Professional Documents
Culture Documents
12 - Page 58 PDF
12 - Page 58 PDF
Uploaded by
vik03223Original Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
12 - Page 58 PDF
12 - Page 58 PDF
Uploaded by
vik03223Copyright:
Available Formats
40
Mechanics of Materials
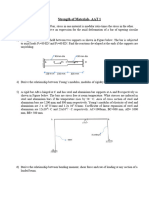
2 . 3 (A). What will be the stress induced in a steel bar when it is heated from 15C to W C , all expansion being prevented? For mild steel, E = 210 GN/mZ and a = 11 x per "C. [lo4 MN/m2".]
2.4 (A). A 75 mm diameter compound bar is constructed by shrinking a circular brass bush onto the outside of a 50 mm diameter solid steel rod. If the compound bar is then subjected to an axial compressive load of 160 kN
determine the load carried by the steel rod and the brass bush and the compressive stress set up in each material. For steel, E = 210 GN/m2; for brass, E = 100 GN/m*. [I. Struct. E.] c100.3, 59.7 kN; 51.1, 24.3 MN/mZ.]
2.5 (B). A steel rod of cross-sectional area 600mm2 and a coaxial copper tube of cross-sectional area loo0 mm2 are firmly attached at their ends to form a compound bar. Determine the stress in the steel and in the copper when the temperature of the bar is raised by 80C and an axial tensile force of 60 kN is applied. For steel, E = 200 GN/m2 with a = 11 x per "C. For copper, E = 100 GN/m2 with a = 16.5 x per "C. [E.I.E.] C94.6, 3.3 MN/m2.]
2.6 (B). A stanchion is formed by buttwelding together four plates of steel to form a square tube of outside crosssection 200 mm x 200 mm. The constant metal thickness is 10 mm. The inside is then filled with concrete. (a) Determine the cross-sectional area of the steel and concrete (b) If E for steel is 200 GN/m2 and this value is twenty times that for the concrete find, when the stanchion carries a load of 368.8 kN, (i) The stress in the concrete (ii) The stress in the steel (iii) The amount the stanchion shortens over a length of 2m. [C.G.] [2, 40 MN/m2; 40 mm]
You might also like
- SOM - Fieldwork 02Document1 pageSOM - Fieldwork 02Alexander MugabeNo ratings yet
- 12 - Page 109 PDFDocument1 page12 - Page 109 PDFvik03223No ratings yet
- MOM Assignment IDocument3 pagesMOM Assignment IAll_regNo ratings yet
- Assignment 1D: by Er.A.P.S.ChadhaDocument14 pagesAssignment 1D: by Er.A.P.S.ChadhaMANISH SHUKLANo ratings yet
- Tutorial 1 Ecs208 - Basic Solid Mechanics Learning Outcome: Thickness 30mmDocument3 pagesTutorial 1 Ecs208 - Basic Solid Mechanics Learning Outcome: Thickness 30mmnurulselangorNo ratings yet
- Simple Stress and StrainDocument3 pagesSimple Stress and StrainManish KumarNo ratings yet
- Simple Stresses and Strains PDFDocument2 pagesSimple Stresses and Strains PDFSai Krishna SK100% (1)
- 7 - MOS-I Assignment QuestionsDocument5 pages7 - MOS-I Assignment QuestionsSrikant Potluri100% (1)
- SOMDocument14 pagesSOMAditya ojhaNo ratings yet
- Ae2203 Ut 2 QP (Set A)Document2 pagesAe2203 Ut 2 QP (Set A)Aravindan SivanandanNo ratings yet
- Som I Iat Ques 2019Document3 pagesSom I Iat Ques 2019Siva RamanNo ratings yet
- Assignment Strength of MaterialsDocument11 pagesAssignment Strength of MaterialsVinay Korukonda0% (1)
- Steel Connection - Tutorial 1Document3 pagesSteel Connection - Tutorial 1Abhishek GuptaNo ratings yet
- Statically Indeterminate MembersDocument7 pagesStatically Indeterminate MembersKhan ToothNo ratings yet
- Assignment 1Document4 pagesAssignment 1TanmayNo ratings yet
- CE8301-Strength of Materials IDocument4 pagesCE8301-Strength of Materials Isyed1188No ratings yet
- Som Prob SetDocument50 pagesSom Prob SetAnonymous mXicTi8hBNo ratings yet
- Robin in DuDocument8 pagesRobin in DuRobin George RejiNo ratings yet
- MOM2Tutorial 10-1Document3 pagesMOM2Tutorial 10-1Ishola mujeebNo ratings yet
- Solid MCQ - 2021 Part B and Part CDocument1 pageSolid MCQ - 2021 Part B and Part Cmithunarjun10108No ratings yet
- Advanced Manufacturing ScienceDocument3 pagesAdvanced Manufacturing Sciencemukesh3021No ratings yet
- QuestionsDocument5 pagesQuestionsAli KasimNo ratings yet
- Department of Mechanical Engineering, MMMUT Gorakhpur BME-14 Mechanics of Solids: Tutorial-4Document3 pagesDepartment of Mechanical Engineering, MMMUT Gorakhpur BME-14 Mechanics of Solids: Tutorial-4abhishek.g.770306No ratings yet
- Tutorial 3Document1 pageTutorial 3SARVAYESWARAN L MX-llNo ratings yet
- Ce 2306 - Design of RC ElementsDocument4 pagesCe 2306 - Design of RC ElementsVincent VivekNo ratings yet
- 9A01401 Strength of Materials - IIDocument4 pages9A01401 Strength of Materials - IIsivabharathamurthyNo ratings yet
- EMG 4103 SOLID AND STRUCTURAL MECHANICS III EXAM (Revised) - PrintreadyDocument4 pagesEMG 4103 SOLID AND STRUCTURAL MECHANICS III EXAM (Revised) - PrintreadyDuncoh DunNo ratings yet
- 9A01301 Mechanics of SolidsDocument4 pages9A01301 Mechanics of SolidssivabharathamurthyNo ratings yet
- Strength of MaterialsDocument6 pagesStrength of MaterialsRafael Santos100% (1)
- Assignment No 1 MD-1..Document3 pagesAssignment No 1 MD-1..Yadnyesh TaNo ratings yet
- Thermal ProblemsDocument2 pagesThermal Problemsحسين علي صبيحNo ratings yet
- CE 6306 / Strength of Materials Mechanical Engineering 2016-17Document6 pagesCE 6306 / Strength of Materials Mechanical Engineering 2016-17amdevaNo ratings yet
- Mechanics of SolidsDocument8 pagesMechanics of SolidsKhaista RahmanNo ratings yet
- Statically Indeterminate MembersDocument8 pagesStatically Indeterminate MembersMo De la RosaNo ratings yet
- Strength of Materials-Homework2Document2 pagesStrength of Materials-Homework2durasteelNo ratings yet
- Mechanics of Solids (CIE 1051) (Makeup)Document5 pagesMechanics of Solids (CIE 1051) (Makeup)Alok KumarNo ratings yet
- FDB ActivityDocument2 pagesFDB ActivityAndrea RowellaNo ratings yet
- PropertiesDocument6 pagesPropertiesmarkalvinbonNo ratings yet
- Prob SheetDocument20 pagesProb SheetAditya ShuklaNo ratings yet
- Note Chapt IIDocument27 pagesNote Chapt IIRitesh KishoreNo ratings yet
- Lovelyprofessional University: Tutorial - Bars of Varying Cross Section SOM MEC040 Time Required: 60 MinutesDocument6 pagesLovelyprofessional University: Tutorial - Bars of Varying Cross Section SOM MEC040 Time Required: 60 MinutesmanishtopsecretsNo ratings yet
- RCD Assignment 1Document5 pagesRCD Assignment 1Ceyn Lumabad0% (1)
- Mar - 19 To 25Document19 pagesMar - 19 To 25betvwyNo ratings yet
- Mechanics of Materials 1 PDFDocument2 pagesMechanics of Materials 1 PDFEj ApeloNo ratings yet
- 9A01601 Design & Drawing of Steel StructuresDocument5 pages9A01601 Design & Drawing of Steel StructuressivabharathamurthyNo ratings yet
- 4 ME Som Model Examination 2013Document3 pages4 ME Som Model Examination 2013BIBIN CHIDAMBARANATHANNo ratings yet
- Worked Solution To Various QuestionsDocument29 pagesWorked Solution To Various QuestionsJohn MutumaNo ratings yet
- Assignment 1Document2 pagesAssignment 1Sahil GaudeNo ratings yet
- 2020 Dec. CE401-EDocument3 pages2020 Dec. CE401-EAKHIL.S1822 CE A 18-22No ratings yet
- Problem Set 2Document4 pagesProblem Set 2anonymouscheNo ratings yet
- Compound Bars: 6.5 MN/m2 (Compressive)Document1 pageCompound Bars: 6.5 MN/m2 (Compressive)vik03223No ratings yet
- Ce6306 16Document3 pagesCe6306 16Arul JONo ratings yet
- QbankDocument8 pagesQbanknkchandruNo ratings yet
- Aat 1Document4 pagesAat 1HARNITH EVILLNo ratings yet
- Sexton's Pocket-Book for Boiler-Makers and Steam Users: Comprising a Variety of Useful Information for Employer and Workmen, Government Inspectors, Board of Trade Surveyors, Engineers in Charge of Works and Ships, Foreman of Manufactories, and the General Steam-Using PublicFrom EverandSexton's Pocket-Book for Boiler-Makers and Steam Users: Comprising a Variety of Useful Information for Employer and Workmen, Government Inspectors, Board of Trade Surveyors, Engineers in Charge of Works and Ships, Foreman of Manufactories, and the General Steam-Using PublicNo ratings yet
- XXth Century Sheet Metal Worker - A Modern Treatise on Modern Sheet Metal WorkFrom EverandXXth Century Sheet Metal Worker - A Modern Treatise on Modern Sheet Metal WorkNo ratings yet
- Composite Structures of Steel and Concrete: Beams, Slabs, Columns and Frames for BuildingsFrom EverandComposite Structures of Steel and Concrete: Beams, Slabs, Columns and Frames for BuildingsNo ratings yet
- A Guide to Some of the Equations used in Constructing a Suspension BridgeFrom EverandA Guide to Some of the Equations used in Constructing a Suspension BridgeNo ratings yet
- D2y dx2 Dy: Mechanics of MaterialsDocument1 pageD2y dx2 Dy: Mechanics of Materialsvik03223No ratings yet
- Slope and Dejection Of: X X X Dy DX X Dy DXDocument1 pageSlope and Dejection Of: X X X Dy DX X Dy DXvik03223No ratings yet
- Slope and Defection of Beams: KN 2 0 K N KNDocument1 pageSlope and Defection of Beams: KN 2 0 K N KNvik03223No ratings yet
- D 2 y M - EX: Slope and Dejection of BeamsDocument1 pageD 2 y M - EX: Slope and Dejection of Beamsvik03223No ratings yet
- 12 - Page 140 PDFDocument1 page12 - Page 140 PDFvik03223No ratings yet
- 12 - Page 138 PDFDocument1 page12 - Page 138 PDFvik03223No ratings yet
- 12 - Page 136 PDFDocument1 page12 - Page 136 PDFvik03223No ratings yet
- Mechanics of Materials: or orDocument1 pageMechanics of Materials: or orvik03223No ratings yet
- 116 Mechanics Materials g5.11Document1 page116 Mechanics Materials g5.11vik03223No ratings yet
- Mechanics: 5.8. Principle of SuperpositionDocument1 pageMechanics: 5.8. Principle of Superpositionvik03223No ratings yet
- 5.7 Slope and Deflection of Beams: (C) Simply Supported Beam With U.D.LDocument1 page5.7 Slope and Deflection of Beams: (C) Simply Supported Beam With U.D.Lvik03223No ratings yet
- Slope and Defection of Beams: Fig. 5.24. Maxwell's Theorem of Reciprocal DisplacementsDocument1 pageSlope and Defection of Beams: Fig. 5.24. Maxwell's Theorem of Reciprocal Displacementsvik03223No ratings yet
- Fig. 4.14. Eccentric Loading of Rectangular Sections-"Middle Third"Document1 pageFig. 4.14. Eccentric Loading of Rectangular Sections-"Middle Third"vik03223No ratings yet
- 12 - Page 137 PDFDocument1 page12 - Page 137 PDFvik03223No ratings yet
- Mechanics Materials Solution: X X X X XDocument1 pageMechanics Materials Solution: X X X X Xvik03223No ratings yet
- Mechanics of Materials: ProblemsDocument1 pageMechanics of Materials: Problemsvik03223No ratings yet
- 5.7. Mohr's "Area-Moment" Method: B.M. DiagramDocument1 page5.7. Mohr's "Area-Moment" Method: B.M. Diagramvik03223No ratings yet
- Slope Deflection of Beams: (A) Deflection Positive UpwardsDocument1 pageSlope Deflection of Beams: (A) Deflection Positive Upwardsvik03223No ratings yet
- 12 - Page 96 PDFDocument1 page12 - Page 96 PDFvik03223No ratings yet
- 12 - Page 128 PDFDocument1 page12 - Page 128 PDFvik03223No ratings yet
- Lo6 Io: Mechanics of MaterialsDocument1 pageLo6 Io: Mechanics of Materialsvik03223No ratings yet
- 12 - Page 122 PDFDocument1 page12 - Page 122 PDFvik03223No ratings yet
- Slope Deflection of Beams: y (Or Dy DX D 2 y EI dx2 D 3 y EI-dx3 D4y EI - dx4Document1 pageSlope Deflection of Beams: y (Or Dy DX D 2 y EI dx2 D 3 y EI-dx3 D4y EI - dx4vik03223No ratings yet
- 12 - Page 125Document1 page12 - Page 125vik03223No ratings yet
- 12 - Page 109 PDFDocument1 page12 - Page 109 PDFvik03223No ratings yet
- 5.1 Continuous Beams-Clapeyron's "Three-Moment" Equation: Slope and Deflection BeamsDocument1 page5.1 Continuous Beams-Clapeyron's "Three-Moment" Equation: Slope and Deflection Beamsvik03223No ratings yet
- Sbpe Ot: A Wirh Moment WithDocument1 pageSbpe Ot: A Wirh Moment Withvik03223No ratings yet
- Slope Deflection Beams 6 A% L: and ofDocument1 pageSlope Deflection Beams 6 A% L: and ofvik03223No ratings yet
- Mechanics of Materials (D) Simply Supported Beam Central Concentrated LoadDocument1 pageMechanics of Materials (D) Simply Supported Beam Central Concentrated Loadvik03223No ratings yet
- 85.1 Slope and Deflection of Beams 6x: l/EZ 1/EZDocument1 page85.1 Slope and Deflection of Beams 6x: l/EZ 1/EZvik03223No ratings yet