Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Ex 2
Ex 2
Uploaded by
Mkt SchrbrOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Ex 2
Ex 2
Uploaded by
Mkt SchrbrCopyright:
Available Formats
763628S CONDENSED MATTER PHYSICS Problem Set 2 Spring 2012
1. Hexagonal closepacked lattice a) Verify that the basis vectors a1 = (a, 0, 0) , a2 =
a a 3 , ,0 2 2
, a3 = (0, 0, c) ,
a , a ,c 2 2 3 2
v1 = (0, 0, 0) , v2 =
result in placing atoms directly over the centers of triangles along the c axis. b) Verify that the hcp lattice forms a closepacked structure when c/a = 8/3. 2. Glide and screw axes a) The hcp lattice contains a screw axis in the c direction. Decribe the Cartesian coordinates of a point through which this axis can pass, so that the lattice remains invariant under translation along c by c/2 followed by rotation through 60 degrees. b) The hcp also has a glide plane parallel to a plane containing both the a and c axes. Describe where this plane may be located, so that translation along c/2 followed by reection about the plane leaves the lattice invariant.
3. Bravais lattices In each of the following cases, indicate whether the structure is a Bravais lattice. If it is, give three primitive vectors; if not, describe it as a Bravais lattice with as small as possible a basis. a) Basecentered cubic (simple cubic with additional points in the centers of the horizontal faces).
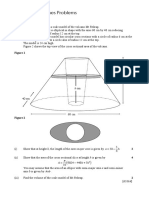
b) Sidecentered cubic (simple cubic with additional points in the centers of the vertical faces). b) Edgecentered cubic (simple cubic with additional points at the midpoints of the lines joining nearest neighbors). 4. Bragg peaks Check that the gure below indeed corresponds to a Bragg peak, i.e. q k0 k = K , where K is a reciprocal lattice vector.
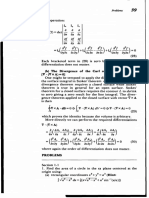
5. Reciprocal lattice Let a1 , a2 , and a3 be the primitive vectors of a Bravais lattice, and b1 , b2 , and b3 the primitive vectors of the corresponding reciprocal lattice. a) Using the construction b1 = 2 a2 a3 a1 (a2 a3 ) (+c.p.) ,
show that the reciprocal lattice of the fcc lattice is bcc with lattice spacing 4/a, and vice versa. b) Find the reciprocal lattice vectors of smallest magnitude for simple cubic, fcc, and bcc lattices, and write down their Miller indices. Show that these correspond to planes in the direct lattice whose distance is d = 2/K .
You might also like
- Geometry Camp 2009: Problem SetDocument7 pagesGeometry Camp 2009: Problem SetMahmudNo ratings yet
- A Methodological Critique of Bandura's Self-Efficacy Theory of Behavior Change.Document2 pagesA Methodological Critique of Bandura's Self-Efficacy Theory of Behavior Change.Mkt SchrbrNo ratings yet
- Ex 1Document1 pageEx 1Tomás RojasNo ratings yet
- HW 1Document2 pagesHW 1honestcheaterNo ratings yet
- HW1Document8 pagesHW1Kevin Johnmar Urcia VidarteNo ratings yet
- P1P2 Revision Worksheet Month-06 (December 2023)Document3 pagesP1P2 Revision Worksheet Month-06 (December 2023)Kana MatabborNo ratings yet
- AS 2050 Take-Home Assignment Due On/before: 4 PM, March 11, 2019Document2 pagesAS 2050 Take-Home Assignment Due On/before: 4 PM, March 11, 2019Vijay ArniNo ratings yet
- HW 2Document1 pageHW 2FABIANO OLIVEIRANo ratings yet
- Geometric Inequalities Marathon - MathlinksDocument9 pagesGeometric Inequalities Marathon - Mathlinksobelix2No ratings yet
- HW 3Document1 pageHW 3meanyackNo ratings yet
- Fisica Del Estado Solido EjerciciosDocument7 pagesFisica Del Estado Solido EjerciciosjelipeNo ratings yet
- Phys 445 Condensed Matter Physics Homework 1: Due To October 1 2010, Friday 9:40 in ClassDocument1 pagePhys 445 Condensed Matter Physics Homework 1: Due To October 1 2010, Friday 9:40 in ClassmeanyackNo ratings yet
- Geometric Inequalities Marathon - The First 100 Problems and SolutionsDocument40 pagesGeometric Inequalities Marathon - The First 100 Problems and SolutionsAltananyNo ratings yet
- Coordbash PDFDocument10 pagesCoordbash PDFdaveNo ratings yet
- 12 Maths Chapter 10 Assignments 1Document2 pages12 Maths Chapter 10 Assignments 1Mohd AsadNo ratings yet
- Phy 403 - 1Document2 pagesPhy 403 - 1Anonymous ezN9YVNo ratings yet
- MaxwellDocument2 pagesMaxwellmarcianoloco100% (1)
- Computer Graphics PYQDocument6 pagesComputer Graphics PYQnitob90303No ratings yet
- Geometric Inequalities Marathon - The First 100 Problems and SolutionsDocument40 pagesGeometric Inequalities Marathon - The First 100 Problems and Solutionssamer_serajNo ratings yet
- Exercise: and 乙ABC=Document5 pagesExercise: and 乙ABC=5D-11-李嘉豪 stu-LI KA HONo ratings yet
- Harder X2 Volumes ProblemsDocument4 pagesHarder X2 Volumes ProblemsyddapNo ratings yet
- Problems Set 2Document2 pagesProblems Set 2Govindanunni PadmakumarNo ratings yet
- The Pascal Theorem and Some Its Generalizations: Dedicated To Professor Andrzej GranasDocument14 pagesThe Pascal Theorem and Some Its Generalizations: Dedicated To Professor Andrzej GranasBarsbold UlziisaikhanNo ratings yet
- Caucasus MO 2018Document3 pagesCaucasus MO 2018Hoàng MinhNo ratings yet
- Tut 01Document1 pageTut 01Sàtyâjit SahooNo ratings yet
- Lissajous FigureDocument4 pagesLissajous FigureSunil Namdev0% (1)
- Vibrant Academy: VG SirDocument3 pagesVibrant Academy: VG SirArman SinghNo ratings yet
- More About Trigonmetry (II) (Q)Document44 pagesMore About Trigonmetry (II) (Q)Chan Kwan Yu QuinnyNo ratings yet
- Automated Discovery of Geometric Theorems Based On Vector EquationsDocument16 pagesAutomated Discovery of Geometric Theorems Based On Vector EquationsNadia SefianyNo ratings yet
- Birla Institute of Technology and Science - Pilani, K K Birla Goa CampusDocument1 pageBirla Institute of Technology and Science - Pilani, K K Birla Goa CampusNikhil JunnarkarNo ratings yet
- P1P2 Revision Worksheet Month: 04 (October 2023) : Syllabus: P1 CH 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6 (Upto Ex: 6A - 6E) P2 Chapter 2Document3 pagesP1P2 Revision Worksheet Month: 04 (October 2023) : Syllabus: P1 CH 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6 (Upto Ex: 6A - 6E) P2 Chapter 2Kana MatabborNo ratings yet
- Exercise Sheet 06Document3 pagesExercise Sheet 06timoiivulaNo ratings yet
- Derivation of Formulas in Spherical Trigonometry BDocument6 pagesDerivation of Formulas in Spherical Trigonometry BSannyBombeoJomocNo ratings yet
- Geometry Exercises 4: T) A + TB, 0 T 1Document4 pagesGeometry Exercises 4: T) A + TB, 0 T 1Esio TrotNo ratings yet
- Yield Line TheoryDocument13 pagesYield Line TheoryTinotenda Privilege TaonaNo ratings yet
- MITRES 6 002S08 Chap01 Pset PDFDocument11 pagesMITRES 6 002S08 Chap01 Pset PDFabha singhNo ratings yet
- Chap 8Document5 pagesChap 8민찬홍No ratings yet
- Drawing Procedure of A Flow NetDocument5 pagesDrawing Procedure of A Flow Nettalukder47-555No ratings yet
- Inter-Material-Istyearem-Mathsia-04 02 Scalar Triple ProductDocument18 pagesInter-Material-Istyearem-Mathsia-04 02 Scalar Triple ProductmohithapanandNo ratings yet
- Geometry FinalDocument5 pagesGeometry FinalPeter V DatoyNo ratings yet
- Problem Set IDocument2 pagesProblem Set ImagnaNo ratings yet
- Phys 460 - Homework 2Document4 pagesPhys 460 - Homework 2ParkVegasNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2 Geometry of CrystalsDocument56 pagesChapter 2 Geometry of CrystalssfdafNo ratings yet
- Crystallography and Structure of Elements: LatticesDocument33 pagesCrystallography and Structure of Elements: LatticesVictor ParraNo ratings yet
- Ax bxc0 X A B B Ac: Formula ListDocument11 pagesAx bxc0 X A B B Ac: Formula ListyingwuenchanNo ratings yet
- Rosin and Pitteway - The Ellipse and The Five-Centred ArchDocument10 pagesRosin and Pitteway - The Ellipse and The Five-Centred Archfmboy700No ratings yet
- Classnote 50ca22ef04818Document24 pagesClassnote 50ca22ef04818Puneet GuptaNo ratings yet
- Mechanism DesignDocument30 pagesMechanism DesignBivas Panigrahi0% (1)
- 2023Document4 pages2023tharaabs78No ratings yet
- Nptel 1 NewDocument49 pagesNptel 1 NewRajashree DateNo ratings yet
- A Some Basic Rules of Tensor Calculus PDFDocument26 pagesA Some Basic Rules of Tensor Calculus PDFrenatotorresa2905No ratings yet
- Regge Calculus in The Canonical Form: Budker Institute of Nuclear Physics, Novosibirsk 630090, RussiaDocument24 pagesRegge Calculus in The Canonical Form: Budker Institute of Nuclear Physics, Novosibirsk 630090, RussiacrocoaliNo ratings yet
- Maths PapetDocument3 pagesMaths PapetAnni_RockstarNo ratings yet
- End of Course Problem Set: A, B, C As IndicatedDocument2 pagesEnd of Course Problem Set: A, B, C As Indicatedprueba1No ratings yet
- 71 VECTOR & 3D PART 4 of 6 PDFDocument18 pages71 VECTOR & 3D PART 4 of 6 PDFwill bellNo ratings yet
- Standard-Slope Integration: A New Approach to Numerical IntegrationFrom EverandStandard-Slope Integration: A New Approach to Numerical IntegrationNo ratings yet
- Handbook of Railroad Construction; For the use of American engineersFrom EverandHandbook of Railroad Construction; For the use of American engineersNo ratings yet
- Watch and Clock Escapements A Complete Study in Theory and Practice of the Lever, Cylinder and Chronometer Escapements, Together with a Brief Account of the Origin and Evolution of the Escapement in HorologyFrom EverandWatch and Clock Escapements A Complete Study in Theory and Practice of the Lever, Cylinder and Chronometer Escapements, Together with a Brief Account of the Origin and Evolution of the Escapement in HorologyNo ratings yet
- Awakening MonsterDocument128 pagesAwakening MonsterMkt SchrbrNo ratings yet
- 56 Preventing Rope Spoilage PDFDocument2 pages56 Preventing Rope Spoilage PDFMkt SchrbrNo ratings yet
- DiffInt PDFDocument2 pagesDiffInt PDFMkt SchrbrNo ratings yet
- Achievement Motivation - Conceptions of Ability, Subjective Experience, Task Choice, and Performance.Document19 pagesAchievement Motivation - Conceptions of Ability, Subjective Experience, Task Choice, and Performance.Mkt SchrbrNo ratings yet
- Theoretical Weaknesses Lead To Practical Problems - The Example of Self-Efficacy TheoryDocument9 pagesTheoretical Weaknesses Lead To Practical Problems - The Example of Self-Efficacy TheoryMkt SchrbrNo ratings yet
- PHZ6426: Fall 2013 Problem Set # 6: Electron Transport. Phonons. Due Monday, 12/02 at The Time of The Class Instructor: D. L. Maslov Maslov@phys - Ufl.edu 392-0513 Rm. 2114 Office Hours: TR 3 pm-4 PMDocument9 pagesPHZ6426: Fall 2013 Problem Set # 6: Electron Transport. Phonons. Due Monday, 12/02 at The Time of The Class Instructor: D. L. Maslov Maslov@phys - Ufl.edu 392-0513 Rm. 2114 Office Hours: TR 3 pm-4 PMMkt SchrbrNo ratings yet
- OweekDocument1 pageOweekMkt SchrbrNo ratings yet
- Notes SpindfsDocument22 pagesNotes SpindfsMkt SchrbrNo ratings yet
- D Band Raman Intensity Calculation in Armchair Edged Graphene NanoribbonsDocument9 pagesD Band Raman Intensity Calculation in Armchair Edged Graphene NanoribbonsMkt SchrbrNo ratings yet
- Full Text 01Document8 pagesFull Text 01Mkt SchrbrNo ratings yet