Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Earn Value Management (Example)
Earn Value Management (Example)
Uploaded by
Muhammad Nasir KhanOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Earn Value Management (Example)
Earn Value Management (Example)
Uploaded by
Muhammad Nasir KhanCopyright:
Available Formats
EARN VALUE MANAGEMENT (Example)
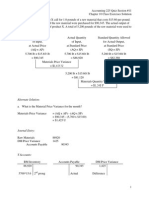
To illustrate the concept of EVM and all the formulas, assume a project that has exactly one task. The task was baselined at 8 hours, but 11 hours have been spent and the estimate to complete is 1 additional hour. The task was to have been completed already. Assume an Hourly Rate of $100 per hour. Using this information:
Hourly Rate = $100 PV or BCWS = Hourly Rate * Total Hours Planned or Scheduled PV = $800 ($100 * 8 hours) AC or ACWP = Hourly Rate * Total Hours Spent AC = $1100 ($100 * 11 hours) EV or BCWP = Baselined Cost * % Complete Actual EV = $734 (baseline of $800 * 91.7% complete) (NOTE % Complete Actual (below) to get the 91.7%) BAC = Baselined Effort-hours * Hourly Rate BAC = $800 (8 hours * $100) EAC = AC + ETC EAC = $1200 (1100 + 100) VAC = BAC - EAC VAC = -$400 ($800 - $1200) % Completed Planned = PV / BAC % Complete Planned = 100% ($800 PV / $800 BAC) % Completed Actual = AC / EAC % Complete Actual = 91.7% ($1100 AC / $1200 EAC) SV = Earned Value (EV) - Planned Value (PV) SV = -$100 ($700 EV - $800 PV) SPI = Earned Value (EV) /Planned Value (PV) SPI = 0.88 ($700 EV / $800 PV) CV = Earned Value (EV) - Actual Cost (AC) CV = -$400 ($700 EV - $1100 AC) indicating a cost overrun CPI = Earned Value (EV) /Actual Cost (AC) CPI = 0.64 ($700 EV / $1100 AC) indicating over budget
............................
D 16, Block D, North Nazimabad, Karachi Tel. 021-204 6177, GSM. 9221 - 300 275 4636, Email: wbsproject@yahoo.com
You might also like
- High Low Method ExercisesDocument4 pagesHigh Low Method ExercisesPhoebe Llamelo67% (12)
- Soal Dan Jawabna Slide 4 Project ManagementDocument3 pagesSoal Dan Jawabna Slide 4 Project ManagementDoni Aditya SaputraNo ratings yet
- Earned Value As Performance ParameterDocument11 pagesEarned Value As Performance Parameterkimo2010xopNo ratings yet
- Earned Value Management: Instructor Hamza EjazDocument27 pagesEarned Value Management: Instructor Hamza EjazShaheena SanaNo ratings yet
- 10-11th Lecture Earned Value ManagementDocument45 pages10-11th Lecture Earned Value Management亗๛『٭SAFI٭』๛No ratings yet
- Earned Value Management ExerciseDocument2 pagesEarned Value Management ExercisetestNo ratings yet
- Earned Value Management (Evm) Interview Questions & Answers: AnswerDocument4 pagesEarned Value Management (Evm) Interview Questions & Answers: AnswerhichemokokNo ratings yet
- EAC and ETC SampleDocument1 pageEAC and ETC Samplekk6969No ratings yet
- EVM - Advanced FormulaDocument33 pagesEVM - Advanced FormulaHuda AlShammariNo ratings yet
- 9th Lecture-PCFM-Project Cost and Financial ManagementDocument12 pages9th Lecture-PCFM-Project Cost and Financial ManagementMuhammad ArshiyaanNo ratings yet
- Sample PMP Earned Value QuestionsDocument9 pagesSample PMP Earned Value QuestionsHamza GhaffarNo ratings yet
- INFINITY - PMP 04 - CostDocument26 pagesINFINITY - PMP 04 - CostOmar KhaledNo ratings yet
- UntitledDocument1 pageUntitledSavan ParmarNo ratings yet
- Project Monitoring and Control (Earned Value Approach)Document15 pagesProject Monitoring and Control (Earned Value Approach)محمد بركاتNo ratings yet
- Sample PMP Earned Value QuestionsDocument9 pagesSample PMP Earned Value QuestionsSajid ZebNo ratings yet
- 06 Eva 2Document17 pages06 Eva 2LukmanNo ratings yet
- Project Tracking in SPMDocument18 pagesProject Tracking in SPMjohn millersNo ratings yet
- CE352-Assignment 1 - Due Date 25-09-20Document15 pagesCE352-Assignment 1 - Due Date 25-09-20IsraelNo ratings yet
- PCFM Quiz 2 + KEYDocument9 pagesPCFM Quiz 2 + KEYRabiya TungNo ratings yet
- PMP - The 12 Essential EVM Formulas Cheat SheetDocument1 pagePMP - The 12 Essential EVM Formulas Cheat SheetMelvin MagbanuaNo ratings yet
- Earned Value - One Page SummaryDocument1 pageEarned Value - One Page Summarymy.nafi.pmp5283No ratings yet
- PM - Cost - Earned Value - Exercises LASTDocument5 pagesPM - Cost - Earned Value - Exercises LASTJuan Auccapiña GuillenNo ratings yet
- How Good Has Our Schedule Performance Been?Document3 pagesHow Good Has Our Schedule Performance Been?farhanyazdaniNo ratings yet
- Earned Value ManagementDocument3 pagesEarned Value ManagementanizamiNo ratings yet
- 19W - ACC4100 - Project Cost Management and FinanceDocument5 pages19W - ACC4100 - Project Cost Management and Financerzsilva0% (1)
- Tabel 1ECFDocument1 pageTabel 1ECFAstrik PrayerNo ratings yet
- Q. No. 1 (Material Variances) Part - 1Document2 pagesQ. No. 1 (Material Variances) Part - 1HelplineNo ratings yet
- NASA EVM Reference Card May 2012 Rev1Document1 pageNASA EVM Reference Card May 2012 Rev1josegabrielrosasNo ratings yet
- Managment AssignmentDocument8 pagesManagment AssignmentMinilik MinilikNo ratings yet
- Sample sums-EVMDocument4 pagesSample sums-EVMShreenidhi M RNo ratings yet
- TUT (4) Q1: Choose The Best AnswerDocument3 pagesTUT (4) Q1: Choose The Best AnswerElzubair EljaaliNo ratings yet
- Formulas / Math For PMP: AtypicalDocument3 pagesFormulas / Math For PMP: AtypicalSudhakar Lakshmana RajNo ratings yet
- PMP FormulasDocument2 pagesPMP FormulasVivekRaptorNo ratings yet
- Assignment #2 DM&DL L Variance With SolutionDocument9 pagesAssignment #2 DM&DL L Variance With SolutionJeannet LagcoNo ratings yet
- Extra Practice Exam 2 SolutionsDocument9 pagesExtra Practice Exam 2 SolutionsSteve SmithNo ratings yet
- Syarikat Perabot Murni Received An Order To Supply 24 Sets of Tables Within A YearDocument2 pagesSyarikat Perabot Murni Received An Order To Supply 24 Sets of Tables Within A YearmaizatulNo ratings yet
- TUTORIALDocument2 pagesTUTORIALren 76No ratings yet
- PMP FormulasDocument2 pagesPMP FormulasSuranjan Kumar DasNo ratings yet
- Earn Value Management (Control Cost) : PercentDocument1 pageEarn Value Management (Control Cost) : PercentMaheswaren MahesNo ratings yet
- Fauzi Ramadhani - 04221025 - Sistem Informasi - ADocument2 pagesFauzi Ramadhani - 04221025 - Sistem Informasi - A4221025 Fauzi RamadhaniNo ratings yet
- Earned Value Assignment 2019Document13 pagesEarned Value Assignment 2019CarlosNo ratings yet
- QS11 - Class Exercises SolutionDocument8 pagesQS11 - Class Exercises Solutionlyk0tex100% (2)
- Earned Value Analysis-PMDocument6 pagesEarned Value Analysis-PMIqraShaheen100% (1)
- PMBOK COSTING - Earned Value ManagementDocument11 pagesPMBOK COSTING - Earned Value ManagementtobagothtiNo ratings yet
- 12-Construction Management - Earned Value ApproachDocument22 pages12-Construction Management - Earned Value Approachمحمد بركاتNo ratings yet
- Earned Value Cheat SheetDocument4 pagesEarned Value Cheat SheetArif NawazNo ratings yet
- EVM ExercisesDocument8 pagesEVM ExercisesRayGaintNo ratings yet
- Chapter 5 Project Monitoring and ControlDocument30 pagesChapter 5 Project Monitoring and ControlYonas YGNo ratings yet
- PCM GroupDocument9 pagesPCM GroupDawit SisayNo ratings yet
- Formula Cost PMPDocument6 pagesFormula Cost PMPPrashanti Sharma ChetriNo ratings yet
- 17 PMP Formulas Mentioned in The PMBOK GuideDocument14 pages17 PMP Formulas Mentioned in The PMBOK GuideStéphane SmetsNo ratings yet
- Earned Value Exercise MEMODocument5 pagesEarned Value Exercise MEMONobukho NjenjeNo ratings yet
- GL1 A2010 Evm - 4Document29 pagesGL1 A2010 Evm - 4RogerQuispeNo ratings yet
- Earned Value Analysis Cheat Sheet 1650957417Document11 pagesEarned Value Analysis Cheat Sheet 1650957417sNo ratings yet
- Chapter No: 07: Cost Theory & AnalysisDocument4 pagesChapter No: 07: Cost Theory & AnalysisDileepHaraniNo ratings yet
- Ch7 9 SolutionDocument16 pagesCh7 9 SolutionMinzaNo ratings yet
- Visual Financial Accounting for You: Greatly Modified Chess Positions as Financial and Accounting ConceptsFrom EverandVisual Financial Accounting for You: Greatly Modified Chess Positions as Financial and Accounting ConceptsNo ratings yet
- Southern Marine Engineering Desk Reference: Second Edition Volume IFrom EverandSouthern Marine Engineering Desk Reference: Second Edition Volume INo ratings yet
- Instructions: 1) Stop The Application If Started 2) Install Application Using Provided Installer and Do Not Reboot 3) Run Patch File Done!Document1 pageInstructions: 1) Stop The Application If Started 2) Install Application Using Provided Installer and Do Not Reboot 3) Run Patch File Done!Muhammad Nasir KhanNo ratings yet
- EPC-Sch4 Anx 3c-Electric Infrastructure Works (11182016) - Clean) - Tracked NasirDocument24 pagesEPC-Sch4 Anx 3c-Electric Infrastructure Works (11182016) - Clean) - Tracked NasirMuhammad Nasir KhanNo ratings yet
- Experience Letter - OCSDocument1 pageExperience Letter - OCSMuhammad Nasir KhanNo ratings yet
- Experience Letter - BNSDocument1 pageExperience Letter - BNSMuhammad Nasir KhanNo ratings yet
- Comments On SGS ProposalDocument1 pageComments On SGS ProposalMuhammad Nasir KhanNo ratings yet
- CongjDocument1 pageCongjMuhammad Nasir KhanNo ratings yet
- Electricity Bill CalculationkjhjDocument1 pageElectricity Bill CalculationkjhjMuhammad Nasir KhanNo ratings yet
- Muhammad Saifullah: Mechanical EngineerDocument3 pagesMuhammad Saifullah: Mechanical EngineerMuhammad Nasir KhanNo ratings yet