Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Keystone Group of Institutions
Keystone Group of Institutions
Uploaded by
Bhupender SharmaCopyright:
Available Formats
You might also like
- Elastic Mechanics AssignmentsDocument8 pagesElastic Mechanics AssignmentsEng Bagaragaza Romuald100% (2)
- AMM Assignment 2Document2 pagesAMM Assignment 2Rino NelsonNo ratings yet
- Theory of Elasticity and StabilityDocument2 pagesTheory of Elasticity and StabilityAmit ThoriyaNo ratings yet
- Answer Any Five Questions.: U Kxy, V Kxy and W 2k (X +y) ZDocument2 pagesAnswer Any Five Questions.: U Kxy, V Kxy and W 2k (X +y) ZNitesh AgrawalNo ratings yet
- Analysis of Stress Tut 1Document2 pagesAnalysis of Stress Tut 1Himanshu KumarNo ratings yet
- Analysis of Stress Tut 1Document2 pagesAnalysis of Stress Tut 1Himanshu KumarNo ratings yet
- M.tech - PTPG - Theory of Elasticity Sep - 10Document1 pageM.tech - PTPG - Theory of Elasticity Sep - 10vempadareddyNo ratings yet
- Analysis of Stress Tut 1Document2 pagesAnalysis of Stress Tut 1Rahul PatraNo ratings yet
- 6-Transformation of Stress & Strain (Jan2013)Document49 pages6-Transformation of Stress & Strain (Jan2013)Mohammad HanafiNo ratings yet
- Theory of Structures IV Question PaperDocument2 pagesTheory of Structures IV Question PaperSourav SilNo ratings yet
- 2015 - 15CD 002 - Advanced Mechanics of Materials PIIDocument1 page2015 - 15CD 002 - Advanced Mechanics of Materials PIIselva_raj215414No ratings yet
- Theory of Elasticity and StabilityDocument2 pagesTheory of Elasticity and StabilityAmit ThoriyaNo ratings yet
- Advanced Mechanics of Solids - Question SetDocument3 pagesAdvanced Mechanics of Solids - Question SetAshish ZachariahNo ratings yet
- B. Tech Degree VI Semester Examination, March 2013.: X y Z Xy ZX YzDocument2 pagesB. Tech Degree VI Semester Examination, March 2013.: X y Z Xy ZX YzKiran ChristopherNo ratings yet
- Assignment 1 2023Document1 pageAssignment 1 2023shivam ojhaNo ratings yet
- Tutorial 1 - Theories of Stress and Strain-2011Document3 pagesTutorial 1 - Theories of Stress and Strain-2011Kiat HauNo ratings yet
- Strength of MaterialDocument80 pagesStrength of Materialpriyankar007No ratings yet
- Exam 04032021Document2 pagesExam 04032021Giannis MamalakisNo ratings yet
- Ae ZG614 Ec-2r First Sem 2022-2023Document3 pagesAe ZG614 Ec-2r First Sem 2022-2023deepakpushpadNo ratings yet
- Mechanics Prelim Doc ExamDocument11 pagesMechanics Prelim Doc ExamlolaNo ratings yet
- BFC 20903 (Mechanics of Materials) Chapter 2: Stress and Strain TransformationDocument27 pagesBFC 20903 (Mechanics of Materials) Chapter 2: Stress and Strain Transformationhamierul mohamadNo ratings yet
- Chapter 6 - COMPLEX STRESSDocument33 pagesChapter 6 - COMPLEX STRESSNurul Raihan Shahizan100% (1)
- Engineering Mechanics KCE 101 2018-19Document3 pagesEngineering Mechanics KCE 101 2018-19Tulsi ChouhanNo ratings yet
- PROB SET For Quiz 3: X Y XyDocument1 pagePROB SET For Quiz 3: X Y XyKaleenaSantosNo ratings yet
- Practise Problems Set02Document5 pagesPractise Problems Set02rohit kumarNo ratings yet
- MME2202 CourseReviewDocument5 pagesMME2202 CourseReviewMatt BrezinaNo ratings yet
- Plane Stress and Plane StrainDocument17 pagesPlane Stress and Plane StrainGiacNo ratings yet
- Machine DesignDocument69 pagesMachine DesignSushant TiwariNo ratings yet
- Static Equilibrium: M M M F F FDocument41 pagesStatic Equilibrium: M M M F F FINMENo ratings yet
- Exam 1 Meem 4150 Oct. 4Th, 2011Document2 pagesExam 1 Meem 4150 Oct. 4Th, 2011Rayleight SilversNo ratings yet
- Basics of Finite Element AnalysisDocument117 pagesBasics of Finite Element AnalysispgkaeroNo ratings yet
- ME 010 503 - AMM Model Question PaperDocument1 pageME 010 503 - AMM Model Question PaperJithin KNo ratings yet
- A Rectangular Steel Bar Having A CrossDocument2 pagesA Rectangular Steel Bar Having A CrossHitesh PrajapatNo ratings yet
- CE: 2051: Advanced Mechanics of Materials: SLIIT/Curtin: Civil Engineering: Year 2 Semester 2 Tutorial 9Document2 pagesCE: 2051: Advanced Mechanics of Materials: SLIIT/Curtin: Civil Engineering: Year 2 Semester 2 Tutorial 9Sayan KirinathanNo ratings yet
- Aerospace Engineering, IIT Kharagpur AE21004, Introduction To Aerospace Structures Exam Date: 15 April 2021 Time: 1.5 Hrs Full Marks: 30Document1 pageAerospace Engineering, IIT Kharagpur AE21004, Introduction To Aerospace Structures Exam Date: 15 April 2021 Time: 1.5 Hrs Full Marks: 30tushar kshirsagarNo ratings yet
- Statics NotesDocument8 pagesStatics NotesRyanCallejaNo ratings yet
- AMM Model QN PaperDocument2 pagesAMM Model QN PaperrpkayNo ratings yet
- Introduction of Solid Mechanics (ME 621) : Problem 1Document4 pagesIntroduction of Solid Mechanics (ME 621) : Problem 1Ritunjay JhaNo ratings yet
- + + 2 I+ 3 x+4 y J+ 2 X + 4 Z K: Analysis of Strain (Tutorial: 2)Document2 pages+ + 2 I+ 3 x+4 y J+ 2 X + 4 Z K: Analysis of Strain (Tutorial: 2)Himanshu KumarNo ratings yet
- Structural Mechanics Assignment HelpDocument29 pagesStructural Mechanics Assignment HelpMechanical Engineering Assignment HelpNo ratings yet
- Chapter 06bDocument17 pagesChapter 06bgioNo ratings yet
- Cochin University of Science and Technology B Tech Degree Iv Semester Examination SUBJECT: ME 403 Advanced Mechanics of Solids (2006)Document3 pagesCochin University of Science and Technology B Tech Degree Iv Semester Examination SUBJECT: ME 403 Advanced Mechanics of Solids (2006)Kiran ChristopherNo ratings yet
- Jest Physics Sample Question PaperDocument3 pagesJest Physics Sample Question PaperSreejith Nhaloor0% (1)
- 3D Stress and Strain Tutorial SheetDocument2 pages3D Stress and Strain Tutorial SheetTasmin Chandran0% (1)
- Elemento FinitoDocument12 pagesElemento FinitoPanchoMiyamotoNo ratings yet
- MD 2Document33 pagesMD 2Wilfredo Nieves OsoriaNo ratings yet
- 3 BalanceDocument7 pages3 BalanceSebastiao SilvaNo ratings yet
- Numerical Examples PDFDocument20 pagesNumerical Examples PDFHamid MasoodNo ratings yet
- Department of Mechanical Engineering: I I, I and The Three Principal StressesDocument1 pageDepartment of Mechanical Engineering: I I, I and The Three Principal StressesAshutosh SharmaNo ratings yet
- 3 Del As Ti CityDocument10 pages3 Del As Ti CityMohammad SalimuddinNo ratings yet
- Theory of Stress: Main PlayerDocument9 pagesTheory of Stress: Main Playerxaaabbb_550464353No ratings yet
- Fem Mid 1 Question BankDocument2 pagesFem Mid 1 Question BankallakagopichandNo ratings yet
- Civil Engineering Systems AnalysisDocument10 pagesCivil Engineering Systems AnalysisNikhil JohnNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3-Load and Stress AnalysisDocument60 pagesChapter 3-Load and Stress AnalysisNguyễnBảoKhánh100% (1)
- Practice Exam 3 KEY (Solutions)Document13 pagesPractice Exam 3 KEY (Solutions)joseNo ratings yet
- MCQ Failure TheoriesDocument46 pagesMCQ Failure TheoriesfdsfsdfsdfsfsNo ratings yet
- O level Physics Questions And Answer Practice Papers 2From EverandO level Physics Questions And Answer Practice Papers 2Rating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Theory of Elastisity, Stability and Dynamics of Structures Common ProblemsFrom EverandTheory of Elastisity, Stability and Dynamics of Structures Common ProblemsNo ratings yet
- Himgiri Zee University: Sub-Interview Call LetterDocument1 pageHimgiri Zee University: Sub-Interview Call LetterBhupender SharmaNo ratings yet
- Aravali College of Engineering and Management: Topic: Synonyms Year: 2 YearDocument3 pagesAravali College of Engineering and Management: Topic: Synonyms Year: 2 YearBhupender SharmaNo ratings yet
- MS - 1st TermDocument2 pagesMS - 1st TermBhupender SharmaNo ratings yet
- Effect On Density During TestDocument1 pageEffect On Density During TestBhupender SharmaNo ratings yet
- Keystone Group of Institutions: B.TECH. 8 Sem (Me) 1 Mid Term Exam 2014 Renewable Energy TechnologyDocument2 pagesKeystone Group of Institutions: B.TECH. 8 Sem (Me) 1 Mid Term Exam 2014 Renewable Energy TechnologyBhupender SharmaNo ratings yet
- Keystone Group of Institutions, PilodDocument2 pagesKeystone Group of Institutions, PilodBhupender SharmaNo ratings yet
- Assignment 2, NTMP'11Document2 pagesAssignment 2, NTMP'11Bhupender SharmaNo ratings yet
- Keystone Group of Institutions: Subject: Engineering ThermodynamicsDocument2 pagesKeystone Group of Institutions: Subject: Engineering ThermodynamicsBhupender SharmaNo ratings yet
- Keystone Group of Institutions Time-Table For Session 2013-2014 (Even Semester) Me (8Th Semester)Document3 pagesKeystone Group of Institutions Time-Table For Session 2013-2014 (Even Semester) Me (8Th Semester)Bhupender SharmaNo ratings yet
- Keystone Group of Institutions: Subject: CADDocument1 pageKeystone Group of Institutions: Subject: CADBhupender SharmaNo ratings yet
- Internal Lab Time Table: 29/11/2013 Auto Engg Lab M1 Morning Production Engg Lab M2 MorningDocument3 pagesInternal Lab Time Table: 29/11/2013 Auto Engg Lab M1 Morning Production Engg Lab M2 MorningBhupender SharmaNo ratings yet
- Time: 3 Hrs. Marks: 80: Keystone Grpup of Institutions Pre-University Test: ME (3 Sem) OopsDocument1 pageTime: 3 Hrs. Marks: 80: Keystone Grpup of Institutions Pre-University Test: ME (3 Sem) OopsBhupender SharmaNo ratings yet
- Keystone Group of Institutions Time-Table For Session 2013-2014 (Even Semester) Me (8Th Semester)Document10 pagesKeystone Group of Institutions Time-Table For Session 2013-2014 (Even Semester) Me (8Th Semester)Bhupender SharmaNo ratings yet
Keystone Group of Institutions
Keystone Group of Institutions
Uploaded by
Bhupender SharmaOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Keystone Group of Institutions
Keystone Group of Institutions
Uploaded by
Bhupender SharmaCopyright:
Available Formats
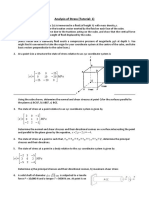
KEYSTONE GROUP OF INSTITUTIONS
B.TECH. 5th SEM (ME) 1st MID TERM EXAM 2013 ADVANCED MECHANICS OF SOLIDS Time: 2 Hrs Max. Marks: 20
Note: All questions are compulsory and carry 4 marks each.
Q.1: Choose the correct answer from the given choices. (A) Principal plane is the plane on which shear stress components are (a) Maximum (b) Minimum (c) Zero (d) 1
(B) Stress vector has (a) One normal and two shear components (b) Two normal and one shear component (c) One normal and one shear component (d) Two normal and two shear components (C) ..of material points before and after deformation is defined by displacement vector. (a) Stress (b) Position (c) Strain (d) Velocity
(D) Gravitational force is a (a) Shear Force (b) Surface Force (c) Impulse Force (d) Body Force Q.2: Derive Cauchys stress formula. OR Define state of strain at a point? Derive the deformation in the neighbourhood of a point. Q.3: What are rectangular stress components? Draw rectangular components for each plane. Also define body force and surface force. OR The following displacement field is imposed on a body
u=(xyi +3x2zj+4k)10-2
Consider a point P and a neighbouring point Q where PQ has the following direction cosines
nx= 0.200, ny=0.800, nz=0.555 Point P has coordinates (2,1,3). If PQ=s, find the components of PQ after deformation. Q.4: What is deviatoric state of stress? Decompose state of stress into hydrostatic and pure shear states. OR At a point P in a body, x=10000 N/cm2, y= -5000 N/cm2 , z= -5000 N/cm2, xy= yz= zx=10000 N/cm2. Determine the normal and shearing stresses on a plane that is equally inclined to all the three axes i.e. nx=ny=nz=1/3. Q5: What are compatibility conditions. Explain and derive the same. OR Derive the expression for the change of length of a linear element.
You might also like
- Elastic Mechanics AssignmentsDocument8 pagesElastic Mechanics AssignmentsEng Bagaragaza Romuald100% (2)
- AMM Assignment 2Document2 pagesAMM Assignment 2Rino NelsonNo ratings yet
- Theory of Elasticity and StabilityDocument2 pagesTheory of Elasticity and StabilityAmit ThoriyaNo ratings yet
- Answer Any Five Questions.: U Kxy, V Kxy and W 2k (X +y) ZDocument2 pagesAnswer Any Five Questions.: U Kxy, V Kxy and W 2k (X +y) ZNitesh AgrawalNo ratings yet
- Analysis of Stress Tut 1Document2 pagesAnalysis of Stress Tut 1Himanshu KumarNo ratings yet
- Analysis of Stress Tut 1Document2 pagesAnalysis of Stress Tut 1Himanshu KumarNo ratings yet
- M.tech - PTPG - Theory of Elasticity Sep - 10Document1 pageM.tech - PTPG - Theory of Elasticity Sep - 10vempadareddyNo ratings yet
- Analysis of Stress Tut 1Document2 pagesAnalysis of Stress Tut 1Rahul PatraNo ratings yet
- 6-Transformation of Stress & Strain (Jan2013)Document49 pages6-Transformation of Stress & Strain (Jan2013)Mohammad HanafiNo ratings yet
- Theory of Structures IV Question PaperDocument2 pagesTheory of Structures IV Question PaperSourav SilNo ratings yet
- 2015 - 15CD 002 - Advanced Mechanics of Materials PIIDocument1 page2015 - 15CD 002 - Advanced Mechanics of Materials PIIselva_raj215414No ratings yet
- Theory of Elasticity and StabilityDocument2 pagesTheory of Elasticity and StabilityAmit ThoriyaNo ratings yet
- Advanced Mechanics of Solids - Question SetDocument3 pagesAdvanced Mechanics of Solids - Question SetAshish ZachariahNo ratings yet
- B. Tech Degree VI Semester Examination, March 2013.: X y Z Xy ZX YzDocument2 pagesB. Tech Degree VI Semester Examination, March 2013.: X y Z Xy ZX YzKiran ChristopherNo ratings yet
- Assignment 1 2023Document1 pageAssignment 1 2023shivam ojhaNo ratings yet
- Tutorial 1 - Theories of Stress and Strain-2011Document3 pagesTutorial 1 - Theories of Stress and Strain-2011Kiat HauNo ratings yet
- Strength of MaterialDocument80 pagesStrength of Materialpriyankar007No ratings yet
- Exam 04032021Document2 pagesExam 04032021Giannis MamalakisNo ratings yet
- Ae ZG614 Ec-2r First Sem 2022-2023Document3 pagesAe ZG614 Ec-2r First Sem 2022-2023deepakpushpadNo ratings yet
- Mechanics Prelim Doc ExamDocument11 pagesMechanics Prelim Doc ExamlolaNo ratings yet
- BFC 20903 (Mechanics of Materials) Chapter 2: Stress and Strain TransformationDocument27 pagesBFC 20903 (Mechanics of Materials) Chapter 2: Stress and Strain Transformationhamierul mohamadNo ratings yet
- Chapter 6 - COMPLEX STRESSDocument33 pagesChapter 6 - COMPLEX STRESSNurul Raihan Shahizan100% (1)
- Engineering Mechanics KCE 101 2018-19Document3 pagesEngineering Mechanics KCE 101 2018-19Tulsi ChouhanNo ratings yet
- PROB SET For Quiz 3: X Y XyDocument1 pagePROB SET For Quiz 3: X Y XyKaleenaSantosNo ratings yet
- Practise Problems Set02Document5 pagesPractise Problems Set02rohit kumarNo ratings yet
- MME2202 CourseReviewDocument5 pagesMME2202 CourseReviewMatt BrezinaNo ratings yet
- Plane Stress and Plane StrainDocument17 pagesPlane Stress and Plane StrainGiacNo ratings yet
- Machine DesignDocument69 pagesMachine DesignSushant TiwariNo ratings yet
- Static Equilibrium: M M M F F FDocument41 pagesStatic Equilibrium: M M M F F FINMENo ratings yet
- Exam 1 Meem 4150 Oct. 4Th, 2011Document2 pagesExam 1 Meem 4150 Oct. 4Th, 2011Rayleight SilversNo ratings yet
- Basics of Finite Element AnalysisDocument117 pagesBasics of Finite Element AnalysispgkaeroNo ratings yet
- ME 010 503 - AMM Model Question PaperDocument1 pageME 010 503 - AMM Model Question PaperJithin KNo ratings yet
- A Rectangular Steel Bar Having A CrossDocument2 pagesA Rectangular Steel Bar Having A CrossHitesh PrajapatNo ratings yet
- CE: 2051: Advanced Mechanics of Materials: SLIIT/Curtin: Civil Engineering: Year 2 Semester 2 Tutorial 9Document2 pagesCE: 2051: Advanced Mechanics of Materials: SLIIT/Curtin: Civil Engineering: Year 2 Semester 2 Tutorial 9Sayan KirinathanNo ratings yet
- Aerospace Engineering, IIT Kharagpur AE21004, Introduction To Aerospace Structures Exam Date: 15 April 2021 Time: 1.5 Hrs Full Marks: 30Document1 pageAerospace Engineering, IIT Kharagpur AE21004, Introduction To Aerospace Structures Exam Date: 15 April 2021 Time: 1.5 Hrs Full Marks: 30tushar kshirsagarNo ratings yet
- Statics NotesDocument8 pagesStatics NotesRyanCallejaNo ratings yet
- AMM Model QN PaperDocument2 pagesAMM Model QN PaperrpkayNo ratings yet
- Introduction of Solid Mechanics (ME 621) : Problem 1Document4 pagesIntroduction of Solid Mechanics (ME 621) : Problem 1Ritunjay JhaNo ratings yet
- + + 2 I+ 3 x+4 y J+ 2 X + 4 Z K: Analysis of Strain (Tutorial: 2)Document2 pages+ + 2 I+ 3 x+4 y J+ 2 X + 4 Z K: Analysis of Strain (Tutorial: 2)Himanshu KumarNo ratings yet
- Structural Mechanics Assignment HelpDocument29 pagesStructural Mechanics Assignment HelpMechanical Engineering Assignment HelpNo ratings yet
- Chapter 06bDocument17 pagesChapter 06bgioNo ratings yet
- Cochin University of Science and Technology B Tech Degree Iv Semester Examination SUBJECT: ME 403 Advanced Mechanics of Solids (2006)Document3 pagesCochin University of Science and Technology B Tech Degree Iv Semester Examination SUBJECT: ME 403 Advanced Mechanics of Solids (2006)Kiran ChristopherNo ratings yet
- Jest Physics Sample Question PaperDocument3 pagesJest Physics Sample Question PaperSreejith Nhaloor0% (1)
- 3D Stress and Strain Tutorial SheetDocument2 pages3D Stress and Strain Tutorial SheetTasmin Chandran0% (1)
- Elemento FinitoDocument12 pagesElemento FinitoPanchoMiyamotoNo ratings yet
- MD 2Document33 pagesMD 2Wilfredo Nieves OsoriaNo ratings yet
- 3 BalanceDocument7 pages3 BalanceSebastiao SilvaNo ratings yet
- Numerical Examples PDFDocument20 pagesNumerical Examples PDFHamid MasoodNo ratings yet
- Department of Mechanical Engineering: I I, I and The Three Principal StressesDocument1 pageDepartment of Mechanical Engineering: I I, I and The Three Principal StressesAshutosh SharmaNo ratings yet
- 3 Del As Ti CityDocument10 pages3 Del As Ti CityMohammad SalimuddinNo ratings yet
- Theory of Stress: Main PlayerDocument9 pagesTheory of Stress: Main Playerxaaabbb_550464353No ratings yet
- Fem Mid 1 Question BankDocument2 pagesFem Mid 1 Question BankallakagopichandNo ratings yet
- Civil Engineering Systems AnalysisDocument10 pagesCivil Engineering Systems AnalysisNikhil JohnNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3-Load and Stress AnalysisDocument60 pagesChapter 3-Load and Stress AnalysisNguyễnBảoKhánh100% (1)
- Practice Exam 3 KEY (Solutions)Document13 pagesPractice Exam 3 KEY (Solutions)joseNo ratings yet
- MCQ Failure TheoriesDocument46 pagesMCQ Failure TheoriesfdsfsdfsdfsfsNo ratings yet
- O level Physics Questions And Answer Practice Papers 2From EverandO level Physics Questions And Answer Practice Papers 2Rating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Theory of Elastisity, Stability and Dynamics of Structures Common ProblemsFrom EverandTheory of Elastisity, Stability and Dynamics of Structures Common ProblemsNo ratings yet
- Himgiri Zee University: Sub-Interview Call LetterDocument1 pageHimgiri Zee University: Sub-Interview Call LetterBhupender SharmaNo ratings yet
- Aravali College of Engineering and Management: Topic: Synonyms Year: 2 YearDocument3 pagesAravali College of Engineering and Management: Topic: Synonyms Year: 2 YearBhupender SharmaNo ratings yet
- MS - 1st TermDocument2 pagesMS - 1st TermBhupender SharmaNo ratings yet
- Effect On Density During TestDocument1 pageEffect On Density During TestBhupender SharmaNo ratings yet
- Keystone Group of Institutions: B.TECH. 8 Sem (Me) 1 Mid Term Exam 2014 Renewable Energy TechnologyDocument2 pagesKeystone Group of Institutions: B.TECH. 8 Sem (Me) 1 Mid Term Exam 2014 Renewable Energy TechnologyBhupender SharmaNo ratings yet
- Keystone Group of Institutions, PilodDocument2 pagesKeystone Group of Institutions, PilodBhupender SharmaNo ratings yet
- Assignment 2, NTMP'11Document2 pagesAssignment 2, NTMP'11Bhupender SharmaNo ratings yet
- Keystone Group of Institutions: Subject: Engineering ThermodynamicsDocument2 pagesKeystone Group of Institutions: Subject: Engineering ThermodynamicsBhupender SharmaNo ratings yet
- Keystone Group of Institutions Time-Table For Session 2013-2014 (Even Semester) Me (8Th Semester)Document3 pagesKeystone Group of Institutions Time-Table For Session 2013-2014 (Even Semester) Me (8Th Semester)Bhupender SharmaNo ratings yet
- Keystone Group of Institutions: Subject: CADDocument1 pageKeystone Group of Institutions: Subject: CADBhupender SharmaNo ratings yet
- Internal Lab Time Table: 29/11/2013 Auto Engg Lab M1 Morning Production Engg Lab M2 MorningDocument3 pagesInternal Lab Time Table: 29/11/2013 Auto Engg Lab M1 Morning Production Engg Lab M2 MorningBhupender SharmaNo ratings yet
- Time: 3 Hrs. Marks: 80: Keystone Grpup of Institutions Pre-University Test: ME (3 Sem) OopsDocument1 pageTime: 3 Hrs. Marks: 80: Keystone Grpup of Institutions Pre-University Test: ME (3 Sem) OopsBhupender SharmaNo ratings yet
- Keystone Group of Institutions Time-Table For Session 2013-2014 (Even Semester) Me (8Th Semester)Document10 pagesKeystone Group of Institutions Time-Table For Session 2013-2014 (Even Semester) Me (8Th Semester)Bhupender SharmaNo ratings yet