Professional Documents
Culture Documents
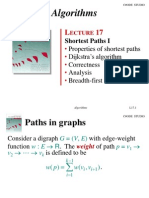
CS 332: Algorithms: Single-Source Shortest Path
CS 332: Algorithms: Single-Source Shortest Path
Uploaded by
Rodolfo Sabala VeilesCopyright:
Available Formats
You might also like
- Graphs: Shortest Paths, Job Scheduling Problem, Huffman CodeDocument25 pagesGraphs: Shortest Paths, Job Scheduling Problem, Huffman CodeVikalp Panseriya100% (1)
- Dies TelDocument28 pagesDies TelAtique KhattakNo ratings yet
- Lecture 26Document80 pagesLecture 26Anonymous niE5VQOHNo ratings yet
- Lecture 25Document63 pagesLecture 25Anonymous niE5VQOHNo ratings yet
- Vdocument - in - Advanced Algorithm Design and AnalysisDocument94 pagesVdocument - in - Advanced Algorithm Design and AnalysisjutuquhNo ratings yet
- Explanation of PrimDocument16 pagesExplanation of PrimdevangNo ratings yet
- Chap 0Document12 pagesChap 0akspengueNo ratings yet
- 600.363/463 Algorithms - Fall 2013 Solution To Assignment 7: (40 Points)Document1 page600.363/463 Algorithms - Fall 2013 Solution To Assignment 7: (40 Points)ashish mehtaNo ratings yet
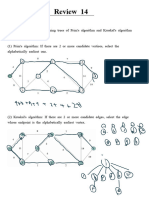
- Review 14 Minimum Spanning TreesDocument2 pagesReview 14 Minimum Spanning Treesmungt0495No ratings yet
- Lect 20Document19 pagesLect 20Hare Krishna RajNo ratings yet
- Design and Analysis of Algorithms CO 401: Ash Mohammad AbbasDocument18 pagesDesign and Analysis of Algorithms CO 401: Ash Mohammad AbbasMohd Nafees AnsariNo ratings yet
- CS 332: Algorithms: Dijkstra's Algorithm Disjoint-Set UnionDocument46 pagesCS 332: Algorithms: Dijkstra's Algorithm Disjoint-Set UnionAnonymous niE5VQOHNo ratings yet
- Gram SchmidtDocument2 pagesGram Schmidtcoolboy_usamaNo ratings yet
- SSSP2Document7 pagesSSSP2joshiparas1234No ratings yet
- 09 CS316 - Algorithms - Graph 3 - SSPDocument29 pages09 CS316 - Algorithms - Graph 3 - SSPEssamNo ratings yet
- INF143Disjoint Set UnionDocument16 pagesINF143Disjoint Set UnionIvan ChurquiNo ratings yet
- DijkstraAlgorithmThe Shortest Path AlgorithmDocument3 pagesDijkstraAlgorithmThe Shortest Path AlgorithmSudharsan Amalraj JothirajNo ratings yet
- 17 Shortest Paths IDocument59 pages17 Shortest Paths ITanmay BaranwalNo ratings yet
- Universidad Politecnica de Madrid Escuela Técnica Superior de Ingenieros Industriales Ingeniería Del Medio AmbienteDocument6 pagesUniversidad Politecnica de Madrid Escuela Técnica Superior de Ingenieros Industriales Ingeniería Del Medio AmbienteDavid PerezNo ratings yet
- Q1. Use IF Statement To Design Positive Edge Triggered SR Flip FlopDocument5 pagesQ1. Use IF Statement To Design Positive Edge Triggered SR Flip Flop213698 ktr.et.ece.15No ratings yet
- Ecen 248 Prelab 10Document2 pagesEcen 248 Prelab 10Rebecca Sontheimer100% (2)
- Bellman FordDocument9 pagesBellman FordIstiaque AhmedNo ratings yet
- Digital Signal Processing: Name:-Ayush Yadav REG. NO.:-17BEC0555 SLOT: - G1+TG1Document11 pagesDigital Signal Processing: Name:-Ayush Yadav REG. NO.:-17BEC0555 SLOT: - G1+TG1Ayush YadavNo ratings yet
- V Adj U V QDocument5 pagesV Adj U V QDiego EspinozaNo ratings yet
- Lec16 DijkstraDocument24 pagesLec16 DijkstrajituNo ratings yet
- Pro 11 and 12Document10 pagesPro 11 and 12PoraNo ratings yet
- Formulas P1Document1 pageFormulas P1josegandica23No ratings yet
- DAA AkshatDocument22 pagesDAA Akshathemuup08No ratings yet
- 17 DifferentiationDocument27 pages17 DifferentiationAdinda ANNo ratings yet
- Shor MediumDocument7 pagesShor Mediuminumpudi.sushanthNo ratings yet
- Dijkstra's AlgorithmDocument59 pagesDijkstra's AlgorithmTanmay BaranwalNo ratings yet
- Graph BFS - DFSDocument64 pagesGraph BFS - DFS19050 Anish RoyNo ratings yet
- אלגוריתמים- הרצאה 7 - Single Source Shortest Path ProblemDocument5 pagesאלגוריתמים- הרצאה 7 - Single Source Shortest Path ProblemRonNo ratings yet
- Gate 2014 SolutionsDocument25 pagesGate 2014 SolutionsNaim Maktumbi NesaragiNo ratings yet
- hw10 Calc3Document11 pageshw10 Calc3crazycatlady1119No ratings yet
- 线性系统理论(s5 1)2023Document164 pages线性系统理论(s5 1)2023562713320sxNo ratings yet
- Devoir 6Document3 pagesDevoir 6Éric JarroldNo ratings yet
- Name - Shashank Vinit Reg No - 1801227689: Lab 3 AssignmentDocument6 pagesName - Shashank Vinit Reg No - 1801227689: Lab 3 AssignmentShashank VinitNo ratings yet
- SV Code ExamplsDocument162 pagesSV Code Examplskavya devulapalliNo ratings yet
- Embalse Lineal Como ODE: Ecuación DiferencialDocument5 pagesEmbalse Lineal Como ODE: Ecuación DiferencialKevin EchêvêrryNo ratings yet
- Small Oscillations, Stability and Normal Modes:: Ij I JDocument1 pageSmall Oscillations, Stability and Normal Modes:: Ij I JShweta SridharNo ratings yet
- Intractable Problems: Part OneDocument29 pagesIntractable Problems: Part OneFahiNo ratings yet
- Intractable Problems: Part OneDocument29 pagesIntractable Problems: Part OneFahiNo ratings yet
- Ecture: 5. Would It Be OK If We Used A Stack Here (As We Could For Topsort) ??Document3 pagesEcture: 5. Would It Be OK If We Used A Stack Here (As We Could For Topsort) ??Kat HawthorneNo ratings yet
- Nicolas Cuadros Taller Final Matematicas AplicadasDocument3 pagesNicolas Cuadros Taller Final Matematicas AplicadasNicolas CuadrosNo ratings yet
- Assignment 4Document3 pagesAssignment 4Hugu JujuNo ratings yet
- SASBTE Solutions 1 4 PDFDocument3 pagesSASBTE Solutions 1 4 PDFEdwinDuranJr.No ratings yet
- SASBTE Solutions 1 4 PDFDocument3 pagesSASBTE Solutions 1 4 PDFEdwinDuranJr.No ratings yet
- A Star Teb01Document4 pagesA Star Teb01utkarshNo ratings yet
- Shortest Paths I: Properties, Dijkstra's Algorithm, Breadth-First SearchDocument38 pagesShortest Paths I: Properties, Dijkstra's Algorithm, Breadth-First SearchYashashavi LadhaNo ratings yet
- GATE 2014 Electronics Engineering Keys & Solution On 16th (Evening Session)Document15 pagesGATE 2014 Electronics Engineering Keys & Solution On 16th (Evening Session)Lokesh Kumar0% (1)
- GM and Pre Cal PTDocument3 pagesGM and Pre Cal PTFrancois DonaireNo ratings yet
- 368 PrimMinSpanningTreeFunctionC++Document2 pages368 PrimMinSpanningTreeFunctionC++Dhruvika HoneyNo ratings yet
- Klausur2023 solutionMKDocument3 pagesKlausur2023 solutionMKRichard SalnikovNo ratings yet
- AP Exp 3.2 - RupeshDocument3 pagesAP Exp 3.2 - RupeshShubham KumarNo ratings yet
- ADS Assignment - 2: Problem Statement: Implement Prim's/Kruskal AlgorithmDocument3 pagesADS Assignment - 2: Problem Statement: Implement Prim's/Kruskal AlgorithmATHARVA DOIFODENo ratings yet
- Algorithm Final Exam (Spring 2009) : NameDocument12 pagesAlgorithm Final Exam (Spring 2009) : Nameきむら たくやNo ratings yet
- NumberTheory Part 2Document22 pagesNumberTheory Part 2MDRAKIB180 107No ratings yet
- Manan DaaDocument32 pagesManan DaaDhruv MishraNo ratings yet
- COS10003 - Computer & Logic Essentials Assignment 3: Algorithms, Graphs and CountingDocument9 pagesCOS10003 - Computer & Logic Essentials Assignment 3: Algorithms, Graphs and CountingHiếu PhanNo ratings yet
- Easy Mod Probs-SolDocument28 pagesEasy Mod Probs-SolYonatan Ysrael ZuritaNo ratings yet
- Combinatorics SyllabusDocument2 pagesCombinatorics SyllabusMiliyon TilahunNo ratings yet
- Edge-Magic Total LabelingsDocument15 pagesEdge-Magic Total LabelingsReni w ningsihNo ratings yet
- Sample Paper: Sof International Mathematics OlympiadDocument2 pagesSample Paper: Sof International Mathematics OlympiadJuna ManroeNo ratings yet
- Graph Theory Tutorial SheetDocument4 pagesGraph Theory Tutorial Sheetavnishgarg96No ratings yet
- BFS DFS Applicatio PDFDocument9 pagesBFS DFS Applicatio PDFVineet Kumar KanthNo ratings yet
- Lecture 14 (BFS, DFS)Document52 pagesLecture 14 (BFS, DFS)avinashNo ratings yet
- 12 Euler Ham PDFDocument10 pages12 Euler Ham PDFErnesy John ArrezaNo ratings yet
- 16.1 Practice ABCDocument2 pages16.1 Practice ABC718697No ratings yet
- Hamiltonion PathDocument15 pagesHamiltonion PathPrince KirarNo ratings yet
- Graphing Quadratic Functions 5Document3 pagesGraphing Quadratic Functions 5Ricardo GarciaNo ratings yet
- DAA Unit IV - Backtracking and Branch Bound PPT by Vijay MantriDocument53 pagesDAA Unit IV - Backtracking and Branch Bound PPT by Vijay Mantriomkarmohare18No ratings yet
- 6.854J / 18.415J Advanced Algorithms : Mit OpencoursewareDocument8 pages6.854J / 18.415J Advanced Algorithms : Mit OpencoursewarejhdmssNo ratings yet
- Problem Sheet-1Document2 pagesProblem Sheet-1Ankit SharmaNo ratings yet
- 1.coordinate Plane-Graphing PointsDocument2 pages1.coordinate Plane-Graphing Pointsavijitcu2007No ratings yet
- Ri) Urh - KL CF Cc!.Ifltation - Al Physics (Document6 pagesRi) Urh - KL CF Cc!.Ifltation - Al Physics (terradeathNo ratings yet
- Unit Test - Slope and Linear GraphsDocument7 pagesUnit Test - Slope and Linear GraphsRomalyn VillegasNo ratings yet
- Midterm 1 SolutionsDocument7 pagesMidterm 1 Solutionsshivani_himaniNo ratings yet
- CSC 224 TreesDocument13 pagesCSC 224 TreesKipyegon CheruiyotNo ratings yet
- Asst6 Math 239Document4 pagesAsst6 Math 239giselle_rochfordNo ratings yet
- Maquina de Vetores SuporteDocument19 pagesMaquina de Vetores SuporteISRAel JuniorNo ratings yet
- Vector Network Analysis - GRASS-WikiDocument6 pagesVector Network Analysis - GRASS-WikiSamuel Fernando Mesa GiraldoNo ratings yet
- CSE2208-Lab ManualDocument28 pagesCSE2208-Lab Manualnadif hasan purnoNo ratings yet
- Modul Biology Juj 2007Document218 pagesModul Biology Juj 2007genga100% (1)
- Rada F. Mihalcea, Dragomir R. Radev - Graph-Based Natural Language Processing and Information Retrieval-Cambridge University Press (2011)Document202 pagesRada F. Mihalcea, Dragomir R. Radev - Graph-Based Natural Language Processing and Information Retrieval-Cambridge University Press (2011)javier veraNo ratings yet
- Order Prime GraphDocument8 pagesOrder Prime GraphsattanathanNo ratings yet
- CD3291 Data Structures and Algorithms Lecture Notes 1Document162 pagesCD3291 Data Structures and Algorithms Lecture Notes 1goldentraders2574No ratings yet
- Data Structure and AlgosDocument4 pagesData Structure and AlgosChemical NITTNo ratings yet
CS 332: Algorithms: Single-Source Shortest Path
CS 332: Algorithms: Single-Source Shortest Path
Uploaded by
Rodolfo Sabala VeilesOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
CS 332: Algorithms: Single-Source Shortest Path
CS 332: Algorithms: Single-Source Shortest Path
Uploaded by
Rodolfo Sabala VeilesCopyright:
Available Formats
David Luebke 1 4/19/2014
CS 332: Algorithms
Single-Source Shortest Path
David Luebke 2 4/19/2014
Review: Prims Algorithm
MST-Prim(G, w, r)
Q = V[G];
for each u e Q
key[u] = ;
key[r] = 0;
p[r] = NULL;
while (Q not empty)
u = ExtractMin(Q);
for each v e Adj[u]
if (v e Q and w(u,v) < key[v])
p[v] = u;
key[v] = w(u,v);
David Luebke 3 4/19/2014
Review: Prims Algorithm
MST-Prim(G, w, r)
Q = V[G];
for each u e Q
key[u] = ;
key[r] = 0;
p[r] = NULL;
while (Q not empty)
u = ExtractMin(Q);
for each v e Adj[u]
if (v e Q and w(u,v) < key[v])
p[v] = u;
key[v] = w(u,v);
14
10
3
6 4
5
2
9
15
8
Run on example graph
David Luebke 4 4/19/2014
Review: Prims Algorithm
MST-Prim(G, w, r)
Q = V[G];
for each u e Q
key[u] = ;
key[r] = 0;
p[r] = NULL;
while (Q not empty)
u = ExtractMin(Q);
for each v e Adj[u]
if (v e Q and w(u,v) < key[v])
p[v] = u;
key[v] = w(u,v);
14
10
3
6 4
5
2
9
15
8
Run on example graph
David Luebke 5 4/19/2014
Review: Prims Algorithm
MST-Prim(G, w, r)
Q = V[G];
for each u e Q
key[u] = ;
key[r] = 0;
p[r] = NULL;
while (Q not empty)
u = ExtractMin(Q);
for each v e Adj[u]
if (v e Q and w(u,v) < key[v])
p[v] = u;
key[v] = w(u,v);
0
14
10
3
6 4
5
2
9
15
8
Pick a start vertex r
r
David Luebke 6 4/19/2014
Review: Prims Algorithm
MST-Prim(G, w, r)
Q = V[G];
for each u e Q
key[u] = ;
key[r] = 0;
p[r] = NULL;
while (Q not empty)
u = ExtractMin(Q);
for each v e Adj[u]
if (v e Q and w(u,v) < key[v])
p[v] = u;
key[v] = w(u,v);
0
14
10
3
6 4
5
2
9
15
8
Red vertices have been removed from Q
u
David Luebke 7 4/19/2014
Review: Prims Algorithm
MST-Prim(G, w, r)
Q = V[G];
for each u e Q
key[u] = ;
key[r] = 0;
p[r] = NULL;
while (Q not empty)
u = ExtractMin(Q);
for each v e Adj[u]
if (v e Q and w(u,v) < key[v])
p[v] = u;
key[v] = w(u,v);
0
3
14
10
3
6 4
5
2
9
15
8
Red arrows indicate parent pointers
u
David Luebke 8 4/19/2014
Review: Prims Algorithm
MST-Prim(G, w, r)
Q = V[G];
for each u e Q
key[u] = ;
key[r] = 0;
p[r] = NULL;
while (Q not empty)
u = ExtractMin(Q);
for each v e Adj[u]
if (v e Q and w(u,v) < key[v])
p[v] = u;
key[v] = w(u,v);
14
0
3
14
10
3
6 4
5
2
9
15
8
u
David Luebke 9 4/19/2014
Review: Prims Algorithm
MST-Prim(G, w, r)
Q = V[G];
for each u e Q
key[u] = ;
key[r] = 0;
p[r] = NULL;
while (Q not empty)
u = ExtractMin(Q);
for each v e Adj[u]
if (v e Q and w(u,v) < key[v])
p[v] = u;
key[v] = w(u,v);
14
0
3
14
10
3
6 4
5
2
9
15
8
u
David Luebke 10 4/19/2014
Review: Prims Algorithm
MST-Prim(G, w, r)
Q = V[G];
for each u e Q
key[u] = ;
key[r] = 0;
p[r] = NULL;
while (Q not empty)
u = ExtractMin(Q);
for each v e Adj[u]
if (v e Q and w(u,v) < key[v])
p[v] = u;
key[v] = w(u,v);
14
0 8
3
14
10
3
6 4
5
2
9
15
8
u
David Luebke 11 4/19/2014
Review: Prims Algorithm
MST-Prim(G, w, r)
Q = V[G];
for each u e Q
key[u] = ;
key[r] = 0;
p[r] = NULL;
while (Q not empty)
u = ExtractMin(Q);
for each v e Adj[u]
if (v e Q and w(u,v) < key[v])
p[v] = u;
key[v] = w(u,v);
10
0 8
3
14
10
3
6 4
5
2
9
15
8
u
David Luebke 12 4/19/2014
Review: Prims Algorithm
MST-Prim(G, w, r)
Q = V[G];
for each u e Q
key[u] = ;
key[r] = 0;
p[r] = NULL;
while (Q not empty)
u = ExtractMin(Q);
for each v e Adj[u]
if (v e Q and w(u,v) < key[v])
p[v] = u;
key[v] = w(u,v);
10
0 8
3
14
10
3
6 4
5
2
9
15
8
u
David Luebke 13 4/19/2014
Review: Prims Algorithm
MST-Prim(G, w, r)
Q = V[G];
for each u e Q
key[u] = ;
key[r] = 0;
p[r] = NULL;
while (Q not empty)
u = ExtractMin(Q);
for each v e Adj[u]
if (v e Q and w(u,v) < key[v])
p[v] = u;
key[v] = w(u,v);
10 2
0 8
3
14
10
3
6 4
5
2
9
15
8
u
David Luebke 14 4/19/2014
Review: Prims Algorithm
MST-Prim(G, w, r)
Q = V[G];
for each u e Q
key[u] = ;
key[r] = 0;
p[r] = NULL;
while (Q not empty)
u = ExtractMin(Q);
for each v e Adj[u]
if (v e Q and w(u,v) < key[v])
p[v] = u;
key[v] = w(u,v);
10 2
0 8 15
3
14
10
3
6 4
5
2
9
15
8
u
David Luebke 15 4/19/2014
Prims Algorithm
MST-Prim(G, w, r)
Q = V[G];
for each u e Q
key[u] = ;
key[r] = 0;
p[r] = NULL;
while (Q not empty)
u = ExtractMin(Q);
for each v e Adj[u]
if (v e Q and w(u,v) < key[v])
p[v] = u;
key[v] = w(u,v);
10 2
0 8 15
3
14
10
3
6 4
5
2
9
15
8
u
David Luebke 16 4/19/2014
Review: Prims Algorithm
MST-Prim(G, w, r)
Q = V[G];
for each u e Q
key[u] = ;
key[r] = 0;
p[r] = NULL;
while (Q not empty)
u = ExtractMin(Q);
for each v e Adj[u]
if (v e Q and w(u,v) < key[v])
p[v] = u;
key[v] = w(u,v);
10 2 9
0 8 15
3
14
10
3
6 4
5
2
9
15
8
u
David Luebke 17 4/19/2014
Review: Prims Algorithm
MST-Prim(G, w, r)
Q = V[G];
for each u e Q
key[u] = ;
key[r] = 0;
p[r] = NULL;
while (Q not empty)
u = ExtractMin(Q);
for each v e Adj[u]
if (v e Q and w(u,v) < key[v])
p[v] = u;
key[v] = w(u,v);
10 2 9
0 8 15
3
4
14
10
3
6 4
5
2
9
15
8
u
David Luebke 18 4/19/2014
Review: Prims Algorithm
MST-Prim(G, w, r)
Q = V[G];
for each u e Q
key[u] = ;
key[r] = 0;
p[r] = NULL;
while (Q not empty)
u = ExtractMin(Q);
for each v e Adj[u]
if (v e Q and w(u,v) < key[v])
p[v] = u;
key[v] = w(u,v);
5 2 9
0 8 15
3
4
14
10
3
6 4
5
2
9
15
8
u
David Luebke 19 4/19/2014
Review: Prims Algorithm
MST-Prim(G, w, r)
Q = V[G];
for each u e Q
key[u] = ;
key[r] = 0;
p[r] = NULL;
while (Q not empty)
u = ExtractMin(Q);
for each v e Adj[u]
if (v e Q and w(u,v) < key[v])
p[v] = u;
key[v] = w(u,v);
5 2 9
0 8 15
3
4
14
10
3
6 4
5
2
9
15
8
u
David Luebke 20 4/19/2014
Review: Prims Algorithm
MST-Prim(G, w, r)
Q = V[G];
for each u e Q
key[u] = ;
key[r] = 0;
p[r] = NULL;
while (Q not empty)
u = ExtractMin(Q);
for each v e Adj[u]
if (v e Q and w(u,v) < key[v])
p[v] = u;
key[v] = w(u,v);
5 2 9
0 8 15
3
4
14
10
3
6 4
5
2
9
15
8
u
David Luebke 21 4/19/2014
Review: Prims Algorithm
MST-Prim(G, w, r)
Q = V[G];
for each u e Q
key[u] = ;
key[r] = 0;
p[r] = NULL;
while (Q not empty)
u = ExtractMin(Q);
for each v e Adj[u]
if (v e Q and w(u,v) < key[v])
p[v] = u;
key[v] = w(u,v);
5 2 9
0 8 15
3
4
14
10
3
6 4
5
2
9
15
8
u
David Luebke 22 4/19/2014
Review: Prims Algorithm
MST-Prim(G, w, r)
Q = V[G];
for each u e Q
key[u] = ;
key[r] = 0;
p[r] = NULL;
while (Q not empty)
u = ExtractMin(Q);
for each v e Adj[u]
if (v e Q and w(u,v) < key[v])
p[v] = u;
key[v] = w(u,v);
5 2 9
0 8 15
3
4
14
10
3
6 4
5
2
9
15
8
u
David Luebke 23 4/19/2014
Review: Prims Algorithm
MST-Prim(G, w, r)
Q = V[G];
for each u e Q
key[u] = ;
key[r] = 0;
p[r] = NULL;
while (Q not empty)
u = ExtractMin(Q);
for each v e Adj[u]
if (v e Q and w(u,v) < key[v])
p[v] = u;
key[v] = w(u,v);
What is the hidden cost in this code?
David Luebke 24 4/19/2014
Review: Prims Algorithm
MST-Prim(G, w, r)
Q = V[G];
for each u e Q
key[u] = ;
key[r] = 0;
p[r] = NULL;
while (Q not empty)
u = ExtractMin(Q);
for each v e Adj[u]
if (v e Q and w(u,v) < key[v])
p[v] = u;
DecreaseKey(v, w(u,v));
David Luebke 25 4/19/2014
Review: Prims Algorithm
MST-Prim(G, w, r)
Q = V[G];
for each u e Q
key[u] = ;
key[r] = 0;
p[r] = NULL;
while (Q not empty)
u = ExtractMin(Q);
for each v e Adj[u]
if (v e Q and w(u,v) < key[v])
p[v] = u;
DecreaseKey(v, w(u,v));
How often is ExtractMin() called?
How often is DecreaseKey() called?
David Luebke 26 4/19/2014
Review: Prims Algorithm
MST-Prim(G, w, r)
Q = V[G];
for each u e Q
key[u] = ;
key[r] = 0;
p[r] = NULL;
while (Q not empty)
u = ExtractMin(Q);
for each v e Adj[u]
if (v e Q and w(u,v) < key[v])
p[v] = u;
key[v] = w(u,v);
What will be the running time?
A: Depends on queue
binary heap: O(E lg V)
Fibonacci heap: O(V lg V + E)
David Luebke 27 4/19/2014
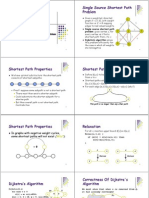
Single-Source Shortest Path
Problem: given a weighted directed graph G,
find the minimum-weight path from a given
source vertex s to another vertex v
Shortest-path = minimum weight
Weight of path is sum of edges
E.g., a road map: what is the shortest path from
Chapel Hill to Charlottesville?
David Luebke 28 4/19/2014
Shortest Path Properties
Again, we have optimal substructure: the
shortest path consists of shortest subpaths:
Proof: suppose some subpath is not a shortest path
There must then exist a shorter subpath
Could substitute the shorter subpath for a shorter path
But then overall path is not shortest path. Contradiction
David Luebke 29 4/19/2014
Shortest Path Properties
Define o(u,v) to be the weight of the shortest
path from u to v
Shortest paths satisfy the triangle inequality:
o(u,v) s o(u,x) + o(x,v)
Proof:
x
u v
This path is no longer than any other path
David Luebke 30 4/19/2014
Shortest Path Properties
In graphs with negative weight cycles, some
shortest paths will not exist (Why?):
< 0
David Luebke 31 4/19/2014
Relaxation
A key technique in shortest path algorithms is
relaxation
Idea: for all v, maintain upper bound d[v] on o(s,v)
Relax(u,v,w) {
if (d[v] > d[u]+w) then d[v]=d[u]+w;
}
9
5
2
7
5
2
Relax
6
5
2
6
5
2
Relax
David Luebke 32 4/19/2014
Bellman-Ford Algorithm
BellmanFord()
for each v e V
d[v] = ;
d[s] = 0;
for i=1 to |V|-1
for each edge (u,v) e E
Relax(u,v, w(u,v));
for each edge (u,v) e E
if (d[v] > d[u] + w(u,v))
return no solution;
Relax(u,v,w): if (d[v] > d[u]+w) then d[v]=d[u]+w
Initialize d[], which
will converge to
shortest-path value o
Relaxation:
Make |V|-1 passes,
relaxing each edge
Test for solution
Under what condition
do we get a solution?
David Luebke 33 4/19/2014
Bellman-Ford Algorithm
BellmanFord()
for each v e V
d[v] = ;
d[s] = 0;
for i=1 to |V|-1
for each edge (u,v) e E
Relax(u,v, w(u,v));
for each edge (u,v) e E
if (d[v] > d[u] + w(u,v))
return no solution;
Relax(u,v,w): if (d[v] > d[u]+w) then d[v]=d[u]+w
What will be the
running time?
David Luebke 34 4/19/2014
Bellman-Ford Algorithm
BellmanFord()
for each v e V
d[v] = ;
d[s] = 0;
for i=1 to |V|-1
for each edge (u,v) e E
Relax(u,v, w(u,v));
for each edge (u,v) e E
if (d[v] > d[u] + w(u,v))
return no solution;
Relax(u,v,w): if (d[v] > d[u]+w) then d[v]=d[u]+w
What will be the
running time?
A: O(VE)
David Luebke 35 4/19/2014
Bellman-Ford Algorithm
BellmanFord()
for each v e V
d[v] = ;
d[s] = 0;
for i=1 to |V|-1
for each edge (u,v) e E
Relax(u,v, w(u,v));
for each edge (u,v) e E
if (d[v] > d[u] + w(u,v))
return no solution;
Relax(u,v,w): if (d[v] > d[u]+w) then d[v]=d[u]+w
B
E
D C
A
-1
2
2
1
-3
5
3
4
Ex: work on board
s
David Luebke 36 4/19/2014
Bellman-Ford
Note that order in which edges are processed affects
how quickly it converges
Correctness: show d[v] = o(s,v) after |V|-1 passes
Lemma: d[v] > o(s,v) always
Initially true
Let v be first vertex for which d[v] < o(s,v)
Let u be the vertex that caused d[v] to change:
d[v] = d[u] + w(u,v)
Then d[v] < o(s,v)
o(s,v) s o(s,u) + w(u,v) (Why?)
o(s,u) + w(u,v) s d[u] + w(u,v) (Why?)
So d[v] < d[u] + w(u,v). Contradiction.
David Luebke 37 4/19/2014
Bellman-Ford
Prove: after |V|-1 passes, all d values correct
Consider shortest path from s to v:
s v
1
v
2
v
3
v
4
v
Initially, d[s] = 0 is correct, and doesnt change (Why?)
After 1 pass through edges, d[v
1
] is correct (Why?) and
doesnt change
After 2 passes, d[v
2
] is correct and doesnt change
Terminates in |V| - 1 passes: (Why?)
What if it doesnt?
David Luebke 38 4/19/2014
DAG Shortest Paths
Problem: finding shortest paths in DAG
Bellman-Ford takes O(VE) time.
How can we do better?
Idea: use topological sort
If were lucky and processes vertices on each shortest
path from left to right, would be done in one pass
Every path in a dag is subsequence of topologically
sorted vertex order, so processing verts in that order, we
will do each path in forward order (will never relax
edges out of vert before doing all edges into vert).
Thus: just one pass. What will be the running time?
David Luebke 39 4/19/2014
Dijkstras Algorithm
If no negative edge weights, we can beat BF
Similar to breadth-first search
Grow a tree gradually, advancing from vertices
taken from a queue
Also similar to Prims algorithm for MST
Use a priority queue keyed on d[v]
David Luebke 40 4/19/2014
Dijkstras Algorithm
Dijkstra(G)
for each v e V
d[v] = ;
d[s] = 0; S = C; Q = V;
while (Q = C)
u = ExtractMin(Q);
S = S U {u};
for each v e u->Adj[]
if (d[v] > d[u]+w(u,v))
d[v] = d[u]+w(u,v);
Relaxation
Step
Note: this
is really a
call to Q->DecreaseKey()
B
C
D A
10
4 3
2
1 5
Ex: run the algorithm
David Luebke 41 4/19/2014
Dijkstras Algorithm
Dijkstra(G)
for each v e V
d[v] = ;
d[s] = 0; S = C; Q = V;
while (Q = C)
u = ExtractMin(Q);
S = S U {u};
for each v e u->Adj[]
if (d[v] > d[u]+w(u,v))
d[v] = d[u]+w(u,v);
How many times is
ExtractMin() called?
How many times is
DecraseKey() called?
What will be the total running time?
David Luebke 42 4/19/2014
Dijkstras Algorithm
Dijkstra(G)
for each v e V
d[v] = ;
d[s] = 0; S = C; Q = V;
while (Q = C)
u = ExtractMin(Q);
S = S U {u};
for each v e u->Adj[]
if (d[v] > d[u]+w(u,v))
d[v] = d[u]+w(u,v);
How many times is
ExtractMin() called?
How many times is
DecraseKey() called?
A: O(E lg V) using binary heap for Q
Can acheive O(V lg V + E) with Fibonacci heaps
David Luebke 43 4/19/2014
Dijkstras Algorithm
Dijkstra(G)
for each v e V
d[v] = ;
d[s] = 0; S = C; Q = V;
while (Q = C)
u = ExtractMin(Q);
S = S U{u};
for each v e u->Adj[]
if (d[v] > d[u]+w(u,v))
d[v] = d[u]+w(u,v);
Correctness: we must show that when u is
removed from Q, it has already converged
David Luebke 44 4/19/2014
Correctness Of Dijkstra's Algorithm
Note that d[v] > o(s,v) v
Let u be first vertex picked s.t. - shorter path than d[u] d[u] > o(s,u)
Let y be first vertex eV-S on actual shortest path from su d[y] = o(s,y)
Because d[x] is set correctly for y's predecessor x e S on the shortest path, and
When we put x into S, we relaxed (x,y), giving d[y] the correct value
s
x
y
u
p
2
p
2
David Luebke 45 4/19/2014
Correctness Of Dijkstra's Algorithm
Note that d[v] > o(s,v) v
Let u be first vertex picked s.t. - shorter path than d[u] d[u] > o(s,u)
Let y be first vertex eV-S on actual shortest path from su d[y] = o(s,y)
d[u] > o(s,u)
= o(s,y) + o(y,u) (Why?)
= d[y] + o(y,u)
> d[y] But if d[u] > d[y], wouldn't have chosen u. Contradiction.
s
x
y
u
p
2
p
2
David Luebke 46 4/19/2014
Disjoint-Set Union Problem
Want a data structure to support disjoint sets
Collection of disjoint sets S = {S
i
}, S
i
S
j
= C
Need to support following operations:
MakeSet(x): S = S U {{x}}
Union(S
i
, S
j
): S = S - {S
i
, S
j
} U{S
i
U S
j
}
FindSet(X): return S
i
e S such that x e S
i
Before discussing implementation details, we
look at example application: MSTs
David Luebke 47 4/19/2014
Kruskals Algorithm
Kruskal()
{
T = C;
for each v e V
MakeSet(v);
sort E by increasing edge weight w
for each (u,v) e E (in sorted order)
if FindSet(u) = FindSet(v)
T = T U {{u,v}};
Union(FindSet(u), FindSet(v));
}
David Luebke 48 4/19/2014
Kruskals Algorithm
Kruskal()
{
T = C;
for each v e V
MakeSet(v);
sort E by increasing edge weight w
for each (u,v) e E (in sorted order)
if FindSet(u) = FindSet(v)
T = T U {{u,v}};
Union(FindSet(u), FindSet(v));
}
2 19
9
1
5
13
17
25
14
8
21
Run the algorithm:
David Luebke 49 4/19/2014
Kruskals Algorithm
Kruskal()
{
T = C;
for each v e V
MakeSet(v);
sort E by increasing edge weight w
for each (u,v) e E (in sorted order)
if FindSet(u) = FindSet(v)
T = T U {{u,v}};
Union(FindSet(u), FindSet(v));
}
2 19
9
1
5
13
17
25
14
8
21
Run the algorithm:
David Luebke 50 4/19/2014
Kruskals Algorithm
Kruskal()
{
T = C;
for each v e V
MakeSet(v);
sort E by increasing edge weight w
for each (u,v) e E (in sorted order)
if FindSet(u) = FindSet(v)
T = T U {{u,v}};
Union(FindSet(u), FindSet(v));
}
2 19
9
1
5
13
17
25
14
8
21
Run the algorithm:
David Luebke 51 4/19/2014
Kruskals Algorithm
Kruskal()
{
T = C;
for each v e V
MakeSet(v);
sort E by increasing edge weight w
for each (u,v) e E (in sorted order)
if FindSet(u) = FindSet(v)
T = T U {{u,v}};
Union(FindSet(u), FindSet(v));
}
2 19
9
1?
5
13
17
25
14
8
21
Run the algorithm:
David Luebke 52 4/19/2014
Kruskals Algorithm
Kruskal()
{
T = C;
for each v e V
MakeSet(v);
sort E by increasing edge weight w
for each (u,v) e E (in sorted order)
if FindSet(u) = FindSet(v)
T = T U {{u,v}};
Union(FindSet(u), FindSet(v));
}
2 19
9
1
5
13
17
25
14
8
21
Run the algorithm:
David Luebke 53 4/19/2014
Kruskals Algorithm
Kruskal()
{
T = C;
for each v e V
MakeSet(v);
sort E by increasing edge weight w
for each (u,v) e E (in sorted order)
if FindSet(u) = FindSet(v)
T = T U {{u,v}};
Union(FindSet(u), FindSet(v));
}
2? 19
9
1
5
13
17
25
14
8
21
Run the algorithm:
David Luebke 54 4/19/2014
Kruskals Algorithm
Kruskal()
{
T = C;
for each v e V
MakeSet(v);
sort E by increasing edge weight w
for each (u,v) e E (in sorted order)
if FindSet(u) = FindSet(v)
T = T U {{u,v}};
Union(FindSet(u), FindSet(v));
}
2 19
9
1
5
13
17
25
14
8
21
Run the algorithm:
David Luebke 55 4/19/2014
Kruskals Algorithm
Kruskal()
{
T = C;
for each v e V
MakeSet(v);
sort E by increasing edge weight w
for each (u,v) e E (in sorted order)
if FindSet(u) = FindSet(v)
T = T U {{u,v}};
Union(FindSet(u), FindSet(v));
}
2 19
9
1
5?
13
17
25
14
8
21
Run the algorithm:
David Luebke 56 4/19/2014
Kruskals Algorithm
Kruskal()
{
T = C;
for each v e V
MakeSet(v);
sort E by increasing edge weight w
for each (u,v) e E (in sorted order)
if FindSet(u) = FindSet(v)
T = T U {{u,v}};
Union(FindSet(u), FindSet(v));
}
2 19
9
1
5
13
17
25
14
8
21
Run the algorithm:
David Luebke 57 4/19/2014
Kruskals Algorithm
Kruskal()
{
T = C;
for each v e V
MakeSet(v);
sort E by increasing edge weight w
for each (u,v) e E (in sorted order)
if FindSet(u) = FindSet(v)
T = T U {{u,v}};
Union(FindSet(u), FindSet(v));
}
2 19
9
1
5
13
17
25
14
8?
21
Run the algorithm:
David Luebke 58 4/19/2014
Kruskals Algorithm
Kruskal()
{
T = C;
for each v e V
MakeSet(v);
sort E by increasing edge weight w
for each (u,v) e E (in sorted order)
if FindSet(u) = FindSet(v)
T = T U {{u,v}};
Union(FindSet(u), FindSet(v));
}
2 19
9
1
5
13
17
25
14
8
21
Run the algorithm:
David Luebke 59 4/19/2014
Kruskals Algorithm
Kruskal()
{
T = C;
for each v e V
MakeSet(v);
sort E by increasing edge weight w
for each (u,v) e E (in sorted order)
if FindSet(u) = FindSet(v)
T = T U {{u,v}};
Union(FindSet(u), FindSet(v));
}
2 19
9?
1
5
13
17
25
14
8
21
Run the algorithm:
David Luebke 60 4/19/2014
Kruskals Algorithm
Kruskal()
{
T = C;
for each v e V
MakeSet(v);
sort E by increasing edge weight w
for each (u,v) e E (in sorted order)
if FindSet(u) = FindSet(v)
T = T U {{u,v}};
Union(FindSet(u), FindSet(v));
}
2 19
9
1
5
13
17
25
14
8
21
Run the algorithm:
David Luebke 61 4/19/2014
Kruskals Algorithm
Kruskal()
{
T = C;
for each v e V
MakeSet(v);
sort E by increasing edge weight w
for each (u,v) e E (in sorted order)
if FindSet(u) = FindSet(v)
T = T U {{u,v}};
Union(FindSet(u), FindSet(v));
}
2 19
9
1
5
13?
17
25
14
8
21
Run the algorithm:
David Luebke 62 4/19/2014
Kruskals Algorithm
Kruskal()
{
T = C;
for each v e V
MakeSet(v);
sort E by increasing edge weight w
for each (u,v) e E (in sorted order)
if FindSet(u) = FindSet(v)
T = T U {{u,v}};
Union(FindSet(u), FindSet(v));
}
2 19
9
1
5
13
17
25
14
8
21
Run the algorithm:
David Luebke 63 4/19/2014
Kruskals Algorithm
Kruskal()
{
T = C;
for each v e V
MakeSet(v);
sort E by increasing edge weight w
for each (u,v) e E (in sorted order)
if FindSet(u) = FindSet(v)
T = T U {{u,v}};
Union(FindSet(u), FindSet(v));
}
2 19
9
1
5
13
17
25
14?
8
21
Run the algorithm:
David Luebke 64 4/19/2014
Kruskals Algorithm
Kruskal()
{
T = C;
for each v e V
MakeSet(v);
sort E by increasing edge weight w
for each (u,v) e E (in sorted order)
if FindSet(u) = FindSet(v)
T = T U {{u,v}};
Union(FindSet(u), FindSet(v));
}
2 19
9
1
5
13
17
25
14
8
21
Run the algorithm:
David Luebke 65 4/19/2014
Kruskals Algorithm
Kruskal()
{
T = C;
for each v e V
MakeSet(v);
sort E by increasing edge weight w
for each (u,v) e E (in sorted order)
if FindSet(u) = FindSet(v)
T = T U {{u,v}};
Union(FindSet(u), FindSet(v));
}
2 19
9
1
5
13
17?
25
14
8
21
Run the algorithm:
David Luebke 66 4/19/2014
Kruskals Algorithm
Kruskal()
{
T = C;
for each v e V
MakeSet(v);
sort E by increasing edge weight w
for each (u,v) e E (in sorted order)
if FindSet(u) = FindSet(v)
T = T U {{u,v}};
Union(FindSet(u), FindSet(v));
}
2 19?
9
1
5
13
17
25
14
8
21
Run the algorithm:
David Luebke 67 4/19/2014
Kruskals Algorithm
Kruskal()
{
T = C;
for each v e V
MakeSet(v);
sort E by increasing edge weight w
for each (u,v) e E (in sorted order)
if FindSet(u) = FindSet(v)
T = T U {{u,v}};
Union(FindSet(u), FindSet(v));
}
2 19
9
1
5
13
17
25
14
8
21?
Run the algorithm:
David Luebke 68 4/19/2014
Kruskals Algorithm
Kruskal()
{
T = C;
for each v e V
MakeSet(v);
sort E by increasing edge weight w
for each (u,v) e E (in sorted order)
if FindSet(u) = FindSet(v)
T = T U {{u,v}};
Union(FindSet(u), FindSet(v));
}
2 19
9
1
5
13
17
25?
14
8
21
Run the algorithm:
David Luebke 69 4/19/2014
Kruskals Algorithm
Kruskal()
{
T = C;
for each v e V
MakeSet(v);
sort E by increasing edge weight w
for each (u,v) e E (in sorted order)
if FindSet(u) = FindSet(v)
T = T U {{u,v}};
Union(FindSet(u), FindSet(v));
}
2 19
9
1
5
13
17
25
14
8
21
Run the algorithm:
David Luebke 70 4/19/2014
Kruskals Algorithm
Kruskal()
{
T = C;
for each v e V
MakeSet(v);
sort E by increasing edge weight w
for each (u,v) e E (in sorted order)
if FindSet(u) = FindSet(v)
T = T U {{u,v}};
Union(FindSet(u), FindSet(v));
}
2 19
9
1
5
13
17
25
14
8
21
Run the algorithm:
David Luebke 71 4/19/2014
Correctness Of Kruskals Algorithm
Sketch of a proof that this algorithm produces
an MST for T:
Assume algorithm is wrong: result is not an MST
Then algorithm adds a wrong edge at some point
If it adds a wrong edge, there must be a lower
weight edge (cut and paste argument)
But algorithm chooses lowest weight edge at each
step. Contradiction
Again, important to be comfortable with cut
and paste arguments
David Luebke 72 4/19/2014
Kruskals Algorithm
Kruskal()
{
T = C;
for each v e V
MakeSet(v);
sort E by increasing edge weight w
for each (u,v) e E (in sorted order)
if FindSet(u) = FindSet(v)
T = T U {{u,v}};
Union(FindSet(u), FindSet(v));
}
What will affect the running time?
David Luebke 73 4/19/2014
Kruskals Algorithm
Kruskal()
{
T = C;
for each v e V
MakeSet(v);
sort E by increasing edge weight w
for each (u,v) e E (in sorted order)
if FindSet(u) = FindSet(v)
T = T U {{u,v}};
Union(FindSet(u), FindSet(v));
}
What will affect the running time?
1 Sort
O(V) MakeSet() calls
O(E) FindSet() calls
O(V) Union() calls
(Exactly how many Union()s?)
David Luebke 74 4/19/2014
Kruskals Algorithm: Running Time
To summarize:
Sort edges: O(E lg E)
O(V) MakeSet()s
O(E) FindSet()s
O(V) Union()s
Upshot:
Best disjoint-set union algorithm makes above 3
operations take O(Eo(E,V)), o almost constant
Overall thus O(E lg E), almost linear w/o sorting
David Luebke 75 4/19/2014
Disjoint Set Union
So how do we implement disjoint-set union?
Nave implementation: use a linked list to
represent each set:
MakeSet(): ??? time
FindSet(): ??? time
Union(A,B): copy elements of A into B: ??? time
David Luebke 76 4/19/2014
Disjoint Set Union
So how do we implement disjoint-set union?
Nave implementation: use a linked list to
represent each set:
MakeSet(): O(1) time
FindSet(): O(1) time
Union(A,B): copy elements of A into B: O(A) time
How long can a single Union() take?
How long will n Union()s take?
David Luebke 77 4/19/2014
Disjoint Set Union: Analysis
Worst-case analysis: O(n
2
) time for n Unions
Union(S
1
, S
2
) copy 1 element
Union(S
2
, S
3
) copy 2 elements
Union(S
n-1
, S
n
) copy n-1 elements
O(n
2
)
Improvement: always copy smaller into larger
Why will this make things better?
What is the worst-case time of Union()?
But now n Unions take only O(n lg n) time!
David Luebke 78 4/19/2014
Amortized Analysis of Disjoint Sets
Amortized analysis computes average times
without using probability
With our new Union(), any individual element is
copied at most lg n times when forming the
complete set from 1-element sets
Worst case: Each time copied, element in smaller set
1st time resulting set size > 2
2nd time > 4
(lg n)th time > n
David Luebke 79 4/19/2014
Amortized Analysis of Disjoint Sets
Since we have n elements each copied at most
lg n times, n Union()s takes O(n lg n) time
We say that each Union() takes O(lg n)
amortized time
Financial term: imagine paying $(lg n) per Union
At first we are overpaying; initial Union $O(1)
But we accumulate enough $ in bank to pay for
later expensive O(n) operation.
Important: amount in bank never goes negative
David Luebke 80 4/19/2014
The End
You might also like
- Graphs: Shortest Paths, Job Scheduling Problem, Huffman CodeDocument25 pagesGraphs: Shortest Paths, Job Scheduling Problem, Huffman CodeVikalp Panseriya100% (1)
- Dies TelDocument28 pagesDies TelAtique KhattakNo ratings yet
- Lecture 26Document80 pagesLecture 26Anonymous niE5VQOHNo ratings yet
- Lecture 25Document63 pagesLecture 25Anonymous niE5VQOHNo ratings yet
- Vdocument - in - Advanced Algorithm Design and AnalysisDocument94 pagesVdocument - in - Advanced Algorithm Design and AnalysisjutuquhNo ratings yet
- Explanation of PrimDocument16 pagesExplanation of PrimdevangNo ratings yet
- Chap 0Document12 pagesChap 0akspengueNo ratings yet
- 600.363/463 Algorithms - Fall 2013 Solution To Assignment 7: (40 Points)Document1 page600.363/463 Algorithms - Fall 2013 Solution To Assignment 7: (40 Points)ashish mehtaNo ratings yet
- Review 14 Minimum Spanning TreesDocument2 pagesReview 14 Minimum Spanning Treesmungt0495No ratings yet
- Lect 20Document19 pagesLect 20Hare Krishna RajNo ratings yet
- Design and Analysis of Algorithms CO 401: Ash Mohammad AbbasDocument18 pagesDesign and Analysis of Algorithms CO 401: Ash Mohammad AbbasMohd Nafees AnsariNo ratings yet
- CS 332: Algorithms: Dijkstra's Algorithm Disjoint-Set UnionDocument46 pagesCS 332: Algorithms: Dijkstra's Algorithm Disjoint-Set UnionAnonymous niE5VQOHNo ratings yet
- Gram SchmidtDocument2 pagesGram Schmidtcoolboy_usamaNo ratings yet
- SSSP2Document7 pagesSSSP2joshiparas1234No ratings yet
- 09 CS316 - Algorithms - Graph 3 - SSPDocument29 pages09 CS316 - Algorithms - Graph 3 - SSPEssamNo ratings yet
- INF143Disjoint Set UnionDocument16 pagesINF143Disjoint Set UnionIvan ChurquiNo ratings yet
- DijkstraAlgorithmThe Shortest Path AlgorithmDocument3 pagesDijkstraAlgorithmThe Shortest Path AlgorithmSudharsan Amalraj JothirajNo ratings yet
- 17 Shortest Paths IDocument59 pages17 Shortest Paths ITanmay BaranwalNo ratings yet
- Universidad Politecnica de Madrid Escuela Técnica Superior de Ingenieros Industriales Ingeniería Del Medio AmbienteDocument6 pagesUniversidad Politecnica de Madrid Escuela Técnica Superior de Ingenieros Industriales Ingeniería Del Medio AmbienteDavid PerezNo ratings yet
- Q1. Use IF Statement To Design Positive Edge Triggered SR Flip FlopDocument5 pagesQ1. Use IF Statement To Design Positive Edge Triggered SR Flip Flop213698 ktr.et.ece.15No ratings yet
- Ecen 248 Prelab 10Document2 pagesEcen 248 Prelab 10Rebecca Sontheimer100% (2)
- Bellman FordDocument9 pagesBellman FordIstiaque AhmedNo ratings yet
- Digital Signal Processing: Name:-Ayush Yadav REG. NO.:-17BEC0555 SLOT: - G1+TG1Document11 pagesDigital Signal Processing: Name:-Ayush Yadav REG. NO.:-17BEC0555 SLOT: - G1+TG1Ayush YadavNo ratings yet
- V Adj U V QDocument5 pagesV Adj U V QDiego EspinozaNo ratings yet
- Lec16 DijkstraDocument24 pagesLec16 DijkstrajituNo ratings yet
- Pro 11 and 12Document10 pagesPro 11 and 12PoraNo ratings yet
- Formulas P1Document1 pageFormulas P1josegandica23No ratings yet
- DAA AkshatDocument22 pagesDAA Akshathemuup08No ratings yet
- 17 DifferentiationDocument27 pages17 DifferentiationAdinda ANNo ratings yet
- Shor MediumDocument7 pagesShor Mediuminumpudi.sushanthNo ratings yet
- Dijkstra's AlgorithmDocument59 pagesDijkstra's AlgorithmTanmay BaranwalNo ratings yet
- Graph BFS - DFSDocument64 pagesGraph BFS - DFS19050 Anish RoyNo ratings yet
- אלגוריתמים- הרצאה 7 - Single Source Shortest Path ProblemDocument5 pagesאלגוריתמים- הרצאה 7 - Single Source Shortest Path ProblemRonNo ratings yet
- Gate 2014 SolutionsDocument25 pagesGate 2014 SolutionsNaim Maktumbi NesaragiNo ratings yet
- hw10 Calc3Document11 pageshw10 Calc3crazycatlady1119No ratings yet
- 线性系统理论(s5 1)2023Document164 pages线性系统理论(s5 1)2023562713320sxNo ratings yet
- Devoir 6Document3 pagesDevoir 6Éric JarroldNo ratings yet
- Name - Shashank Vinit Reg No - 1801227689: Lab 3 AssignmentDocument6 pagesName - Shashank Vinit Reg No - 1801227689: Lab 3 AssignmentShashank VinitNo ratings yet
- SV Code ExamplsDocument162 pagesSV Code Examplskavya devulapalliNo ratings yet
- Embalse Lineal Como ODE: Ecuación DiferencialDocument5 pagesEmbalse Lineal Como ODE: Ecuación DiferencialKevin EchêvêrryNo ratings yet
- Small Oscillations, Stability and Normal Modes:: Ij I JDocument1 pageSmall Oscillations, Stability and Normal Modes:: Ij I JShweta SridharNo ratings yet
- Intractable Problems: Part OneDocument29 pagesIntractable Problems: Part OneFahiNo ratings yet
- Intractable Problems: Part OneDocument29 pagesIntractable Problems: Part OneFahiNo ratings yet
- Ecture: 5. Would It Be OK If We Used A Stack Here (As We Could For Topsort) ??Document3 pagesEcture: 5. Would It Be OK If We Used A Stack Here (As We Could For Topsort) ??Kat HawthorneNo ratings yet
- Nicolas Cuadros Taller Final Matematicas AplicadasDocument3 pagesNicolas Cuadros Taller Final Matematicas AplicadasNicolas CuadrosNo ratings yet
- Assignment 4Document3 pagesAssignment 4Hugu JujuNo ratings yet
- SASBTE Solutions 1 4 PDFDocument3 pagesSASBTE Solutions 1 4 PDFEdwinDuranJr.No ratings yet
- SASBTE Solutions 1 4 PDFDocument3 pagesSASBTE Solutions 1 4 PDFEdwinDuranJr.No ratings yet
- A Star Teb01Document4 pagesA Star Teb01utkarshNo ratings yet
- Shortest Paths I: Properties, Dijkstra's Algorithm, Breadth-First SearchDocument38 pagesShortest Paths I: Properties, Dijkstra's Algorithm, Breadth-First SearchYashashavi LadhaNo ratings yet
- GATE 2014 Electronics Engineering Keys & Solution On 16th (Evening Session)Document15 pagesGATE 2014 Electronics Engineering Keys & Solution On 16th (Evening Session)Lokesh Kumar0% (1)
- GM and Pre Cal PTDocument3 pagesGM and Pre Cal PTFrancois DonaireNo ratings yet
- 368 PrimMinSpanningTreeFunctionC++Document2 pages368 PrimMinSpanningTreeFunctionC++Dhruvika HoneyNo ratings yet
- Klausur2023 solutionMKDocument3 pagesKlausur2023 solutionMKRichard SalnikovNo ratings yet
- AP Exp 3.2 - RupeshDocument3 pagesAP Exp 3.2 - RupeshShubham KumarNo ratings yet
- ADS Assignment - 2: Problem Statement: Implement Prim's/Kruskal AlgorithmDocument3 pagesADS Assignment - 2: Problem Statement: Implement Prim's/Kruskal AlgorithmATHARVA DOIFODENo ratings yet
- Algorithm Final Exam (Spring 2009) : NameDocument12 pagesAlgorithm Final Exam (Spring 2009) : Nameきむら たくやNo ratings yet
- NumberTheory Part 2Document22 pagesNumberTheory Part 2MDRAKIB180 107No ratings yet
- Manan DaaDocument32 pagesManan DaaDhruv MishraNo ratings yet
- COS10003 - Computer & Logic Essentials Assignment 3: Algorithms, Graphs and CountingDocument9 pagesCOS10003 - Computer & Logic Essentials Assignment 3: Algorithms, Graphs and CountingHiếu PhanNo ratings yet
- Easy Mod Probs-SolDocument28 pagesEasy Mod Probs-SolYonatan Ysrael ZuritaNo ratings yet
- Combinatorics SyllabusDocument2 pagesCombinatorics SyllabusMiliyon TilahunNo ratings yet
- Edge-Magic Total LabelingsDocument15 pagesEdge-Magic Total LabelingsReni w ningsihNo ratings yet
- Sample Paper: Sof International Mathematics OlympiadDocument2 pagesSample Paper: Sof International Mathematics OlympiadJuna ManroeNo ratings yet
- Graph Theory Tutorial SheetDocument4 pagesGraph Theory Tutorial Sheetavnishgarg96No ratings yet
- BFS DFS Applicatio PDFDocument9 pagesBFS DFS Applicatio PDFVineet Kumar KanthNo ratings yet
- Lecture 14 (BFS, DFS)Document52 pagesLecture 14 (BFS, DFS)avinashNo ratings yet
- 12 Euler Ham PDFDocument10 pages12 Euler Ham PDFErnesy John ArrezaNo ratings yet
- 16.1 Practice ABCDocument2 pages16.1 Practice ABC718697No ratings yet
- Hamiltonion PathDocument15 pagesHamiltonion PathPrince KirarNo ratings yet
- Graphing Quadratic Functions 5Document3 pagesGraphing Quadratic Functions 5Ricardo GarciaNo ratings yet
- DAA Unit IV - Backtracking and Branch Bound PPT by Vijay MantriDocument53 pagesDAA Unit IV - Backtracking and Branch Bound PPT by Vijay Mantriomkarmohare18No ratings yet
- 6.854J / 18.415J Advanced Algorithms : Mit OpencoursewareDocument8 pages6.854J / 18.415J Advanced Algorithms : Mit OpencoursewarejhdmssNo ratings yet
- Problem Sheet-1Document2 pagesProblem Sheet-1Ankit SharmaNo ratings yet
- 1.coordinate Plane-Graphing PointsDocument2 pages1.coordinate Plane-Graphing Pointsavijitcu2007No ratings yet
- Ri) Urh - KL CF Cc!.Ifltation - Al Physics (Document6 pagesRi) Urh - KL CF Cc!.Ifltation - Al Physics (terradeathNo ratings yet
- Unit Test - Slope and Linear GraphsDocument7 pagesUnit Test - Slope and Linear GraphsRomalyn VillegasNo ratings yet
- Midterm 1 SolutionsDocument7 pagesMidterm 1 Solutionsshivani_himaniNo ratings yet
- CSC 224 TreesDocument13 pagesCSC 224 TreesKipyegon CheruiyotNo ratings yet
- Asst6 Math 239Document4 pagesAsst6 Math 239giselle_rochfordNo ratings yet
- Maquina de Vetores SuporteDocument19 pagesMaquina de Vetores SuporteISRAel JuniorNo ratings yet
- Vector Network Analysis - GRASS-WikiDocument6 pagesVector Network Analysis - GRASS-WikiSamuel Fernando Mesa GiraldoNo ratings yet
- CSE2208-Lab ManualDocument28 pagesCSE2208-Lab Manualnadif hasan purnoNo ratings yet
- Modul Biology Juj 2007Document218 pagesModul Biology Juj 2007genga100% (1)
- Rada F. Mihalcea, Dragomir R. Radev - Graph-Based Natural Language Processing and Information Retrieval-Cambridge University Press (2011)Document202 pagesRada F. Mihalcea, Dragomir R. Radev - Graph-Based Natural Language Processing and Information Retrieval-Cambridge University Press (2011)javier veraNo ratings yet
- Order Prime GraphDocument8 pagesOrder Prime GraphsattanathanNo ratings yet
- CD3291 Data Structures and Algorithms Lecture Notes 1Document162 pagesCD3291 Data Structures and Algorithms Lecture Notes 1goldentraders2574No ratings yet
- Data Structure and AlgosDocument4 pagesData Structure and AlgosChemical NITTNo ratings yet