Professional Documents
Culture Documents
LP Ni Lhen
LP Ni Lhen
Uploaded by
api-248948961Copyright:
Available Formats
You might also like
- Lab Report Plant TissuesDocument8 pagesLab Report Plant TissuesMOHD MU'IZZ BIN MOHD SHUKRI100% (6)
- Science-4 Q2 Week-3Document8 pagesScience-4 Q2 Week-3Jhon Mark BalansagNo ratings yet
- Daily Lesson Plan SCIENCE 4 WEEK 3Document24 pagesDaily Lesson Plan SCIENCE 4 WEEK 3Carol Gelbolingo100% (2)
- Industrial Training Handbook USIMDocument10 pagesIndustrial Training Handbook USIMmasyieraziNo ratings yet
- Gilmore - 2007-Authentic Materials and Authenticity in Foreign Language LearningDocument23 pagesGilmore - 2007-Authentic Materials and Authenticity in Foreign Language LearningDao Mai Phuong100% (1)
- Arendt - Thinking and Moral ConsiderationDocument31 pagesArendt - Thinking and Moral ConsiderationBen SeftonNo ratings yet
- Math9 Q1 M6 FinalDocument15 pagesMath9 Q1 M6 FinalRachelleNo ratings yet
- Q2W4 ScienceDocument4 pagesQ2W4 ScienceJj MendozaNo ratings yet
- SCIENCEDocument10 pagesSCIENCESomen SahaNo ratings yet
- Plant Parts and Its Function: Module 1 For CollegeDocument9 pagesPlant Parts and Its Function: Module 1 For CollegeYan DechosNo ratings yet
- Lab Rep 3Document19 pagesLab Rep 3Reign RosadaNo ratings yet
- Quisao Lab Act 4Document3 pagesQuisao Lab Act 4PaulNo ratings yet
- Activity Sheet 1 GenBio2Document4 pagesActivity Sheet 1 GenBio2Sean MatuguinasNo ratings yet
- Exploring Plant Reproduction and Seed Dispersal - Grade 9Document8 pagesExploring Plant Reproduction and Seed Dispersal - Grade 9DiakogeorgiouSavvas0% (1)
- Grade 6 - SSES - Science - Q2 - Wk5 - GLAKDocument20 pagesGrade 6 - SSES - Science - Q2 - Wk5 - GLAKMelanie TrinidadNo ratings yet
- STD 6 Getting To Know PlantsDocument5 pagesSTD 6 Getting To Know PlantsHIRAL SOLANKINo ratings yet
- Morphology of Flowering PlantsDocument29 pagesMorphology of Flowering PlantssaleemNo ratings yet
- Root - LPDocument4 pagesRoot - LPNicole CaraitNo ratings yet
- Biology Plant Morphology 1 MobileDocument15 pagesBiology Plant Morphology 1 Mobilevishnuvaradan3No ratings yet
- 03 Stems ScriptDocument10 pages03 Stems Scriptasmeraamde21No ratings yet
- Lesson Plan Morphology of Flowering PlantsDocument12 pagesLesson Plan Morphology of Flowering PlantsSHILPA AGARWAL100% (1)
- Activity 5 Type of Root System Preiy Julian M. de GuiaDocument4 pagesActivity 5 Type of Root System Preiy Julian M. de GuiaPreiy Julian De GuiaNo ratings yet
- Morphology of PlantsDocument58 pagesMorphology of PlantsRishikesh PandeyNo ratings yet
- Plants and Seeds: A 1st Grade Unit On Plants, Seeds, and How They Survive and GrowDocument8 pagesPlants and Seeds: A 1st Grade Unit On Plants, Seeds, and How They Survive and Growapi-337085136No ratings yet
- Villanueva - Bot01 Lab Act #4Document14 pagesVillanueva - Bot01 Lab Act #4Kath ErineNo ratings yet
- Morphology of Flowering Plants Class 11 Notes CBSE Biology Chapter 5 (PDF)Document29 pagesMorphology of Flowering Plants Class 11 Notes CBSE Biology Chapter 5 (PDF)pranjalutherNo ratings yet
- Plant Classification and IdentificationDocument5 pagesPlant Classification and IdentificationgeraintNo ratings yet
- k12 Bio1 Exer6 RootsDocument3 pagesk12 Bio1 Exer6 RootsJohn Matthew Jobo100% (1)
- Q2 G5 Science M2Document33 pagesQ2 G5 Science M2Maricar AtienzaNo ratings yet
- Lecture 10 Parts of A PlantDocument6 pagesLecture 10 Parts of A PlantkedeshiaNo ratings yet
- BIOLO001plants Parts and Function EditedDocument18 pagesBIOLO001plants Parts and Function EditedChristine angel mae BalsomoNo ratings yet
- Inter-material-Istyearem-botany-unit II Morphology of Flowering Plants 5Document18 pagesInter-material-Istyearem-botany-unit II Morphology of Flowering Plants 5shashinetharapolu2925No ratings yet
- Science5 q2 Mod4 TheReproductivePartsInPlantsAndTheirFunctions v2Document19 pagesScience5 q2 Mod4 TheReproductivePartsInPlantsAndTheirFunctions v2Sharen limNo ratings yet
- Lesson Plan Roots and StemsDocument5 pagesLesson Plan Roots and Stemsapi-548717522No ratings yet
- Second Form COVER PAGE WEEK 5-6Document14 pagesSecond Form COVER PAGE WEEK 5-6Antonio PechNo ratings yet
- Getting To Know Plants (G6) : Handout I. Short Answer QuestionsDocument4 pagesGetting To Know Plants (G6) : Handout I. Short Answer Questionsdon shiphrahNo ratings yet
- Getting To Know Plants (G6) : Handout I. Short Answer QuestionsDocument4 pagesGetting To Know Plants (G6) : Handout I. Short Answer Questionsdon shiphrahNo ratings yet
- Science B. G8 3rdDocument16 pagesScience B. G8 3rdBen sik ali mohamedNo ratings yet
- Lesson 27 Terrestrial PlantsDocument3 pagesLesson 27 Terrestrial PlantsMaricel Cebrero Santiago100% (4)
- CSO Olympiad Book For Class 4Document17 pagesCSO Olympiad Book For Class 4Aswani PokuriNo ratings yet
- 3 13+seed+dispersalDocument4 pages3 13+seed+dispersaltharangaNo ratings yet
- The Leaf: Short Notes Class 6 ScienceDocument4 pagesThe Leaf: Short Notes Class 6 ScienceParimala DhanasekaranNo ratings yet
- Botany RootsDocument49 pagesBotany Rootsartadiel28No ratings yet
- Darlene Krizian G. Dayuha A8A56: Bio100 - General BotanyDocument2 pagesDarlene Krizian G. Dayuha A8A56: Bio100 - General BotanyDarlene KrizianNo ratings yet
- Activity No. 5: Answers in Red ColorDocument9 pagesActivity No. 5: Answers in Red Colormasor100% (1)
- Phytography:RootDocument10 pagesPhytography:RootCarl Buscato100% (1)
- Science lp5 Day 50Document2 pagesScience lp5 Day 50RichardDumlaoNo ratings yet
- Lecture 21 The Stem (Primary Structure of Flowering Plant Body)Document9 pagesLecture 21 The Stem (Primary Structure of Flowering Plant Body)maheen akramNo ratings yet
- Morphology of Flowering Plants: The RootDocument14 pagesMorphology of Flowering Plants: The RootbOKALNo ratings yet
- Subject-Biology Chapter - 5 Morphology of Flowering PlantsDocument35 pagesSubject-Biology Chapter - 5 Morphology of Flowering PlantsNikunj kumar chaurasiyaNo ratings yet
- Lesson 1 Teachers PlanDocument1 pageLesson 1 Teachers PlanHolly WestNo ratings yet
- Earth and Life Science - G11 - John Mark de SagunDocument48 pagesEarth and Life Science - G11 - John Mark de SagunsailorNo ratings yet
- Botany 101Document7 pagesBotany 101Gladdin ChloeNo ratings yet
- Lesson Plan Roots and StemsDocument5 pagesLesson Plan Roots and Stemsapi-548691094No ratings yet
- 03-Flowering PlantsDocument45 pages03-Flowering PlantsMaku MichaelNo ratings yet
- Plant Parts: Purpose Background InformationDocument6 pagesPlant Parts: Purpose Background InformationSasmita NayakNo ratings yet
- Plant Parts: Purpose Background InformationDocument6 pagesPlant Parts: Purpose Background InformationJosiah Christian De BienNo ratings yet
- BIO 204 - L - SIM - ULOeDocument13 pagesBIO 204 - L - SIM - ULOeNickylla Bacaro PinoNo ratings yet
- Plant Anatomy: Angiosperm CategoriesDocument5 pagesPlant Anatomy: Angiosperm CategoriesRizka Apriliana KumalasariNo ratings yet
- I. Objectives:: 4. Appreciate The Purpose and Importance of ClassificationDocument7 pagesI. Objectives:: 4. Appreciate The Purpose and Importance of ClassificationBethymay EspinosaNo ratings yet
- LP Science2 q2w5Document7 pagesLP Science2 q2w5Gaila Mae Abejuela SanorjoNo ratings yet
- Plant Physiology PPT 9Document53 pagesPlant Physiology PPT 9sargonsielaNo ratings yet
- How Plants Grow - With Information on the Biology of Plant Cells, Roots, Leaves and FlowersFrom EverandHow Plants Grow - With Information on the Biology of Plant Cells, Roots, Leaves and FlowersNo ratings yet
- 2012KGSP Final)Document35 pages2012KGSP Final)Mainul Islam AamitNo ratings yet
- LESSON PLAN Cls 11 Imbunatatit 2Document10 pagesLESSON PLAN Cls 11 Imbunatatit 2Roxana NeleapcaNo ratings yet
- ESU Mauritius Newsletter December 2013Document550 pagesESU Mauritius Newsletter December 2013Ashesh RamjeeawonNo ratings yet
- AMH2010 Fall 2014 MWFDocument7 pagesAMH2010 Fall 2014 MWFSfagDagadgadNo ratings yet
- Xavier Alumni Times - August 2013Document28 pagesXavier Alumni Times - August 2013Martin GomezNo ratings yet
- Maximilianus Rafael Sutoyo - CV (OCT 2019)Document2 pagesMaximilianus Rafael Sutoyo - CV (OCT 2019)Rafael SutoyoNo ratings yet
- 2022 2023 - RPMS Portfolio Template G4Document38 pages2022 2023 - RPMS Portfolio Template G4Perla PortugalNo ratings yet
- Quick Guide For Competence AssessmentsDocument7 pagesQuick Guide For Competence AssessmentsHussain AbazeedNo ratings yet
- Ecs 595b Topic 3 DQ 1Document3 pagesEcs 595b Topic 3 DQ 1Hamna MushtaqNo ratings yet
- Matsui Jurina Long Interview - Entame Magazine (Released End of March 2012) .Document4 pagesMatsui Jurina Long Interview - Entame Magazine (Released End of March 2012) .Claudia Eunike LangiNo ratings yet
- Symposium Newsletter - Project RISHIDocument2 pagesSymposium Newsletter - Project RISHIProjectRISHINo ratings yet
- Book Notes A Mind For NumbersDocument5 pagesBook Notes A Mind For NumbersBenico van der Westhuizen100% (4)
- Problem Center DesignDocument13 pagesProblem Center Designاحمد رجبNo ratings yet
- 3 Domains of LearningDocument6 pages3 Domains of LearningRose Marie HermosaNo ratings yet
- Block-4 MS-91 Unit-4 PDFDocument24 pagesBlock-4 MS-91 Unit-4 PDFAnonymous P1xUTHstHTNo ratings yet
- Pedagogy MCQs PDF BookDocument91 pagesPedagogy MCQs PDF BookWasim khan100% (3)
- Action Research Proposal of Tle GroupDocument5 pagesAction Research Proposal of Tle GroupEnelra Recamara AzaurNo ratings yet
- NUM Survival Guide 2013-2014 PDFDocument56 pagesNUM Survival Guide 2013-2014 PDFPeterNo ratings yet
- Katie Miller TCNJ ResumeDocument3 pagesKatie Miller TCNJ Resumeapi-284814564No ratings yet
- Civl4403 UWA Unit OutlineDocument2 pagesCivl4403 UWA Unit OutlineSuman SahaNo ratings yet
- 1 Bell Hooks Critical ThinkingDocument5 pages1 Bell Hooks Critical ThinkingStephanie Camille SobremesanaNo ratings yet
- 2020 Book EmpoweringTeachersToBuildABett PDFDocument140 pages2020 Book EmpoweringTeachersToBuildABett PDFyejjey14No ratings yet
- Lesson 1: Who Is Trainer And/or Assessor?: ObjectivesDocument9 pagesLesson 1: Who Is Trainer And/or Assessor?: ObjectivesJerome LumapagNo ratings yet
- INTJ CareersDocument2 pagesINTJ CareersPaul OleaNo ratings yet
- Components of Special and Inclusive EducationDocument33 pagesComponents of Special and Inclusive EducationJohn Lorenz MacalinaoNo ratings yet
- English Exam Paper Paper Doc YEAR 3 TESTDocument8 pagesEnglish Exam Paper Paper Doc YEAR 3 TESTN.AqilahNo ratings yet
LP Ni Lhen
LP Ni Lhen
Uploaded by
api-248948961Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
LP Ni Lhen
LP Ni Lhen
Uploaded by
api-248948961Copyright:
Available Formats
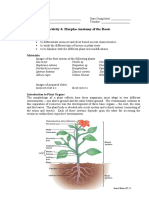
Republic of the Philippines SORSOGON STATE COLLEGE- Castilla Campus Mayon, Castilla, Sorsogon Lesson Plan in Vocational Agriculture
I- Objectives At the end of the lesson the pupils should be able to: 1. Define roots and its parts; 2. Identify the different root types; 3. Classify root types from varied plant species; and 4. Realize the importance of roots in the growth of plants. II- Subject Matter: Morphology of Roots Reference/s: Simpson, Micheal G. . 2010. Plants Systematics. 2nd edition. ELSEVIER Inc. , USA. Materials: Meta cards, illustrations, hand outs III- Procedure A. Preliminaries 1. Prayer 2. Greetings and introductory message 3. Review of the previous lesson B. Motivation Word Hunt C. Lesson Proper Teachers Activity Based from the activity that we did, what do you think is our lesson today? Define roots.
Students Activity Morphology of roots Roots are plant organ that function in anchorage and in absorption of water and minerals
Teacher Activity Let us have an activity. Group yourselves into five. I have here meta cards and posted on the board are the definition of the word written on the meta cards. After 10 minutes, present your works by posting the meta cards beside the definition of the word.
Do you have questions? If none, lets proceed to the roots types. Let us have another activity. Same group will do. You are to define the words posted on the board by selecting on the table the appropriate definition.
Students Activity Presentation of each group. Root hairs- epidermal cells away from root tip develop hair- like extensions which increases the surface area available for water and mineral absorption. Pericycle- lateral roots developed by cell division within it. A cylindrical layer of parenchyma cells located just inside the endodermis itself. Radicle- first root to develop in a vascular plant. Primary root- when radical continues to develop after embryo growth. Lateral roots- roots which arise from other roots. Adventitious roots- roots arise from a nonroot organ (stem or leaf) (presentation) If the primary becomes dominant- tap root. Plants are describe if they have or has tap root- tap root system Biennial plants have this type of roots which tap root has become greatly thickened, accumulating reservoir of high energy storage compounds (usually starch)- Storage roots Ephiphytic plkants has this root type wherein adventitious roots generally do not enter the soil and may absorb water and minerals from air or run- off from plants- Aerial roots Bulbs and corms has this roots that contract vertically functioning to pull the root stock further into the soil.- contractile roots A parasitic plant specialized roots, penetrating the tissues of a host plantshausteria Adventitious roots grow from the base of the stem and function to further support the plant- prop roots Some swamps/ marshes has this roots that grow upwardly from soil to air that function to obtain additional oxygen-
pneumatophores Enlarged, horizontally spreading and often vertically thickened roots at the base of trees that aid in mechanical support; found in certain tropical or marsh/ swamp trees species Any other question? If none, that ends our lesson today.
IV-
V-
Evaluation Write in your own words the importance of roots in a plant and how it help the other parts of the plant like leaves, flowers, stem and fruits. Assignment Read and study about morphology of fruits.
Prepared by MENDEZ, ROSELINE V. BSAD Ag.Ed. III
You might also like
- Lab Report Plant TissuesDocument8 pagesLab Report Plant TissuesMOHD MU'IZZ BIN MOHD SHUKRI100% (6)
- Science-4 Q2 Week-3Document8 pagesScience-4 Q2 Week-3Jhon Mark BalansagNo ratings yet
- Daily Lesson Plan SCIENCE 4 WEEK 3Document24 pagesDaily Lesson Plan SCIENCE 4 WEEK 3Carol Gelbolingo100% (2)
- Industrial Training Handbook USIMDocument10 pagesIndustrial Training Handbook USIMmasyieraziNo ratings yet
- Gilmore - 2007-Authentic Materials and Authenticity in Foreign Language LearningDocument23 pagesGilmore - 2007-Authentic Materials and Authenticity in Foreign Language LearningDao Mai Phuong100% (1)
- Arendt - Thinking and Moral ConsiderationDocument31 pagesArendt - Thinking and Moral ConsiderationBen SeftonNo ratings yet
- Math9 Q1 M6 FinalDocument15 pagesMath9 Q1 M6 FinalRachelleNo ratings yet
- Q2W4 ScienceDocument4 pagesQ2W4 ScienceJj MendozaNo ratings yet
- SCIENCEDocument10 pagesSCIENCESomen SahaNo ratings yet
- Plant Parts and Its Function: Module 1 For CollegeDocument9 pagesPlant Parts and Its Function: Module 1 For CollegeYan DechosNo ratings yet
- Lab Rep 3Document19 pagesLab Rep 3Reign RosadaNo ratings yet
- Quisao Lab Act 4Document3 pagesQuisao Lab Act 4PaulNo ratings yet
- Activity Sheet 1 GenBio2Document4 pagesActivity Sheet 1 GenBio2Sean MatuguinasNo ratings yet
- Exploring Plant Reproduction and Seed Dispersal - Grade 9Document8 pagesExploring Plant Reproduction and Seed Dispersal - Grade 9DiakogeorgiouSavvas0% (1)
- Grade 6 - SSES - Science - Q2 - Wk5 - GLAKDocument20 pagesGrade 6 - SSES - Science - Q2 - Wk5 - GLAKMelanie TrinidadNo ratings yet
- STD 6 Getting To Know PlantsDocument5 pagesSTD 6 Getting To Know PlantsHIRAL SOLANKINo ratings yet
- Morphology of Flowering PlantsDocument29 pagesMorphology of Flowering PlantssaleemNo ratings yet
- Root - LPDocument4 pagesRoot - LPNicole CaraitNo ratings yet
- Biology Plant Morphology 1 MobileDocument15 pagesBiology Plant Morphology 1 Mobilevishnuvaradan3No ratings yet
- 03 Stems ScriptDocument10 pages03 Stems Scriptasmeraamde21No ratings yet
- Lesson Plan Morphology of Flowering PlantsDocument12 pagesLesson Plan Morphology of Flowering PlantsSHILPA AGARWAL100% (1)
- Activity 5 Type of Root System Preiy Julian M. de GuiaDocument4 pagesActivity 5 Type of Root System Preiy Julian M. de GuiaPreiy Julian De GuiaNo ratings yet
- Morphology of PlantsDocument58 pagesMorphology of PlantsRishikesh PandeyNo ratings yet
- Plants and Seeds: A 1st Grade Unit On Plants, Seeds, and How They Survive and GrowDocument8 pagesPlants and Seeds: A 1st Grade Unit On Plants, Seeds, and How They Survive and Growapi-337085136No ratings yet
- Villanueva - Bot01 Lab Act #4Document14 pagesVillanueva - Bot01 Lab Act #4Kath ErineNo ratings yet
- Morphology of Flowering Plants Class 11 Notes CBSE Biology Chapter 5 (PDF)Document29 pagesMorphology of Flowering Plants Class 11 Notes CBSE Biology Chapter 5 (PDF)pranjalutherNo ratings yet
- Plant Classification and IdentificationDocument5 pagesPlant Classification and IdentificationgeraintNo ratings yet
- k12 Bio1 Exer6 RootsDocument3 pagesk12 Bio1 Exer6 RootsJohn Matthew Jobo100% (1)
- Q2 G5 Science M2Document33 pagesQ2 G5 Science M2Maricar AtienzaNo ratings yet
- Lecture 10 Parts of A PlantDocument6 pagesLecture 10 Parts of A PlantkedeshiaNo ratings yet
- BIOLO001plants Parts and Function EditedDocument18 pagesBIOLO001plants Parts and Function EditedChristine angel mae BalsomoNo ratings yet
- Inter-material-Istyearem-botany-unit II Morphology of Flowering Plants 5Document18 pagesInter-material-Istyearem-botany-unit II Morphology of Flowering Plants 5shashinetharapolu2925No ratings yet
- Science5 q2 Mod4 TheReproductivePartsInPlantsAndTheirFunctions v2Document19 pagesScience5 q2 Mod4 TheReproductivePartsInPlantsAndTheirFunctions v2Sharen limNo ratings yet
- Lesson Plan Roots and StemsDocument5 pagesLesson Plan Roots and Stemsapi-548717522No ratings yet
- Second Form COVER PAGE WEEK 5-6Document14 pagesSecond Form COVER PAGE WEEK 5-6Antonio PechNo ratings yet
- Getting To Know Plants (G6) : Handout I. Short Answer QuestionsDocument4 pagesGetting To Know Plants (G6) : Handout I. Short Answer Questionsdon shiphrahNo ratings yet
- Getting To Know Plants (G6) : Handout I. Short Answer QuestionsDocument4 pagesGetting To Know Plants (G6) : Handout I. Short Answer Questionsdon shiphrahNo ratings yet
- Science B. G8 3rdDocument16 pagesScience B. G8 3rdBen sik ali mohamedNo ratings yet
- Lesson 27 Terrestrial PlantsDocument3 pagesLesson 27 Terrestrial PlantsMaricel Cebrero Santiago100% (4)
- CSO Olympiad Book For Class 4Document17 pagesCSO Olympiad Book For Class 4Aswani PokuriNo ratings yet
- 3 13+seed+dispersalDocument4 pages3 13+seed+dispersaltharangaNo ratings yet
- The Leaf: Short Notes Class 6 ScienceDocument4 pagesThe Leaf: Short Notes Class 6 ScienceParimala DhanasekaranNo ratings yet
- Botany RootsDocument49 pagesBotany Rootsartadiel28No ratings yet
- Darlene Krizian G. Dayuha A8A56: Bio100 - General BotanyDocument2 pagesDarlene Krizian G. Dayuha A8A56: Bio100 - General BotanyDarlene KrizianNo ratings yet
- Activity No. 5: Answers in Red ColorDocument9 pagesActivity No. 5: Answers in Red Colormasor100% (1)
- Phytography:RootDocument10 pagesPhytography:RootCarl Buscato100% (1)
- Science lp5 Day 50Document2 pagesScience lp5 Day 50RichardDumlaoNo ratings yet
- Lecture 21 The Stem (Primary Structure of Flowering Plant Body)Document9 pagesLecture 21 The Stem (Primary Structure of Flowering Plant Body)maheen akramNo ratings yet
- Morphology of Flowering Plants: The RootDocument14 pagesMorphology of Flowering Plants: The RootbOKALNo ratings yet
- Subject-Biology Chapter - 5 Morphology of Flowering PlantsDocument35 pagesSubject-Biology Chapter - 5 Morphology of Flowering PlantsNikunj kumar chaurasiyaNo ratings yet
- Lesson 1 Teachers PlanDocument1 pageLesson 1 Teachers PlanHolly WestNo ratings yet
- Earth and Life Science - G11 - John Mark de SagunDocument48 pagesEarth and Life Science - G11 - John Mark de SagunsailorNo ratings yet
- Botany 101Document7 pagesBotany 101Gladdin ChloeNo ratings yet
- Lesson Plan Roots and StemsDocument5 pagesLesson Plan Roots and Stemsapi-548691094No ratings yet
- 03-Flowering PlantsDocument45 pages03-Flowering PlantsMaku MichaelNo ratings yet
- Plant Parts: Purpose Background InformationDocument6 pagesPlant Parts: Purpose Background InformationSasmita NayakNo ratings yet
- Plant Parts: Purpose Background InformationDocument6 pagesPlant Parts: Purpose Background InformationJosiah Christian De BienNo ratings yet
- BIO 204 - L - SIM - ULOeDocument13 pagesBIO 204 - L - SIM - ULOeNickylla Bacaro PinoNo ratings yet
- Plant Anatomy: Angiosperm CategoriesDocument5 pagesPlant Anatomy: Angiosperm CategoriesRizka Apriliana KumalasariNo ratings yet
- I. Objectives:: 4. Appreciate The Purpose and Importance of ClassificationDocument7 pagesI. Objectives:: 4. Appreciate The Purpose and Importance of ClassificationBethymay EspinosaNo ratings yet
- LP Science2 q2w5Document7 pagesLP Science2 q2w5Gaila Mae Abejuela SanorjoNo ratings yet
- Plant Physiology PPT 9Document53 pagesPlant Physiology PPT 9sargonsielaNo ratings yet
- How Plants Grow - With Information on the Biology of Plant Cells, Roots, Leaves and FlowersFrom EverandHow Plants Grow - With Information on the Biology of Plant Cells, Roots, Leaves and FlowersNo ratings yet
- 2012KGSP Final)Document35 pages2012KGSP Final)Mainul Islam AamitNo ratings yet
- LESSON PLAN Cls 11 Imbunatatit 2Document10 pagesLESSON PLAN Cls 11 Imbunatatit 2Roxana NeleapcaNo ratings yet
- ESU Mauritius Newsletter December 2013Document550 pagesESU Mauritius Newsletter December 2013Ashesh RamjeeawonNo ratings yet
- AMH2010 Fall 2014 MWFDocument7 pagesAMH2010 Fall 2014 MWFSfagDagadgadNo ratings yet
- Xavier Alumni Times - August 2013Document28 pagesXavier Alumni Times - August 2013Martin GomezNo ratings yet
- Maximilianus Rafael Sutoyo - CV (OCT 2019)Document2 pagesMaximilianus Rafael Sutoyo - CV (OCT 2019)Rafael SutoyoNo ratings yet
- 2022 2023 - RPMS Portfolio Template G4Document38 pages2022 2023 - RPMS Portfolio Template G4Perla PortugalNo ratings yet
- Quick Guide For Competence AssessmentsDocument7 pagesQuick Guide For Competence AssessmentsHussain AbazeedNo ratings yet
- Ecs 595b Topic 3 DQ 1Document3 pagesEcs 595b Topic 3 DQ 1Hamna MushtaqNo ratings yet
- Matsui Jurina Long Interview - Entame Magazine (Released End of March 2012) .Document4 pagesMatsui Jurina Long Interview - Entame Magazine (Released End of March 2012) .Claudia Eunike LangiNo ratings yet
- Symposium Newsletter - Project RISHIDocument2 pagesSymposium Newsletter - Project RISHIProjectRISHINo ratings yet
- Book Notes A Mind For NumbersDocument5 pagesBook Notes A Mind For NumbersBenico van der Westhuizen100% (4)
- Problem Center DesignDocument13 pagesProblem Center Designاحمد رجبNo ratings yet
- 3 Domains of LearningDocument6 pages3 Domains of LearningRose Marie HermosaNo ratings yet
- Block-4 MS-91 Unit-4 PDFDocument24 pagesBlock-4 MS-91 Unit-4 PDFAnonymous P1xUTHstHTNo ratings yet
- Pedagogy MCQs PDF BookDocument91 pagesPedagogy MCQs PDF BookWasim khan100% (3)
- Action Research Proposal of Tle GroupDocument5 pagesAction Research Proposal of Tle GroupEnelra Recamara AzaurNo ratings yet
- NUM Survival Guide 2013-2014 PDFDocument56 pagesNUM Survival Guide 2013-2014 PDFPeterNo ratings yet
- Katie Miller TCNJ ResumeDocument3 pagesKatie Miller TCNJ Resumeapi-284814564No ratings yet
- Civl4403 UWA Unit OutlineDocument2 pagesCivl4403 UWA Unit OutlineSuman SahaNo ratings yet
- 1 Bell Hooks Critical ThinkingDocument5 pages1 Bell Hooks Critical ThinkingStephanie Camille SobremesanaNo ratings yet
- 2020 Book EmpoweringTeachersToBuildABett PDFDocument140 pages2020 Book EmpoweringTeachersToBuildABett PDFyejjey14No ratings yet
- Lesson 1: Who Is Trainer And/or Assessor?: ObjectivesDocument9 pagesLesson 1: Who Is Trainer And/or Assessor?: ObjectivesJerome LumapagNo ratings yet
- INTJ CareersDocument2 pagesINTJ CareersPaul OleaNo ratings yet
- Components of Special and Inclusive EducationDocument33 pagesComponents of Special and Inclusive EducationJohn Lorenz MacalinaoNo ratings yet
- English Exam Paper Paper Doc YEAR 3 TESTDocument8 pagesEnglish Exam Paper Paper Doc YEAR 3 TESTN.AqilahNo ratings yet