Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Tutorial6 Frictions
Tutorial6 Frictions
Uploaded by
Shimon JosephCopyright:
Available Formats
You might also like
- Frictional ForcesDocument2 pagesFrictional ForcesSpammerNo ratings yet
- Mechanics of Materials-1 - 2-Mark Question and AnswersDocument10 pagesMechanics of Materials-1 - 2-Mark Question and AnswersSrikant PotluriNo ratings yet
- FrictionDocument31 pagesFrictionNIKHIL GOYALNo ratings yet
- Biomechancal Principles in Orthodontics / Orthodontic Courses by Indian Dental AcademyDocument84 pagesBiomechancal Principles in Orthodontics / Orthodontic Courses by Indian Dental Academyindian dental academy100% (1)
- Design of Curved BeamsDocument21 pagesDesign of Curved Beamsniranjan preddyNo ratings yet
- Engr. Yoshiaki C. Mikami, Bsce Msce-Ste RMP: Prepared byDocument27 pagesEngr. Yoshiaki C. Mikami, Bsce Msce-Ste RMP: Prepared byDenzel NgNo ratings yet
- Viva Voice-Engineering Mechanics: Experiment No.-1Document28 pagesViva Voice-Engineering Mechanics: Experiment No.-1Achint Verma100% (1)
- 004 Lec. 4 Stress Analysis (ME 276)Document30 pages004 Lec. 4 Stress Analysis (ME 276)IslamNo ratings yet
- Analysis of Joists Beams and GirdersDocument23 pagesAnalysis of Joists Beams and GirdersMonica Ann Louise IntongNo ratings yet
- A General Theory of Strength For Anisotropic Materials - Tsai1971Document23 pagesA General Theory of Strength For Anisotropic Materials - Tsai1971Hiến Đinh VănNo ratings yet
- Module 1 PDFDocument18 pagesModule 1 PDFZoro RoronoaNo ratings yet
- Theoretical Q - ADocument15 pagesTheoretical Q - AFarhan Ateef RaadNo ratings yet
- ST7103-Theory of Elasticity and Plasticity Question Bank PDFDocument11 pagesST7103-Theory of Elasticity and Plasticity Question Bank PDFNiranjan Shuttler Craze100% (2)
- 2 Marks SOM RejinpaulDocument12 pages2 Marks SOM Rejinpaull8o8r8d8s8i8v8No ratings yet
- محمدعبدالخالق محمدعبده - Biomechanics-Assignment-2Document8 pagesمحمدعبدالخالق محمدعبده - Biomechanics-Assignment-2محمدعبدالخالق العلوانيNo ratings yet
- Sliding Friction: Equipment IncludedDocument6 pagesSliding Friction: Equipment IncludedSchatzRajputNo ratings yet
- 2019-20 Lecture 3 - AMI 4105 DAM (Stress Analysis)Document43 pages2019-20 Lecture 3 - AMI 4105 DAM (Stress Analysis)Aodi NabothNo ratings yet
- Var Load DesignDocument31 pagesVar Load DesignRounak AgrawalNo ratings yet
- Draft ISRM Suggested Method For The Complete Stress-Strain Cure For Intact Rock in Uniaxial Compression - (Parametros para El Ensayo)Document11 pagesDraft ISRM Suggested Method For The Complete Stress-Strain Cure For Intact Rock in Uniaxial Compression - (Parametros para El Ensayo)Jorge VelasquezNo ratings yet
- Strength of Materials: Machine Design 1Document28 pagesStrength of Materials: Machine Design 1John ReyNo ratings yet
- Es7 Lecture2 EquilibriumDocument12 pagesEs7 Lecture2 EquilibriumadobongmerlatNo ratings yet
- Mechanic Module Olivar Amarille RagasDocument24 pagesMechanic Module Olivar Amarille RagaschristianhamphreyrulebetoNo ratings yet
- SOm QBDocument40 pagesSOm QBSivaNo ratings yet
- Experiment No 4: Title Buckling Analysis of Beam, Critical Loading, Modes Shapes and Factor of Safety in Ansys TheoryDocument13 pagesExperiment No 4: Title Buckling Analysis of Beam, Critical Loading, Modes Shapes and Factor of Safety in Ansys Theorymuhammad usamaNo ratings yet
- Mechanical TestingDocument21 pagesMechanical TestingMING LIAONo ratings yet
- Dom 2 MarkDocument34 pagesDom 2 MarkJaya RajNo ratings yet
- Lab ReportDocument3 pagesLab ReportMuhammad Abdullah Zafar GhauriNo ratings yet
- Bme Cia IDocument2 pagesBme Cia Idharmaraj_meapNo ratings yet
- Module 2 StrainDocument34 pagesModule 2 StrainNathaniel BaguioNo ratings yet
- 15 Me 61Document47 pages15 Me 61danknaka jayNo ratings yet
- Southard Et Al. (2007) Friction Does Not Increase Anchorage LoadingDocument3 pagesSouthard Et Al. (2007) Friction Does Not Increase Anchorage LoadingDominikaSkórkaNo ratings yet
- Ce 6501 Sructural Analysis - I Question Bank - Kesavan Edition 2015Document24 pagesCe 6501 Sructural Analysis - I Question Bank - Kesavan Edition 2015senthurrNo ratings yet
- Mech 3-Module 2Document39 pagesMech 3-Module 2Mark Angelo SalazarNo ratings yet
- Strength 2 Marks All 5 UnitsDocument27 pagesStrength 2 Marks All 5 UnitsparathNo ratings yet
- PHYSICS Key Answers - Docx-1Document11 pagesPHYSICS Key Answers - Docx-1labonetelabs21No ratings yet
- FrictionDocument19 pagesFrictionksdndknNo ratings yet
- ShipS G5 Santos Nevarez Ortega Ortega ZambranoDocument7 pagesShipS G5 Santos Nevarez Ortega Ortega ZambranoPaúl ZambranoNo ratings yet
- Important Note On Slope Stability AnalysisDocument23 pagesImportant Note On Slope Stability AnalysisJerry FtNo ratings yet
- VIVA Questions and AnswersDocument6 pagesVIVA Questions and AnswersHarshit VaibhaviNo ratings yet
- Strength of Materials - 2 Marks - All 5 UnitsDocument27 pagesStrength of Materials - 2 Marks - All 5 UnitsMohan Prasad.M89% (38)
- SOM 2 MarksDocument8 pagesSOM 2 MarksSiva ShanmugamNo ratings yet
- Mechanical Behaviour of MaterialsDocument48 pagesMechanical Behaviour of Materialsedua777ytNo ratings yet
- Mekanika Kekuatan Material - Kul 1Document23 pagesMekanika Kekuatan Material - Kul 1lia tyyanNo ratings yet
- Lab 2Document8 pagesLab 2Max BicknellNo ratings yet
- Reliability and Sensitivity Analysis Of: TrussesDocument2 pagesReliability and Sensitivity Analysis Of: Trussesgeorgelennon68No ratings yet
- Unit 1 Force AnalysisDocument3 pagesUnit 1 Force AnalysisSudipta NathNo ratings yet
- Subject Title: Strength of Materials Class: Second Year: Instructor Name: Dr. Ziad Sh. AL SarrafDocument46 pagesSubject Title: Strength of Materials Class: Second Year: Instructor Name: Dr. Ziad Sh. AL SarrafHumam Al-fayyadhNo ratings yet
- Null 3Document4 pagesNull 3Yajnadatta PattanayakNo ratings yet
- P141L07 Lab Manual v20201209Document7 pagesP141L07 Lab Manual v20201209Deep PrajapatiNo ratings yet
- Kung PH.D., A.M.I.C.E.: Founda'I'Jon VibrationsDocument16 pagesKung PH.D., A.M.I.C.E.: Founda'I'Jon Vibrationsjoake spasNo ratings yet
- Check The Reactions You GetDocument1 pageCheck The Reactions You GetAnkit GargNo ratings yet
- Ijer 2015 1013Document6 pagesIjer 2015 1013Subu ManiNo ratings yet
- Module ThreeDocument59 pagesModule ThreeAndrei Jose GilNo ratings yet
- Module 7 Work and EnergyDocument13 pagesModule 7 Work and EnergyRhonalyn IlaganNo ratings yet
- 25528L Inclined Planes G4Document10 pages25528L Inclined Planes G4lahiruniNo ratings yet
- Jahangirabad Instiute of Technology Barabanki Department of Mechanical EngineeringDocument23 pagesJahangirabad Instiute of Technology Barabanki Department of Mechanical EngineeringMuhammad ImranNo ratings yet
- Negative Mass and Negative Refractive Index in Atom Nuclei - Nuclear Wave Equation - Gravitational and Inertial Control: Part 6: Gravitational and Inertial Control, #6From EverandNegative Mass and Negative Refractive Index in Atom Nuclei - Nuclear Wave Equation - Gravitational and Inertial Control: Part 6: Gravitational and Inertial Control, #6No ratings yet
- Qualifying Round 2013 TestDocument1 pageQualifying Round 2013 TestShimon JosephNo ratings yet
- Dos and Donts PDFDocument1 pageDos and Donts PDFShimon JosephNo ratings yet
- AM 110 Engineering Mechanics: Tutorial 3-Equilibrium of Structural SystemsDocument2 pagesAM 110 Engineering Mechanics: Tutorial 3-Equilibrium of Structural SystemsShimon JosephNo ratings yet
- Tut 2Document2 pagesTut 2Shimon JosephNo ratings yet
- Tut 1Document2 pagesTut 1Shimon JosephNo ratings yet
- Chemistry Model PaperDocument31 pagesChemistry Model PaperShimon JosephNo ratings yet
Tutorial6 Frictions
Tutorial6 Frictions
Uploaded by
Shimon JosephCopyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Tutorial6 Frictions
Tutorial6 Frictions
Uploaded by
Shimon JosephCopyright:
Available Formats
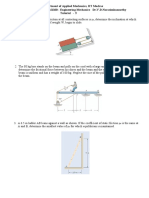
` DEPARTMENTOFAPPLIEDMECHANICS INDIANINSTITUTEOFTECHNOLOGYMADRAS AM1100EngineeringMechanics Tutorial#6:FrictionsandApplications 1. If the coefficient of static friction at all contacting surfaces is s ,determinetheinclinationatwhichtheidenticalblocks,each ofweightW,begintoslide. 2.
2.The80kgboystandsonthebeamandpullsonthecordwith a force large enough to cause him to sleep. If s 0.4 , determinethefrictionalforcebetweenhisshoesandthebeam and the reactions at A and B. The beam is uniform and has a weight of 100 kg. Neglect the size of the pulleys and the thicknessofthebeam. 3. If the jack is required to lift the 200kg crate, determine the horizontal force that must be applied perpendicular to the handle at E. Each single square threaded screw has a mean diameterof25mmandaleadof7.5mm.Thecoefficientofstatic frictionis s 0.25 . 4.ColumnDissubjectedtoaverticalloadof8000Kg.Itissupportedon twoidenticalwedgesAandBforwhichthecoefficientofstaticfriction at the contacting surfaces between A and B and between B and C is If the forces P and P' are removed, are the wedges selflocking? The contactingsurfacebetweenAandDissmooth. 5. Blocks A and B have a mass of 100 kg and 150 kg, respectively.IfthecoefficientofstaticfrictionbetweenAand B and between B and C is s 0.25 and between the ropes 0.25 ,determinethesmallestforceF andthepegsDandE s neededtocausemotionofblockBifP=30N.
Dr. S. F. Ali for CRC 202
You might also like
- Frictional ForcesDocument2 pagesFrictional ForcesSpammerNo ratings yet
- Mechanics of Materials-1 - 2-Mark Question and AnswersDocument10 pagesMechanics of Materials-1 - 2-Mark Question and AnswersSrikant PotluriNo ratings yet
- FrictionDocument31 pagesFrictionNIKHIL GOYALNo ratings yet
- Biomechancal Principles in Orthodontics / Orthodontic Courses by Indian Dental AcademyDocument84 pagesBiomechancal Principles in Orthodontics / Orthodontic Courses by Indian Dental Academyindian dental academy100% (1)
- Design of Curved BeamsDocument21 pagesDesign of Curved Beamsniranjan preddyNo ratings yet
- Engr. Yoshiaki C. Mikami, Bsce Msce-Ste RMP: Prepared byDocument27 pagesEngr. Yoshiaki C. Mikami, Bsce Msce-Ste RMP: Prepared byDenzel NgNo ratings yet
- Viva Voice-Engineering Mechanics: Experiment No.-1Document28 pagesViva Voice-Engineering Mechanics: Experiment No.-1Achint Verma100% (1)
- 004 Lec. 4 Stress Analysis (ME 276)Document30 pages004 Lec. 4 Stress Analysis (ME 276)IslamNo ratings yet
- Analysis of Joists Beams and GirdersDocument23 pagesAnalysis of Joists Beams and GirdersMonica Ann Louise IntongNo ratings yet
- A General Theory of Strength For Anisotropic Materials - Tsai1971Document23 pagesA General Theory of Strength For Anisotropic Materials - Tsai1971Hiến Đinh VănNo ratings yet
- Module 1 PDFDocument18 pagesModule 1 PDFZoro RoronoaNo ratings yet
- Theoretical Q - ADocument15 pagesTheoretical Q - AFarhan Ateef RaadNo ratings yet
- ST7103-Theory of Elasticity and Plasticity Question Bank PDFDocument11 pagesST7103-Theory of Elasticity and Plasticity Question Bank PDFNiranjan Shuttler Craze100% (2)
- 2 Marks SOM RejinpaulDocument12 pages2 Marks SOM Rejinpaull8o8r8d8s8i8v8No ratings yet
- محمدعبدالخالق محمدعبده - Biomechanics-Assignment-2Document8 pagesمحمدعبدالخالق محمدعبده - Biomechanics-Assignment-2محمدعبدالخالق العلوانيNo ratings yet
- Sliding Friction: Equipment IncludedDocument6 pagesSliding Friction: Equipment IncludedSchatzRajputNo ratings yet
- 2019-20 Lecture 3 - AMI 4105 DAM (Stress Analysis)Document43 pages2019-20 Lecture 3 - AMI 4105 DAM (Stress Analysis)Aodi NabothNo ratings yet
- Var Load DesignDocument31 pagesVar Load DesignRounak AgrawalNo ratings yet
- Draft ISRM Suggested Method For The Complete Stress-Strain Cure For Intact Rock in Uniaxial Compression - (Parametros para El Ensayo)Document11 pagesDraft ISRM Suggested Method For The Complete Stress-Strain Cure For Intact Rock in Uniaxial Compression - (Parametros para El Ensayo)Jorge VelasquezNo ratings yet
- Strength of Materials: Machine Design 1Document28 pagesStrength of Materials: Machine Design 1John ReyNo ratings yet
- Es7 Lecture2 EquilibriumDocument12 pagesEs7 Lecture2 EquilibriumadobongmerlatNo ratings yet
- Mechanic Module Olivar Amarille RagasDocument24 pagesMechanic Module Olivar Amarille RagaschristianhamphreyrulebetoNo ratings yet
- SOm QBDocument40 pagesSOm QBSivaNo ratings yet
- Experiment No 4: Title Buckling Analysis of Beam, Critical Loading, Modes Shapes and Factor of Safety in Ansys TheoryDocument13 pagesExperiment No 4: Title Buckling Analysis of Beam, Critical Loading, Modes Shapes and Factor of Safety in Ansys Theorymuhammad usamaNo ratings yet
- Mechanical TestingDocument21 pagesMechanical TestingMING LIAONo ratings yet
- Dom 2 MarkDocument34 pagesDom 2 MarkJaya RajNo ratings yet
- Lab ReportDocument3 pagesLab ReportMuhammad Abdullah Zafar GhauriNo ratings yet
- Bme Cia IDocument2 pagesBme Cia Idharmaraj_meapNo ratings yet
- Module 2 StrainDocument34 pagesModule 2 StrainNathaniel BaguioNo ratings yet
- 15 Me 61Document47 pages15 Me 61danknaka jayNo ratings yet
- Southard Et Al. (2007) Friction Does Not Increase Anchorage LoadingDocument3 pagesSouthard Et Al. (2007) Friction Does Not Increase Anchorage LoadingDominikaSkórkaNo ratings yet
- Ce 6501 Sructural Analysis - I Question Bank - Kesavan Edition 2015Document24 pagesCe 6501 Sructural Analysis - I Question Bank - Kesavan Edition 2015senthurrNo ratings yet
- Mech 3-Module 2Document39 pagesMech 3-Module 2Mark Angelo SalazarNo ratings yet
- Strength 2 Marks All 5 UnitsDocument27 pagesStrength 2 Marks All 5 UnitsparathNo ratings yet
- PHYSICS Key Answers - Docx-1Document11 pagesPHYSICS Key Answers - Docx-1labonetelabs21No ratings yet
- FrictionDocument19 pagesFrictionksdndknNo ratings yet
- ShipS G5 Santos Nevarez Ortega Ortega ZambranoDocument7 pagesShipS G5 Santos Nevarez Ortega Ortega ZambranoPaúl ZambranoNo ratings yet
- Important Note On Slope Stability AnalysisDocument23 pagesImportant Note On Slope Stability AnalysisJerry FtNo ratings yet
- VIVA Questions and AnswersDocument6 pagesVIVA Questions and AnswersHarshit VaibhaviNo ratings yet
- Strength of Materials - 2 Marks - All 5 UnitsDocument27 pagesStrength of Materials - 2 Marks - All 5 UnitsMohan Prasad.M89% (38)
- SOM 2 MarksDocument8 pagesSOM 2 MarksSiva ShanmugamNo ratings yet
- Mechanical Behaviour of MaterialsDocument48 pagesMechanical Behaviour of Materialsedua777ytNo ratings yet
- Mekanika Kekuatan Material - Kul 1Document23 pagesMekanika Kekuatan Material - Kul 1lia tyyanNo ratings yet
- Lab 2Document8 pagesLab 2Max BicknellNo ratings yet
- Reliability and Sensitivity Analysis Of: TrussesDocument2 pagesReliability and Sensitivity Analysis Of: Trussesgeorgelennon68No ratings yet
- Unit 1 Force AnalysisDocument3 pagesUnit 1 Force AnalysisSudipta NathNo ratings yet
- Subject Title: Strength of Materials Class: Second Year: Instructor Name: Dr. Ziad Sh. AL SarrafDocument46 pagesSubject Title: Strength of Materials Class: Second Year: Instructor Name: Dr. Ziad Sh. AL SarrafHumam Al-fayyadhNo ratings yet
- Null 3Document4 pagesNull 3Yajnadatta PattanayakNo ratings yet
- P141L07 Lab Manual v20201209Document7 pagesP141L07 Lab Manual v20201209Deep PrajapatiNo ratings yet
- Kung PH.D., A.M.I.C.E.: Founda'I'Jon VibrationsDocument16 pagesKung PH.D., A.M.I.C.E.: Founda'I'Jon Vibrationsjoake spasNo ratings yet
- Check The Reactions You GetDocument1 pageCheck The Reactions You GetAnkit GargNo ratings yet
- Ijer 2015 1013Document6 pagesIjer 2015 1013Subu ManiNo ratings yet
- Module ThreeDocument59 pagesModule ThreeAndrei Jose GilNo ratings yet
- Module 7 Work and EnergyDocument13 pagesModule 7 Work and EnergyRhonalyn IlaganNo ratings yet
- 25528L Inclined Planes G4Document10 pages25528L Inclined Planes G4lahiruniNo ratings yet
- Jahangirabad Instiute of Technology Barabanki Department of Mechanical EngineeringDocument23 pagesJahangirabad Instiute of Technology Barabanki Department of Mechanical EngineeringMuhammad ImranNo ratings yet
- Negative Mass and Negative Refractive Index in Atom Nuclei - Nuclear Wave Equation - Gravitational and Inertial Control: Part 6: Gravitational and Inertial Control, #6From EverandNegative Mass and Negative Refractive Index in Atom Nuclei - Nuclear Wave Equation - Gravitational and Inertial Control: Part 6: Gravitational and Inertial Control, #6No ratings yet
- Qualifying Round 2013 TestDocument1 pageQualifying Round 2013 TestShimon JosephNo ratings yet
- Dos and Donts PDFDocument1 pageDos and Donts PDFShimon JosephNo ratings yet
- AM 110 Engineering Mechanics: Tutorial 3-Equilibrium of Structural SystemsDocument2 pagesAM 110 Engineering Mechanics: Tutorial 3-Equilibrium of Structural SystemsShimon JosephNo ratings yet
- Tut 2Document2 pagesTut 2Shimon JosephNo ratings yet
- Tut 1Document2 pagesTut 1Shimon JosephNo ratings yet
- Chemistry Model PaperDocument31 pagesChemistry Model PaperShimon JosephNo ratings yet