Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Memory Management
Memory Management
Uploaded by
rvk386Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Memory Management
Memory Management
Uploaded by
rvk386Copyright:
Available Formats
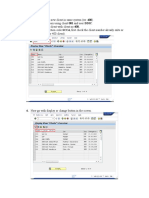
Memory Management SAP Memory Management ?
Controls the internal memory utilization of the work process by using pr ofile parameters that is it controls the growth of the user context data. ? How work processes using the memory and the SAP buffers. ? Provides memory to the work process as on when required from different l ocations i.e., roll/extended/heap. From release 3.0, Memory management makes us of extended memory to optimize the access to the user contexts and avoids overhead on roll-in/roll-out tasks that i s the user contexts were in the roll files and had to be copied from one place t o another. With this new memory management those copy functions are handled by j ust reassigning pointers in the main memory. User Context Data is defined as user data which is kept by the system between di alog steps to continue the processing of the transaction. These data are authorizations, internal tables, runtime environment management information, dialog steps info, Program pointers, Report list, Set/Get parameters(most recent input of the user).
??Data in R/3 roll memory is copied during context switch. ??Data in R/3 extended memory is mapped during context switch. ??Data in R/3 heap memory can never leave the work process. If heap memory is al located, the work process is exclusively assigned to one user in PRIV mode.
You might also like
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeFrom EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (5835)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreFrom EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1093)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItFrom EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (852)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceFrom EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (590)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceFrom EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (903)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeFrom EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (541)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersFrom EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (350)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureFrom EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (474)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesFrom EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (824)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)From EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (122)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerFrom EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (271)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingFrom EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (405)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyFrom EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2259)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)From EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Rating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (98)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaFrom EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (266)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryFrom EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (231)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnFrom EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (234)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealFrom EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (74)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaFrom EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (45)
- SAP Client Specific Change Option in SCC4Document3 pagesSAP Client Specific Change Option in SCC4rvk386No ratings yet
- TcodesDocument3 pagesTcodesrvk386No ratings yet
- TcodesDocument3 pagesTcodesrvk386No ratings yet
- Basis TipsDocument9 pagesBasis Tipsrvk386No ratings yet
- Procedure For Creating A New Client in Same SystemDocument6 pagesProcedure For Creating A New Client in Same Systemrvk386No ratings yet
- What Is An Instance of An SAP System?Document1 pageWhat Is An Instance of An SAP System?rvk386No ratings yet
- Inspection With Material Specification-QMDocument8 pagesInspection With Material Specification-QMrvk38650% (2)
- REM e T eDocument22 pagesREM e T ervk386No ratings yet
- Batch Determination PPDocument13 pagesBatch Determination PPrvk386No ratings yet
- QM OverviewDocument16 pagesQM Overviewrvk386No ratings yet
- Collective OrderDocument26 pagesCollective Orderrvk386100% (1)
- Production StrategyDocument3 pagesProduction Strategyrvk386No ratings yet
- REM e T eDocument22 pagesREM e T ervk386No ratings yet
- Tcodes For Pp-PiDocument4 pagesTcodes For Pp-Pirvk386No ratings yet
- Splits Work Center and Routing: Posts: 72 Joined: Tue Jun 17, 2003 9:28 PM Location: AustraliaDocument3 pagesSplits Work Center and Routing: Posts: 72 Joined: Tue Jun 17, 2003 9:28 PM Location: Australiarvk386No ratings yet