Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Power System Syllabus
Power System Syllabus
Uploaded by
Ravi SharmaCopyright:
Available Formats
You might also like
- Syllabus 2Document2 pagesSyllabus 2lekshmipriya9No ratings yet
- Electrical Core CourseDocument13 pagesElectrical Core CourseShiva ShakthiNo ratings yet
- Anna University Tiruchirappalli Tiruchirappalli - 620 024Document22 pagesAnna University Tiruchirappalli Tiruchirappalli - 620 024mdiliasNo ratings yet
- Tamil Nadu Public Service Commission: Code No.206Document4 pagesTamil Nadu Public Service Commission: Code No.206Kaviarasu ThangarajNo ratings yet
- M. Tech. in Power Systems / Power Engineering / Electrical Power Systems Syllabus of Paper - 1Document4 pagesM. Tech. in Power Systems / Power Engineering / Electrical Power Systems Syllabus of Paper - 1Karthik ThirumalaNo ratings yet
- 38 Electrical Engg UgDocument4 pages38 Electrical Engg UgSriSelvi S S SNo ratings yet
- EPSDocument28 pagesEPSChakala BhargavNo ratings yet
- PHD Entrance TestDocument3 pagesPHD Entrance TestmjrsudhakarNo ratings yet
- Power Systems IIDocument2 pagesPower Systems IIrameshNo ratings yet
- ELG4126: Sustainable Power Systems: Concepts and Applications: You Should Be Familiar WithDocument40 pagesELG4126: Sustainable Power Systems: Concepts and Applications: You Should Be Familiar WithJameson CongoNo ratings yet
- SyllabusDocument3 pagesSyllabushamesNo ratings yet
- EPSDocument31 pagesEPSChakala BhargavNo ratings yet
- Elecrical EngineeringDocument1 pageElecrical EngineeringUdit Sangwan JaatNo ratings yet
- Eee515 Power SystemDocument2 pagesEee515 Power Systemmanan jeeNo ratings yet
- 1 EE301 Power Generation, Transmission and ProtectionDocument4 pages1 EE301 Power Generation, Transmission and ProtectionAnuja VargheseNo ratings yet
- 1 EE301 Power Generation, Transmission and Protection PDFDocument4 pages1 EE301 Power Generation, Transmission and Protection PDFHaripriya k aNo ratings yet
- 5TH Sem SyllabusDocument16 pages5TH Sem SyllabusHunter HarshaNo ratings yet
- Amie Syllabus Sec B ElectricalDocument19 pagesAmie Syllabus Sec B ElectricalvenkatNo ratings yet
- Sub Engrr Electrical - KSEBDocument4 pagesSub Engrr Electrical - KSEBk keralaNo ratings yet
- Deputy Engineer ElectricalDocument3 pagesDeputy Engineer ElectricalSargi BeepumohanNo ratings yet
- Distribution of Electric Power PDFDocument2 pagesDistribution of Electric Power PDFJosua Sudrajat Marbun67% (6)
- Syllabus B ElectricalDocument6 pagesSyllabus B ElectricalnetprosenjitNo ratings yet
- T&D SyllabusDocument1 pageT&D SyllabusarunjiboseNo ratings yet
- Section BeeDocument14 pagesSection BeeTILAK PATELNo ratings yet
- Syllabus EEE 2019Document5 pagesSyllabus EEE 2019jaberyemeniNo ratings yet
- 132 20 Assistant Electrical InspectorDocument3 pages132 20 Assistant Electrical Inspectorajith sNo ratings yet
- Ee2303 Transmission and DistributionDocument2 pagesEe2303 Transmission and DistributionMuruga RajNo ratings yet
- Power System Analysis.: Unit I IntroductionDocument7 pagesPower System Analysis.: Unit I IntroductionJagadeesh MannivannanNo ratings yet
- Hours Sem. Exam MarksDocument24 pagesHours Sem. Exam MarksshafinshamsudheenNo ratings yet
- Ps 9221 Power System ProtectionDocument24 pagesPs 9221 Power System Protectionsyed1188No ratings yet
- PrudviallaDocument4 pagesPrudviallaPrudhvi AllaNo ratings yet
- Of in EGAT 500 Transinission System: An Analysis Switching Overvoltages KVDocument5 pagesOf in EGAT 500 Transinission System: An Analysis Switching Overvoltages KVKarina LozadaNo ratings yet
- EE301 Power Generation Transmission and Protection PDFDocument3 pagesEE301 Power Generation Transmission and Protection PDFMalavika SNo ratings yet
- Ee2036 Flexible Ac Transmission SystemsDocument2 pagesEe2036 Flexible Ac Transmission SystemsAnbalagan GuruNo ratings yet
- Eee 35Document4 pagesEee 35likhonNo ratings yet
- III Sem SyllbusDocument11 pagesIII Sem SyllbusS B RajNo ratings yet
- Eeguc: Unit I Power GenerationDocument3 pagesEeguc: Unit I Power GenerationJagadeesh MannivannanNo ratings yet
- Ap Eee SyllabusDocument3 pagesAp Eee SyllabusSujith kumarNo ratings yet
- Transmission and DistributionDocument4 pagesTransmission and DistributionMuthamizhan ThiyagarajanNo ratings yet
- Prediction of Transmission Line Overloading UsingDocument23 pagesPrediction of Transmission Line Overloading UsingDevendra SharmaNo ratings yet
- ELECTRICAL TNPSC Engineering Service ExamDocument3 pagesELECTRICAL TNPSC Engineering Service ExamM KumarNo ratings yet
- Electrical Distribution System TopicsDocument20 pagesElectrical Distribution System TopicsIvar Nilasta100% (2)
- Ee801 Power Quality 1. Introduction To Power QualityDocument3 pagesEe801 Power Quality 1. Introduction To Power QualityNarmatha BalachandarNo ratings yet
- Ee2351 PsaDocument2 pagesEe2351 PsaanbuelectricalNo ratings yet
- Harmonic Distortion Caused by Suburban and Underground Rolling Stock With DC Motors - 00618538Document7 pagesHarmonic Distortion Caused by Suburban and Underground Rolling Stock With DC Motors - 00618538npfhNo ratings yet
- Tsgenco-Exam Syllabus SaimedhaDocument14 pagesTsgenco-Exam Syllabus SaimedhasaimedhaNo ratings yet
- Power System EquivalentsDocument6 pagesPower System Equivalentsdallisrinivas14No ratings yet
- Ee6501 Power System AnalysisDocument2 pagesEe6501 Power System AnalysiskrishnandrkNo ratings yet
- Kseb Ae SyllabusDocument4 pagesKseb Ae SyllabusStech 007No ratings yet
- RSMSSB JEN Electrical SyllabusDocument2 pagesRSMSSB JEN Electrical Syllabusashwinivema1980No ratings yet
- PsocDocument1 pagePsocGayan ShashiNo ratings yet
- Power System - Farari 100Document30 pagesPower System - Farari 100Rakesh Kumar RanjanNo ratings yet
- EEE 6th Sem SyllabusDocument6 pagesEEE 6th Sem SyllabusRajesh0% (1)
- Point Wise Notes From AIDocument19 pagesPoint Wise Notes From AIkuldiprana111000No ratings yet
- Curriculum For MTech in Power Systems ProgrammeDocument20 pagesCurriculum For MTech in Power Systems ProgrammeheerapotterNo ratings yet
- Hybrid Passive Filter Design - 2007Document6 pagesHybrid Passive Filter Design - 2007Rizqy Capten Tsubasa OzoraNo ratings yet
- Power System Analysis Syallbus MG Univ KeralaDocument1 pagePower System Analysis Syallbus MG Univ KeralaChristy CyriacNo ratings yet
- Distribution of Electrical Power: Lecture Notes of Distribution of Electrical Power CourseFrom EverandDistribution of Electrical Power: Lecture Notes of Distribution of Electrical Power CourseNo ratings yet
- Investigation of the Usefulness of the PowerWorld Simulator Program: Developed by "Glover, Overbye & Sarma" in the Solution of Power System ProblemsFrom EverandInvestigation of the Usefulness of the PowerWorld Simulator Program: Developed by "Glover, Overbye & Sarma" in the Solution of Power System ProblemsNo ratings yet
- Electric Power Transmission: Lecture Notes of Electric Power Transmission CourseFrom EverandElectric Power Transmission: Lecture Notes of Electric Power Transmission CourseRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- SUNPACKDocument2 pagesSUNPACKRavi SharmaNo ratings yet
- Name of The Student: ANSWER KEY Roll No.: Set:1 Quiz: Power System Lab-1Document1 pageName of The Student: ANSWER KEY Roll No.: Set:1 Quiz: Power System Lab-1Ravi SharmaNo ratings yet
- Mid-Term Examination: RE-APPEAR (New Scheme)Document1 pageMid-Term Examination: RE-APPEAR (New Scheme)Ravi SharmaNo ratings yet
- Power System Lab Quiz Set 1Document3 pagesPower System Lab Quiz Set 1Ravi SharmaNo ratings yet
- Name of The Student: ANSWER KEY Roll No.: Set:1 Quiz: Power System Lab-1Document1 pageName of The Student: ANSWER KEY Roll No.: Set:1 Quiz: Power System Lab-1Ravi SharmaNo ratings yet
- Power System 1 Lab Quiz Set2Document4 pagesPower System 1 Lab Quiz Set2Ravi SharmaNo ratings yet
- Holidays' Homework: Class - VDocument4 pagesHolidays' Homework: Class - VRavi SharmaNo ratings yet
- SHS™ Solar Controller: - High Reliability - Low Cost - Electronic Protections - Tropicalization - Easy To UseDocument2 pagesSHS™ Solar Controller: - High Reliability - Low Cost - Electronic Protections - Tropicalization - Easy To UseRavi SharmaNo ratings yet
- DC Solar Pumps New-3 PDFDocument3 pagesDC Solar Pumps New-3 PDFRavi SharmaNo ratings yet
- HVDCDocument1 pageHVDCRavi SharmaNo ratings yet
- ApplicationDocument1 pageApplicationRavi SharmaNo ratings yet
- ps2 SyllabusDocument1 pageps2 SyllabusRavi SharmaNo ratings yet
- Em Ii PDFDocument76 pagesEm Ii PDFRavi SharmaNo ratings yet
- List of Nominations Received For This Schedule: Execution of Nofn Utilizing FTTH Tech. (Batch No:1)Document3 pagesList of Nominations Received For This Schedule: Execution of Nofn Utilizing FTTH Tech. (Batch No:1)Ravi SharmaNo ratings yet
- ICEEE2015Document1 pageICEEE2015Ravi SharmaNo ratings yet
- Power in India From Different SourcesDocument1 pagePower in India From Different SourcesRavi SharmaNo ratings yet
- Dynamic Voltage Restorer Against Voltage SagDocument6 pagesDynamic Voltage Restorer Against Voltage SaghusamyesilNo ratings yet
- DigsilentDocument2 pagesDigsilentRavi SharmaNo ratings yet
- UPSC - Registration SlipDocument1 pageUPSC - Registration SlipRavi SharmaNo ratings yet
Power System Syllabus
Power System Syllabus
Uploaded by
Ravi SharmaOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Power System Syllabus
Power System Syllabus
Uploaded by
Ravi SharmaCopyright:
Available Formats
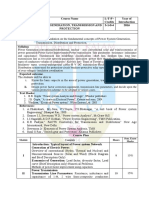
EE253 POWER SYSTEMS I (3-1-0)4 Introduction - generation of electric power -conventional sources (qualitative) general layout of power system-
m- characteristics of steam, hydro, nuclear and gas power plants- non conventional sources (qualitative)- ocean, tidal, wind, solar, fuel cells, geo-thermal etc.economics of generation- introduction- definitions- cost of electrical energy- fixed and running costs- tariffs.a.c. distribution-introduction- ac distribution- -ph, !-ph(!-wirw and "wire) systems- busbar arrangement- selection of site for substation.overhead line insulatorsintroduction- types of insulators- potential distribution- testing of insulators.insulated cablesintroduction- insulation- grading of cables- overhead lines versus underground cables- types of cables.inductance and capacitance calculations of transmission lines -inductance and capacitance of lines- composite conductors- transposition- bundled conductors.coronaintroduction- corona loss- factors affecting corona loss- interference between power and communication lines. EE351 POWER SYSTEM OPERATION AND CONTROL (3-1-0)4 #oad flow studies- introduction- bus classification- load flow equations- iterative methods fast decoupled methods system data for load flow study-, p q control- effect of synchronous machine excitation power angle of a synchronous machine, specification of bus voltages. capacitor ban$s, control by transformers- economic operation of power systems- distribution of load between units within a plant and system- calculation of loss coefficients- load frequency control- introduction, load frequency problem, p-f control channel- q-v control channelmathematical models of power system- p-f control of single and two control areas- power system stability- the stability problem, swing equation, equal area criterion- methods to improve steady state and transient stability- voltage stability. power system deregulation(qualitative treatment)- introduction- power system restructuring modelsresponsibilities and functions of independent system operator (iso) iso models- available transfer capability(atc)- mar$et power- congestion management- ancillary services.
You might also like
- Syllabus 2Document2 pagesSyllabus 2lekshmipriya9No ratings yet
- Electrical Core CourseDocument13 pagesElectrical Core CourseShiva ShakthiNo ratings yet
- Anna University Tiruchirappalli Tiruchirappalli - 620 024Document22 pagesAnna University Tiruchirappalli Tiruchirappalli - 620 024mdiliasNo ratings yet
- Tamil Nadu Public Service Commission: Code No.206Document4 pagesTamil Nadu Public Service Commission: Code No.206Kaviarasu ThangarajNo ratings yet
- M. Tech. in Power Systems / Power Engineering / Electrical Power Systems Syllabus of Paper - 1Document4 pagesM. Tech. in Power Systems / Power Engineering / Electrical Power Systems Syllabus of Paper - 1Karthik ThirumalaNo ratings yet
- 38 Electrical Engg UgDocument4 pages38 Electrical Engg UgSriSelvi S S SNo ratings yet
- EPSDocument28 pagesEPSChakala BhargavNo ratings yet
- PHD Entrance TestDocument3 pagesPHD Entrance TestmjrsudhakarNo ratings yet
- Power Systems IIDocument2 pagesPower Systems IIrameshNo ratings yet
- ELG4126: Sustainable Power Systems: Concepts and Applications: You Should Be Familiar WithDocument40 pagesELG4126: Sustainable Power Systems: Concepts and Applications: You Should Be Familiar WithJameson CongoNo ratings yet
- SyllabusDocument3 pagesSyllabushamesNo ratings yet
- EPSDocument31 pagesEPSChakala BhargavNo ratings yet
- Elecrical EngineeringDocument1 pageElecrical EngineeringUdit Sangwan JaatNo ratings yet
- Eee515 Power SystemDocument2 pagesEee515 Power Systemmanan jeeNo ratings yet
- 1 EE301 Power Generation, Transmission and ProtectionDocument4 pages1 EE301 Power Generation, Transmission and ProtectionAnuja VargheseNo ratings yet
- 1 EE301 Power Generation, Transmission and Protection PDFDocument4 pages1 EE301 Power Generation, Transmission and Protection PDFHaripriya k aNo ratings yet
- 5TH Sem SyllabusDocument16 pages5TH Sem SyllabusHunter HarshaNo ratings yet
- Amie Syllabus Sec B ElectricalDocument19 pagesAmie Syllabus Sec B ElectricalvenkatNo ratings yet
- Sub Engrr Electrical - KSEBDocument4 pagesSub Engrr Electrical - KSEBk keralaNo ratings yet
- Deputy Engineer ElectricalDocument3 pagesDeputy Engineer ElectricalSargi BeepumohanNo ratings yet
- Distribution of Electric Power PDFDocument2 pagesDistribution of Electric Power PDFJosua Sudrajat Marbun67% (6)
- Syllabus B ElectricalDocument6 pagesSyllabus B ElectricalnetprosenjitNo ratings yet
- T&D SyllabusDocument1 pageT&D SyllabusarunjiboseNo ratings yet
- Section BeeDocument14 pagesSection BeeTILAK PATELNo ratings yet
- Syllabus EEE 2019Document5 pagesSyllabus EEE 2019jaberyemeniNo ratings yet
- 132 20 Assistant Electrical InspectorDocument3 pages132 20 Assistant Electrical Inspectorajith sNo ratings yet
- Ee2303 Transmission and DistributionDocument2 pagesEe2303 Transmission and DistributionMuruga RajNo ratings yet
- Power System Analysis.: Unit I IntroductionDocument7 pagesPower System Analysis.: Unit I IntroductionJagadeesh MannivannanNo ratings yet
- Hours Sem. Exam MarksDocument24 pagesHours Sem. Exam MarksshafinshamsudheenNo ratings yet
- Ps 9221 Power System ProtectionDocument24 pagesPs 9221 Power System Protectionsyed1188No ratings yet
- PrudviallaDocument4 pagesPrudviallaPrudhvi AllaNo ratings yet
- Of in EGAT 500 Transinission System: An Analysis Switching Overvoltages KVDocument5 pagesOf in EGAT 500 Transinission System: An Analysis Switching Overvoltages KVKarina LozadaNo ratings yet
- EE301 Power Generation Transmission and Protection PDFDocument3 pagesEE301 Power Generation Transmission and Protection PDFMalavika SNo ratings yet
- Ee2036 Flexible Ac Transmission SystemsDocument2 pagesEe2036 Flexible Ac Transmission SystemsAnbalagan GuruNo ratings yet
- Eee 35Document4 pagesEee 35likhonNo ratings yet
- III Sem SyllbusDocument11 pagesIII Sem SyllbusS B RajNo ratings yet
- Eeguc: Unit I Power GenerationDocument3 pagesEeguc: Unit I Power GenerationJagadeesh MannivannanNo ratings yet
- Ap Eee SyllabusDocument3 pagesAp Eee SyllabusSujith kumarNo ratings yet
- Transmission and DistributionDocument4 pagesTransmission and DistributionMuthamizhan ThiyagarajanNo ratings yet
- Prediction of Transmission Line Overloading UsingDocument23 pagesPrediction of Transmission Line Overloading UsingDevendra SharmaNo ratings yet
- ELECTRICAL TNPSC Engineering Service ExamDocument3 pagesELECTRICAL TNPSC Engineering Service ExamM KumarNo ratings yet
- Electrical Distribution System TopicsDocument20 pagesElectrical Distribution System TopicsIvar Nilasta100% (2)
- Ee801 Power Quality 1. Introduction To Power QualityDocument3 pagesEe801 Power Quality 1. Introduction To Power QualityNarmatha BalachandarNo ratings yet
- Ee2351 PsaDocument2 pagesEe2351 PsaanbuelectricalNo ratings yet
- Harmonic Distortion Caused by Suburban and Underground Rolling Stock With DC Motors - 00618538Document7 pagesHarmonic Distortion Caused by Suburban and Underground Rolling Stock With DC Motors - 00618538npfhNo ratings yet
- Tsgenco-Exam Syllabus SaimedhaDocument14 pagesTsgenco-Exam Syllabus SaimedhasaimedhaNo ratings yet
- Power System EquivalentsDocument6 pagesPower System Equivalentsdallisrinivas14No ratings yet
- Ee6501 Power System AnalysisDocument2 pagesEe6501 Power System AnalysiskrishnandrkNo ratings yet
- Kseb Ae SyllabusDocument4 pagesKseb Ae SyllabusStech 007No ratings yet
- RSMSSB JEN Electrical SyllabusDocument2 pagesRSMSSB JEN Electrical Syllabusashwinivema1980No ratings yet
- PsocDocument1 pagePsocGayan ShashiNo ratings yet
- Power System - Farari 100Document30 pagesPower System - Farari 100Rakesh Kumar RanjanNo ratings yet
- EEE 6th Sem SyllabusDocument6 pagesEEE 6th Sem SyllabusRajesh0% (1)
- Point Wise Notes From AIDocument19 pagesPoint Wise Notes From AIkuldiprana111000No ratings yet
- Curriculum For MTech in Power Systems ProgrammeDocument20 pagesCurriculum For MTech in Power Systems ProgrammeheerapotterNo ratings yet
- Hybrid Passive Filter Design - 2007Document6 pagesHybrid Passive Filter Design - 2007Rizqy Capten Tsubasa OzoraNo ratings yet
- Power System Analysis Syallbus MG Univ KeralaDocument1 pagePower System Analysis Syallbus MG Univ KeralaChristy CyriacNo ratings yet
- Distribution of Electrical Power: Lecture Notes of Distribution of Electrical Power CourseFrom EverandDistribution of Electrical Power: Lecture Notes of Distribution of Electrical Power CourseNo ratings yet
- Investigation of the Usefulness of the PowerWorld Simulator Program: Developed by "Glover, Overbye & Sarma" in the Solution of Power System ProblemsFrom EverandInvestigation of the Usefulness of the PowerWorld Simulator Program: Developed by "Glover, Overbye & Sarma" in the Solution of Power System ProblemsNo ratings yet
- Electric Power Transmission: Lecture Notes of Electric Power Transmission CourseFrom EverandElectric Power Transmission: Lecture Notes of Electric Power Transmission CourseRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- SUNPACKDocument2 pagesSUNPACKRavi SharmaNo ratings yet
- Name of The Student: ANSWER KEY Roll No.: Set:1 Quiz: Power System Lab-1Document1 pageName of The Student: ANSWER KEY Roll No.: Set:1 Quiz: Power System Lab-1Ravi SharmaNo ratings yet
- Mid-Term Examination: RE-APPEAR (New Scheme)Document1 pageMid-Term Examination: RE-APPEAR (New Scheme)Ravi SharmaNo ratings yet
- Power System Lab Quiz Set 1Document3 pagesPower System Lab Quiz Set 1Ravi SharmaNo ratings yet
- Name of The Student: ANSWER KEY Roll No.: Set:1 Quiz: Power System Lab-1Document1 pageName of The Student: ANSWER KEY Roll No.: Set:1 Quiz: Power System Lab-1Ravi SharmaNo ratings yet
- Power System 1 Lab Quiz Set2Document4 pagesPower System 1 Lab Quiz Set2Ravi SharmaNo ratings yet
- Holidays' Homework: Class - VDocument4 pagesHolidays' Homework: Class - VRavi SharmaNo ratings yet
- SHS™ Solar Controller: - High Reliability - Low Cost - Electronic Protections - Tropicalization - Easy To UseDocument2 pagesSHS™ Solar Controller: - High Reliability - Low Cost - Electronic Protections - Tropicalization - Easy To UseRavi SharmaNo ratings yet
- DC Solar Pumps New-3 PDFDocument3 pagesDC Solar Pumps New-3 PDFRavi SharmaNo ratings yet
- HVDCDocument1 pageHVDCRavi SharmaNo ratings yet
- ApplicationDocument1 pageApplicationRavi SharmaNo ratings yet
- ps2 SyllabusDocument1 pageps2 SyllabusRavi SharmaNo ratings yet
- Em Ii PDFDocument76 pagesEm Ii PDFRavi SharmaNo ratings yet
- List of Nominations Received For This Schedule: Execution of Nofn Utilizing FTTH Tech. (Batch No:1)Document3 pagesList of Nominations Received For This Schedule: Execution of Nofn Utilizing FTTH Tech. (Batch No:1)Ravi SharmaNo ratings yet
- ICEEE2015Document1 pageICEEE2015Ravi SharmaNo ratings yet
- Power in India From Different SourcesDocument1 pagePower in India From Different SourcesRavi SharmaNo ratings yet
- Dynamic Voltage Restorer Against Voltage SagDocument6 pagesDynamic Voltage Restorer Against Voltage SaghusamyesilNo ratings yet
- DigsilentDocument2 pagesDigsilentRavi SharmaNo ratings yet
- UPSC - Registration SlipDocument1 pageUPSC - Registration SlipRavi SharmaNo ratings yet