Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Intro CH 12bbuilding Information System
Intro CH 12bbuilding Information System
Uploaded by
api-2477142570 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
34 views20 pagesOriginal Title
intro ch 12bbuilding information system
Copyright
© Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Available Formats
PPT, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Available Formats
Download as PPT, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as ppt, pdf, or txt
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
34 views20 pagesIntro CH 12bbuilding Information System
Intro CH 12bbuilding Information System
Uploaded by
api-247714257Copyright:
Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Available Formats
Download as PPT, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as ppt, pdf, or txt
You are on page 1of 20
McGraw-Hill Technology Education McGraw-Hill Technology Education
Copyright 2006 by The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. All rights reserved. Copyright 2006 by The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. All rights reserved.
Chapter 12B
Building Information Systems
McGraw-Hill Technology Education
Copyright 2006 by The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. All rights reserved.
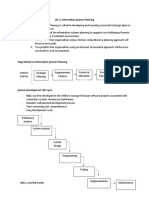
Systems Development Life Cycle
Organized way to build information systems Consists of five phases
Entire usable life of the system
12B-3
SDLC
12B-4
Systems Development Life Cycle
Phase 1: needs analysis
Users identify a need Solves three main problems
Define the problem Present possible solutions Determine the best solution
Technology analysts talk with users Define the problem using a description tool A solution is presented to a manager
12B-5
Systems Development Life Cycle
Phase 2: Systems design
Solution is defined
Data storage User interface Reports
Several design tools
Top down design Bottom up design
CASE tools used to build prototypes
Computer aided software engineering
12B-6
Systems Development Life Cycle
Phase 3: Development
Solution to the problem is built Programmers play a key role Solutions may be purchased Solutions may be built locally Technical writers create instructions Solution is repeatedly tested
12B-7
Systems Development Life Cycle
Phase 4: Implementation
Installation of hardware and software Users must convert to the solution
Direct conversion Parallel conversion Phased conversion Pilot conversion
Trainers and support personnel are critical
12B-8
SDLC Conversion
12B-9
Systems Development Life Cycle
Phase 5: Maintenance
IT professionals continue to monitor Bugs are fixed New features are added Users often suggest bugs or features
12B-10
Evolving System Design Methods
Problems with SDLC
SDLC is an old process Very slow process Companies need to respond quickly
12B-11
Evolving System Design Methods
Rapid Application Design (RAD)
Develops IS systems quickly Several products exist Slightly different development phases
12B-12
RAD SDLC
12B-13
Evolving System Design Methods
RAD Phase 1: Requirements planning
Requirements for project are defined Joint requirements planning (JRP)
Involves programmers and managers
Managers from affected departments provide guidance
12B-14
Evolving System Design Methods
RAD Phase 2: User design
Joint application design (JAD)
System analysts and users
User provides the details System analyst solve the technical details
12B-15
Evolving System Design Methods
RAD Phase 3: Rapid construction
IS professionals develop the project A variety of tools can be used Users approve each portion
12B-16
Evolving System Design Methods
RAD Phase 4: Transition
System is tested on sample data Users are trained on the sample New system runs parallel to existing Phase complete when bugs are gone Old system removed
12B-17
Evolving System Design Methods
RAD Phase 5: Maintenance
Traditionally not part of RAD All systems need periodic maintenance
12B-18
Evolving System Design Methods
Object Oriented Systems Analysis
OOSA Project elements are defined using objects
Objects are self contained programming constructs Objects have data and functionality
Objects are linked together Java and C++ are typical tools
12B-19
Chapter 12B
End of Chapter
McGraw-Hill Technology Education
Copyright 2006 by The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. All rights reserved.
You might also like
- Google Cloud Platform for Data Engineering: From Beginner to Data Engineer using Google Cloud PlatformFrom EverandGoogle Cloud Platform for Data Engineering: From Beginner to Data Engineer using Google Cloud PlatformRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Lesson 1 - The Database Environment and Development ProcessDocument47 pagesLesson 1 - The Database Environment and Development ProcessGintoki Sakata0% (1)
- TAFJ R18 Release NotesDocument10 pagesTAFJ R18 Release NotesGopal ArunachalamNo ratings yet
- Dynamic Action To Send MailDocument13 pagesDynamic Action To Send Mailshotbomb100% (1)
- Non Spatial FieldsDocument19 pagesNon Spatial FieldsMariano Serrano0% (1)
- Intro CH 12BDocument20 pagesIntro CH 12Bapi-3831049No ratings yet
- Intro CH 12BDocument20 pagesIntro CH 12BHanzla HanzlaNo ratings yet
- Mcgraw-Hill Technology Education Mcgraw-Hill Technology EducationDocument20 pagesMcgraw-Hill Technology Education Mcgraw-Hill Technology EducationShahid MehmoodNo ratings yet
- Chapter2 SDLCDocument18 pagesChapter2 SDLCHarpreet RaiNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Systems Analysis and DesignDocument74 pagesIntroduction To Systems Analysis and Designsona_gold1367No ratings yet
- Systems Development Life Cycle (SDLC)Document29 pagesSystems Development Life Cycle (SDLC)mary ann joaquinNo ratings yet
- SDLCDocument55 pagesSDLCkipropc183No ratings yet
- Systems Development: Mcgraw-Hill/Irwin © 2008 The Mcgraw-Hill Companies, All Rights ReservedDocument58 pagesSystems Development: Mcgraw-Hill/Irwin © 2008 The Mcgraw-Hill Companies, All Rights ReservedRolando MauliNo ratings yet
- Lesson 18: SystemsDocument6 pagesLesson 18: Systemsbuddhika madusankaNo ratings yet
- Database Systems: Design, Implementation, and ManagementDocument56 pagesDatabase Systems: Design, Implementation, and ManagementShayan BalochNo ratings yet
- 03 SDLC Dan MethodologyDocument64 pages03 SDLC Dan MethodologyRianNo ratings yet
- Chapter1 SDLCDocument33 pagesChapter1 SDLCMarthea Andrea DaluyonNo ratings yet
- Software Development LifecyclesDocument38 pagesSoftware Development LifecyclesJunaid FarooqNo ratings yet
- Information Systems DevelopmenttDocument24 pagesInformation Systems DevelopmenttZyra MediosNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1.Document25 pagesChapter 1.Jossy MollaNo ratings yet
- Rapid Application DevelopmentDocument12 pagesRapid Application DevelopmentPradeep Kumar PandeyNo ratings yet
- Kaedah Analisis Dan Reka Bentuk Bab 1Document27 pagesKaedah Analisis Dan Reka Bentuk Bab 1MOHD AFFENDI BIN JOULANo ratings yet
- Acquiring IT AppDocument25 pagesAcquiring IT AppRufino Reyes IIINo ratings yet
- Systems Development: Mcgraw-Hill/Irwin © 2008 The Mcgraw-Hill Companies, All Rights ReservedDocument30 pagesSystems Development: Mcgraw-Hill/Irwin © 2008 The Mcgraw-Hill Companies, All Rights Reservedpalashkhare11No ratings yet
- Database Systems Design, Implementation, and Management Eighth Edition-Ch09Document50 pagesDatabase Systems Design, Implementation, and Management Eighth Edition-Ch09zero_xcare100% (2)
- RAD & The Dynamic Systems Development MethodDocument6 pagesRAD & The Dynamic Systems Development MethodCedric CedricNo ratings yet
- Analysis and Design: of E-Commerce SystemsDocument50 pagesAnalysis and Design: of E-Commerce Systemshamedsky100% (1)
- SDLCDocument55 pagesSDLCswapnil_022No ratings yet
- Information System DevelopmentDocument57 pagesInformation System DevelopmentVinay AroraNo ratings yet
- CASE Tools - PPTDocument29 pagesCASE Tools - PPTsbr11No ratings yet
- Mcgraw-Hill/Irwin Mcgraw-Hill/IrwinDocument70 pagesMcgraw-Hill/Irwin Mcgraw-Hill/IrwinArslan SaleemNo ratings yet
- Phases SDLC Awad 4Document39 pagesPhases SDLC Awad 4Tanveer KaurNo ratings yet
- The Systems Development EnvironmentDocument47 pagesThe Systems Development EnvironmentAditya BhusalNo ratings yet
- Developing Business/It Solutions: Mcgraw-Hill/Irwin Mcgraw-Hill/IrwinDocument65 pagesDeveloping Business/It Solutions: Mcgraw-Hill/Irwin Mcgraw-Hill/IrwinNad Leira AllertseNo ratings yet
- Chapter 12Document35 pagesChapter 12Ammar YasserNo ratings yet
- Dcit 24 Lec 2Document25 pagesDcit 24 Lec 2jaesthminieNo ratings yet
- Systems Development: Planning LifecycleDocument30 pagesSystems Development: Planning Lifecyclesiesta60No ratings yet
- System Development Life Cycle PresentationDocument25 pagesSystem Development Life Cycle PresentationMuhammad TaimurNo ratings yet
- Week 1 Module 1Document19 pagesWeek 1 Module 1Beth RichardsNo ratings yet
- Systems Analysis & Database Management Systems: INFS7007Document50 pagesSystems Analysis & Database Management Systems: INFS7007Anu SachdevaNo ratings yet
- Principles of Information Systems Eighth Edition: Systems Development: Investigation and AnalysisDocument65 pagesPrinciples of Information Systems Eighth Edition: Systems Development: Investigation and AnalysisNagunuri SrinivasNo ratings yet
- SDLC 1 24Document24 pagesSDLC 1 24Tanveer KaurNo ratings yet
- Software Development Life Cycle (SDLC)Document52 pagesSoftware Development Life Cycle (SDLC)Rama ReddyNo ratings yet
- RAD DevelopmentDocument52 pagesRAD DevelopmentUCIZAMBO ITNo ratings yet
- Analysis of Three System Development MethodologiesDocument4 pagesAnalysis of Three System Development MethodologiesCamille MathewsNo ratings yet
- Week 2Document24 pagesWeek 27x6t2v4j6xNo ratings yet
- SEG3560 Introduction To E-Commerce: Tutorial 3 - System Analysis & DesignDocument57 pagesSEG3560 Introduction To E-Commerce: Tutorial 3 - System Analysis & Designhquinn21No ratings yet
- WH 7 Cls 12Document33 pagesWH 7 Cls 12Veronica GavanNo ratings yet
- 03 MethodologyDocument38 pages03 MethodologyBlak Rak'anNo ratings yet
- SADCHAP04Document52 pagesSADCHAP04Adjarko PhilipNo ratings yet
- LEC 3 Information System PlanningDocument6 pagesLEC 3 Information System PlanningJEMIMA MILES CASIBUANo ratings yet
- System Development Life Cycle PresentationDocument25 pagesSystem Development Life Cycle Presentationsalim bba90% (10)
- System Development Lifecycle: Comp403Document39 pagesSystem Development Lifecycle: Comp403Nicole RomeroNo ratings yet
- Computer Fundamentals (CS-101 & CS101L)Document42 pagesComputer Fundamentals (CS-101 & CS101L)aliNo ratings yet
- DBLCDocument16 pagesDBLCRabindra P.SinghNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 SummaryDocument10 pagesChapter 1 SummaryGeorge Adly Kamel FahmyNo ratings yet
- Kendall7e - ch06 Agile Modeling and PrototypingDocument52 pagesKendall7e - ch06 Agile Modeling and PrototypingMeynard BaptistaNo ratings yet
- SADCHAP04Document50 pagesSADCHAP04Karen Yvonne R. BilonNo ratings yet
- Systems Design: Mcgraw-Hill/Irwin © 2008 The Mcgraw-Hill Companies, All Rights ReservedDocument33 pagesSystems Design: Mcgraw-Hill/Irwin © 2008 The Mcgraw-Hill Companies, All Rights ReservedALINo ratings yet
- SAP Basis Configuration Frequently Asked QuestionsFrom EverandSAP Basis Configuration Frequently Asked QuestionsRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (4)
- Lecture 3 ManagementDocument15 pagesLecture 3 Managementapi-247714257No ratings yet
- Lec1 P&ao 12bmeDocument20 pagesLec1 P&ao 12bmeapi-247714257No ratings yet
- Introduction To Medical Informatics and Its ComponentsDocument18 pagesIntroduction To Medical Informatics and Its Componentsapi-247714257No ratings yet
- Data ProcessingDocument15 pagesData Processingapi-247714257No ratings yet
- Chapter 1Document16 pagesChapter 1api-247714257No ratings yet
- Lec7 8Document27 pagesLec7 8api-247714257No ratings yet
- Introduction To Social SciencesDocument26 pagesIntroduction To Social Sciencesapi-2477142570% (1)
- Lec3 4Document35 pagesLec3 4api-247714257No ratings yet
- Lab 5 MsDocument2 pagesLab 5 Msapi-247714257No ratings yet
- Lab 4 MsDocument1 pageLab 4 Msapi-247714257No ratings yet
- Lec 07Document25 pagesLec 07api-247714257No ratings yet
- Competitions Rules FinalDocument8 pagesCompetitions Rules Finalapi-247714257No ratings yet
- Besal-2014 FormDocument1 pageBesal-2014 Formapi-247714257No ratings yet
- Introduction To DSPDocument35 pagesIntroduction To DSPapi-247714257No ratings yet
- Lec 45Document73 pagesLec 45api-247714257No ratings yet
- Model Answers For Chapter 7: CLASSIFICATION AND REGRESSION TREESDocument3 pagesModel Answers For Chapter 7: CLASSIFICATION AND REGRESSION TREESTest TestNo ratings yet
- Microsoft Deployment-Chad DeguiraDocument39 pagesMicrosoft Deployment-Chad Deguiraapi-292673191No ratings yet
- Latitude-E6230 Reference Guide En-UsDocument46 pagesLatitude-E6230 Reference Guide En-UsoyadieyeNo ratings yet
- TheraWii Design PDFDocument18 pagesTheraWii Design PDFGeorge K. ChebororNo ratings yet
- Administrator Guide PAN-OS 7.1 PDFDocument922 pagesAdministrator Guide PAN-OS 7.1 PDFReggie ChaosLives DavisNo ratings yet
- 66234en PDFDocument532 pages66234en PDFMarian ButerchiNo ratings yet
- ClicknDecide - NSI - Training Part2 Management Console Configuration - enDocument107 pagesClicknDecide - NSI - Training Part2 Management Console Configuration - enDenaNo ratings yet
- Latch Vs Flip FlopDocument2 pagesLatch Vs Flip Flop3nadhs100% (1)
- Vsphere Esxi Vcenter Server 55 Security GuideDocument176 pagesVsphere Esxi Vcenter Server 55 Security GuideJesús Manuel Viña IglesiasNo ratings yet
- ELEC692 VLSI Signal Processing Architecture: Architecture For Fourier TransformDocument40 pagesELEC692 VLSI Signal Processing Architecture: Architecture For Fourier TransformNavneeth GnlNo ratings yet
- 0461 Chapter 9 Creating Rich Content in ASP NetDocument37 pages0461 Chapter 9 Creating Rich Content in ASP Netpradeepgoud1210No ratings yet
- Focom Manual enDocument43 pagesFocom Manual enIulianCiobanuNo ratings yet
- Editing and Updating Data in Gridview Using Sqldatasource Control - Part 17Document2 pagesEditing and Updating Data in Gridview Using Sqldatasource Control - Part 17shradha11No ratings yet
- Computer Network: Answer Question I and Any FOUR From The RestDocument19 pagesComputer Network: Answer Question I and Any FOUR From The Restshyjuother9773No ratings yet
- 2.DAO Factory Design PatternDocument8 pages2.DAO Factory Design PatternkasimNo ratings yet
- ORACLE PLSQL Midterm Part 4 SOLUTIONSDocument17 pagesORACLE PLSQL Midterm Part 4 SOLUTIONScrispy_joyNo ratings yet
- Question Bank BBEDocument7 pagesQuestion Bank BBEKingshuk RoyNo ratings yet
- DEFCON 22 Zoltan Balazs Bypass Firewalls Application Whitelists in 20 Seconds UPDATEDDocument60 pagesDEFCON 22 Zoltan Balazs Bypass Firewalls Application Whitelists in 20 Seconds UPDATEDSudhanshu Shekhar SharmaNo ratings yet
- New, Changed, and Deprecated Features For Microsoft Dynamics AX 2012Document207 pagesNew, Changed, and Deprecated Features For Microsoft Dynamics AX 2012Bo JensenNo ratings yet
- Object Oriented System (Cse 601)Document56 pagesObject Oriented System (Cse 601)vadkill2006No ratings yet
- Properties of Regular Languages: Prof. Busch - LSU 1Document29 pagesProperties of Regular Languages: Prof. Busch - LSU 1sat258No ratings yet
- MIS - 104: Computing Fundamentals: BBA Department of MIS University of DhakaDocument22 pagesMIS - 104: Computing Fundamentals: BBA Department of MIS University of DhakaMahbubNo ratings yet
- Obtaining A WHQL Certified USB Driver PackageDocument2 pagesObtaining A WHQL Certified USB Driver PackageDavid QuelhasNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Information Technology: DR Dharmendra Kumar KanchanDocument83 pagesIntroduction To Information Technology: DR Dharmendra Kumar KanchanSadhika KatiyarNo ratings yet
- COBOL ProgrammingDocument228 pagesCOBOL ProgrammingAditi BistNo ratings yet
- Quick Guide To CPX-FB13 ProfibusDPV A2xDocument2 pagesQuick Guide To CPX-FB13 ProfibusDPV A2xbeforeRG100% (1)
- 15MPE1019Document12 pages15MPE1019Polumuri RamanaNo ratings yet