Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Based On Infrastructure
Based On Infrastructure
Uploaded by
Chinmoy GhoraiOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Based On Infrastructure
Based On Infrastructure
Uploaded by
Chinmoy GhoraiCopyright:
Available Formats
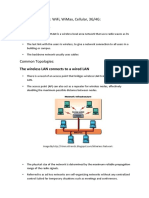
Classification of wireless networks Based on infrastructure Based on mobility Based on size of network Based on infrastructure Infrastructure networks Base
Base station/ Access point infrastructure Generally one-hop networks E.g.: Cellular, Wireless LANs,
Ad-hoc networks Remote nodes capable of coordinating to form a network Multi-hop wireless links common
Based on Mobility Static wireless networks Why do we need wireless access in such scenarios? Harsh Terrain Cost-effectiveness
E.g.: Enabling internet access to a remote village
Mobile wireless networks A part of wireless nodes are mobile E.g.: Cellular networks, Mobile Ad-hoc networks (MANETs)
Challenges: Sustaining opened connections
Naming
E.g.: Mobile IP
Moving to different network
Based on size of the network Body Area Networks E.g.: Sensors inserted inside the body coordinate
Personal Area Networks E.g.: Home Networking, Bluetooth and Zigbee networks
Local Area Networks E.g.: Wireless LANs, WiFi
Metropolitan Area Networks E.g.: Community wireless networks
Wide Area Networks E.g.: Cellular and Satellite networks
Wireless Networks
Based on infrastructure
Based on mobility
Based on size of network
Infrastructure networks E.g.: Cellular, Wireless LANs
Static wireless networks E.g.: Enabling internet access to a remote village
LAN E.g.: Wireless LANs, WiFi
Ad-hoc networks E.g.: Multi-hop wireless links
Mobile wireless networks E.g.: Cellular networks, Mobile Ad-hoc networks (MANETs)
MAN E.g.: Community wireless networks
WAN E.g.: Cellular and Satellite networks
You might also like
- Wireless Computer NetworkingDocument6 pagesWireless Computer Networkingsirus starNo ratings yet
- Wireless Communication1234Document13 pagesWireless Communication1234AbhijitNo ratings yet
- Wireless NetworkingDocument11 pagesWireless NetworkingSoumitri MukherjeeNo ratings yet
- Mobile Computing Unit 2Document158 pagesMobile Computing Unit 2Sabhya SharmaNo ratings yet
- WCMC Chapter 1 - IntroductionDocument35 pagesWCMC Chapter 1 - IntroductionGetaneh AwokeNo ratings yet
- How The Two Adhoc Networks Can Be Different: Manet & WSNS: Vandana Jindal, A.K.Verma, Seema BawaDocument5 pagesHow The Two Adhoc Networks Can Be Different: Manet & WSNS: Vandana Jindal, A.K.Verma, Seema BawaVikram HegdeNo ratings yet
- Aim: Study WDN, Its Types and Cellular Network Theory: Wireless NetworkDocument12 pagesAim: Study WDN, Its Types and Cellular Network Theory: Wireless NetworkShekhar DahiyaNo ratings yet
- LAN - Local Area NetworkDocument25 pagesLAN - Local Area Networkprasd08No ratings yet
- SETTING-UP COMPUTER NETWORKS1Document31 pagesSETTING-UP COMPUTER NETWORKS1Richard SugboNo ratings yet
- Unit - 1 Wireless Network Definition - What Does Wireless Network Mean?Document21 pagesUnit - 1 Wireless Network Definition - What Does Wireless Network Mean?thilagaNo ratings yet
- Cross Layer Doc EditedDocument52 pagesCross Layer Doc EditedStartechnico TechnocratsNo ratings yet
- 1.1 General: Wireless NetworksDocument52 pages1.1 General: Wireless NetworksStartechnico TechnocratsNo ratings yet
- Cross Layer Doc EditedDocument52 pagesCross Layer Doc EditedStartechnico TechnocratsNo ratings yet
- Week 1 Theory NotesDocument6 pagesWeek 1 Theory NotesZzzzNo ratings yet
- Wireless NetworkiDocument13 pagesWireless Networkiaditya negiNo ratings yet
- WCMC Chapter 1 - Introduction UpdatedDocument34 pagesWCMC Chapter 1 - Introduction Updatedmelesew mossieNo ratings yet
- Basics Mesh NetworksDocument6 pagesBasics Mesh NetworksPrasad KaleNo ratings yet
- WCMC Chapter 1 - IntroductionDocument32 pagesWCMC Chapter 1 - Introductiontyv89783No ratings yet
- Telecommunications, The Internet, and Wireless TechnologyDocument28 pagesTelecommunications, The Internet, and Wireless TechnologyvivianrereloluwaNo ratings yet
- Vtc4pjpoqyem0fafwygz Signature Poli 170330091323 - CompressedDocument13 pagesVtc4pjpoqyem0fafwygz Signature Poli 170330091323 - CompressedAmitNo ratings yet
- Lecture 1 Fundamental Techniques in The Design and Operation of First, Second, andDocument9 pagesLecture 1 Fundamental Techniques in The Design and Operation of First, Second, andayanali6337No ratings yet
- FTTA - Fiber To The AntennaDocument16 pagesFTTA - Fiber To The AntennaNaresh YadavNo ratings yet
- Section 1 - Distinguish Among Ttypes of NetworksDocument7 pagesSection 1 - Distinguish Among Ttypes of NetworksJade SpencerNo ratings yet
- WC Unit-1Document35 pagesWC Unit-1Gopi Krishna stylish foreverNo ratings yet
- Lecture - 4 PDFDocument34 pagesLecture - 4 PDFLatera FekedeNo ratings yet
- 7 Types of Computer Networks ScriptDocument3 pages7 Types of Computer Networks ScriptJeetNo ratings yet
- Wireless NetworksDocument2 pagesWireless NetworksRahul KshirsagarNo ratings yet
- Wireless NetworkDocument5 pagesWireless NetworkSoumitri MukherjeeNo ratings yet
- Wimax Quick GuideDocument16 pagesWimax Quick GuideramyaNo ratings yet
- LAN (Local Area Network) : Network. Common Examples of Area Network Types AreDocument7 pagesLAN (Local Area Network) : Network. Common Examples of Area Network Types AreSharifah JaafarNo ratings yet
- Connection Method: Arpa ArpanetDocument9 pagesConnection Method: Arpa ArpanetpraveenembassyNo ratings yet
- New Microsoft Word DocumentDocument2 pagesNew Microsoft Word Documentmiddlesex5No ratings yet
- Wireless and Mobile Communications: Dr. Surbhi SharmaDocument42 pagesWireless and Mobile Communications: Dr. Surbhi SharmaShubham MittalNo ratings yet
- Intoduction To Computer NetworksDocument9 pagesIntoduction To Computer NetworksPrashant SinghNo ratings yet
- Introduction To NetworkDocument5 pagesIntroduction To NetworkDiaryJade Peña CortesNo ratings yet
- Mba AssignmentDocument17 pagesMba AssignmentFatima AliNo ratings yet
- Wireless Communication: - B Y Vaneetg. Pokhrajp. Ayush D. Sahil KDocument11 pagesWireless Communication: - B Y Vaneetg. Pokhrajp. Ayush D. Sahil KAyush DevalNo ratings yet
- Unit I:: Nodes) Connected by Communication Links. A Node Can Be A Computer, PrinterDocument27 pagesUnit I:: Nodes) Connected by Communication Links. A Node Can Be A Computer, PrinterPavanNo ratings yet
- Network 1Document15 pagesNetwork 1Gaurav MishraNo ratings yet
- CH-1 Wireless Communication: What Is Mobile Computing?Document9 pagesCH-1 Wireless Communication: What Is Mobile Computing?tomakobNo ratings yet
- Wireless TechnologyDocument27 pagesWireless TechnologyHoney ShewkaniNo ratings yet
- Handout (I.t.)Document7 pagesHandout (I.t.)Ryhaan HussainNo ratings yet
- Wireless - Merits & DemeritsDocument10 pagesWireless - Merits & DemeritsAnirudhan RaviNo ratings yet
- 3G vs. Wifi: Presented By:-DEEPAK GUPTA 0911HDSSD104Document36 pages3G vs. Wifi: Presented By:-DEEPAK GUPTA 0911HDSSD104Deepak GuptaNo ratings yet
- Wireless and Mobile CommunicationsDocument45 pagesWireless and Mobile Communicationsumer plays gameNo ratings yet
- Arunachalam PL: Presented & Performed byDocument34 pagesArunachalam PL: Presented & Performed byRam PrasathNo ratings yet
- UNIT 3 Notes For Students - 2Document49 pagesUNIT 3 Notes For Students - 2deepesh_gaonkarNo ratings yet
- AIM: Case Study On Wireless Access Point TheoryDocument4 pagesAIM: Case Study On Wireless Access Point TheoryHarshad SolankiNo ratings yet
- Presentation On Wireless Technologies Submitted By:-Arvind ROLL NO..17 10809501Document18 pagesPresentation On Wireless Technologies Submitted By:-Arvind ROLL NO..17 10809501Chaitali BinzadeNo ratings yet
- Computer Network ConceptsDocument8 pagesComputer Network ConceptsMozart Luther MagbanuaNo ratings yet
- Modul 2 EnglishDocument10 pagesModul 2 EnglishblablablaNo ratings yet
- Cambridge Grade 6 - Connections Are Made Accessing The InternetDocument24 pagesCambridge Grade 6 - Connections Are Made Accessing The InternetNAZREEN SHANIYASNo ratings yet
- Networking Concepts - BasicsDocument33 pagesNetworking Concepts - BasicsSukh SandhuNo ratings yet
- Wireless IntroductionDocument2 pagesWireless Introductionloka08260No ratings yet
- Types of Wireless Applications: RadioDocument6 pagesTypes of Wireless Applications: RadioAbdulkerim TiriasNo ratings yet
- Wi-Max & Wi-MAXDocument31 pagesWi-Max & Wi-MAXkumarswamykcNo ratings yet
- Topics in Computer Networks: by Mr. Fasee Ullah CUSIT PeshawarDocument37 pagesTopics in Computer Networks: by Mr. Fasee Ullah CUSIT PeshawarNewklear HurtedNo ratings yet
- Wireless and Mobile Networks - 2022Document69 pagesWireless and Mobile Networks - 2022Jiru MuletaNo ratings yet