document20 pagesCurriculum Vitae: July 2010Ghulam MurtazaNo ratings yet
- Physics DPP 1Document1 pagePhysics DPP 1Crazy iitphysicsNo ratings yet
- QuantumDocument15 pagesQuantumThakuri Praveen ChandNo ratings yet
- Magnetic Monopole Dynamics, Supersymmetry, and DualityDocument253 pagesMagnetic Monopole Dynamics, Supersymmetry, and Dualityrc85948No ratings yet
- Quantum Chromodynamics: Standard Model Particle PhysicsDocument4 pagesQuantum Chromodynamics: Standard Model Particle PhysicsDexterNo ratings yet
- Fermi Gas Model (2c)Document2 pagesFermi Gas Model (2c)Langgeng Asmoro100% (1)
- Freelancer Misc. Data BaseDocument145 pagesFreelancer Misc. Data BaseJevoun TyrellNo ratings yet
- Kuliah 19 - Momentum Sudut (English)Document3 pagesKuliah 19 - Momentum Sudut (English)SuranewNo ratings yet
Quantum Atomic Physics Eg Photoelectric Affect Formula Sheet Study Tool Physics A
Quantum Atomic Physics Eg Photoelectric Affect Formula Sheet Study Tool Physics A
Uploaded by
rohitpatyalOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Quantum Atomic Physics Eg Photoelectric Affect Formula Sheet Study Tool Physics A
Quantum Atomic Physics Eg Photoelectric Affect Formula Sheet Study Tool Physics A
Uploaded by
rohitpatyalCopyright:
Available Formats
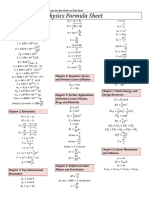
Electromagnetic forces acts on electrons-holds atoms together Strong Nuclear force acts on nucleons-holds nucleus together Weak Nuclear
force acts on nucleons-radioactive decay Gravitational forces acts on all matter- holds planets together
Photo electric effect
Lights can be particle & come in small packets called photons Short light or U.V on metal surface are ejected as photocurrent bound to surface with binding energy called the work function W only ejected if frequency of incident light exceeds the MIN threshold frequency for that particular metal f>F0 Using light with larger f increases the KE of ejected Once photocurrent is registered, increasing intensity will increase photocurrent Negative potential V is applied to collector plate (anode) which repels the and when large enough to stop photocurrent then this is stopping potential or cut-off voltage & the current will flatten out to a maximum.
Photon Momentum (the Compton effect) = = mc = hf c
= photon momentum = = = = =
ALL PARTICLES BEHAVE AS WAVES
Plancks Black body radiation
A Black body wont reflect any light (or other electromagnetic radiation) When heated it will emit electromagnetic radiation (eg hot plate)
WAVE PARTICLE DUALITY Debrogil wavelength = =
CONSERVATION OF MOMENTUM m1u1 + m 2u2 = m1v1 + m 2v2 F= momentum (P) =N time
= =
CONSERVATION OF KINETIC ENERGY
= .
W=
m1v21 + m2v22 = m1u21 + m2u22
ELECTRON GUN
= 1 = 1.6 1019 = energy Joules = frequency of the emitted radiation = planck constant = . s =
= = =
= .
X-Ray Scattering- The Compton affect & light pressure
/
E J
= = .
= =
= () = De Brogile-Davisson & Germer Apparatus
E f E = hf h = f = = = E= =
Black body radiation Energy created by moving between defined energy level within the atom (transitions). Certain states of vibrations are more likely- hence the peak in the frequency distribution curve Atoms can only vibrate at a certain frequency Light energy not given of continuesly but in small energy packets called Quanta or Photons WAVE MODEL FAILS BECAUSE PREDICTS Increasing Intensity should increase KE of e Photoelectric effect will occur for all frequencies but in fact there is a threshold frequency
= 700 109 = 400 109
White light= = Wavelengths decrease Refracts more critical angle decreases frequency increases
+
Electrons from filament F are accelerated by a variable potential difference V. After scattering from crystal C they are collected by detector D
Photoelectric apparatus
Ionisation -process of removing electron or more from a neutral atom creating a pos+ charged atom. Ionisation energy=w
= =
= Energy of higher orbital = Energy of lower orbital
The total energy E of the electron in such an orbit (this can also be found on the diagram below)
A ZX
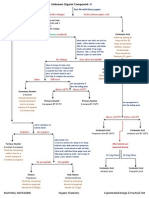
A=Mass Number of nucleons (protons & Neutrons) Z=Atomic Number= Number of protons in nucleus 1 = mass of 12 6 C = . 2 Mass of- Proton=1.007276 u Neutron=1.008665 u Electron=.000549 u 1u=931 MeV (binding energy) Mass of constituents>actual mass Transmutation (EG caused by ALPHA BOMBARDMENT)
Positively charged particles being emitted from the nucleus of radioactive atoms. Alpha Particles- collide with matter and slow down transferring their kinetic energy to the other molecules shaking many of them apart leaving a trail of pos & neg ions in their wake. Electrons being emmited from the nucleus of radioactive atoms Beta Particles- move at very high speeds. Smaller & more penetrating than alpha particles High energy electromagnetic rays/photons being emitted from the nucleus of an atom. Happens around other decay when the atom rearranges itself to be more stable. -13 Gamma Particles- Extremely small ( -10 m) & most penetrating. (no charge)
En =
E1 n2
En = nhf
= 2.17 1018 13.6 = The energy of that nuber orbital = number of the orbital where e is
Alpha Decay (ATOMS HEAVIER THAN URANIUM-238)
A ZX
A 4 Z 2Y
+4 2 He + energy ()
Beta Decay (ATOM HAS SURPLUS OF NEUTRONS)
Bohr model of atom
Electron will only radiate energy in exact quanta. move inward to nucleus until stable state is reached.
A ZX
A Z+1 Y
+ 0 1 e + energy ()
Positron Decay (SURPLUS OF PROTONS)
A ZX
A 0 Z 1 Y + +1 e + energy
()
Radius of Hydrogen atom= 5 1011
Mass Defect represents mass that has been converted into binding energy
Nuclide-Name & symbol of a particular atomic species eg C or H etc
Einstein said Matter & Energy are not separate quantities but are different forms of one another =
Nucleus=
1 10,000
size of whole atom
() BINDING ENERGY (relates to fo) E = (Mass Actual Mass) c 2 Mass Defect=Mass-Actual Mass Fission- Breaks apart Fusion- Puts together Tritium- 3 1 HALF LIFE N 1 = ( )n NO 2 log N 1 = n log NO 2
Mass of proton=mass of neutron Nucleus=99% of mass of whole atom
Thompsons Plum pudding model No good because tiny particles fired at atom and can pass thru
Determine potential (accelerating portential) V(volts) when an electron (or particle) is shot through single slit or double slit grating.
1.
Determine wave length SINGLE SLIT 2L w= = d DOUBLE SLIT L w= = d = width of central maximum = distance between slits = distance to screen
Isotopes have same nuber of protons but different number of neutrons to original element & will behave similar More protons= bigger atom=helps stability because seperates charges
n=
2.
Strong Nuclear Force (binding energy) only affects within distance of 5 1015 Adding protons does not increase the strong nuclear force No stable nuclides have E>8 Proton + Electron = Neutron
time t = time of half life t 1
2
Use wavelength to determine momentumhence find the velocity h h = = mv p =
N = number of particles NO = Initial number of particles
3.
Velocity determines potential difference (Volts) 1 W = qV = mv 2 2 =
Mark Riley markriley85@hotmail.com
You might also like
- Physics Final (Cheat Sheet) With ProblemsDocument2 pagesPhysics Final (Cheat Sheet) With ProblemsRSlipkov97% (97)
- Grade 11 Physics Study Guide / Notes For Final Exam SPH3U1Document23 pagesGrade 11 Physics Study Guide / Notes For Final Exam SPH3U1Niki79% (14)
- Ultimate Physics Cheat SheetDocument2 pagesUltimate Physics Cheat SheetNehal VoraNo ratings yet
- Physics I Final Cheat SheetDocument1 pagePhysics I Final Cheat SheetJsea2011100% (1)
- Optics Formula Sheet Study Sheet PhysicsA 2010Document1 pageOptics Formula Sheet Study Sheet PhysicsA 2010Mark Riley100% (1)
- Optics Formula Sheet Study Sheet PhysicsA 2010Document1 pageOptics Formula Sheet Study Sheet PhysicsA 2010Mark Riley100% (1)
- Physics Exam Cheat SheetDocument3 pagesPhysics Exam Cheat SheetJib Bros100% (4)
- Physics Formula SheetDocument12 pagesPhysics Formula SheetRohit Ghere100% (4)
- Physics2A CheatSheetDocument1 pagePhysics2A CheatSheetNastassja LopezNo ratings yet
- Physics EquationsDocument5 pagesPhysics Equationsanon-992211100% (64)
- Physics 1121 A Cheat SheetDocument8 pagesPhysics 1121 A Cheat SheetAmmar Tirmzey100% (1)
- Halzen and MartinDocument412 pagesHalzen and Martinapi-3797443100% (1)
- Fluids Dynamics Formula SheetDocument2 pagesFluids Dynamics Formula SheetMark Riley88% (8)
- Freshman Physics Formula SheetDocument6 pagesFreshman Physics Formula SheetMickey Boy83% (6)
- MCAT Physics Formula SheetDocument3 pagesMCAT Physics Formula Sheetemma_reese100% (2)
- Grade 11 Physics - Kinematics ReviewDocument2 pagesGrade 11 Physics - Kinematics Reviewfairwayhills70275% (12)
- Heat & Determining Enthalpy Change (Lab Assessment) Part I & Part 2Document8 pagesHeat & Determining Enthalpy Change (Lab Assessment) Part I & Part 2Mark Riley81% (16)
- Fluids Dynamics Formula SheetDocument2 pagesFluids Dynamics Formula SheetMark Riley88% (8)
- Subject Test - Advanced Physics - Chegg IndiaDocument2 pagesSubject Test - Advanced Physics - Chegg IndiaSanjeevkumarSingh50% (6)
- (Lauri H.J. Lajunen) Spectrochemical AnalysisDocument258 pages(Lauri H.J. Lajunen) Spectrochemical AnalysisAndrew CarrNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Quantum Computing - Quantum Circuit ElementsDocument13 pagesIntroduction To Quantum Computing - Quantum Circuit ElementsSaikiranKumarNo ratings yet
- Formula Sheet Physics 133Document12 pagesFormula Sheet Physics 133Muhammad IshtiaqNo ratings yet
- Formula Sheet For Grade 10 NewDocument4 pagesFormula Sheet For Grade 10 NewNo PainNo ratings yet
- Physics Formula SheetDocument4 pagesPhysics Formula SheetfabolaNo ratings yet
- Inorganic Memory Chart PDFDocument22 pagesInorganic Memory Chart PDFUtkarsh GuptaNo ratings yet
- Limits of FunctionsDocument11 pagesLimits of Functionsnormasulasa100% (1)
- Tau ThetaDocument3 pagesTau Thetapradeep reddy0% (1)
- SPH3U1 Exam Review NotesDocument26 pagesSPH3U1 Exam Review Notesrahihot100% (1)
- Formula Booklet Physics XIDocument35 pagesFormula Booklet Physics XIsreenatpppp84% (147)
- Mathematics Formula SheetDocument35 pagesMathematics Formula SheetChandra Kishore Paul67% (3)
- Optics Cheat SheetDocument1 pageOptics Cheat SheetAlex MuresanNo ratings yet
- Concentration Cheat Sheet PDFDocument2 pagesConcentration Cheat Sheet PDFimec_coordinator7353No ratings yet
- Unit III Quantum MechanicsDocument148 pagesUnit III Quantum MechanicsPrince JunejaNo ratings yet
- Evidence For Wave-Particle DualityDocument24 pagesEvidence For Wave-Particle DualitySudipta DasNo ratings yet
- Vce Unit 3 and 4 Physics Cheat SheetDocument2 pagesVce Unit 3 and 4 Physics Cheat SheetRameesha AizazNo ratings yet
- Day 31Document10 pagesDay 31g.sathyanarayanan252008No ratings yet
- Smart Revision Quantum PhysicsDocument18 pagesSmart Revision Quantum PhysicsZAIHASRA BINTI AHMAD KPM-GuruNo ratings yet
- Dual Nature NotesDocument4 pagesDual Nature Noteswifohiw819No ratings yet
- Modern PhysicsDocument11 pagesModern PhysicsPuja KumariNo ratings yet
- 2023 F5 UT MemoDocument2 pages2023 F5 UT Memo2B-11 HO HOI TINGNo ratings yet
- Particle Wave DualityDocument24 pagesParticle Wave DualityIsrael PopeNo ratings yet
- CHAPTER-1 SummaryDocument8 pagesCHAPTER-1 SummaryRaven John Yecyec RufinoNo ratings yet
- Optical Fiber Communications: Lecture 2: Physics of LightDocument15 pagesOptical Fiber Communications: Lecture 2: Physics of Lightjeddo2005No ratings yet
- Chapter II: Interaction of Electromagnetic Radiation With Atoms and MoleculesDocument14 pagesChapter II: Interaction of Electromagnetic Radiation With Atoms and Moleculeskiswah computersNo ratings yet
- Photoelectric Effect: Day Thirty TwoDocument9 pagesPhotoelectric Effect: Day Thirty TwoPrayas RaneNo ratings yet
- Kuliah-19 Dualisme Partikel GelombangDocument24 pagesKuliah-19 Dualisme Partikel GelombangNeni Fitria RahayuNo ratings yet
- LMR Final Physics 3.30 - RemovedDocument13 pagesLMR Final Physics 3.30 - RemovedEco DudeNo ratings yet
- 1237.quantum Mechanics 1Document94 pages1237.quantum Mechanics 1cattlNo ratings yet
- QM 2020-21 Sem1Document79 pagesQM 2020-21 Sem1wzardking69No ratings yet
- PYL101 QM Lecture 3Document16 pagesPYL101 QM Lecture 3mukeshNo ratings yet
- Morden PhysicsDocument37 pagesMorden PhysicsSimilinga MnyongeNo ratings yet
- 1.1.6 Einstein Coefficients - 1: Rate EquationDocument15 pages1.1.6 Einstein Coefficients - 1: Rate Equationshouravme2k11No ratings yet
- Short Notes - Modern Physics by Gulshan JhaDocument3 pagesShort Notes - Modern Physics by Gulshan JhaSHIVI DwivediNo ratings yet
- EP 1108 Photoelectric EffectDocument12 pagesEP 1108 Photoelectric EffectAryam SharmaNo ratings yet
- Light and Matter FormulaeDocument2 pagesLight and Matter FormulaefizzvineNo ratings yet
- TUNNELLINGDocument14 pagesTUNNELLINGkumarmanojod010215No ratings yet
- Physics - 1 - LESSON 1 (Final Term - Summer 23)Document18 pagesPhysics - 1 - LESSON 1 (Final Term - Summer 23)fardinmojumdar123No ratings yet
- Particle Nature of Light - Sunday 7 FebpptxDocument33 pagesParticle Nature of Light - Sunday 7 Febpptxtohfeh kassemNo ratings yet
- Efek Foto ListrikDocument38 pagesEfek Foto ListrikZAHWA RIZZI ANINo ratings yet
- Dual Nature of Matter and RadiationDocument14 pagesDual Nature of Matter and RadiationAmrit AnuragNo ratings yet
- SFI 5800 Spectroscopy General3Document10 pagesSFI 5800 Spectroscopy General3Alejandra Ayulo CumpalliNo ratings yet
- Quantum Mechanics and Atomic Theory: Chapter 12, J. Ren, 2021 1Document97 pagesQuantum Mechanics and Atomic Theory: Chapter 12, J. Ren, 2021 1Babeejay2No ratings yet
- Physics Module Three ReviewDocument22 pagesPhysics Module Three Reviewshan mackNo ratings yet
- Feynman Lectures Simplified 2B: Magnetism & ElectrodynamicsFrom EverandFeynman Lectures Simplified 2B: Magnetism & ElectrodynamicsNo ratings yet
- Feynman Lectures Simplified 2A: Maxwell's Equations & ElectrostaticsFrom EverandFeynman Lectures Simplified 2A: Maxwell's Equations & ElectrostaticsNo ratings yet
- Feynman Lectures Simplified 2C: Electromagnetism: in Relativity & in Dense MatterFrom EverandFeynman Lectures Simplified 2C: Electromagnetism: in Relativity & in Dense MatterNo ratings yet
- Unified Field Theory in a Nutshell1: The Quest for the Theory of EverythingFrom EverandUnified Field Theory in a Nutshell1: The Quest for the Theory of EverythingNo ratings yet
- Dimensional Analysis: A Simple ExampleDocument10 pagesDimensional Analysis: A Simple ExampleMark RileyNo ratings yet
- Physics - Relationships Between The Equations Linear and Angular Motion. Torque, Momentum, Angular Velocity EtcDocument2 pagesPhysics - Relationships Between The Equations Linear and Angular Motion. Torque, Momentum, Angular Velocity EtcMark Riley100% (2)
- Organic Chemistry - Esters Lab & Lab Report (Making Scents of Esters)Document7 pagesOrganic Chemistry - Esters Lab & Lab Report (Making Scents of Esters)Mark Riley86% (14)
- Senior Maths Formula SheetDocument2 pagesSenior Maths Formula SheetMark Riley100% (2)
- Maths Assignment - With Roller Coaster QuestionDocument12 pagesMaths Assignment - With Roller Coaster QuestionMark Riley100% (1)
- Physics Lab - Magnetic Field Strengths Practical Reports (REALLY BASIC)Document7 pagesPhysics Lab - Magnetic Field Strengths Practical Reports (REALLY BASIC)Mark Riley100% (2)
- Lab8 Part I (Major Assessment) Design A Flow Chart To Determine An Unknown Organic Compound - (BEST FLOW CHART EVER)Document1 pageLab8 Part I (Major Assessment) Design A Flow Chart To Determine An Unknown Organic Compound - (BEST FLOW CHART EVER)Mark Riley50% (2)
- Physics Lab Assessment 7 PARTA - The Conservation of Energy (Elastic Potential Energy) Practical ReportDocument8 pagesPhysics Lab Assessment 7 PARTA - The Conservation of Energy (Elastic Potential Energy) Practical ReportMark Riley67% (3)
- Missing Page From - Determining Unknown Organic Compound Lab ReportDocument1 pageMissing Page From - Determining Unknown Organic Compound Lab ReportMark RileyNo ratings yet
- Chemistry Lab Assessment - Oxidation & Reduction - Redox Reactions Lab ReportDocument5 pagesChemistry Lab Assessment - Oxidation & Reduction - Redox Reactions Lab ReportMark Riley100% (11)
- Chem - Redox Formula Sheet (Never Completely Finished), Electrolytic Cells, Voltaic Cells, Electric PotentialsDocument2 pagesChem - Redox Formula Sheet (Never Completely Finished), Electrolytic Cells, Voltaic Cells, Electric PotentialsMark Riley100% (2)
- String Theory Problem Set 1 HarvardDocument2 pagesString Theory Problem Set 1 Harvardbelderandover09No ratings yet
- Full Text 01Document128 pagesFull Text 01Renan Alves100% (1)
- MIT Quantum Therory NotesDocument40 pagesMIT Quantum Therory Notespck87No ratings yet
- Feynman Diagrams: Particle and Nuclear PhysicsDocument20 pagesFeynman Diagrams: Particle and Nuclear PhysicsAyushi ShumanNo ratings yet
- Rutu Gate PDFDocument2 pagesRutu Gate PDFRuturaj MendhegiriNo ratings yet
- Objective Type Questions Chapter # 1 The Scope of Physics: Compiled By: Faizan AhmedDocument2 pagesObjective Type Questions Chapter # 1 The Scope of Physics: Compiled By: Faizan AhmedHyder Ali RindNo ratings yet
- XXCVDocument26 pagesXXCVRevolution WorldNo ratings yet
- Deformations and Theoretical NuclearDocument28 pagesDeformations and Theoretical NuclearbinifsNo ratings yet
- Chapter 20 Exercise Short QuestionsDocument2 pagesChapter 20 Exercise Short Questionssaifullah629No ratings yet
- The Students' ProblemDocument21 pagesThe Students' ProblemAmairaNo ratings yet
- Electric Charge: - 1 Class 10 - ElectricityDocument4 pagesElectric Charge: - 1 Class 10 - ElectricityAaryanNo ratings yet
- 3 Quantum Mechanics IntroDocument79 pages3 Quantum Mechanics IntroShan Yu XuanNo ratings yet
- QuarksDocument243 pagesQuarksManfred Manfrito100% (1)
- Supersymmetric Hyperbolic Calogero-Sutherland Models by GaugingDocument18 pagesSupersymmetric Hyperbolic Calogero-Sutherland Models by GaugingSomanshu KumarNo ratings yet
- A Semi-Detailed Lesson Plan in TLE 7 (Productivity, Humility) Common Carpentry Tools January 25, 2017Document2 pagesA Semi-Detailed Lesson Plan in TLE 7 (Productivity, Humility) Common Carpentry Tools January 25, 2017gaea lou50% (4)
- An Interview With Alain Connes PDFDocument45 pagesAn Interview With Alain Connes PDFDhinakaran SampathNo ratings yet
- M103-Conducting - Quantum TheroyDocument13 pagesM103-Conducting - Quantum Theroymades samiNo ratings yet
- 2004 Ams Nim Paper DraftDocument254 pages2004 Ams Nim Paper DraftMarco IncagliNo ratings yet
- Curriculum Vitae: July 2010Document20 pagesCurriculum Vitae: July 2010Ghulam MurtazaNo ratings yet
- Physics DPP 1Document1 pagePhysics DPP 1Crazy iitphysicsNo ratings yet
- QuantumDocument15 pagesQuantumThakuri Praveen ChandNo ratings yet
- Magnetic Monopole Dynamics, Supersymmetry, and DualityDocument253 pagesMagnetic Monopole Dynamics, Supersymmetry, and Dualityrc85948No ratings yet
- Quantum Chromodynamics: Standard Model Particle PhysicsDocument4 pagesQuantum Chromodynamics: Standard Model Particle PhysicsDexterNo ratings yet
- Fermi Gas Model (2c)Document2 pagesFermi Gas Model (2c)Langgeng Asmoro100% (1)
- Freelancer Misc. Data BaseDocument145 pagesFreelancer Misc. Data BaseJevoun TyrellNo ratings yet
- Kuliah 19 - Momentum Sudut (English)Document3 pagesKuliah 19 - Momentum Sudut (English)SuranewNo ratings yet