Professional Documents
Culture Documents
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
27 viewsNumbered Circles Arrows Arrow Labels: Possible Transitions Change in Number of Packets in System
Numbered Circles Arrows Arrow Labels: Possible Transitions Change in Number of Packets in System
Uploaded by
assassinhpThis document describes birth-death processes and queuing models such as M/M/1, M/M/1 with balking, M/M/1/K, M/M/∞, and M/M/m. It includes definitions of the notation used for queuing models including the distribution of inter-arrival times and services, number of servers, storage capacity, and queuing discipline. Transition rates and equations are provided for several common queuing models.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You might also like
- HW2 2021 CS4215Document5 pagesHW2 2021 CS4215Dan PlămădealăNo ratings yet
- ReviewCh9 M M 1 QueueDocument24 pagesReviewCh9 M M 1 QueueBomezzZ EnterprisesNo ratings yet
- QueueingDocument50 pagesQueueingJagan RajendiranNo ratings yet
- Comparison of Multi-Carrier Modulation TechniquesDocument1 pageComparison of Multi-Carrier Modulation TechniquesGagandeep KaurNo ratings yet
- Lms PDFDocument11 pagesLms PDFsalehNo ratings yet
- Project Report: Queuing of Network PacketsDocument13 pagesProject Report: Queuing of Network Packetsrocks271089No ratings yet
- Basic Elements of Queueing Models: Arrival CharacteristicsDocument22 pagesBasic Elements of Queueing Models: Arrival CharacteristicsBerhanu tessemaNo ratings yet
- Queuing Theory and Traffic Analysis CS 552 Richard Martin Rutgers UniversityDocument149 pagesQueuing Theory and Traffic Analysis CS 552 Richard Martin Rutgers UniversitySenthil SoundarajanNo ratings yet
- Lect19 Applicationo of ProbbabilityDocument8 pagesLect19 Applicationo of ProbbabilityMary BeachNo ratings yet
- EEE-354: Telecommunication Systems EngineeringDocument23 pagesEEE-354: Telecommunication Systems EngineeringBilal HabibNo ratings yet
- Lecture 8 20240427-HandoutDocument42 pagesLecture 8 20240427-HandoutReedusNo ratings yet
- QueueingTheory IDocument33 pagesQueueingTheory Itarcher1987No ratings yet
- Pro ReportDocument5 pagesPro Reportmh.arab100% (1)
- LMS Adaptive FilterDocument11 pagesLMS Adaptive FilterNandakumar SamyNo ratings yet
- Experiment No. 5 Study of The Effect of A Forward-Path Lead Compensator On The Performance of A Linear Feedback Control SystemDocument3 pagesExperiment No. 5 Study of The Effect of A Forward-Path Lead Compensator On The Performance of A Linear Feedback Control SystemSubhaNo ratings yet
- Littles LawDocument22 pagesLittles LawupamaharikrishnanNo ratings yet
- Networks Part1Document9 pagesNetworks Part1dayas1979No ratings yet
- Review of Previous Lecture: SYSC 4607 - Slide Set 15 OutlineDocument5 pagesReview of Previous Lecture: SYSC 4607 - Slide Set 15 OutlinechitraselvakumarNo ratings yet
- Queueing Theory: Frank Y. S. LinDocument50 pagesQueueing Theory: Frank Y. S. LinsuhasNo ratings yet
- Unwrap Signal Phase - Simulink - MathWorks IndiaDocument5 pagesUnwrap Signal Phase - Simulink - MathWorks IndiaSamruddha ThakurNo ratings yet
- Maximum Ratio Combining For A WCDMA Rake ReceiverDocument8 pagesMaximum Ratio Combining For A WCDMA Rake ReceivertycoonaNo ratings yet
- Expt 7 Steady State Error - CAÑETEDocument8 pagesExpt 7 Steady State Error - CAÑETEJHUSTINE CAÑETENo ratings yet
- Ece131l Exp2Document5 pagesEce131l Exp2Carmela SapalaranNo ratings yet
- Control Systems K-NotesDocument35 pagesControl Systems K-NotesAkashGaurav100% (1)
- Formula Notes Control SystemsDocument9 pagesFormula Notes Control SystemsMohanMishra0% (1)
- Equalization in A Wideband TDMA System: - Three Basic Equalization MethodsDocument29 pagesEqualization in A Wideband TDMA System: - Three Basic Equalization Methodsydeolal176No ratings yet
- Unit 8: Frequency-Domain Analysis of Control SystemDocument12 pagesUnit 8: Frequency-Domain Analysis of Control SystemMazin AbdallaNo ratings yet
- PAPR Reduction of An MC-CDMA System Using SLM Technique: Gagandeep Kaur, Rajbir KaurDocument5 pagesPAPR Reduction of An MC-CDMA System Using SLM Technique: Gagandeep Kaur, Rajbir KaurIjarcet JournalNo ratings yet
- Digital Signal Processing (Final Term) (Copy)Document16 pagesDigital Signal Processing (Final Term) (Copy)Basel ElsebaeyNo ratings yet
- CH 11Document48 pagesCH 11Bulli KoteswararaoNo ratings yet
- WiMAX Channel Simulation Uni ReportDocument5 pagesWiMAX Channel Simulation Uni Reportandygray119No ratings yet
- Sistem Kontrol Digital: Bab 1. PendahuluanDocument62 pagesSistem Kontrol Digital: Bab 1. PendahuluanMuhammad TaufikNo ratings yet
- N Modular RedundancyDocument15 pagesN Modular RedundancyShambhu KhanalNo ratings yet
- CSD Experiment No 8Document9 pagesCSD Experiment No 8Gourav PalNo ratings yet
- Http://worldconferences - Net - Proceedings of Regional Conference On Knowledge Integration in Information Technology - June 2010 - All ArticlesDocument757 pagesHttp://worldconferences - Net - Proceedings of Regional Conference On Knowledge Integration in Information Technology - June 2010 - All ArticlesKhirulnizam Abd RahmanNo ratings yet
- Feedback and Control Systems HandoutsDocument17 pagesFeedback and Control Systems HandoutsGERON, VENICE V.No ratings yet
- Control System - UploadDocument2 pagesControl System - Uploadbijaya sahaNo ratings yet
- 1 Integration2010 ProceedingsDocument6 pages1 Integration2010 ProceedingsKhirulnizam Abd RahmanNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3 Media Access ControlDocument27 pagesChapter 3 Media Access ControlcarklounNo ratings yet
- Eee342 hw3 PDFDocument2 pagesEee342 hw3 PDFRedion XhepaNo ratings yet
- Viterbi DecodingDocument4 pagesViterbi DecodingGaurav NavalNo ratings yet
- Ece131l Exp6Document4 pagesEce131l Exp6Carmela SapalaranNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3 Media Access Control OriginalDocument28 pagesChapter 3 Media Access Control OriginalNagnath HavapnorNo ratings yet
- Mobile Communications: Week 2-3: Signal Propagation and Path Loss/ShadowingDocument64 pagesMobile Communications: Week 2-3: Signal Propagation and Path Loss/Shadowing이동준No ratings yet
- 4 - Difference Equations and Filtering - Week 5Document41 pages4 - Difference Equations and Filtering - Week 5renatto.guiusseppe.peraltaNo ratings yet
- Control Systems K-NotesDocument33 pagesControl Systems K-NotesvidhikhabyaNo ratings yet
- Control System Lab ManualDocument31 pagesControl System Lab Manualdebnath.soumi19No ratings yet
- MIT16 36s09 Lec21 22Document41 pagesMIT16 36s09 Lec21 22komutsatiriNo ratings yet
- Module 4: Time Response of Discrete Time Systems: Lecture Note 1Document5 pagesModule 4: Time Response of Discrete Time Systems: Lecture Note 1nirmal_inbox100% (1)
- Amil NIS: Department of Radioelectronics Faculty of Electrical Engineering Czech Tech. University in PragueDocument30 pagesAmil NIS: Department of Radioelectronics Faculty of Electrical Engineering Czech Tech. University in PragueAr FatimzahraNo ratings yet
- Conditional Random Fields: Probabilistic Models For Segmenting and Labeling Sequence DataDocument28 pagesConditional Random Fields: Probabilistic Models For Segmenting and Labeling Sequence Dataclliu168No ratings yet
- Revision PDFDocument11 pagesRevision PDFsdsds-54No ratings yet
- Synthesizeable Verilog Code ExamplesDocument9 pagesSynthesizeable Verilog Code ExamplesSiva Krishna BandiNo ratings yet
- Steady State ErrorsDocument41 pagesSteady State ErrorsMuhammad Noman KhanNo ratings yet
- AssignmentDocument6 pagesAssignmentMuhammad DaniyalNo ratings yet
- Backpropagation: Fundamentals and Applications for Preparing Data for Training in Deep LearningFrom EverandBackpropagation: Fundamentals and Applications for Preparing Data for Training in Deep LearningNo ratings yet
- Fundamentals of Electronics 3: Discrete-time Signals and Systems, and Quantized Level SystemsFrom EverandFundamentals of Electronics 3: Discrete-time Signals and Systems, and Quantized Level SystemsNo ratings yet
- Adaptive Filter: Enhancing Computer Vision Through Adaptive FilteringFrom EverandAdaptive Filter: Enhancing Computer Vision Through Adaptive FilteringNo ratings yet
Numbered Circles Arrows Arrow Labels: Possible Transitions Change in Number of Packets in System
Numbered Circles Arrows Arrow Labels: Possible Transitions Change in Number of Packets in System
Uploaded by
assassinhp0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
27 views4 pagesThis document describes birth-death processes and queuing models such as M/M/1, M/M/1 with balking, M/M/1/K, M/M/∞, and M/M/m. It includes definitions of the notation used for queuing models including the distribution of inter-arrival times and services, number of servers, storage capacity, and queuing discipline. Transition rates and equations are provided for several common queuing models.
Original Description:
Queuing
Original Title
Queuing
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentThis document describes birth-death processes and queuing models such as M/M/1, M/M/1 with balking, M/M/1/K, M/M/∞, and M/M/m. It includes definitions of the notation used for queuing models including the distribution of inter-arrival times and services, number of servers, storage capacity, and queuing discipline. Transition rates and equations are provided for several common queuing models.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pdf or txt
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
27 views4 pagesNumbered Circles Arrows Arrow Labels: Possible Transitions Change in Number of Packets in System
Numbered Circles Arrows Arrow Labels: Possible Transitions Change in Number of Packets in System
Uploaded by
assassinhpThis document describes birth-death processes and queuing models such as M/M/1, M/M/1 with balking, M/M/1/K, M/M/∞, and M/M/m. It includes definitions of the notation used for queuing models including the distribution of inter-arrival times and services, number of servers, storage capacity, and queuing discipline. Transition rates and equations are provided for several common queuing models.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pdf or txt
You are on page 1of 4
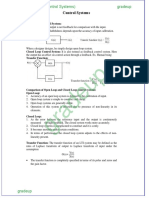
Birth-Death Processes
- Numbered circles = states =number of packets in system
- Arrows = possible transitions =change in number of packets in system
- Arrow labels =transition rates between states
-
k
=birth-rate when process in state k =arrival rate of packets, k in system
-
k
=death-rat when process in state k =departure rate when k in system
A/B/m/K/p queuing discipline
- A =the distribution of inter-arrival times;
- B =the distribution of service times;
o M =Memoryless or Markovian = Exponentially distributed inter-arrival times or
services times
o GI =General independent (unknown distribution but with independent arrival
times)
o G =General distribution (unknown distribution)
- m =number of servers in the system;
- K = storage capacity of the overall system =number of queuing places +number of
servers;
- p = the number of users of the system (if not specified, p = infinite);
- queuing discipline ={FCFS, LCFS, Priority}.
M/M/1
M/M/1 with Balking
(Discouraged)
M/M/1/K
M/M/
M/M/m
M/M/m/m Loss System
M/M/1
M/M/1 with
Balking
(Discouraged) M/M/1/K M/M/ M/M/m M/M/m/m Loss System
0
1 p
=
0
p e
=
0 1
1
1
K
p
0
p e
=
( ) 1
k
k
p =
( / )
!
k
k
p e
k
=
1
(1 )
1
k
k K
p
For 1 = then
1
1
k
p
K
=
+
( / )
!
k
k
p e
k
=
Erlang C Formula
Erlang B Formula
Call Blocking
Probability
Average number
of customers in
system
1
N
1
1
(K 1)
1 1
K
K
N
+
+
+
=
N a
= =
1
T
=
1
1
1
K
eff
K
N N
T
+
= =
| |
|
\ .
1
T
=
W
=
You might also like
- HW2 2021 CS4215Document5 pagesHW2 2021 CS4215Dan PlămădealăNo ratings yet
- ReviewCh9 M M 1 QueueDocument24 pagesReviewCh9 M M 1 QueueBomezzZ EnterprisesNo ratings yet
- QueueingDocument50 pagesQueueingJagan RajendiranNo ratings yet
- Comparison of Multi-Carrier Modulation TechniquesDocument1 pageComparison of Multi-Carrier Modulation TechniquesGagandeep KaurNo ratings yet
- Lms PDFDocument11 pagesLms PDFsalehNo ratings yet
- Project Report: Queuing of Network PacketsDocument13 pagesProject Report: Queuing of Network Packetsrocks271089No ratings yet
- Basic Elements of Queueing Models: Arrival CharacteristicsDocument22 pagesBasic Elements of Queueing Models: Arrival CharacteristicsBerhanu tessemaNo ratings yet
- Queuing Theory and Traffic Analysis CS 552 Richard Martin Rutgers UniversityDocument149 pagesQueuing Theory and Traffic Analysis CS 552 Richard Martin Rutgers UniversitySenthil SoundarajanNo ratings yet
- Lect19 Applicationo of ProbbabilityDocument8 pagesLect19 Applicationo of ProbbabilityMary BeachNo ratings yet
- EEE-354: Telecommunication Systems EngineeringDocument23 pagesEEE-354: Telecommunication Systems EngineeringBilal HabibNo ratings yet
- Lecture 8 20240427-HandoutDocument42 pagesLecture 8 20240427-HandoutReedusNo ratings yet
- QueueingTheory IDocument33 pagesQueueingTheory Itarcher1987No ratings yet
- Pro ReportDocument5 pagesPro Reportmh.arab100% (1)
- LMS Adaptive FilterDocument11 pagesLMS Adaptive FilterNandakumar SamyNo ratings yet
- Experiment No. 5 Study of The Effect of A Forward-Path Lead Compensator On The Performance of A Linear Feedback Control SystemDocument3 pagesExperiment No. 5 Study of The Effect of A Forward-Path Lead Compensator On The Performance of A Linear Feedback Control SystemSubhaNo ratings yet
- Littles LawDocument22 pagesLittles LawupamaharikrishnanNo ratings yet
- Networks Part1Document9 pagesNetworks Part1dayas1979No ratings yet
- Review of Previous Lecture: SYSC 4607 - Slide Set 15 OutlineDocument5 pagesReview of Previous Lecture: SYSC 4607 - Slide Set 15 OutlinechitraselvakumarNo ratings yet
- Queueing Theory: Frank Y. S. LinDocument50 pagesQueueing Theory: Frank Y. S. LinsuhasNo ratings yet
- Unwrap Signal Phase - Simulink - MathWorks IndiaDocument5 pagesUnwrap Signal Phase - Simulink - MathWorks IndiaSamruddha ThakurNo ratings yet
- Maximum Ratio Combining For A WCDMA Rake ReceiverDocument8 pagesMaximum Ratio Combining For A WCDMA Rake ReceivertycoonaNo ratings yet
- Expt 7 Steady State Error - CAÑETEDocument8 pagesExpt 7 Steady State Error - CAÑETEJHUSTINE CAÑETENo ratings yet
- Ece131l Exp2Document5 pagesEce131l Exp2Carmela SapalaranNo ratings yet
- Control Systems K-NotesDocument35 pagesControl Systems K-NotesAkashGaurav100% (1)
- Formula Notes Control SystemsDocument9 pagesFormula Notes Control SystemsMohanMishra0% (1)
- Equalization in A Wideband TDMA System: - Three Basic Equalization MethodsDocument29 pagesEqualization in A Wideband TDMA System: - Three Basic Equalization Methodsydeolal176No ratings yet
- Unit 8: Frequency-Domain Analysis of Control SystemDocument12 pagesUnit 8: Frequency-Domain Analysis of Control SystemMazin AbdallaNo ratings yet
- PAPR Reduction of An MC-CDMA System Using SLM Technique: Gagandeep Kaur, Rajbir KaurDocument5 pagesPAPR Reduction of An MC-CDMA System Using SLM Technique: Gagandeep Kaur, Rajbir KaurIjarcet JournalNo ratings yet
- Digital Signal Processing (Final Term) (Copy)Document16 pagesDigital Signal Processing (Final Term) (Copy)Basel ElsebaeyNo ratings yet
- CH 11Document48 pagesCH 11Bulli KoteswararaoNo ratings yet
- WiMAX Channel Simulation Uni ReportDocument5 pagesWiMAX Channel Simulation Uni Reportandygray119No ratings yet
- Sistem Kontrol Digital: Bab 1. PendahuluanDocument62 pagesSistem Kontrol Digital: Bab 1. PendahuluanMuhammad TaufikNo ratings yet
- N Modular RedundancyDocument15 pagesN Modular RedundancyShambhu KhanalNo ratings yet
- CSD Experiment No 8Document9 pagesCSD Experiment No 8Gourav PalNo ratings yet
- Http://worldconferences - Net - Proceedings of Regional Conference On Knowledge Integration in Information Technology - June 2010 - All ArticlesDocument757 pagesHttp://worldconferences - Net - Proceedings of Regional Conference On Knowledge Integration in Information Technology - June 2010 - All ArticlesKhirulnizam Abd RahmanNo ratings yet
- Feedback and Control Systems HandoutsDocument17 pagesFeedback and Control Systems HandoutsGERON, VENICE V.No ratings yet
- Control System - UploadDocument2 pagesControl System - Uploadbijaya sahaNo ratings yet
- 1 Integration2010 ProceedingsDocument6 pages1 Integration2010 ProceedingsKhirulnizam Abd RahmanNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3 Media Access ControlDocument27 pagesChapter 3 Media Access ControlcarklounNo ratings yet
- Eee342 hw3 PDFDocument2 pagesEee342 hw3 PDFRedion XhepaNo ratings yet
- Viterbi DecodingDocument4 pagesViterbi DecodingGaurav NavalNo ratings yet
- Ece131l Exp6Document4 pagesEce131l Exp6Carmela SapalaranNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3 Media Access Control OriginalDocument28 pagesChapter 3 Media Access Control OriginalNagnath HavapnorNo ratings yet
- Mobile Communications: Week 2-3: Signal Propagation and Path Loss/ShadowingDocument64 pagesMobile Communications: Week 2-3: Signal Propagation and Path Loss/Shadowing이동준No ratings yet
- 4 - Difference Equations and Filtering - Week 5Document41 pages4 - Difference Equations and Filtering - Week 5renatto.guiusseppe.peraltaNo ratings yet
- Control Systems K-NotesDocument33 pagesControl Systems K-NotesvidhikhabyaNo ratings yet
- Control System Lab ManualDocument31 pagesControl System Lab Manualdebnath.soumi19No ratings yet
- MIT16 36s09 Lec21 22Document41 pagesMIT16 36s09 Lec21 22komutsatiriNo ratings yet
- Module 4: Time Response of Discrete Time Systems: Lecture Note 1Document5 pagesModule 4: Time Response of Discrete Time Systems: Lecture Note 1nirmal_inbox100% (1)
- Amil NIS: Department of Radioelectronics Faculty of Electrical Engineering Czech Tech. University in PragueDocument30 pagesAmil NIS: Department of Radioelectronics Faculty of Electrical Engineering Czech Tech. University in PragueAr FatimzahraNo ratings yet
- Conditional Random Fields: Probabilistic Models For Segmenting and Labeling Sequence DataDocument28 pagesConditional Random Fields: Probabilistic Models For Segmenting and Labeling Sequence Dataclliu168No ratings yet
- Revision PDFDocument11 pagesRevision PDFsdsds-54No ratings yet
- Synthesizeable Verilog Code ExamplesDocument9 pagesSynthesizeable Verilog Code ExamplesSiva Krishna BandiNo ratings yet
- Steady State ErrorsDocument41 pagesSteady State ErrorsMuhammad Noman KhanNo ratings yet
- AssignmentDocument6 pagesAssignmentMuhammad DaniyalNo ratings yet
- Backpropagation: Fundamentals and Applications for Preparing Data for Training in Deep LearningFrom EverandBackpropagation: Fundamentals and Applications for Preparing Data for Training in Deep LearningNo ratings yet
- Fundamentals of Electronics 3: Discrete-time Signals and Systems, and Quantized Level SystemsFrom EverandFundamentals of Electronics 3: Discrete-time Signals and Systems, and Quantized Level SystemsNo ratings yet
- Adaptive Filter: Enhancing Computer Vision Through Adaptive FilteringFrom EverandAdaptive Filter: Enhancing Computer Vision Through Adaptive FilteringNo ratings yet