Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Impact of Plato's Book "The Republic" On Modern Society
Impact of Plato's Book "The Republic" On Modern Society
Uploaded by
Adeel AhmedCopyright:
Available Formats
You might also like
- DNI Information - Introduction and HazardsDocument32 pagesDNI Information - Introduction and HazardsAdeel Ahmed85% (13)
- CSS Political Science Notes - IDocument18 pagesCSS Political Science Notes - IM Faadi Malik55% (11)
- Politics, Governance, and Other Key ConceptsDocument22 pagesPolitics, Governance, and Other Key ConceptsMissMae QATNo ratings yet
- Who Was Plato?Document2 pagesWho Was Plato?pacoNo ratings yet
- An Introduction To: Western Political ThoughtDocument41 pagesAn Introduction To: Western Political Thoughtسارہ آفندیNo ratings yet
- Intro To Westen Political ThoughtDocument39 pagesIntro To Westen Political Thoughtkaneenika raviNo ratings yet
- Plato 3Document3 pagesPlato 3Eman FatimahNo ratings yet
- Political Philosophy: Political Philosophy, Branch of Philosophy That Is Concerned, at The Most AbstractDocument3 pagesPolitical Philosophy: Political Philosophy, Branch of Philosophy That Is Concerned, at The Most AbstractRed MonteroNo ratings yet
- Assignment No. 1 What Is Political Science What Is A State Ella Jovelle L. Montales BA PolSci 3ADocument2 pagesAssignment No. 1 What Is Political Science What Is A State Ella Jovelle L. Montales BA PolSci 3Aellamontales387No ratings yet
- The Need For Political TheoryDocument13 pagesThe Need For Political TheoryShivaang MaheshwariNo ratings yet
- Political Science - Britannica Online EncyclopediaDocument26 pagesPolitical Science - Britannica Online EncyclopediaAlmiralyn SuelloNo ratings yet
- Political Philosophy - Britannica Online EncyclopediaDocument33 pagesPolitical Philosophy - Britannica Online Encyclopediarourk512No ratings yet
- Contemporary Political Thought and AnalysisDocument2 pagesContemporary Political Thought and Analysisjohebsharear22No ratings yet
- Political Science SoftDocument6 pagesPolitical Science Softyasirbalka2No ratings yet
- WARREN, Mark E. DemocracyDocument14 pagesWARREN, Mark E. DemocracyDaniel PimentelNo ratings yet
- ThesisDocument19 pagesThesisrichie sNo ratings yet
- Content TheoriesDocument13 pagesContent TheoriesEiza Angela SebastianNo ratings yet
- Political Philosophy - Methodology - Internet Encyclopedia of PhilosophyDocument19 pagesPolitical Philosophy - Methodology - Internet Encyclopedia of PhilosophyRMFrancisco2No ratings yet
- Behaviouralism and Other Modern TheoryDocument35 pagesBehaviouralism and Other Modern TheoryGood ProgrammerNo ratings yet
- SIW SociologyDocument6 pagesSIW SociologyAlisha AktherNo ratings yet
- 50 BPS53 2020110305274749Document35 pages50 BPS53 2020110305274749Ankit KumarNo ratings yet
- Appro Update - Political ScienceDocument12 pagesAppro Update - Political ScienceMansi BaghelNo ratings yet
- Aristotles Relevanceto Modern Democratic TheoryDocument13 pagesAristotles Relevanceto Modern Democratic TheoryGauri DesaiNo ratings yet
- Article Review On Normative Political TheorYDocument5 pagesArticle Review On Normative Political TheorYMoumita SinghaNo ratings yet
- Funda Lord Pasa Mo Po Ako PLSDocument12 pagesFunda Lord Pasa Mo Po Ako PLSrj8jg2yp62No ratings yet
- The GreeksDocument2 pagesThe GreeksNinz Delos Santos DumpitNo ratings yet
- Polsc 3 Intro To Political TheoryDocument7 pagesPolsc 3 Intro To Political TheoryChesly Elys P. BerteNo ratings yet
- Study Session 10-1Document15 pagesStudy Session 10-1Omojuola TimothyNo ratings yet
- Polsc 3 Lesson 1 5 1Document13 pagesPolsc 3 Lesson 1 5 1sigaleya83No ratings yet
- ZBZBDocument2 pagesZBZBVagueBlurNo ratings yet
- Political Theory - Meaning and ApproachesDocument10 pagesPolitical Theory - Meaning and Approachesavilasha bhattNo ratings yet
- Political Thought Is A Vast and Complex Field That Encompasses The Study of IdeasDocument11 pagesPolitical Thought Is A Vast and Complex Field That Encompasses The Study of IdeasAkinkunmi OlanrewajuNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Political Theory:: Distinction/ ComparisonDocument4 pagesIntroduction To Political Theory:: Distinction/ ComparisonMicah JavierNo ratings yet
- Reading Material Pol. Sci. - II Mod. 1Document44 pagesReading Material Pol. Sci. - II Mod. 1DEVANSHU RATHORENo ratings yet
- Introduction and AnalysisDocument4 pagesIntroduction and AnalysisLuis Fernando Abello RayoNo ratings yet
- Reflection Paper: AristotleDocument3 pagesReflection Paper: AristotleJhonmark TemonioNo ratings yet
- Pateman DahlDocument14 pagesPateman DahlDayana ReveloNo ratings yet
- Political ScienceDocument22 pagesPolitical Sciencemihaela buzatuNo ratings yet
- Political Thought of Plato and AristotleDocument6 pagesPolitical Thought of Plato and AristotleSorin Bobeică100% (1)
- Syllabus /plato JZTDocument82 pagesSyllabus /plato JZTZEE zee100% (1)
- What Is Plato's Argument For The Conclusion That Philosophers Should Rule?Document6 pagesWhat Is Plato's Argument For The Conclusion That Philosophers Should Rule?xabitonNo ratings yet
- Politics ReportDocument16 pagesPolitics ReportJulie IINo ratings yet
- Political Philosophy Essay - Fernanda OrtizDocument6 pagesPolitical Philosophy Essay - Fernanda OrtizScribdTranslationsNo ratings yet
- Political Science, The Systematic Study of Governance by TheDocument1 pagePolitical Science, The Systematic Study of Governance by TheAriel Carl Angelo BalletaNo ratings yet
- Royer Jed. M. Quiñones Pol Sci 71Document6 pagesRoyer Jed. M. Quiñones Pol Sci 71Erika Jean QuinonesNo ratings yet
- UNGS 1301-Greek Philosopher Contributions To Modern Thoughts.Document9 pagesUNGS 1301-Greek Philosopher Contributions To Modern Thoughts.nur athirahNo ratings yet
- What Is Political Theory2721603119340Document9 pagesWhat Is Political Theory2721603119340MehmanNo ratings yet
- Plato AssignmentDocument1 pagePlato Assignmentkatpotayre potayreNo ratings yet
- What Is PoliticsDocument10 pagesWhat Is PoliticsRodnie Flores BaguioNo ratings yet
- Meaning and Importance of PhilosophyDocument9 pagesMeaning and Importance of PhilosophyjayNo ratings yet
- SEM 2 P.S - Aprroches To Study of Political ThoughtDocument11 pagesSEM 2 P.S - Aprroches To Study of Political ThoughtNamiraNo ratings yet
- Greek LegacyDocument5 pagesGreek LegacyBeverly RamosNo ratings yet
- Approaches of Political Theory FinalDocument23 pagesApproaches of Political Theory FinalSaudi abiola100% (1)
- Political Science Sem 1 NotesDocument47 pagesPolitical Science Sem 1 NotesKashvi AhlawatNo ratings yet
- Political ScienceDocument22 pagesPolitical Sciencemihaela buzatu100% (1)
- Political Systems - Edited (1) .EditedDocument5 pagesPolitical Systems - Edited (1) .EditedLeornard MukuruNo ratings yet
- Political PsychologyDocument11 pagesPolitical PsychologyOluwasegun OdofinNo ratings yet
- Research Paper 2Document16 pagesResearch Paper 2Rajveer GuptaNo ratings yet
- Confucian Virtue PDFDocument202 pagesConfucian Virtue PDFmftorrestNo ratings yet
- 974 ArticleText 1757 1 10 20210129Document7 pages974 ArticleText 1757 1 10 20210129Satvik M.No ratings yet
- Political Equality: An Essay in Democratic TheoryFrom EverandPolitical Equality: An Essay in Democratic TheoryRating: 3 out of 5 stars3/5 (1)
- National Maritime Oil/HNS Spill Contingency PlanDocument36 pagesNational Maritime Oil/HNS Spill Contingency PlanAdeel AhmedNo ratings yet
- EnviroSEP - Oil & Water SeparatorDocument4 pagesEnviroSEP - Oil & Water SeparatorAdeel AhmedNo ratings yet
- 2-Ethyl Hexanol: Cautionary Response InformationDocument2 pages2-Ethyl Hexanol: Cautionary Response InformationAdeel AhmedNo ratings yet
- FMS Hse Induction TrainingDocument42 pagesFMS Hse Induction TrainingAdeel Ahmed100% (2)
- InfoBulletin 3 2021 Hazardous and Non Hazardous Waste Processing and Rec...Document17 pagesInfoBulletin 3 2021 Hazardous and Non Hazardous Waste Processing and Rec...Adeel AhmedNo ratings yet
- Personal Protective EquipmentDocument41 pagesPersonal Protective EquipmentAdeel AhmedNo ratings yet
- Asphalt Industry Award Ma000054 Pay GuideDocument6 pagesAsphalt Industry Award Ma000054 Pay GuideAdeel AhmedNo ratings yet
- Accident Reporting FairdealDocument34 pagesAccident Reporting FairdealAdeel AhmedNo ratings yet
- 3-Emergency PreparednessDocument50 pages3-Emergency PreparednessAdeel AhmedNo ratings yet
- S DynamicSimulation PetrofacDocument3 pagesS DynamicSimulation PetrofacAdeel AhmedNo ratings yet
- Accident - Incident InvestigationDocument7 pagesAccident - Incident InvestigationAdeel AhmedNo ratings yet
- Census2006 RawMasterDocument1,567 pagesCensus2006 RawMasterAdeel AhmedNo ratings yet
- Requirements: Submission Requirements / Marking CriteriaDocument1 pageRequirements: Submission Requirements / Marking CriteriaAdeel AhmedNo ratings yet
- Mass Balance (Final)Document26 pagesMass Balance (Final)Adeel AhmedNo ratings yet
- Oxygen Gas Producing PlantDocument29 pagesOxygen Gas Producing PlantAdeel Ahmed0% (1)
- Crash Unit Investigation PlannerDocument2 pagesCrash Unit Investigation PlannerAdeel AhmedNo ratings yet
- Water CoolerDocument1 pageWater CoolerAdeel AhmedNo ratings yet
- Report On Audit Planning and Approach of QLD FitsDocument10 pagesReport On Audit Planning and Approach of QLD FitsAdeel AhmedNo ratings yet
Impact of Plato's Book "The Republic" On Modern Society
Impact of Plato's Book "The Republic" On Modern Society
Uploaded by
Adeel AhmedOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Impact of Plato's Book "The Republic" On Modern Society
Impact of Plato's Book "The Republic" On Modern Society
Uploaded by
Adeel AhmedCopyright:
Available Formats
Impact of Platos Book The Republic on Modern society
Plato (c.427-347 B.C.E.) developed such distinctive areas of philosophy as epistemology, ethics, and aesthetics. He was also the ideal political theorist whose thoughts had a deep impact on successive political theory Plato made immense contributions to contemporary political theory by unfolding, simplifying, and systematizing psychological and sociopolitical issues. The Republic's main contribution to political science is its stress on the role of thoughts, principles, and morals in politics. He attaches significance to ideas and an intellect not limited by custom, instead of material or chronological factors. He questions "what ought to be" in political affairs, and strains such moral and ethical principles as fairness and good quality as being the main criterion of normative communal theory.
These contributions are very relevant now, for the primary dilemma today is the reconciliation of the traditional aim of politics-to facilitate human beings to survive good and just lives in a political community-with the contemporary demand of social thought, which is to attain scientific knowledge of the mechanism of society On the other hand, Plato's non-democratic point of view includes some superior points that are used in current political systems. For instance, modern democracies are usually representative, as an alternative of Athens' direct variety, which Plato believes inclines toward the oppression of bulk. The present judiciary system, including a constitutional court and judges, represents the supremacy of knowledge's quality over the majoritys quantity. Moreover, the main foundation of a self-governing state's system of government, meritocracy, refers to officials chosen on merit, which is alike to Plato's ideas.
You might also like
- DNI Information - Introduction and HazardsDocument32 pagesDNI Information - Introduction and HazardsAdeel Ahmed85% (13)
- CSS Political Science Notes - IDocument18 pagesCSS Political Science Notes - IM Faadi Malik55% (11)
- Politics, Governance, and Other Key ConceptsDocument22 pagesPolitics, Governance, and Other Key ConceptsMissMae QATNo ratings yet
- Who Was Plato?Document2 pagesWho Was Plato?pacoNo ratings yet
- An Introduction To: Western Political ThoughtDocument41 pagesAn Introduction To: Western Political Thoughtسارہ آفندیNo ratings yet
- Intro To Westen Political ThoughtDocument39 pagesIntro To Westen Political Thoughtkaneenika raviNo ratings yet
- Plato 3Document3 pagesPlato 3Eman FatimahNo ratings yet
- Political Philosophy: Political Philosophy, Branch of Philosophy That Is Concerned, at The Most AbstractDocument3 pagesPolitical Philosophy: Political Philosophy, Branch of Philosophy That Is Concerned, at The Most AbstractRed MonteroNo ratings yet
- Assignment No. 1 What Is Political Science What Is A State Ella Jovelle L. Montales BA PolSci 3ADocument2 pagesAssignment No. 1 What Is Political Science What Is A State Ella Jovelle L. Montales BA PolSci 3Aellamontales387No ratings yet
- The Need For Political TheoryDocument13 pagesThe Need For Political TheoryShivaang MaheshwariNo ratings yet
- Political Science - Britannica Online EncyclopediaDocument26 pagesPolitical Science - Britannica Online EncyclopediaAlmiralyn SuelloNo ratings yet
- Political Philosophy - Britannica Online EncyclopediaDocument33 pagesPolitical Philosophy - Britannica Online Encyclopediarourk512No ratings yet
- Contemporary Political Thought and AnalysisDocument2 pagesContemporary Political Thought and Analysisjohebsharear22No ratings yet
- Political Science SoftDocument6 pagesPolitical Science Softyasirbalka2No ratings yet
- WARREN, Mark E. DemocracyDocument14 pagesWARREN, Mark E. DemocracyDaniel PimentelNo ratings yet
- ThesisDocument19 pagesThesisrichie sNo ratings yet
- Content TheoriesDocument13 pagesContent TheoriesEiza Angela SebastianNo ratings yet
- Political Philosophy - Methodology - Internet Encyclopedia of PhilosophyDocument19 pagesPolitical Philosophy - Methodology - Internet Encyclopedia of PhilosophyRMFrancisco2No ratings yet
- Behaviouralism and Other Modern TheoryDocument35 pagesBehaviouralism and Other Modern TheoryGood ProgrammerNo ratings yet
- SIW SociologyDocument6 pagesSIW SociologyAlisha AktherNo ratings yet
- 50 BPS53 2020110305274749Document35 pages50 BPS53 2020110305274749Ankit KumarNo ratings yet
- Appro Update - Political ScienceDocument12 pagesAppro Update - Political ScienceMansi BaghelNo ratings yet
- Aristotles Relevanceto Modern Democratic TheoryDocument13 pagesAristotles Relevanceto Modern Democratic TheoryGauri DesaiNo ratings yet
- Article Review On Normative Political TheorYDocument5 pagesArticle Review On Normative Political TheorYMoumita SinghaNo ratings yet
- Funda Lord Pasa Mo Po Ako PLSDocument12 pagesFunda Lord Pasa Mo Po Ako PLSrj8jg2yp62No ratings yet
- The GreeksDocument2 pagesThe GreeksNinz Delos Santos DumpitNo ratings yet
- Polsc 3 Intro To Political TheoryDocument7 pagesPolsc 3 Intro To Political TheoryChesly Elys P. BerteNo ratings yet
- Study Session 10-1Document15 pagesStudy Session 10-1Omojuola TimothyNo ratings yet
- Polsc 3 Lesson 1 5 1Document13 pagesPolsc 3 Lesson 1 5 1sigaleya83No ratings yet
- ZBZBDocument2 pagesZBZBVagueBlurNo ratings yet
- Political Theory - Meaning and ApproachesDocument10 pagesPolitical Theory - Meaning and Approachesavilasha bhattNo ratings yet
- Political Thought Is A Vast and Complex Field That Encompasses The Study of IdeasDocument11 pagesPolitical Thought Is A Vast and Complex Field That Encompasses The Study of IdeasAkinkunmi OlanrewajuNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Political Theory:: Distinction/ ComparisonDocument4 pagesIntroduction To Political Theory:: Distinction/ ComparisonMicah JavierNo ratings yet
- Reading Material Pol. Sci. - II Mod. 1Document44 pagesReading Material Pol. Sci. - II Mod. 1DEVANSHU RATHORENo ratings yet
- Introduction and AnalysisDocument4 pagesIntroduction and AnalysisLuis Fernando Abello RayoNo ratings yet
- Reflection Paper: AristotleDocument3 pagesReflection Paper: AristotleJhonmark TemonioNo ratings yet
- Pateman DahlDocument14 pagesPateman DahlDayana ReveloNo ratings yet
- Political ScienceDocument22 pagesPolitical Sciencemihaela buzatuNo ratings yet
- Political Thought of Plato and AristotleDocument6 pagesPolitical Thought of Plato and AristotleSorin Bobeică100% (1)
- Syllabus /plato JZTDocument82 pagesSyllabus /plato JZTZEE zee100% (1)
- What Is Plato's Argument For The Conclusion That Philosophers Should Rule?Document6 pagesWhat Is Plato's Argument For The Conclusion That Philosophers Should Rule?xabitonNo ratings yet
- Politics ReportDocument16 pagesPolitics ReportJulie IINo ratings yet
- Political Philosophy Essay - Fernanda OrtizDocument6 pagesPolitical Philosophy Essay - Fernanda OrtizScribdTranslationsNo ratings yet
- Political Science, The Systematic Study of Governance by TheDocument1 pagePolitical Science, The Systematic Study of Governance by TheAriel Carl Angelo BalletaNo ratings yet
- Royer Jed. M. Quiñones Pol Sci 71Document6 pagesRoyer Jed. M. Quiñones Pol Sci 71Erika Jean QuinonesNo ratings yet
- UNGS 1301-Greek Philosopher Contributions To Modern Thoughts.Document9 pagesUNGS 1301-Greek Philosopher Contributions To Modern Thoughts.nur athirahNo ratings yet
- What Is Political Theory2721603119340Document9 pagesWhat Is Political Theory2721603119340MehmanNo ratings yet
- Plato AssignmentDocument1 pagePlato Assignmentkatpotayre potayreNo ratings yet
- What Is PoliticsDocument10 pagesWhat Is PoliticsRodnie Flores BaguioNo ratings yet
- Meaning and Importance of PhilosophyDocument9 pagesMeaning and Importance of PhilosophyjayNo ratings yet
- SEM 2 P.S - Aprroches To Study of Political ThoughtDocument11 pagesSEM 2 P.S - Aprroches To Study of Political ThoughtNamiraNo ratings yet
- Greek LegacyDocument5 pagesGreek LegacyBeverly RamosNo ratings yet
- Approaches of Political Theory FinalDocument23 pagesApproaches of Political Theory FinalSaudi abiola100% (1)
- Political Science Sem 1 NotesDocument47 pagesPolitical Science Sem 1 NotesKashvi AhlawatNo ratings yet
- Political ScienceDocument22 pagesPolitical Sciencemihaela buzatu100% (1)
- Political Systems - Edited (1) .EditedDocument5 pagesPolitical Systems - Edited (1) .EditedLeornard MukuruNo ratings yet
- Political PsychologyDocument11 pagesPolitical PsychologyOluwasegun OdofinNo ratings yet
- Research Paper 2Document16 pagesResearch Paper 2Rajveer GuptaNo ratings yet
- Confucian Virtue PDFDocument202 pagesConfucian Virtue PDFmftorrestNo ratings yet
- 974 ArticleText 1757 1 10 20210129Document7 pages974 ArticleText 1757 1 10 20210129Satvik M.No ratings yet
- Political Equality: An Essay in Democratic TheoryFrom EverandPolitical Equality: An Essay in Democratic TheoryRating: 3 out of 5 stars3/5 (1)
- National Maritime Oil/HNS Spill Contingency PlanDocument36 pagesNational Maritime Oil/HNS Spill Contingency PlanAdeel AhmedNo ratings yet
- EnviroSEP - Oil & Water SeparatorDocument4 pagesEnviroSEP - Oil & Water SeparatorAdeel AhmedNo ratings yet
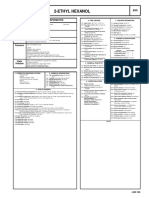
- 2-Ethyl Hexanol: Cautionary Response InformationDocument2 pages2-Ethyl Hexanol: Cautionary Response InformationAdeel AhmedNo ratings yet
- FMS Hse Induction TrainingDocument42 pagesFMS Hse Induction TrainingAdeel Ahmed100% (2)
- InfoBulletin 3 2021 Hazardous and Non Hazardous Waste Processing and Rec...Document17 pagesInfoBulletin 3 2021 Hazardous and Non Hazardous Waste Processing and Rec...Adeel AhmedNo ratings yet
- Personal Protective EquipmentDocument41 pagesPersonal Protective EquipmentAdeel AhmedNo ratings yet
- Asphalt Industry Award Ma000054 Pay GuideDocument6 pagesAsphalt Industry Award Ma000054 Pay GuideAdeel AhmedNo ratings yet
- Accident Reporting FairdealDocument34 pagesAccident Reporting FairdealAdeel AhmedNo ratings yet
- 3-Emergency PreparednessDocument50 pages3-Emergency PreparednessAdeel AhmedNo ratings yet
- S DynamicSimulation PetrofacDocument3 pagesS DynamicSimulation PetrofacAdeel AhmedNo ratings yet
- Accident - Incident InvestigationDocument7 pagesAccident - Incident InvestigationAdeel AhmedNo ratings yet
- Census2006 RawMasterDocument1,567 pagesCensus2006 RawMasterAdeel AhmedNo ratings yet
- Requirements: Submission Requirements / Marking CriteriaDocument1 pageRequirements: Submission Requirements / Marking CriteriaAdeel AhmedNo ratings yet
- Mass Balance (Final)Document26 pagesMass Balance (Final)Adeel AhmedNo ratings yet
- Oxygen Gas Producing PlantDocument29 pagesOxygen Gas Producing PlantAdeel Ahmed0% (1)
- Crash Unit Investigation PlannerDocument2 pagesCrash Unit Investigation PlannerAdeel AhmedNo ratings yet
- Water CoolerDocument1 pageWater CoolerAdeel AhmedNo ratings yet
- Report On Audit Planning and Approach of QLD FitsDocument10 pagesReport On Audit Planning and Approach of QLD FitsAdeel AhmedNo ratings yet