Professional Documents
Culture Documents
The Processor (CPU) : It Consists of Two Parts
The Processor (CPU) : It Consists of Two Parts
Uploaded by
MuktadirhasanOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
The Processor (CPU) : It Consists of Two Parts
The Processor (CPU) : It Consists of Two Parts
Uploaded by
MuktadirhasanCopyright:
Available Formats
The Processor (CPU)
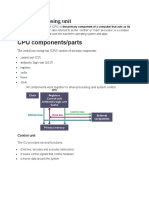
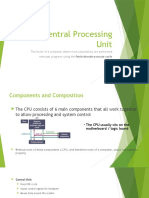
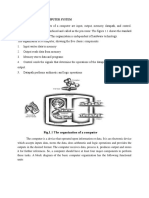
A Processor is a multipurpose, programmable device, designed to incorporate the functions of a Computers CPU on a single IC, which accepts digital data as input, processes it according to instructions stored in its memory and provides results as output. It consists of two parts: Processing Unit/Control Unit (CU): Tells computer system how to carry out a programs instructions. Arithmetic Logic Unit (ALU): Performs arithmetic operations, logical operations, and controls the speed of operations
An example of Processor
Main memory (RAM)
It is called: primary storage, internal memory, Random Access Memory Ram(RAM) Data can be stored and retrieved from anywhere It needs approximately equal amount of time Its volatile and stores data temporarily It determines the speed and amount of data can be processed
Lose information when not powered
Registers
A register is a mall amount of memory available as a part for microprocessor that temporarily stores data during processing and provide working areas. Holds materials to be processed immediately Loads instructions and data in registers before processing Provides fastest way to access data Types of Registers Instruction register (holds instruction being executed) Address register (holds locations of data to be processed) Program register (holds status information) Accumulator (holds the results of the ALUs logic operations)
You might also like
- Lecture 1 Computer FundamentalsDocument2 pagesLecture 1 Computer FundamentalsSitmCompSansthanNo ratings yet
- The Central Presentation Unit: What Is The CPU? The Microprocessor Structure of The CPU Parts of The CPUDocument13 pagesThe Central Presentation Unit: What Is The CPU? The Microprocessor Structure of The CPU Parts of The CPUBrandonNo ratings yet
- UNIT 2 - Computer System HardwareDocument17 pagesUNIT 2 - Computer System HardwareComputer75% (4)
- Pps NotesDocument193 pagesPps Notesatulya singhNo ratings yet
- Pps Notes (4 Files Merged)Document175 pagesPps Notes (4 Files Merged)atulya singhNo ratings yet
- Name - I-WPS OfficeDocument2 pagesName - I-WPS OfficeleramooluwatosinjohnNo ratings yet
- Computer OrganizationDocument16 pagesComputer OrganizationInnocent ChukwumaNo ratings yet
- Computing FundamentalsDocument10 pagesComputing Fundamentalsitezaz ahmedNo ratings yet
- File 1674110529 5000677 1.1FunctionalblocksofacomputerCPUmemoryinput-outputsubsystemscontrolunitDocument3 pagesFile 1674110529 5000677 1.1FunctionalblocksofacomputerCPUmemoryinput-outputsubsystemscontrolunitManaswi GargNo ratings yet
- 13.01 Lesson Notes Input DevicesDocument20 pages13.01 Lesson Notes Input DevicesjeannenhangaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3Document8 pagesChapter 3HeinNo ratings yet
- Central Processing UnitDocument5 pagesCentral Processing Unitchintu yadavNo ratings yet
- Fundamental of Computer ProgrammingDocument93 pagesFundamental of Computer ProgrammingSarmi HarshaNo ratings yet
- CSC 111 - (3) Computer HardwareDocument39 pagesCSC 111 - (3) Computer Hardwarevictoriaiyanuoluwa40No ratings yet
- Computer ArchitectureDocument5 pagesComputer Architectureapi-417400228No ratings yet
- Muhammad Zeeshan CMS ID:17187 Subject:Itc Teacher:Sir Sibghatullah Program:Bs Chemical (2)Document9 pagesMuhammad Zeeshan CMS ID:17187 Subject:Itc Teacher:Sir Sibghatullah Program:Bs Chemical (2)Junaid KhurshidNo ratings yet
- Lec 3Document4 pagesLec 3CJ SNo ratings yet
- HardwareDocument26 pagesHardwareSHITAL PRAJAPATINo ratings yet
- CPU - Central Processing UnitDocument10 pagesCPU - Central Processing UnitJay Ambadkar100% (5)
- Computer System Computer ArchitectureDocument7 pagesComputer System Computer ArchitectureSuman Samal MagarNo ratings yet
- Components of A ComputerDocument5 pagesComponents of A ComputersoujanaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2Document15 pagesChapter 2Ramya RamamurthyNo ratings yet
- Acn CpuDocument9 pagesAcn CpuHarshraj SinghNo ratings yet
- Chapter ThreeDocument14 pagesChapter ThreeHabtie TesfahunNo ratings yet
- CO - OS Unit-1 (Part1)Document40 pagesCO - OS Unit-1 (Part1)ffjsNo ratings yet
- Block Diagram of CoimputerDocument4 pagesBlock Diagram of CoimputerShailaja VadgaonkarNo ratings yet
- Computer Organisation: CPU ArchitectureDocument4 pagesComputer Organisation: CPU ArchitectureSamhunguNo ratings yet
- In The Heart of Computers-Trabalho de TraduçãoDocument2 pagesIn The Heart of Computers-Trabalho de TraduçãoMaiPereiraSilva100% (1)
- Unit 1 - Computer Organization and Architecture - WWW - Rgpvnotes.inDocument33 pagesUnit 1 - Computer Organization and Architecture - WWW - Rgpvnotes.inRanjana DalwaniNo ratings yet
- Computer OrganizationDocument11 pagesComputer OrganizationChristian Jhay OigaNo ratings yet
- The Central Processing UnitDocument14 pagesThe Central Processing UnitBwoii SammsNo ratings yet
- 212 CPU & RegistersDocument7 pages212 CPU & RegistersSantosh ChandraNo ratings yet
- Cpu Final NotesDocument6 pagesCpu Final NotesSonu zehen001No ratings yet
- General Organisation of A Micro ProcessorDocument8 pagesGeneral Organisation of A Micro ProcessornelsrodrigNo ratings yet
- Computer System and Its ComponentsDocument14 pagesComputer System and Its ComponentsAleeza gondalNo ratings yet
- GROUPN5Document5 pagesGROUPN5marcolifa167No ratings yet
- Functional Components of A ComputerDocument11 pagesFunctional Components of A Computerypk10072003No ratings yet
- ASSIGNMENTDocument5 pagesASSIGNMENTTakir MasalinNo ratings yet
- Lecture 5Document20 pagesLecture 5ranaabdullah49677No ratings yet
- Von NeumannDocument22 pagesVon NeumannĐường Minh TríNo ratings yet
- COA NotesDocument49 pagesCOA Noteseunicewamuyu76No ratings yet
- 05 System UnitnDocument9 pages05 System UnitnInomusa MhlopeNo ratings yet
- Programming For Problem Solving-NotesDocument52 pagesProgramming For Problem Solving-NotesVeeramaniNo ratings yet
- Lesson: The Computer System HardwareDocument9 pagesLesson: The Computer System HardwareKim - Gabriel TanNo ratings yet
- What Is A Computer?Document20 pagesWhat Is A Computer?Arpita SrivastavaNo ratings yet
- Week 3Document17 pagesWeek 3Abdullatif KhanNo ratings yet
- Lec04 - Types of RegistersDocument17 pagesLec04 - Types of RegistersBilal ImranNo ratings yet
- I O D S S D: Nput AND Utput Evices Econda RY Torage EvicesDocument5 pagesI O D S S D: Nput AND Utput Evices Econda RY Torage EvicesBhaskar NaiduNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Computer HardwareDocument5 pagesIntroduction To Computer HardwareMartin YaoNo ratings yet
- Hardware Organisation of Computers and MicroprocessorsDocument33 pagesHardware Organisation of Computers and MicroprocessorsUchenna OgunkaNo ratings yet
- YideDocument1 pageYideFikru TesefayeNo ratings yet
- Coa Unit-1Document21 pagesCoa Unit-1singhshiva8082No ratings yet
- Introduction To Computer Application: Course Code: IS-125Document11 pagesIntroduction To Computer Application: Course Code: IS-125Sohail KhanNo ratings yet
- Unit 4 Computer Organization OrganizationDocument71 pagesUnit 4 Computer Organization OrganizationYash DongareNo ratings yet
- X86 Modes Processors: Basic Design of MicrocomputerDocument2 pagesX86 Modes Processors: Basic Design of MicrocomputerBianca Axel GarciaNo ratings yet
- What Is RegisterDocument2 pagesWhat Is RegisterHaris Akram100% (1)
- عمورDocument10 pagesعمورshehtao407No ratings yet
- Components of Computer: Hardware Software HardwareDocument9 pagesComponents of Computer: Hardware Software Hardwarerashidqureshi6944No ratings yet
- Computer Scince Engineering Part2Document5 pagesComputer Scince Engineering Part2shubberselmanNo ratings yet
- Internship Report On Employee Satisfaction of Bengal Group of IndustriesDocument39 pagesInternship Report On Employee Satisfaction of Bengal Group of IndustriesMuktadirhasan100% (1)
- Questionnaire of Measuring Employee Satisfaction at Bengal Group of IndustriesDocument2 pagesQuestionnaire of Measuring Employee Satisfaction at Bengal Group of IndustriesMuktadirhasanNo ratings yet
- Md. Jahidur Rahman Zia: ObjectiveDocument3 pagesMd. Jahidur Rahman Zia: ObjectiveMuktadirhasanNo ratings yet
- Md. Muktadir Hasan: Name of Degree Institute Board/ University Result (G.P.A) Year of PassingDocument2 pagesMd. Muktadir Hasan: Name of Degree Institute Board/ University Result (G.P.A) Year of PassingMuktadirhasanNo ratings yet
- Hanger Industry Based On Porter's Five ForcesDocument4 pagesHanger Industry Based On Porter's Five ForcesMuktadirhasanNo ratings yet
- Assignment On Padma Islami Life Insurance Co. Ltd.Document21 pagesAssignment On Padma Islami Life Insurance Co. Ltd.Muktadirhasan100% (3)
- Assignment On Computer HardwareDocument9 pagesAssignment On Computer HardwareMuktadirhasan100% (1)
- A Report On HR Practice in GP, by Rangdhonu, Dept - MarketingDocument34 pagesA Report On HR Practice in GP, by Rangdhonu, Dept - MarketingMuktadirhasanNo ratings yet